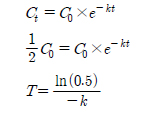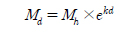It is important to understand residual patterns of pesticides applied on crops for ensuring their safety in agricultural products. However, there are few studies on the residual patterns of pesticides in minor crops, which are small in cultivation area. In this study, residual amounts of bifenthrin and chlorfenapyr sprayed on perilla leaf as a minor crop were investigated to know their residual patterns.
Bifenthrin and chlorfenapyr were sprayed 2 or 3 times on perilla leaves at a week interval prior to harvest, and the perilla leaves were collected at 0, 1, 3, 5 and 7 days after the final application of pesticides. Recoveries for residual analysis of pesticides spiked on perilla leaves with concentrations of 0.1 and 0.5 mg/kg were 81.9-104.8%. The residual amounts of pesticides interpreted using first order kinetics model show that dissipation constants of bifenthrin and chlorfenapyr in perilla leaves were 0.0724-0.0535 and 0.0948-0.0821 day-1, respectively. In addition, the dissipation half-lives in perilla leaves were 9.6-12.9 days for bifenthrin and 7.3-8.4 days for chlorfenapyr. When pre-harvest residue limits (PHRL) of bifenthrin and chlorfenapyr at 10 days before harvest calculated on the basis of the dissipation constants and maximum residue limits of the pesticides were calculated as 17.1 for bifenthrin and 15.9 mg/kg for chlorfenapyr.
Therefore, the PHRL calculated using the time-dependant residual patterns of pesticides in perilla leaves and their regression analysis may be used as experimental evidences in order to ensure the safety of pesticides in perilla leaves before harvest.
농작물에 사용되는 농약은 그 목적을 달성한 후에도 작물에 잔류하여 안전성 문제를 야기할 수 있다(Jung
그러나 들깻잎을 포함한 소면적 재배 작물의 경우 등록된 농약이 많지 않아(Lee
살충제 bifenthrin과 chlorfenapyr는 배추, 시금치, 파 및 들깨 등의 엽채류에서 나방류 방제를 위하여 품목이 고시되어 있다(Korea Crop Protection Association, 2014). NAQS의 안전성조사 결과, bifenthrin 및 chlorfenapyr의 부적합율은 각각 0.6~1.6 및 0.2~0.3%로 낮은 수준이었으나 검출횟수는 각각 341~385 및 1,379~1,406건으로 높은 편이었다(NAQS report, 2011; NAQS report, 2012).
작물에 약제가 살포된 후 농약의 초기 부착량 및 재배 기간 동안 작물 중 잔류농약의 반감기(half-life)를 조사하여 잔류양상을 규명하는 것은 최종 생산된 농산물의 안전성을 확보하기 위해 중요한 일이다. 최근까지 농약의 잔류양상을 예측하기 위해 여러 kinetics model들이 적용되어 연구되어 왔으나(Park
본 논문은 들깻잎에 대하여 bifenthrin 및 chlorfenapyr를 2회 및 3회 살포한 후 두 농약의 경시적인 잔류양상을 조사하고 first order kinetics model을 적용하여 감소상수 및 반감기를 산출하여 재배기간 중 안전한 농산물을 생산 관리하기 위하여 수행하였다.
