The genera Pseudokeronopsis and Uroleptopsis are included in the family Pseudokeronopsidae which was established by Borror and Wicklow (1983).
The Pseudokeronopsis consists of 10 species and all mem-bers have frontal cirri arranged as a bicorona, which continue posteriorly to two midventral rows and marginal cirri on each side of the body (Borror and Wicklow, 1983; Berger, 2006; Song et al., 2006). Identification of species in the Pseudokeronopsis, however, is somewhat difficult because the diagnostic keys such as body shape, body colour, body size and ciliary pattern either are overlapped or similar among congeners (Song et al., 2006).
Kahl (1932) established the genus Uroleptopsis due to the lack of transverse cirri in some species on classification in Holosticha (Keronopsis). Later, Berger (2004) redescribed Uroleptopsis citrina by its morphology and morphogenesis, and divided Uroleptopsis into the two subgenus, Uroleptopsis(Uroleptopsis) and Uroleptopsis (Plesiouroleptopsis), thro-ugh the presence of cirrus II/2 in the ordinary position, right of the undulating membranes.
In this study, we described two marine ciliates new to Korea, P. carnea and U. citrina, based on live and protargol-impregnated specimens. Moreover, the sequences of the small subunit ribosomal RNA (SSU rRNA) gene from two species were determined and compared with those of known sequences obtained from the NCBI website.
The specimens of Pseudokeronopsis carnea were collected from Incheon harbor in the Yellow Sea ( salinity, 28.5‰; temperature, 15℃; 37? 26?N, 126? 35?E), Korea, in November 2010, and those of Uroleptopsis citrina were collected from Guryongpo, Pohang in the East Sea (salinity, 32.3‰; tempera-ture, 24.1℃; 35? 59?N, 129? 33?E), Korea, in September 2008.
After collection and isolation, specimens were maintained in the laboratory, either as pure or raw cultures in Petri dishes and 50 mL tissue culture flasks (Greiner Bio-one, Fricken-hausen, Germany). Autoclaved seawater was supplied with putting rice grains as a substrate for bacterial growth (Jung et al., 2011). The living specimens were observed under a light microscope ( Leica DM2500; Leica Microsystems, Wetzlar, Germany) at 50-1,000 magnification. Protargol impregnation was applied according to Foissner (1991) to reveal the infraciliature.
Terminology and classification are mostly according to Berger (2006) and Lynn (2008).
A cell (single specimens of each species) was transferred to a 1.5 mL microtube with a minimum volume of water. Geno-mic DNAs were extracted using a RED-Extract-N-Amp Tis-sue PCR kit (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA), according to the manufacturer’s protocol. The nearly complete SSU rRNA genes were amplified by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) with the universal eukaryotic primers: New EukA (5?-CTG GTT GAT YCT GCC AGT-3?), modified from Medlin et al. (1988), and LSU rev3 (Sonnenberg et al., 2007) primers. The optimized conditions for this process were as follows: Denaturation at 94℃ for 3 min followed by 35 cycles of denatura-tion at 95℃ for 15 sec, annealing at 58℃ for 30 sec, extension at 72℃ for 4 min, and then a final extension step at 72℃ for 7 min. The PCR products were purified with the QIAquick® PCR Purification kit (Qiagen, Valencia, CA, USA). Three internal primers were used for sequencing: 18S+810 (5?-GCC GGA ATA CAT TAG CAT GG-3?) and 18S-300 (5?-CAT GGT AGT CCA ATA CAC TAC-3?) and 18S+1470(5?-TCT GTG ATG CCC TTA GAT GTC-3?). Sequencing in both directions was conducted by an ABI 3700 Sequencer(Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA).
The sequencing fragments of the SSU rRNA gene were combined via BioEdit (Hall, 1999) and were aligned using Clustal X 1.81 (Jeanmougin et al., 1998). Mega 4.0 (Tamura et al., 2007) was used to calculate genetic distance by applying the Kimura two-parameter distance method (Kimura, 1980).
