Cytogenetic analysis was conducted to obtain basic information for chromosome manipulation of starry flounder
어류의 염색체 조작을 통한 자성발생성 2배체 생산은 단기간에 순계를 확립할 수 있는 장점이 있고, 특히 그의 성결정 기작이 암컷동형접합성(XX female)일 경우 유도된 자성발생성 암컷을 생리학적 성전환 기법으로 생산한 가짜 수컷과 대조군 암컷을 교배시킴으로서 전 암컷집단을 손쉽게 생산할 수 있는 이점이 있어 많은 양식어류에 적용되어왔다(Kim et al., 1993). 넙치,
그간 자성발생성 2배체는 감성돔 또는 참돔의 정자를 불활성화시켜 유도한 바 있다(Kim et al., 1993; Yamamoto, 1999). 그러나 상기 어종들은 모두 봄에 산란하는 종으로 이들 종의 정자를 이용하는데 제한이 있으므로 이를 해소하기 위한 적절한 어종의 선택이 필요하다.
강도다리(
이에 본 연구에서는 저수온기 넙치의 자성발생성 2배체 유도에 강도다리의 정자를 이용하고자 본 종에 대한 세포의 크기와 DNA 함량 등을 조사하였고, 본종이 넙치와 잡종이 유도(Nam et al., 2008) 되는 점을 감안, 염색체에 대한 핵형 분석과 아울러, Ag-NOR banding을 실시함으로써 불완전한 처리에 의해 두 종간 잡종 또는 잡종 3배체가 유도되었을 시, 넙치의 염색체와 쉽게 구별할 수 있는 마커 염색체를 찾고자 하였다.
세포유전학적 분석을 위하여 거제도의 민간양식장과 부산시 남천동의 수산시장에서 구입한 어체중 350-500 g의 강도다리 14마리를 사용하였다.
적혈구의 세포와 핵 크기를 측정하기 위해 강도다리의 미병부 미부정맥으로부터 말초혈액을 채취한 후 슬라이드에 도말하여 95% ethanol에서 5분간 고정한 다음 5% Giemsa 염색 용액에서 15분간 염색하였다. 적혈구 세포와 핵의 장경(a) 및 단경(b)을 광학현미경에서 micrometer로 측정하였다. 표면적은 (a)·(b)·π/4 (Sezaki and Kobayashi, 1978), 부피는 4(a/2)·(b/2)2·π/3 (Lemoine and Smith, 1980)의 공식에 의하여 계산하였다.
DNA 함량을 분석하기 위해 Flowcytometry를 수행하였다. 강도다리의 꼬리지느러미를 면도칼로 세절한 후 nucleic extraction buffer (Partec, Germany)을 250 μL 넣고 20분간 암실에서 반응시킨 뒤, staining buffer (Partec, Germany)를 1 mL 첨가하여 암실에서 1시간 동안 반응하였다. 염색한 시료를 30 μm 체로 거른 뒤 PartecPA-Ⅱ flowcytometer (Partec, Germany)로 DNA 함량을 측정하였다.
강도다리의 염색체 수 판별 및 핵형 분석을 위해 신장직접법(Kim et al., 1982)을 이용하였다. 실험군에 colchicine을 5-10 μg/g 체중의 용량으로 복강 주사하고 4-5시간 방치한 후 신장을 적출 세절한 후 상온에서 저장액(0.075 M KCl)에 처리하고 고정액(ethanol : glacial acetic acid = 3: 1)으로 3회에 걸쳐 고정하였다. 슬라이드 표본은 공기건조법으로 작성되었으며, 작성된 슬라이드 표본은 5% Giemsa 염색 용액에 15분간 염색하여 광학 현미경에서 중기 염색체 상을 관찰하였다. 각 슬라이드당 10여개의 판독 가능한 염색체 중기 분열상을 대상으로 계수 하였으며, 분열상이 뚜렷한 시료를 대상으로 사진 촬영하여 핵형을 분석하였다.
>
염색체의 Nuclear organizer regions (NORs) 분석
강도다리의 염색체 NORs를 분석하기 위해 Goodpasture and Bloom (1975)의 방법을 약간 수정하여 사용하였다.