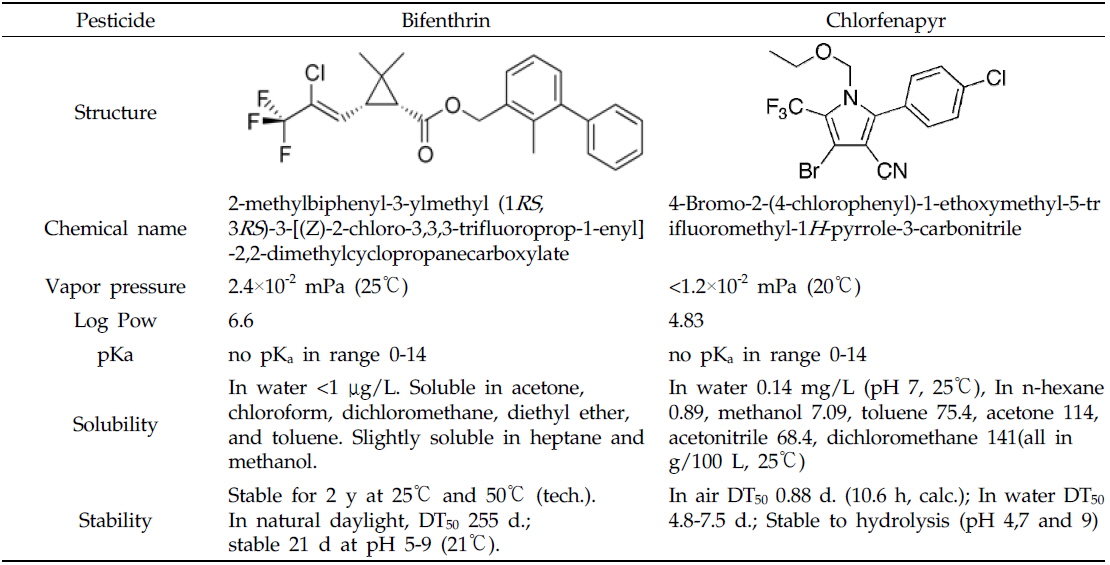
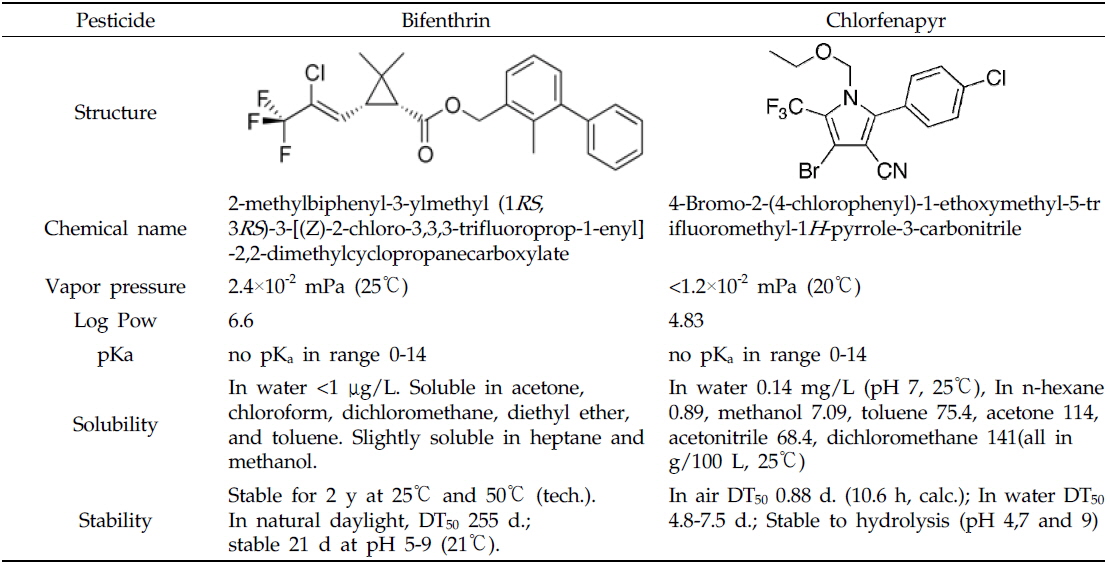
Bifenthrin의 표준품은 Dr. Ehrenstorfer GmbH(Augsburg, Germany)사의 순도 95.0%를 구입하였으며, chlorfenapyr의 표준품은 BASF(Ludwigshafen, Germany)사의 순도 99.7%를 분양 받아 사용하였다. 두 농약을 일정한 농도로 acetone에 희석하여 working solution으로 제조한 후 사용하였으며 두 농약의 물리화학적 성질은 Table 1과 같다. 농약제품은 bifenthrin의 경우 유효성분 함량 1% 유제(타스타, (주)영일케미컬)를 사용하였고 chlorfenapyr의 경우 유효성분 함량 10% 액상수화제(섹큐어, (주)동부팜한농)를 사용하였다. 잔류농약분석에 사용된 acetone, acetonitrile, methylene chloride, 및 n-hexane은 Burdick & Jackson Inc.(Muskegon, MI, USA)에서, sodium chloride(EP급)와 sodium sulfate(GR급)는 Junsei Chemical Co.(Tokyo, Japan)에서 구입하였다. Florisil은 Sigma-Aldrich Chemical Co.(St. Louis, MO, USA)제품을 사용하였다.
