White stain symptom caused by
Environment-friendly materials were tested for control activity against
We were selected sulphur and Sodium-Dichloroisocyannurate(NaDCC) based on the results of experiments
최근 포도생육기간 내 기상조건이 고온다습한 조건이 되면서 포도의 병해충 밀도가 증가하고 있는데, 이 중 포도재배 시 문제가 되고 있는 포도흰얼룩증상은 포도 과실표면에 흰색의 가루가 묻은 것처럼 보이는 증상으로 1990년대 후반 처음 보고되었으며, 수확기에 급격히 발생하여 포도의 품질을 저하시켜 경제적 손실을 유발하고 있다. 포도흰얼룩증상을 유발하는 원인균으로는
식물 병해충의 방제를 위한 침투성 약제의 지속적 사용은 저항성 균의 출현의 원인이 되었으며, 이에 따른 약제 사용량의 증가로 환경오염 등의 문제가 야기되었다(Goodwin
포도흰얼룩증상은 포도의 수확기에 발생하기 때문에 이 증상이 다발하여도 합성농약을 살포하지 못하여 방제가 어려우나, 아직까지 친환경방제법을 활용한 연구결과는 없다. 따라서 본 연구는 여러 농자재를 활용한 포도흰얼룩증상의 친환경방제법을 확립하고자 수행하였다.
포도흰얼룩증상의 친환경방제를 위한 자재 선발을 위해 공시자재로 친환경농자재로 등록된 Borno (보르노, 중앙프라자), Bordeaux (보르도153, 중앙프라자, CM100, 중앙프라자), Sulphur (유황153, 창일바이오)와 염소계 살균소독제로 농산물의 살균시 사용(Lim
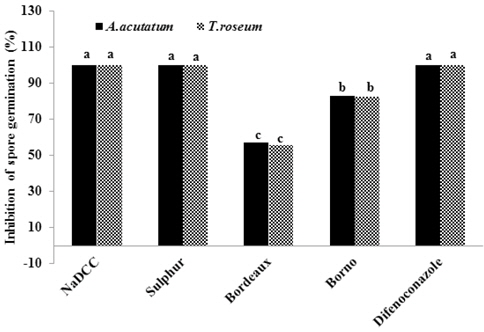
포자발아 억제율={(1-처리구 발아율)×100}/무처리 발아율
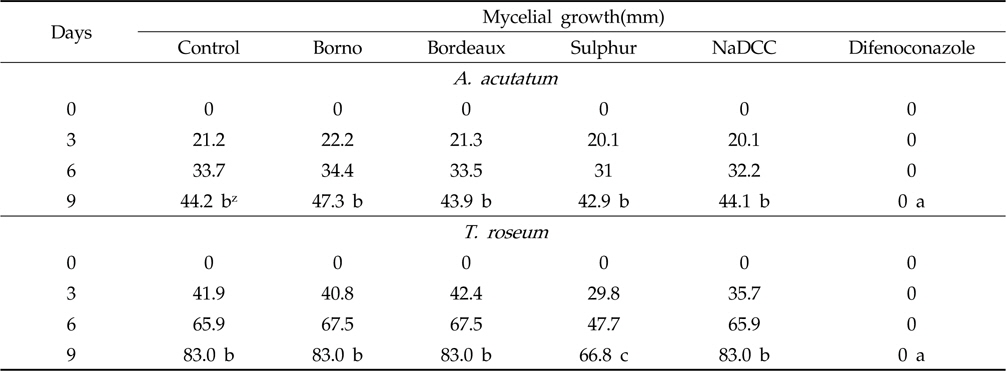
평판배지 상에서 균사생장 억제효과를 검정하기 위하여 멸균한 감자한천배지(Potato Dextrose Agar, PDA)를 50∼60℃로 식힌 다음, 공시자재의 최종 희석배수가 1000배가 되도록 혼합하여 petri dish에 분주하였다. PDA에서 배양한 균주의 선단부위를 cork borer (No. 2, DAIHAN, Korea)를 이용하여 취한 균총을 공시자재가 혼합된 배지의 중앙에 치상하였다. 시험은 3반복으로 실시하였고, 25℃ 배양기에서 배양하면서 2일 간격으로 균사직경을 측정하였다. 균사생장 억제율은 Choi 등(2006)의 방법에 따라 아래와 같이 산출하였다.
