본 연구에서는 전과정평가 방법론을 사용하여 연구 단계에 있는 폐폴리우레탄으로부터 폴리올을 재활용하는 기술의 전 과정평가를 수행하여, 이 재활용 기술의 환경부하를 산출하고 환경 성과를 개선하기 위한 향후 방향을 제시하였다. 현재 연구 단계의 재활용 기술과 예상 가능한 양산 단계의 재활용 기술의 환경부하를 신재 폴리올의 환경부하와 비교한 결과, 각각 93%, 60%로 환경개선 효과가 각각 7%, 40% 수준에 이르는 것으로 나타났다. 또한 전과정평가 결과로 향후 폴리올 재활용 기술에서 환경 부하를 줄이려면 알킬렌옥사이드와 스팀 사용을 줄이거나 대체하는 것이 바람직하다는 결론을 도출하였다.
A life cycle assessment (LCA) methodology was employed to evaluate environmental impact of recycled polyol from polyurethane in an R&D stage and to suggest future direction for improvement of environmental performance of the recycling technology. The comparison result shows between recycled polyol in the developing stage and in the anticipated mass production with virgin polyol production that environmental impact of recycled polyol of the developing stage and the anticipated mass production level correspond to 93%, 60% of that of virgin polyol, respectively. The LCA result identifies improvement areas of reducing environmental impact in recycling polyols, that is, use of alkylene oxide and steam. In the future research, this must be taken into consideration for better performance of recycling technology.
폴리우레탄 폼 스크랩은 폐전기전자 제품의 증가로 인해 발생량이 꾸준히 증가하고 있으며, 현재 대부분 소각하는 실정이다. 폴리우레탄 폼 스크랩 소각 시 발생하는 HCN은 대기오염 유발과 소각 설비의 부식을 야기하는 등의 문제가 있다. 이러한 환경적 문제점을 개선하고 재활용 자원을 개발하여 국가 자원 경쟁력을 강화하기 위해 전북대학교에서 폴리우레탄 폼 스크랩을 재활용하여 폴리올을 재생하는 기술을 연구하고 있다[1].
한편 재활용 기술 역시 투입되는 에너지 및 자원과 배출되는 대기 및 수질 오염물질로 인해 환경오염이 발생된다. 따라서 재활용 기술로 생산되는 재생재의 환경 영향을 분석하는 것은 재활용 기술의 환경 가치를 파악하고 재활용 기술의 환경 영향을 개선하기 위해 필요한 항목을 도출할 수 있어 중요하다.
본 연구는 폴리우레탄 폼 스크랩을 재활용하여 생산한 재생 폴리올의 전과정평가와 신재 폴리올과 환경영향의 비교를 통해 재생 폴리올의 환경 성능을 파악하고 폴리우레탄 폼 스크랩 재활용 기술의 환경 영향을 개선할 수 있는 방향을 도출하기 위해 수행되었다.
재생 폴리올의 전과정평가는 재생 폴리올의 주요 환경영향 범주 및 물질별로 정량적인 환경영향을 평가하여 신재 폴리올의 환경영향과 비교하기 위하여 수행되었다. 보다 현실적인 비교를 위해 현재 연구 개발 수준 및 양산 단계의 예상 공정 수준에 대하여 전과정평가를 수행하였다[2,3].
2.2.1. 기능 및 기능단위 설정
본 전과정평가의 기능, 기능단위 및 기준흐름은 Table 1과 같다.
[Table 1.] Function, functional unit and reference flow of recycled polyol
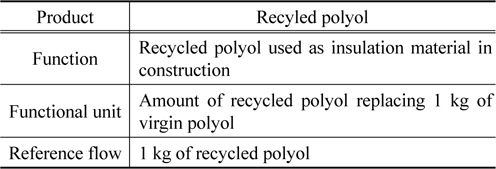
Function, functional unit and reference flow of recycled polyol
2.2.2. 시스템경계
본 연구의 시스템 경계는 폴리우레탄 폼 스크랩 재활용 공정의 Gate to Gate로 설정하였다. 실제 폼 스크랩을 재활용하기 위해서는 폼 스크랩을 수집하는 수집 공정, 재활용 공장으로 이동하는 수송 공정, 타 물질과 분리하는 선별 공정이 존재할 것이나, 현재 소각 시에도 수집, 수송 및 선별 공정이 필요하며, 대상 기술이 현재 개발 중이어서 해당 데이터 수집이 불가능한 점을 고려하여 수집, 수송 및 선별 공정은 본 연구의 시스템 경계에서 제외하였다.