[Table 1.] Physico-chemical properties of the applied pesticides
Physico-chemical properties of the applied pesticides
시험 포장은 경상북도 경산시 하양읍 청천리에 위치한 시설재배 하우스를 임대하였으며, 재래종 들깻잎을 시험에 이용하였다. 처리구는 2.5 m×3.0 m, 완충거리 0.5 m를 한 처리구로 하였으며 재식밀도는 20 cm×20 cm였다. 포장 시험 기간은 2014년 9월 5일부터 2014년 9월 26일까지 진행되었으며, 들깻잎의 재배는 농가의 관행적인 방법에 따라 실시하였다. 재배기간 중 관개수는 비닐하우스 상부에 설치된 스프링쿨러를 이용하여 7일에 한 번씩 가로 5.0 m×세로 5.0 m의 재배면적 당 약 1.5 L/min의 물을 20분간 급수하였으며, 시험기간 중 포장의 온도와 습도는 각각 평균 24.8±2.6℃ 및 67.3±6.6%로 유지하였다. 약제살포는 bifenthrin은 1,000배, chlorfenapyr는 2,000배 희석하여 배부식 분무기를 사용하여 20 psi의 압력으로 분당 1,500 mL로 살포하였다. 살포 시기 및 횟수는 7일 간격으로 2회 및 3회 처리하였으며, 들깻잎 시료는 최종 약제 살포 2시간 후 수확한 0일차를 포함하여 일주일간 0, 1, 3, 5 및 7일차에 수확하였다. 채취된 시료는 즉시 실험실로 운반하여 개별 무게를 측정하였다. 채취된 시료는 균질화 한 후 잔류농약 분석 직전까지 -20℃의 냉동고에 보관하였다.
들깻잎 중 bifenthrin 및 chlorfenapyr의 잔류농약분석 방법은 식품공전 잔류농약 분석법을 참조 및 변형하여 적용하였다(MFDS Report, 2013). 들깻잎 시료 10 g에 일정량의 acetone을 첨가하고 homogenizer에서 3분간 12,000 rpm으로 추출하여 추출물을 Celite 545에 통과시켜 여과한 후 1.0 L 분액여두에 옮기고 50 mL 포화식염수와 450 mL 증류수를 가하여 dichloromethane 50 mL로 2회 분배 추출하였다. 추출액을 anhydrous sodium sulfate에 통과시켜 탈수하고 40℃ 수욕상에서 감압농축한 후 농축물을 일정량의 hexane에 재용해하여 정제과정에 사용하였다. 시험에 사용된 Florisil은 잔류농약분석시험 하루 전 200℃의 oven에서 활성화하여 사용하였다. Glass column (16 mm I.D.×40 cm, PTFE 부착)에 10 g의 Florisil과 일정량의 무수 sodium sulfate를 차례로 습식 충전한 후 column 상부에 hexane으로 재용해한 시료액을 부하하고 50 mL의 hexane으로 1차 용출시켜 흘려버린 후, 50 mL의 hexane/acetone(95/5, v/v)으로 2차 용출시켜 그 용출액을 분취하였다. 분취한 용출액을 감압농축한 뒤 잔사를 acetone에 재용해하여 1.0 μL씩 GC-ECD(Shimadzu GC-2010, Japan)에 주입하여 나타난 chromatogram상의 peak area를 표준검량선과 비교하여 잔류량을 산출하였다. 회수율 시험은 bifenthrin 및 chlorfenapyr를 들깻잎 시료에 각각 0.1 및 0.5 mg/kg이 되도록 처리한 다음 상기의 방법으로 추출, 정제한 후 GC-ECD로 분석하여 측정된 농약의 잔류량을 계산한 후 회수율을 구하였다.