Korean name: 1*뚱뚱이홍색위각모충 (신칭)
Phylum Ciliophora Doflein, 1901
Class Spirotrichea Butschli, 1889
Order Urostylida Jankowski, 1979
Family Pseudokeronopsidae Borror and Wicklow, 1983
Genus Pseudokeronopsis Borror and Wicklow, 1983
1*Pseudokeronopsis carnea (Cohn, 1866)
Wirnsberger et al., 1987 (Table 1, Figs.1 A-D, 2)
Oxytricha flava var. carnea Cohn, 1866: 288, 300.
Holosticha (Keronopsis) rubra var. carnea (Cohn, 1866) Kahl, 1932: 573.
Pseudokeronopsis carnea (Cohn, 1866) nov. comb. Wirns-berger et al., 1987: 79, fig. 9, Tables .1-3
Pseudokeronopsis rubra sensu Shi and Xu, 2003: 23-30.
Pseudokeronopsis pararubra Hu, Warren and Suzuki, 2004: 351-368.
Pseudokeronopsis carnea (Cohn, 1866) Wirnsberger et al.,
1987, Song et al., 2006: 271-287, figs.1 A-G, 2, 3, 9C, Tables .1-3
Material examined. One population was obtained from In-cheon harbor on November 2, 2010.
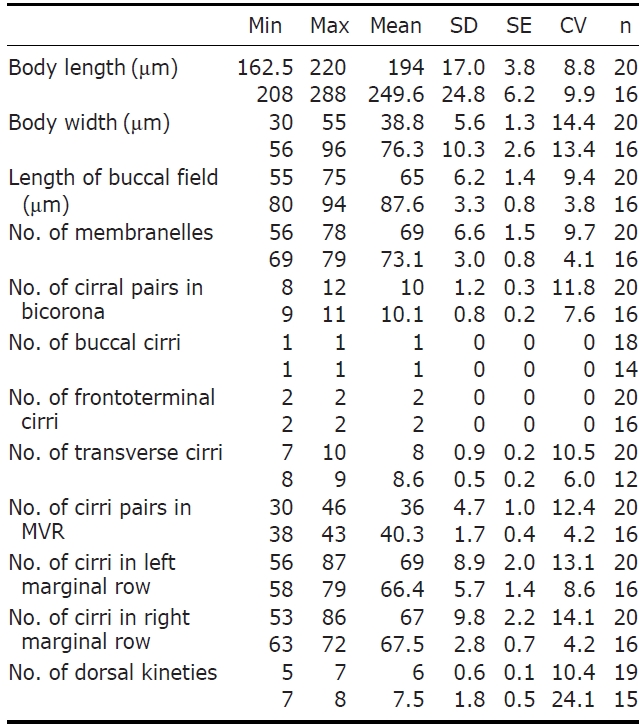
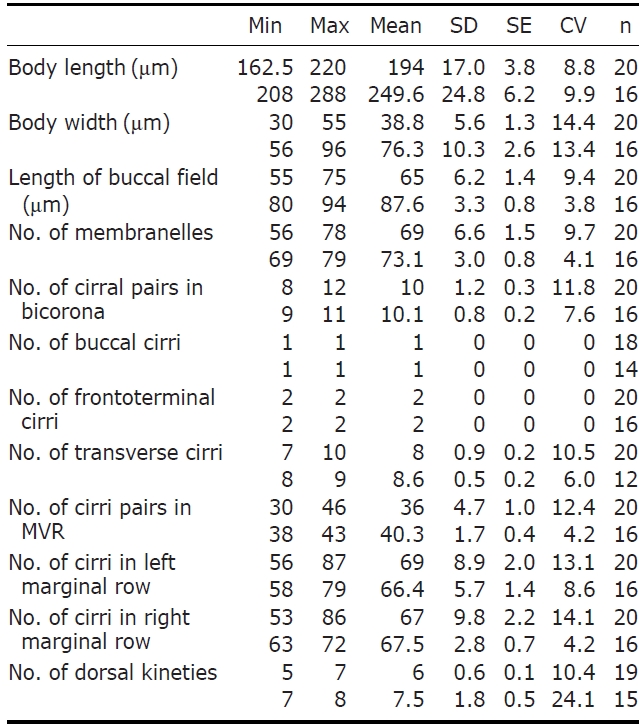
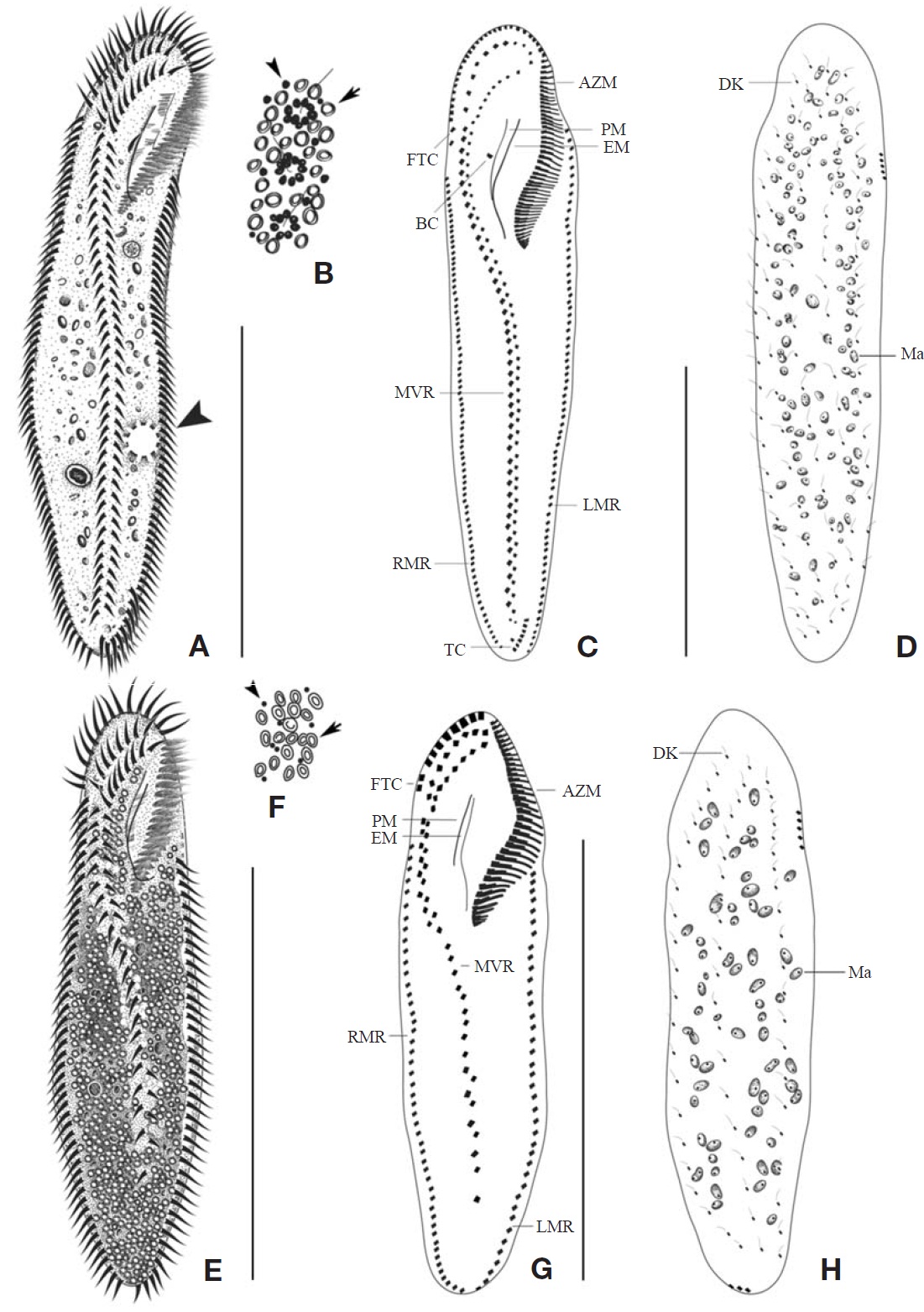
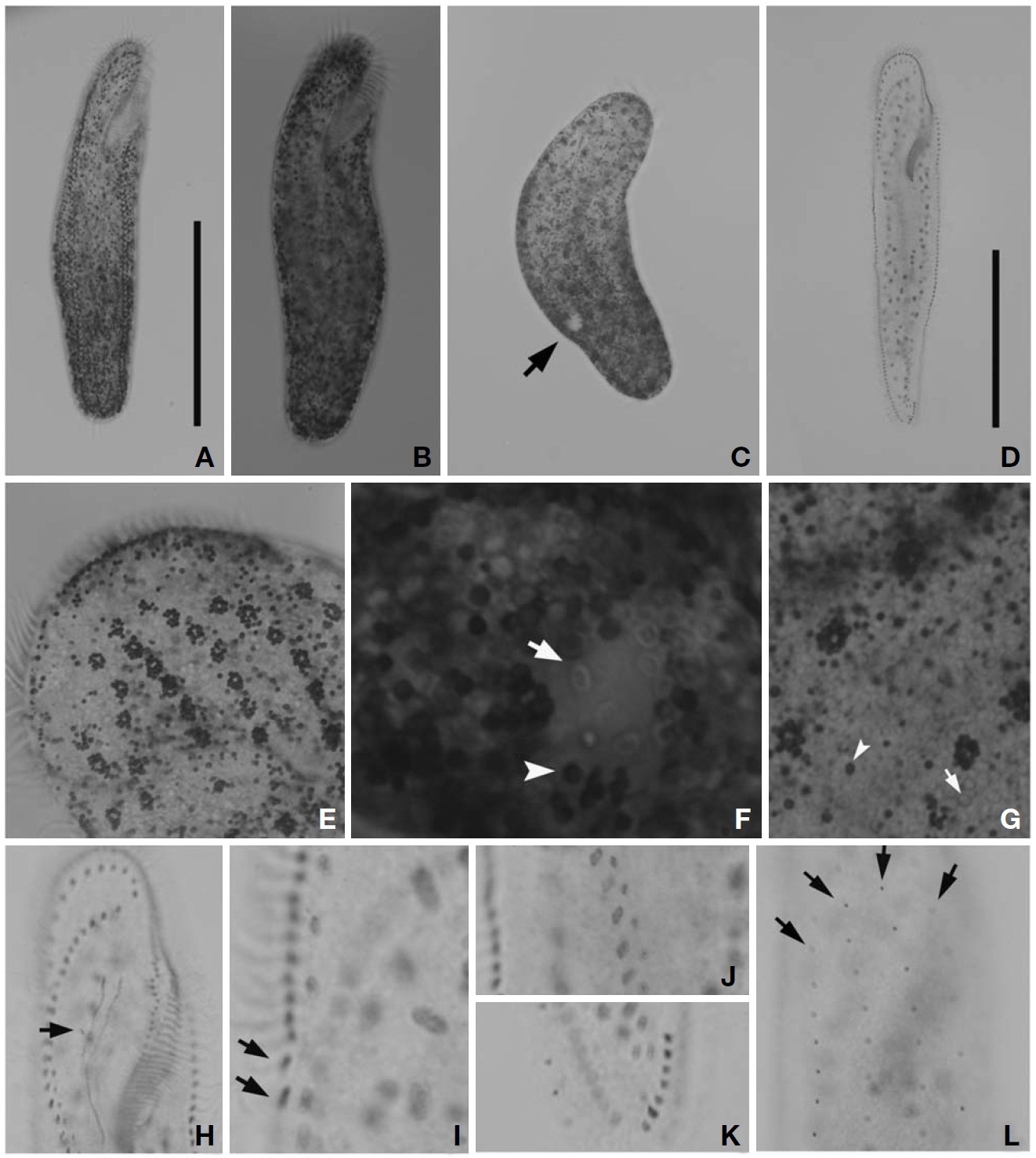
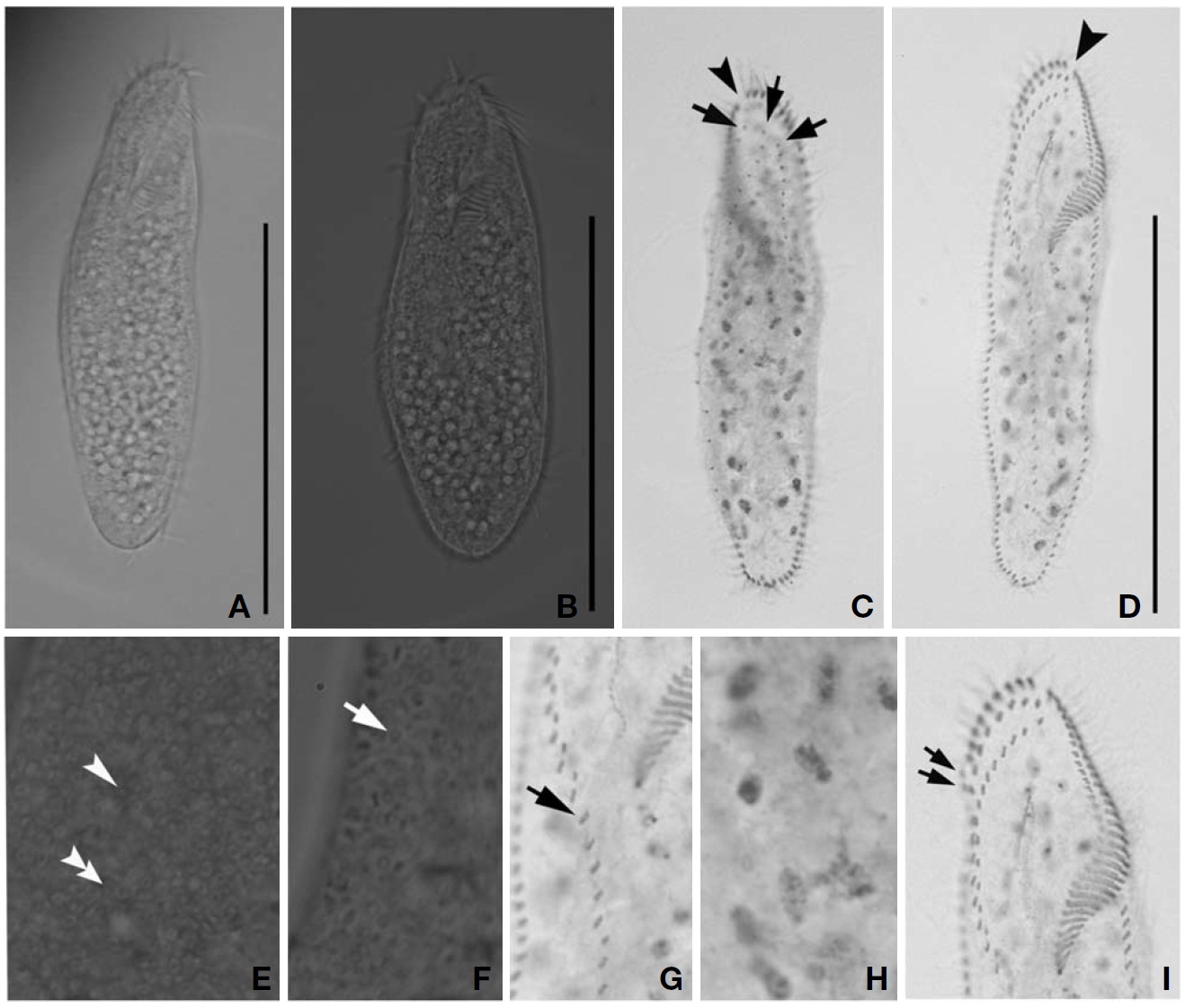
Description. Cell in vivo slender shape, 190-255×55-70 ㎛, usually 225×61.3 ㎛ (Figs.1 A, 2A); anterior end bluntly rounded (Fig.2 B); posterior end inconspicuously narrowed; both anterior and posterior ends round; dorsoventrally flattened. Contractile vacuole located on the left side usually in posterior 1/3-2/5 (Figs.1 A, arrowhead; 2C, arrow); reddish cortex due to underlying reddish-brown or orange-red in colour cortical granules, which are around both dorsal kine-ties and cirri (Fig.2 E; F, G, arrowhead); cortical granules colourless, blood cell shaped, scattered throughout the cell body (Fig.2F, G, arrow).