균사생장 억제율={(1-처리구 균사생장)×100}/무처리 균사생장
실내실험에서 발아 억제 또는 균사생장 억제효과가 확인된 공시자재들을 경기도 안성시 미양면과 경기도 화성시 서신면에 소재한 포도농가에서 포장시험을 실시하여 방제효과를 조사하였다. 포도흰얼룩증상의 발병초기부터 공시자재를 일주일 간격으로 3회 살포 후 무처리구와 발병율을 비교 분석하였다. 재배법상 과일봉지를 괘대하지 않는 거봉은 과실에 직접 분무 살포 하였으며, 과일봉지를 괘대하여 재배하는 캠벨얼리는 과일봉지를 씌운 채로 이병가지를 중점으로 살포하였다. 각 처리구에서 무작위로 수확하여 전체 조사과실중 이병과실의 비율을 조사하였으며, 방제가는 아래 식에 의거 산출하였다.
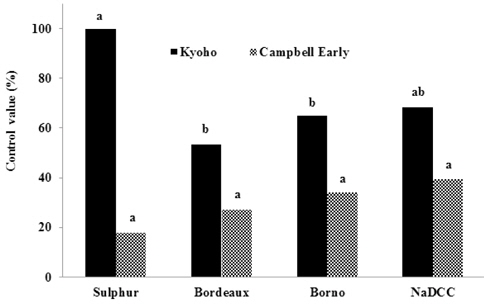
방제가={(1-처리구 발병율)×100}/무처리구 발병율
실내 및 포장실험으로 선발된 약제의 방제효과 및 약효 지속기간을 조사하기 위하여 경기도 안성시 미양면 소재의 거봉 포도농장과 경기도 화성시 서신면 소재의 캠벨얼리 포도농장에서 시험을 수행하였다. 공시한 친환경 자재는 포도흰얼룩증상의 발병 초기부터 1주일 간격으로 2∼3회 살포하였다. 각 처리구에서 무작위로 수확하여 전체 조사과실중 이병과실의 비율을 조사하였으며, 방제가는 약제선발을 위한 포장시험과 동일한 방법으로 산출하였다. 포도생육시기 및 약제처리 후 포도흰얼룩병원균의 밀도는 과실 1g 당 콜로니수로 조사하였다.
수집된 자료의 정리와 통계는 MS-EXCEL 2010과 SAS (version 8.0)를 이용하였으며, 처리평균간 비교는 DUNCAN 다중검정을 하여 유의확률
최근 농약사용의 최소화를 위해 천적을 이용하거나 선택적 독성을 지니는 농약을 선발하여 병해충을 종합적으로 관리하는 방안(Metcalf, 1994)이 꾸준히 시도되고 있다.
포도흰얼룩증상의 원인균인
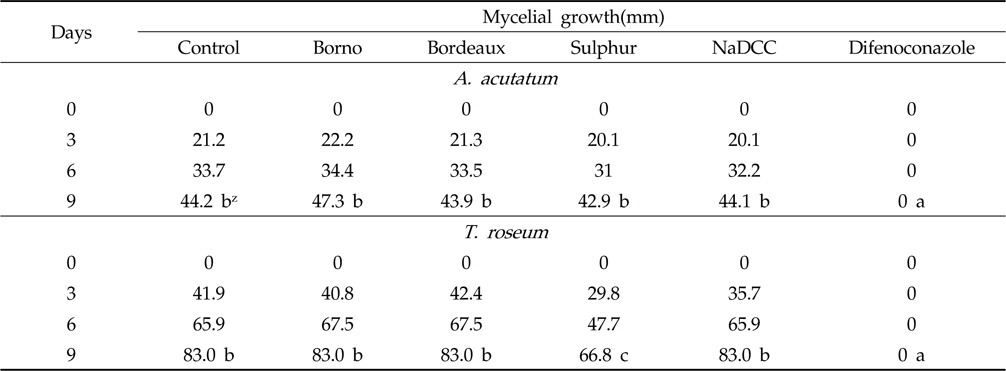
Inhibition of mycelial growth of A. acutatum and T. roseum on PDA plates by the Borno, Bordeaux, Sulphur, NaDCC and Difenoconazole
Defenoconazole의 생물학적 반감기는 풋마늘에서는 3.8일(Kang
거봉과 캠벨얼리에 공시자재를 살포하여 포도흰얼룩증상의 발생억제 효과를 조사하였다(Fig. 2). 과일에 공시자재를 직접 살포한 거봉 포도의 경우 Sulphur와 NaDCC 처리시 60% 이상의 방제효과가 있었다. 봉지를 씌운 후 살포한 캠벨얼리 포도에서는 NaDCC 처리의 경우 약 40%의 방제효과를 나타내어 가장 효과가 높았으나, 공시자재간 처리효과에 대한 통계적 유의성은 없었다. Bordeaux의 경우에는 과일에 직접 살포할 경우 약흔이 남아 과실의 상품성을 떨어뜨릴 수 있을 것으로 판단되었다. 따라서 포도흰얼룩병의 방제에는 균사생장 억제효과와 포자발아 억제효과가 있고 포장 방제실험에서 과실에 직접 살포시 60%이상의 방제 효과가 인정된 Sulphur과 NaDCC가 유용할 것으로 판단되었다.