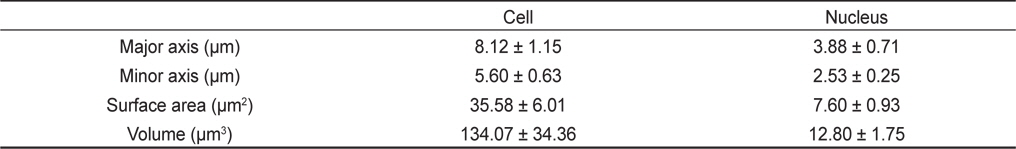
어류의 적혈구 세포 및 핵의 크기 조사는 배수체의 판단 기준 및 잡종의 세포유전학적 특징을 연구하는데 유용하게 이용되고 있다(Benfey, 1989). 이에 강도다리의 세포 및 핵의 크기를 측정한 결과 적혈구 세포 장축은 8.12±1.15 μm, 단축은 5.60±0.63 μm였으며, 표면적은 35.58±6.01 μm2, 부피는 134.07±34.36 μm3였다. 또한 적혈구 핵의 장축은 3.88±0.71 μm, 단축은 2.53±0.25 μm였으며, 표면적은 7.60±0.93 μm2, 부피는 12.80±1.75 μm3로 관찰되었다(Table 1). 이를 Kim et al. (1993)이 보고한 넙치와 비교 시 적혈구 세포의 표면적 및 부피는 85-87% 정도로서 앞으로 본종을 이용하여 자성발생성 넙치 생산 시 이를 분석할 수 있는 하나의 기준이 될 수 있을 것으로 생각된다.
[Table 1.] Comparison of cell and nuclear sizes of Platichthys stellatus
Comparison of cell and nuclear sizes of Platichthys stellatus
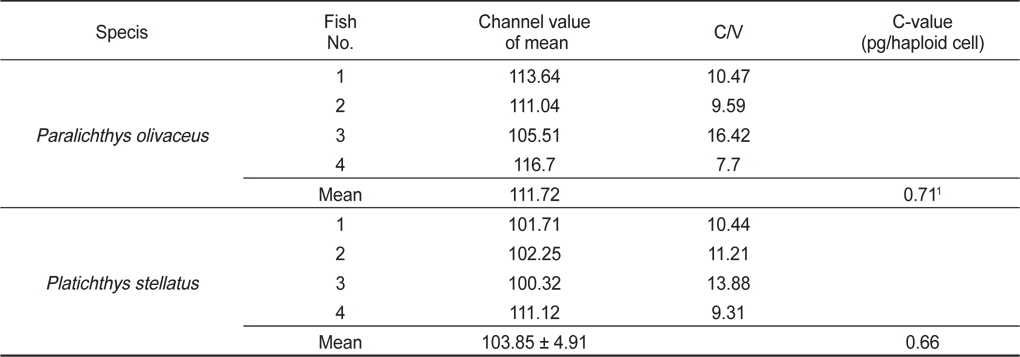
DNA 함량은 종에 따라 고유하며 진화 정도에 따라 일반적으로 증가하고, 단시간에 정확하게 그 함량을 분석할 수 있는 장점이 있어 종 고유의 특성을 분석하는데 유용하게 사용되고 있다(Byrappa, 2003). 따라서 앞으로 넙치의 자성발생성 개체를 유도 시 적절치 못한 조건에 의해 유도된 잡종 또는 잡종 3배체를 DNA 분석을 통해 선별하기 위해 이미 보고되어 있는 넙치(0.71 pg/haploid cell; Animal genome size database, 2014)를 대조군으로 하여 측정한 결과, 강도다리의 DNA 함량은 0.66 pg/haploid cell로 확인되어(Table 2) 넙치의 93%로서 앞으로 자성발생성 넙치, 넙치와 강도다리간 잡종 및 잡종 3배체의 DNA 함량 분석에 유용하게 쓰일 수 있을 것으로 사료된다.