The adoral zone of membranelles distinct, approximately 1/3 of the cell length, and composed of about 69 membran-elles(Fig.2 D, H). Bicorona of frontal cirri slightly enlarged,composed of about 8-12 cirral pairs, extending as a midven-tral complex consecutively. One buccal cirrus near the paro-ral membrane (Fig.2 H, arrow), whereas two frontoterminal cirri behind the distal end of the adoral zone (Fig.2 I, arrows); midventral complex distinctly separated rows (Fig.2 J), com-posed of 30-46 cirral pairs, terminating near transverse cirri; both posterior ends of marginal cirral rows not overlapped; 7-10 transverse cirri located between both posterior ends of the left and right marginal cirral rows (Fig.2 K). Almost no gap found between the midventral rows and the transverse cirri; from five to seven dorsal kineties (Figs.1 D; 2L, arrows).
Distribution. North Sea, German, Denmark, Mediterranean,Yugoslavia, China and Korea (this study).
Remarks. Cohn (1866) published Oxytricha flava var. carnea without any illustration. As the former species is almost iden-tical to P. flava, he classified it as a variety of Oxytricha flava.The derivation of the name was not given in the original description of P. carnea.The meaning of carnea in Latin is “fleshy.” In 1882, Kent transferred Oxytricha rubra to the genus Holosticha. Kahl (1932) classified Keronopsis as a subgenus of Holosticha.Then, Kahl named it Holosticha (Keronopsis) rubra var. carnea. Even after several taxono-mists recorded this species, they were considered it Pseudo-keronopsis rubra or P. flava in confusion. Entz (1884) con-sidered P. carnea as a transitional form between P. rubra and P. flava.The neotype of P. carnea was fixed by Wirns-berger et al. (1987) and until now, a Chinese population of P. carnea has been redescribed solely (Song et al., 2006).
Eight species among the genus Pseudokeronopsis live in marine habitats. Because Pseudokeronopsis species are somewhat difficult to classify and identify among congeners, the colour as main diagnostic key is the critical factor disting-uishing P. carnea from the other congeners (Hu and Song, 2001). The orange-red colour of cortical granules is essen-tial for identifying P. carnea (vs. colourless, P. decolar and P. ovalis; yellow, P. flavicans and P. flava; brick-red, P.rubra; yellow-greenish, P. sepetibensis; brick-red and yellow, P. multinucleata). Moreover, with the exception of the colour of the cortical granules, the ciliary pattern and position of the contractile vacuole support species separation (Song et al., 2002; Berger, 2006). Like the name suggests, this species has the most plump body shape among the congeners. Alth-ough the anterior end is bluntly rounded, the posterior end is inconspicuously narrowed. This species can be separated from the other congeners by having: more cirral pairs in both the bicorona and the midventral rows; more transverse cirri; more dorsal kineties; a contractile vacuole in the posterior half of the cell, usually in the posterior 1/3-2/5; more conspi-cuous pigment granules, always dark red or orange-red. The number of adoral membranelles in this organism is also con-spicuously more than that of other congeners. In addition, the adoral zone of membranelles is relatively long compared to body length (ratio, 1 : 3), and almost no gap exists bet-ween the midventral rows and the transverse cirri.