2.2.3. 가정 및 제한 사항
본 연구에서는 재활용 공정에 투입, 배출되는 물질에 대한 모든 데이터를 포함하는 것을 원칙으로 하였다. 그러나 폼 스크랩은 기존에 소각되는 폐기물을 사용하여 스크랩의 환경부하는 “0”으로 가정하였다. 투입되는 물질 중 촉매는 매우 소량이 투입되어 제외하였다. 에너지로 사용되는 스팀은 발열량 데이터의 부재로 일반 조건 하의 스팀 발열량을 적용하였다. 경유는 연소 시 대기 배출물이 발생하는데 데이터가 수집되지 못해 IPCC 가이드라인[4]을 참고로 계산하였다.
2.2.4. 할당
대상 기술의 생산 공정에서 부산물이 발생하지 않아 할당을 수행하지 않았다.
2.3.1. 공정흐름도
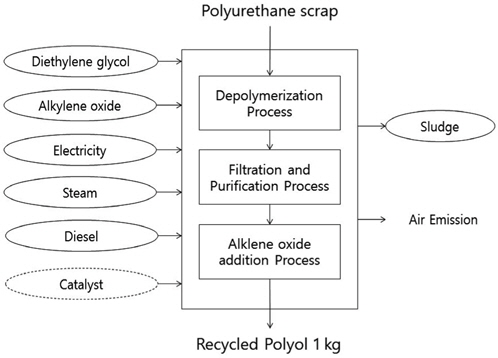
폴리우레탄 폼 스크랩 재활용을 위한 단위 공정을 기중으로 공정흐름도(process flow diagram)를 작성하였다. 단위 공정은 데이터 수집의 용이성과 공정 특성 등을 고려하여 해중합, 여과 및 정제, 알킬렌 옥사이드 첨가의 3개로 구분하였다. 공정흐름도는 Figure 1에 나타내었다.
2.3.2. 데이터 수집 및 계산
① 데이터 범주
본 연구의 데이터 범주는 원료물질, 보조물질, 용수, 에너지, 제품, 부산물, 대기 배출물, 수계 배출물 및 폐기물로 구분하였다.
② 데이터 수집
데이터 수집은 재활용 기술 개발 기관의 현장데이터를 우선 적용하기 위해 설문서를 통하여 현장 데이터를 수집하였다. 데이터 수집이 불가능한 경우 계산 및 추정을 통하여 데이터를 수집 및 보완하였다.
LCI 데이터베이스의 사용은 원료물질, 보조물질, 에너지 등의 상위흐름 및 하위흐름 연결을 위한 데이터베이스를 활용하는 것으로 국내 LCI 데이터베이스는 환경부와 산업통상자 원부(구 지식경제부)에서 구축한 데이터베이스를 적용하고[5], 해외 LCI 데이터베이스는 Ecoinvent에서 구축 한 데이터베이스를 사용하였다[6].