[Table 2.] Genome size of Platichthys stellatus determined by flow cytometry
Genome size of Platichthys stellatus determined by flow cytometry
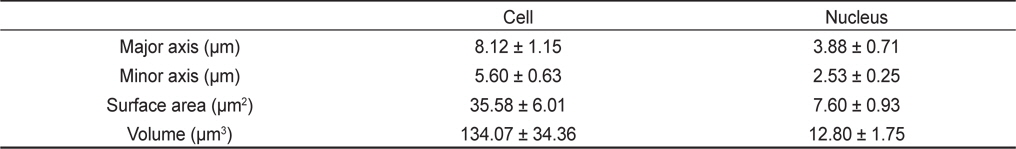
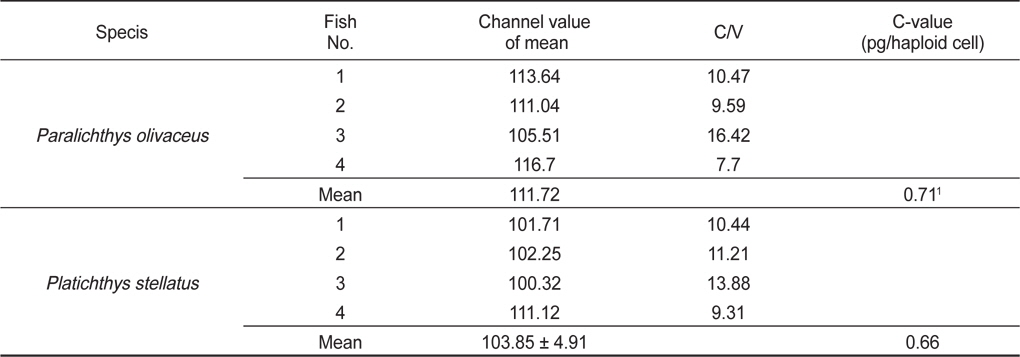
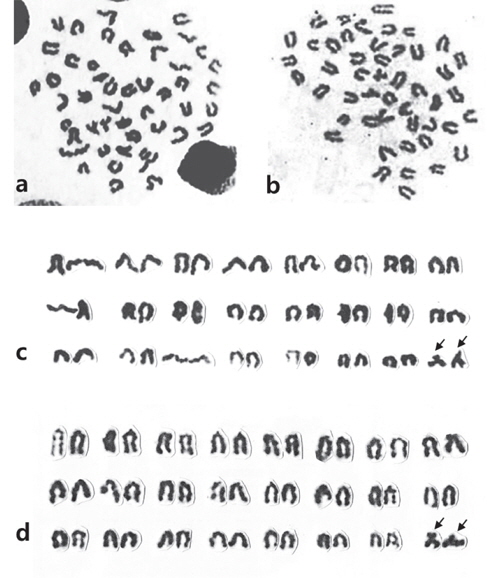
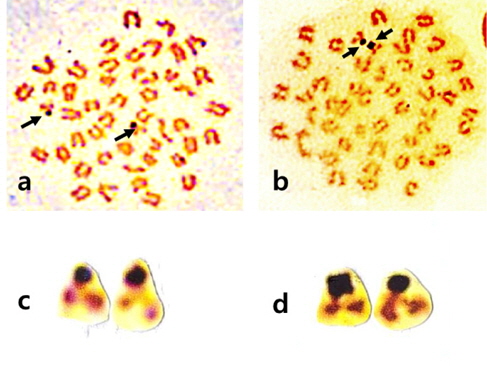
Fig. 1a와 1b는 강도다리의 암컷 및 수컷의 중기분열상이다. 강도다리 암컷 2마리, 수컷 5마리를 대상으로 각 개체당 10개 이상의 중기분열상을 분석한 결과, 강도다리의 염색체 수는 2n=48 그리고 핵형은 차단부염색체가 24쌍이었다. 암∙수간 염색체수의 차이는 없었으며, 개체간 및 세포간 염색체 다형현상도 관찰되지 않았다(Fig. 1c - 1d). 그러나 암수 모두 가장 작은 1쌍의 차단부 염색체의 단완 부위가 매우 큰 것이 관찰 되었으나 Ag-NOR banding 결과 그 부위가 매우 진하게 염색되어 인형성 부위인 것으로 판명되었다(Fig. 2).
중국산 강도다리의 경우 Li (2009)는 2n=48이며 46 단부 염색체와 1 쌍의 차중부 염색체로 구성되어 있다고 보고한 바 있다. 그러나 본 연구에서 Ag-NOR banding 방법을 통하여 이들 염색체를 분석한 결과, 일반염색에 의하여 진하게 염색되는 한 쌍의 작은 차단부 염색체의 단완 부위는 NOR positive 부분인 것으로 확인되었다. 따라서 앞으로 중국산 강도다리에 대하여 Ag-NOR banding을 통해 재분석을 하여야 할 것으로 생각된다.