The Korean population, Pseudokeronopsis carnea, has a few differences from the Chinese population of P. carnea (Song et al., 2006) as follows: (1) dorsal kineties (5-7 vs. 7-8); and (2) transverse cirri (on average 8 vs. 8.6). In addition, we ascertained that the sequence was successfully amplified on the partial region of the SSU rRNA gene and the amplified se-quence length is 1,756 bp (GenBank accession no: JN714476) and shows 99.89% similarity with the Chinese population (GenBank accession no: AY881633).
1*Genus Uroleptopsis (Uroleptopsis) Kahl, 1932
2*Uroleptopsis citrina Kahl, 1932 (Table 2, Figs.1 E-H, 3)
Uroleptopsis citrina Kahl, 1932: 543, fig.87 ; Kahl, 1933:107, fig. 1612.; Kudo, 1950: 672; Borror, 1972: 11; Berger, 2004: 99-121, 5-28, 35-42, table 1.
Material examined. One population was obtained from Guryongpo, Pohang in September 2008.
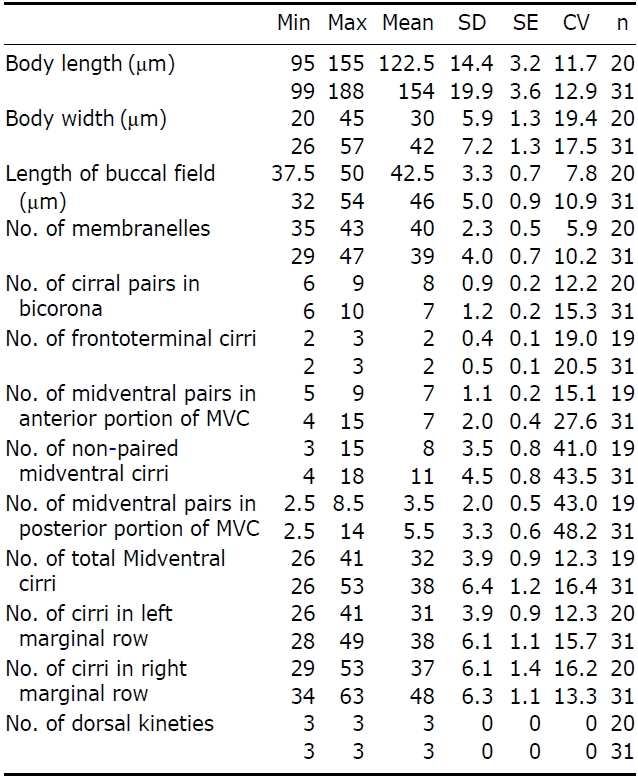
Description. Cell in vivo slender shape, 118-165× 45-55 ㎛, usually 130.2× 50 ㎛ (Figs.1 E, 3A, B); body shape elon-gate-elliptical; both anterior and posterior ends round and dorsoventrally flattened. Contractile vacuole difficult to recognize, located on the left side of usually slightly squeezed cells. Body colour is lemon-yellow due to cortical granules,
which are around both dorsal kineties and cirri; cortical gra-nules colourless, blood cell shaped, scattered throughout the cell body (Figs.1F, 3E, F).
The adoral zone of membranelles distinct; about 1/3 of cell length, and composed of about 40 membranelles (Fig.3 D, I), left anterior corner a minute process causing a break (Fig.3 C, D, arrowhead). Bicorona of frontal cirri slightly enlarged, composed of about 6-9 cirral pairs, extending as a midventral complex consecutively (Fig.3 I). Midventral complex distin-ctly separated rows, composed of 26-35 cirri containing anterior, single cirri (Fig.3 G, arrow) in middle portion, posterior portion. Two or three frontoterminal cirri behind the distal end of the adoral zone (Fig.3 I, arrows); invariably three dorsal kineties (Figs.1 H; 3C, arrows); of particular interest, there is no buccal cirrus and transverse cirri.