GC-ECD의 컬럼은 DB-5 capillary column[30 mL.× 0.25 mm I.D., 0.25 μm film thickness(J&W Scientific, USA)]를 사용하였고 온도조건은 column oven은 bifenthrin 분석 시 120℃에서 2분간 유지한 다음 분당 8℃의 비율로 280℃까지 가온한 뒤 8분간 유지하였고, chlorfenapyr는 150℃에서 2분간 유지한 다음 분당 10℃의 비율로 280℃까지 가온한 뒤 5분간 유지하였으며, injector의 경우 260℃, detector의 경우 300℃였다. 이동상 가스(N2) 및 makeup gas(N2/Air)는 각각 분당 1 및 30 mL의 유속으로 흘려주었으며, 최종 시료 용액은 1.0 μL를 split mode(split ratio 1:50)로 주입하여 분석하였다.
정량분석을 위한 bifenthrin 및 chlorfenapyr의 표준검량선은 각 농약의 표준품을 acetone으로 희석하여 0.05, 0.1, 0.2, 0.5, 1.0, 2.0 및 5.0 mg/L의 working solution을 조제하여 각각 1.0 μL씩 GC-ECD에 주입하여 나타난 chromatogram 상의 peak 면적을 이용하여 작성하였다.
들깻잎 중 bifenthrin 및 chlorfenapyr의 반감기(
위 식에서
출하 전 농약 잔류허용기준(pre-harvest residue limit, PHRL)은 작물 수확 시 잔류농약이 잔류허용기준을 초과하지 않도록 수확 전 재배 과정에서 농약 잔류량을 예측한 값으로(Kim
위 식에서
시험농약의 정량분석을 위한 bifenthrin 및 chlorfenapyr의 표준검량선은 상관계수(
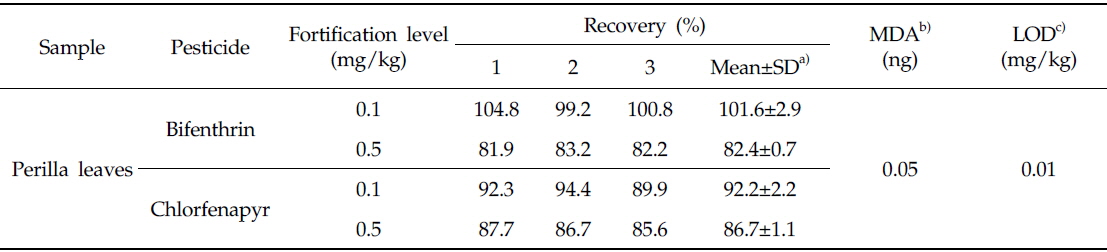
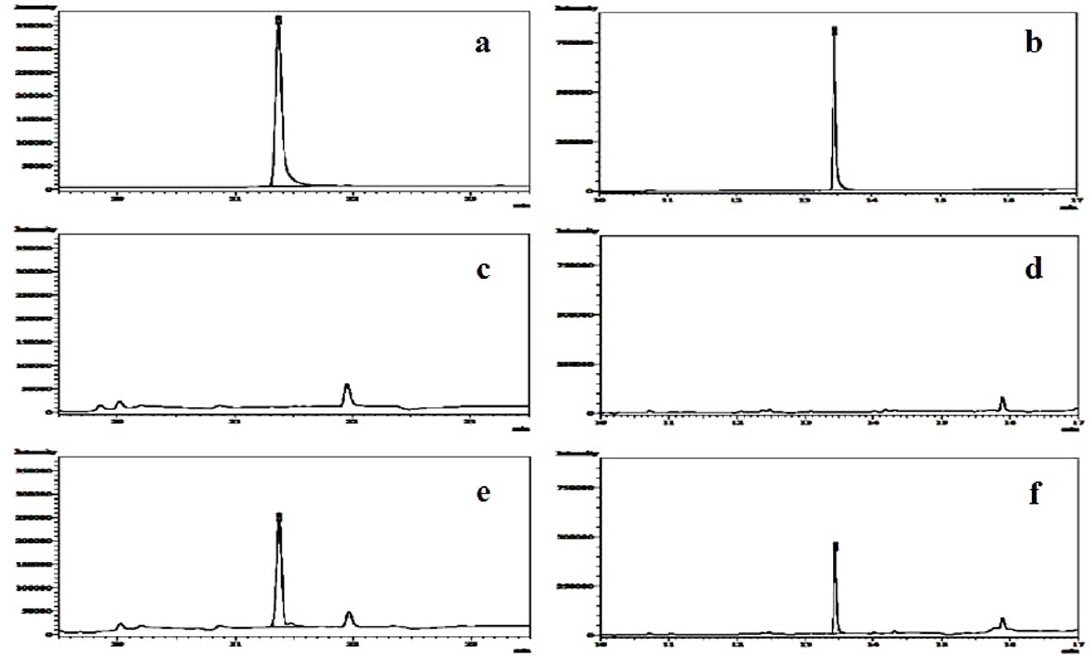