전과정 영향평가는 분류화(classification), 특성화(characterization), 정규화(normalization) 단계로 수행했으며, 특성화 값과 정규화 값은 환경성적표지제도(환경부)의 방법론을 적용하여 도출하였다.
2.4.1. 특성화 결과
① 현재 재활용 기술 수준 특성화 결과
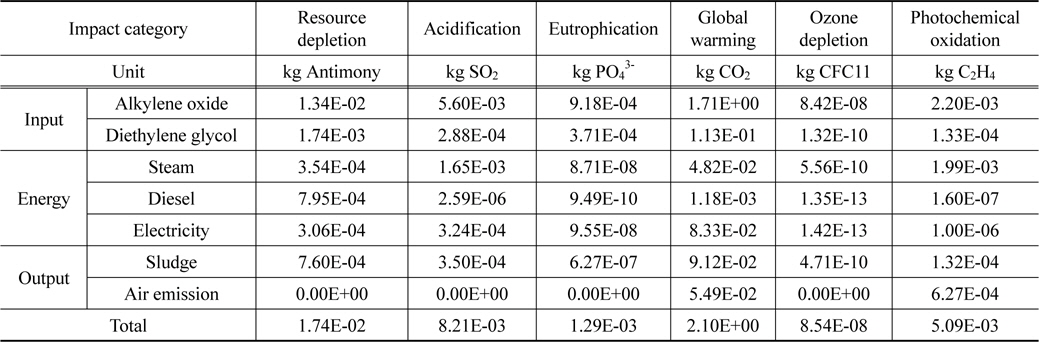
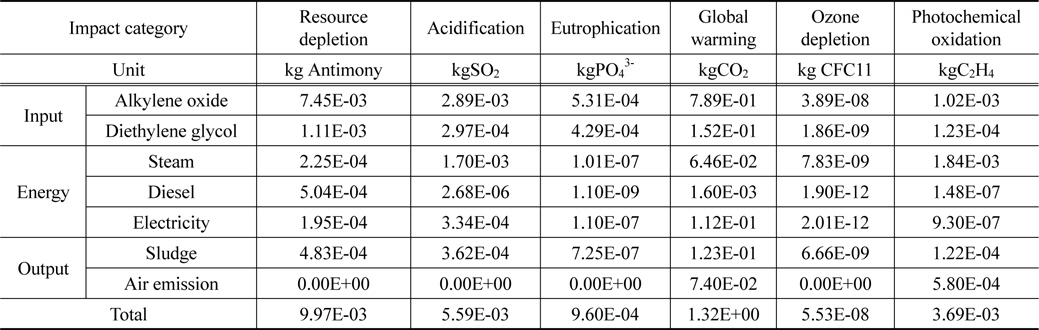
재생 폴리올 생산을 위한 공정에서 가장 큰 영향으로 나타난 물질은 알킬렌옥사이드와 디에틸렌글리콜이었다. 알킬렌옥사이드의 경우 대부분의 범주에서 전체 환경영향의 절반이상을 차지하고 있다. 특히 오존층 파괴(8.42E-08 kg CFC11)와 지구온난화(1.71E+00 kg CO2), 자원소모(1.34E-02 kg Antimony)에서 주요 환경 영향의 원인으로 나타났다. 디에틸렌글리콜은 부영양화(3.71E-04 kg PO43-)와 지구온난화(1.13E-01 kg CO2)에서 주요 환경영향의 원인으로 나타났으며, 스팀 사용을 인한 영향은 광화학산화물생성(1.99E-03 kg C2H4)과 산성화(1.65E-03 kg SO2)에서 주요하게 나타났다. 물질에 의한 영향은 Table 2와 Figure 2에 나타내었다.
[Table 2.] Characterization result of recycled polyol at current status
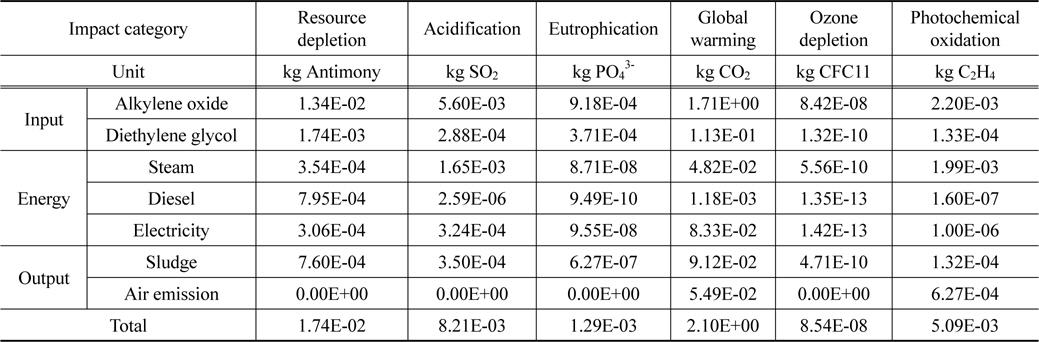
Characterization result of recycled polyol at current status
② 양산 단계 예상 수준 특성화 결과
재생 폴리올 생산을 위한 공정에서 가장 큰 영향으로 나타난 물질은 알킬렌옥사이드와 에너지로 사용된 스팀으로 나타났다. 알킬렌옥사이드는 자원소모, 산성화, 부영양화, 지구온난화 및 오존층 파괴의 영향범주에서 가장 높은 영향을 나타냈으며, 스팀은 산성화와 광화학산화물생성 범주에서 높은 영향을 나타내었다. 물질에 의한 영향은 다음 Table 3과 Figure 3에 나타내었다.