Distribution. Adriatic Sea, and Korea (this study).
Remarks. Kahl (1932) established the genus Uroleptopsis and described firstly U. citrina. Later, Berger (2004) rede-scribed U. citrina of the Adriatic Sea by its morphology and morphogenesis. Uroleptopsis citrina has a gap in the adoral zone and lacks transverse cirri. The loss of the transverse cirri is the main diagnostic character to separate U. citrina from other Pseudokeronopsidae species. This species has conspicuous differences from the congener U. ignea as fol-
lows: presence of a buccal cirrus and the pattern of the mid-ventral complex. Circumstantially, U. citrina lacks a buccal cirrus in the ordinary position, right of the paroral, whereas is present in U. ignea. Also, the anterior and posterior portion of the midventral complex in this species primarily consist of ordinary midventral pairs; the middle portion is compos-ed only of the right cirri of the cirral pairs, whereas the an-terior portion of the midventral complex in U. ignea is com-posed of paired cirri, and the middle and posterior portion consist of non-paired cirri (Mihailowitsch and Wilbert, 1990). Yellow cortical granules and ring-shaped structures are under-neath the cell surface. Consequently, U. ignea is transferred to the subgenus Uroleptopsis (Plesiouroleptopsis) by Berger (2004).
Also, U. citrina is a little different from Pseudokeronopsis flava in that the cell colour is yellow. However, P. flava has one buccal cirrus in the ordinary position, 2-4 transverse cirri, 3-4 dorsal kineties, and lacks a break in the adoral zone (Song et al., 2004).
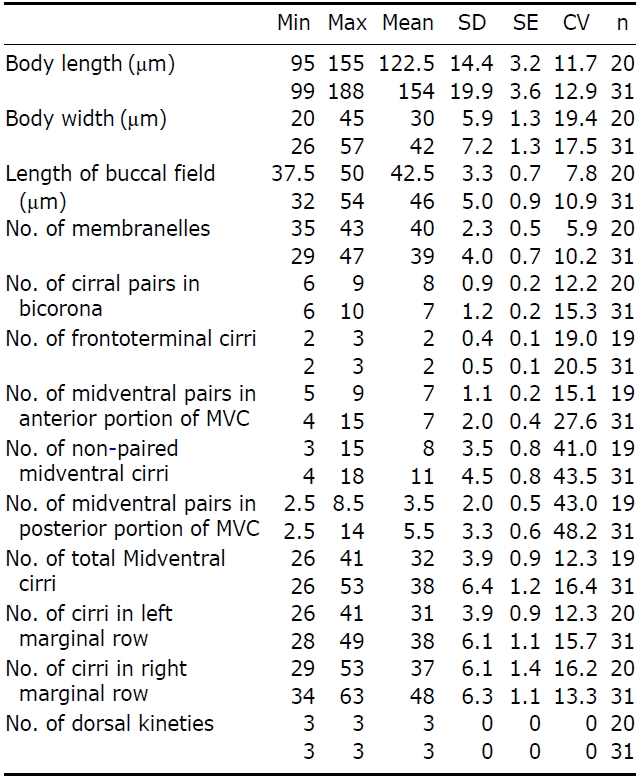
The Korean population, U. citrina, has a few differences from the Adriatic Sea population of U. citrina (Berger, 2004) as follows: (1) left marginal cirri (26-41 vs. 28-49); (2) right marginal cirri (29-53 vs. 34-63); and (3) single midventral cirri (on average 8 vs. 11). Additionally, we ascertained that the sequence was successfully amplified on the partial region of the SSU rRNA gene and the amplified sequence length is 1,754 bp (GenBank accession no: JN714477) and shows 99.88% similarity with that of Chinese population (GenBank accession no: GU437211). Unfortunately, no Adriatic Sea population sequence is available in GenBank.