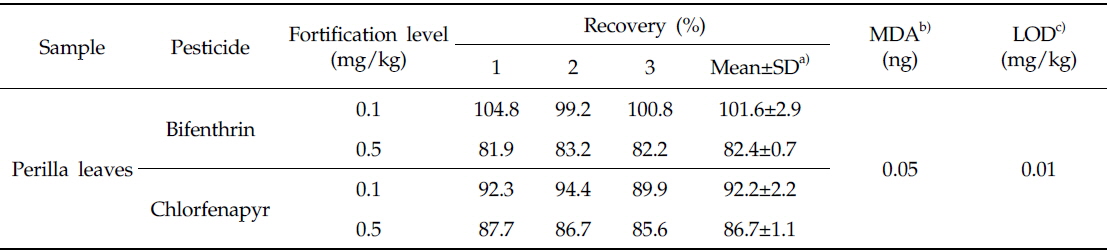
들깻잎 중 bifenthin 및 chlorfenapyr의 회수율시험 결과는 Table 2와 같다. 들깻잎 중 bifenthin의 회수율은 81.9-104.8%, chlorfenapyr의 회수율은 85.6-94.4%로 나타났으며 변이계수는 2.9% 이하로 나타나 잔류농약분석법 기준인 회수율 범위 70-120%와 변이계수 10% 이내를 만족하였다. 두 농약의 검출한계는 모두 0.01 mg/kg이었으며 GC-ECD 크로마토그램 상에 시료의 간섭 피크는 존재하지 않았다(Fig. 1).
Recoveries and limits of detection for residual analysis of bifenthrin and chlorfenapyr in perilla leaves
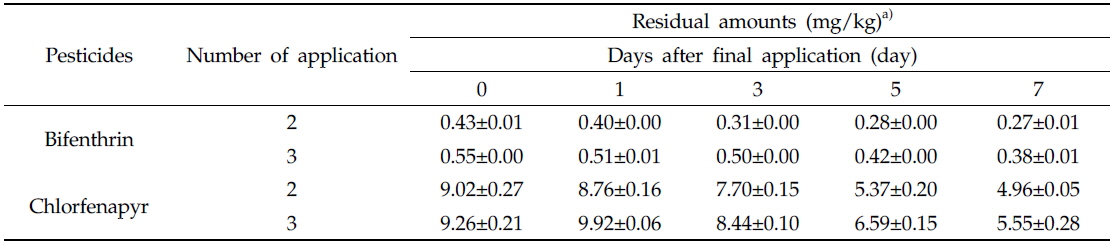
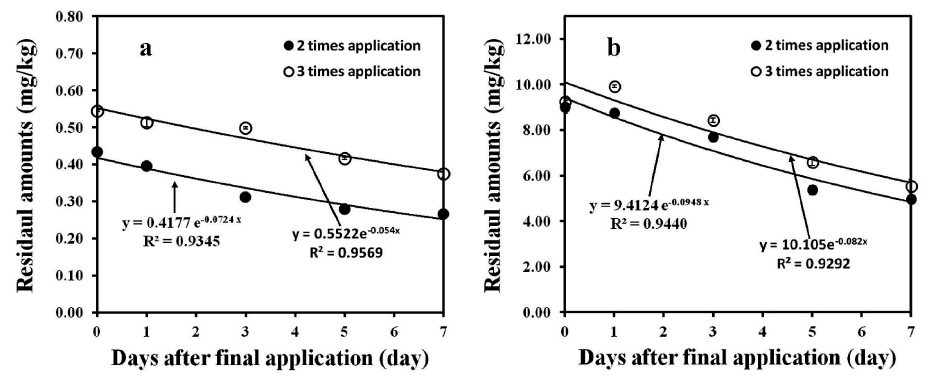
최종 약제 살포 후 일주일간 채취한 들깻잎의 무게는 최저 1.11±0.15 g에서 최고 1.36±0.19 g 사이로(Fig. 2), 들깻잎 시료는 일자별로 균일하게 채취하였다. 들깻잎 중 bifenthrin 및 chlorfenapyr의 잔류량을 조사한 결과는 Table 3에 나타내었다. Bifenthrin의 초기 잔류량은 2회 및 3회 처리구에서 각각 0.43 및 0.55 mg/kg으로 나타났으며, 일주일 경과 후 잔류량이 0.27 및 0.38 mg/kg으로 나타나 초기 잔류량의 30.9-37.2%가 소실되었다. 반면에 chlorfenapyr의 경우 초기 잔류량은 2회 처리구에서 9.02 mg/kg, 3회 처리구에서 9.26 mg/kg으로 나타났으며 수확일 시료에서 40.1-45.0% 감소하여 4.96 및 5.55 mg/kg으로 잔류하였다.