[Table 3.] Characterization result of recycled polyol at anticipated mass production
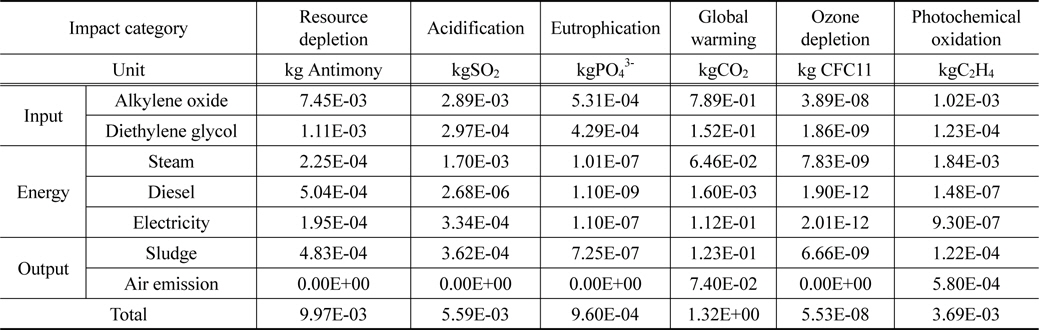
Characterization result of recycled polyol at anticipated mass production
2.4.2. 정규화 결과
① 현재 재활용 기술 수준 정규화 결과
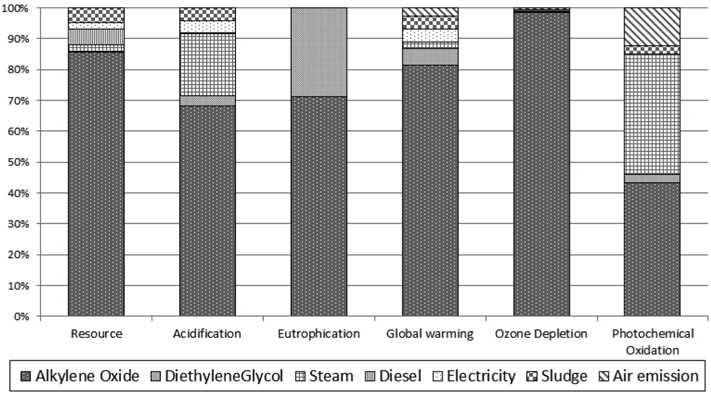
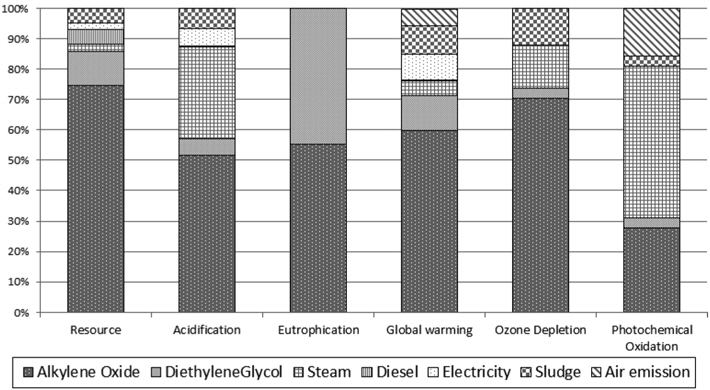
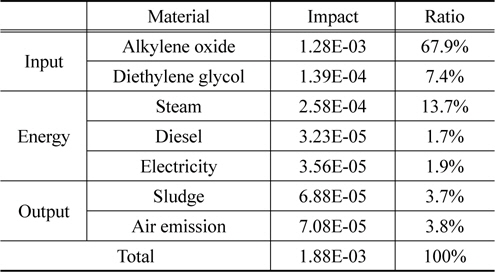
현재 재활용 기술 수준에서 재생 폴리올의 정규화 결과를 살펴보면, 알킬렌옥사이드가 67.9%로 가장 높은 환경영향을 나타냈으며, 다음은 스팀이 13.7%로 나타났다.
영향범주 별 정규화 결과는 자원소모가 37.2%, 광화학산화물생성이 26.3%, 지구온난화가 20.2%로 뒤를 이었다. 자원소모와 지구온난화의 핵심 요소는 알킬렌옥사이드이며, 광화학산화물생성의 핵심 요소는 스팀 사용이다.
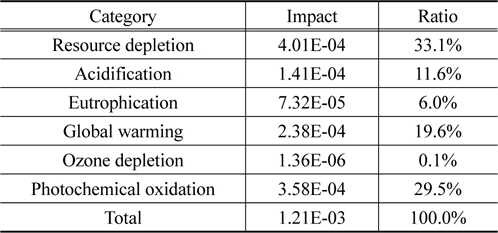
② 양산 단계 예상 수준 정규화 결과
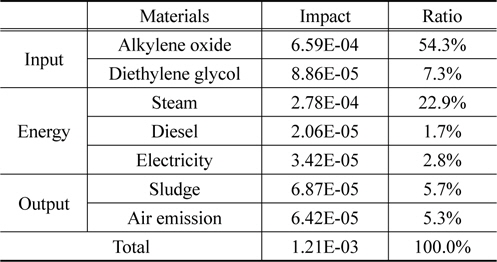
양산 단계 예상 수준 재생 폴리올의 정규화 결과를 살펴보면, 알킬렌옥사이드가 54.3%로 가장 높은 환경영향을 나타냈으며, 다음은 스팀이 22.9%로 나타났다.