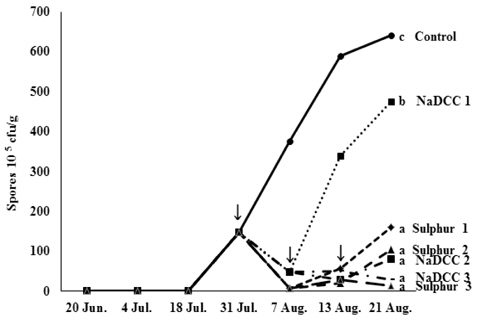
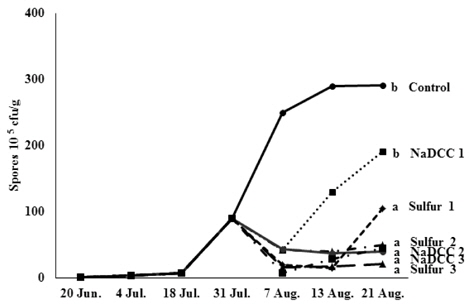
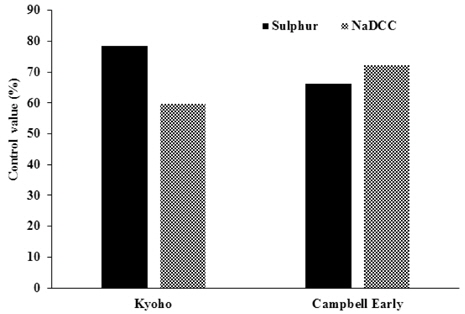
자재 선발 시험에서 효과가 인정된 Sulphur과 NaDCC의 포도흰얼룩증상에 대한 방제 효과를 실험하였다. 캠벨얼리와 거봉 과수원에서 발병초기부터 수확말기까지 NaDCC와 Sulphur의 살포횟수를 달리하여 포도흰얼룩증상의 억제효과를 조사하였다(Fig. 3 & 4). 병원균의 밀도가 증가하기 시작한 7월 말에 1차 살포를 실시한 결과 NaDCC와 Sulphur 처리구 모두 병원균의 밀도가 감소하였으나 무처리구는 병원균의 밀도가 급격히 증가하였다. NaDCC 1회 살포 처리구의 경우 약제살포 7일 이후부터 다시 병원균의 밀도가 상승하였으며, Sulphur 1회 살포 처리구는 14일 이후부터 병원균의 밀도가 증가하여 NaDCC와 Sulphur의 약효지속기간은 각각 7일과 14일로 판단되었다. 선발된 공시자재를 1회 살포 후 7일 간격으로 1회 또는 2회 추가 살포한 경우 병원균의 밀도가 지속적으로 낮게 유지되었다. 발병 초기부터 7일 간격으로 3회 처리 후 7일 째에 Sulphur과 NaDCC의 살포에 따른 방제가를 조사한 결과, 거봉에서는 각각 78.31%, 59.71%의 방제효과가 있었으며, 캠벨얼리에서는 66.19%, 72.26%의 방제효과가 있었다(Fig. 5). 따라서 포도흰얼룩증상의 예방 및 확산을 억제하기 위한 방제에 ulphur 및 NaDCC의 적용이 가능할 것으로 생각된다.