[Table 3.] Residual amounts of bifenthrin and chlorfenapyr in perilla leaves after final application
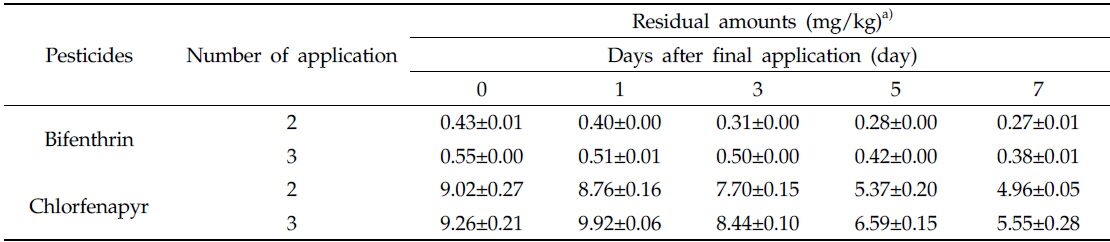
Residual amounts of bifenthrin and chlorfenapyr in perilla leaves after final application
이론적으로는 동일 조건에서 농약의 살포 횟수를 달리하면 감소상소
이 결과를 바탕으로 작성한 들깻잎 중 bifenthrin 및 chlorfenapyr의 소실곡선을 Fig. 3에 나타내었다. Bifenthrin의 회귀방정식은 2회 및 3회 처리구에서 각각 y=0.4177e-0.0724x (
들깻잎 중 bifenthrin 및 chlorfenapyr의 잔류량 감소 요인은 두 농약의 증기압이 각각 2.4×10-2 mPa 및 1.2×10-2 mPa로 낮은 편이며, Log Kow값도 bifenthrin은 6.0 이상이며 chlorfenapyr의 경우 4.8로 극성이 비교적 낮아서(Macbean, 2012), 휘산 및 강우식 관수에 의해 소실될 가능성보다 다른 요인이 더 크게 작용할 것으로 생각된다. 이전 연구에 따르면 들깻잎과 같이 단기간에 성장이 빠른 작물의 경우 작물 중 농약의 반감기는 작물의 비대성장이 가장 큰 요인으로 보고되고 있으며(Lee
산출된 방정식으로부터 들깻잎 중 bifenthrin의 반감기를 산출한 결과 2회 처리구에서 9.6일, 3회 처리구에서 12.9일로 나타났다. Ko 등(2003)의 연구에 따르면 들깻잎 중 bifenthrin의 반감기는 2.2-4.8일로 보고되어 본 연구 결과보다 짧았으나(Ko
엽채류 중 bifenthrin과 chlorfenapyr의 잔류양상 연구에서 Park 등(2012)은 쪽파와 부추에 대해 bifenthrin 및 chlorfenapyr의 반감기를 조사한 결과 bifenthrin은 3.8-11.5일, chlorfenapyr는 6.6-13.4일로 나타났다고 보고하였으며(Park
>
Pre-harvest Residue Limit (PHRL) 산출
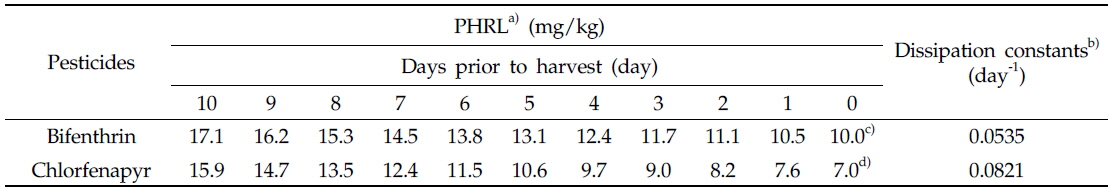
우리나라에서 들깻잎 중 bifenthrin 및 chlorfenapr의 잔류허용기준은 각각 10.0 및 7.0 mg/kg으로 설정되어 있다(MFDS report, 2012). 본 연구 결과에 따르면 들깻잎 중 bifenthrin의 최대 잔류량은 2회 및 3회 처리구 전체에서 잔류허용기준 이하로 나타났다. 반면에, chlorfenapyr의 경우 초기 잔류량이 각 처리구에서 9.02 및 9.92 mg/kg으로 나타나 잔류허용기준을 초과하였으나 시간의 경과에 따라 잔류량은 감소하여 최종 약제 살포 5일 후 2회 처리구에서 5.37 mg/kg, 3회 처리구에서 6.59 mg/kg으로 잔류허용기준 미만으로 나타났다.
두 농약의 2회 및 3회 처리구의 감소상수 중 낮은 감소상수를 이용하여 산출한 PHRL은 Table 4와 같으며, 이에 따르면 수확 10일 전 들깻잎 중 bifenthin 및 chlorfenapyr의 잔류량이 각각 17.1 및 15.9 mg/kg으로 잔류할 경우 수확예정일에 두 농약의 잔류허용기준 이하로 잔류할 것으로 예상할 수 있다. 이러한 PHRL 산출 방법은 들깻잎과 같은 연속 수확 소면적 재배 작물의 안전성 확보를 위한 유용한 기준설정 방법으로 사용될 수 있을 것으로 생각된다.
[Table 4.] Pre-harvest residue limits of bifenthin and chlorfenapyr in perilla leaves
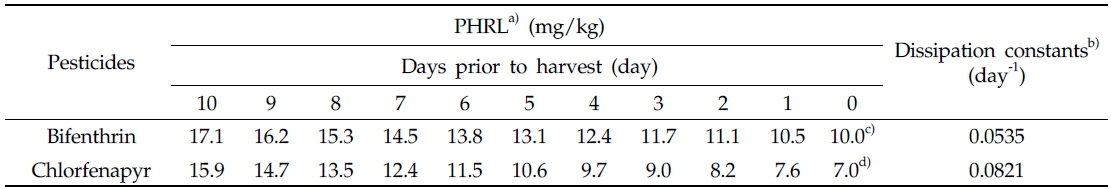
Pre-harvest residue limits of bifenthin and chlorfenapyr in perilla leaves