영향범주 별 정규화 결과는 자원소모가 33.1%, 광화학산화물생성이 29.5%, 지구온난화가 19.6%로 뒤를 이었다. 자원소모와 지구온난화의 핵심 요소는 알킬렌옥사이드이며, 광화학산화물생성의 핵심 요소는 스팀 사용이다.
[Table 4.] Normalization result of recycled polyol at current status
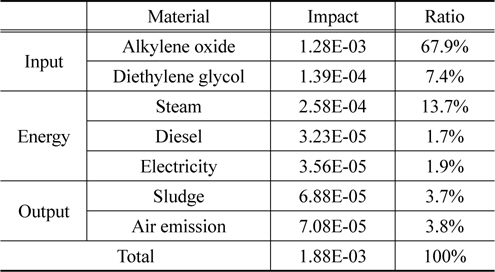
Normalization result of recycled polyol at current status
[Table 5.] Normalization result of recycled polyol at current status in terms of impact categories
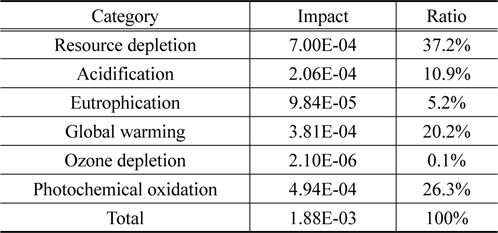
Normalization result of recycled polyol at current status in terms of impact categories
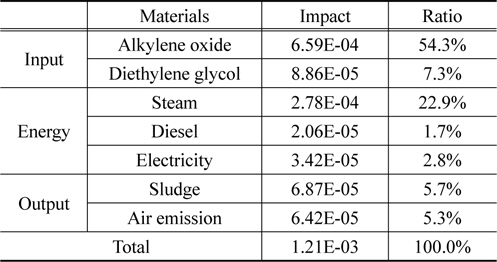
Normalization result of recycled polyol at anticipated mass production in terms of materials used
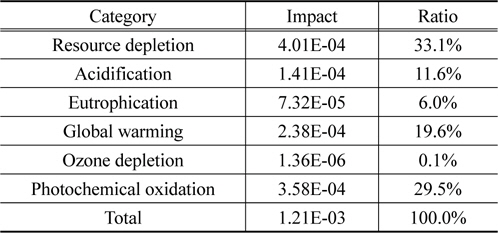
Normalization result of recycled polyol at anticipated mass production in terms of impact categories
[Table 8.] Characterization result of virgin polyol in terms of impact categories
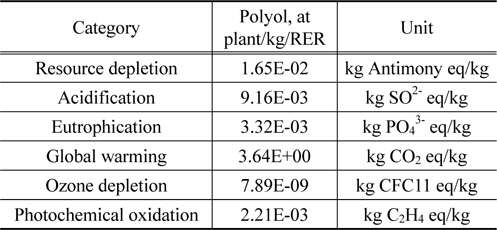
Characterization result of virgin polyol in terms of impact categories
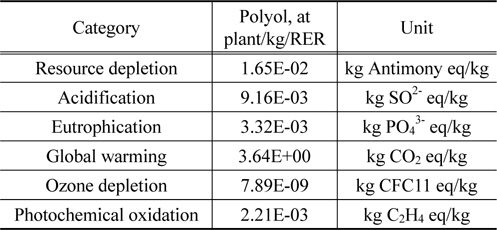
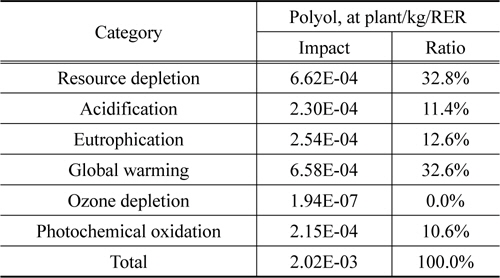
신재 폴리올의 전과정평가 값은 해외 Eco-invent에서 개발한 폴리올(Polyol, at plant) LCI 데이터베이스의 값을 적용하였다.
3.1.1. 특성화 결과 및 특성화 값 비교
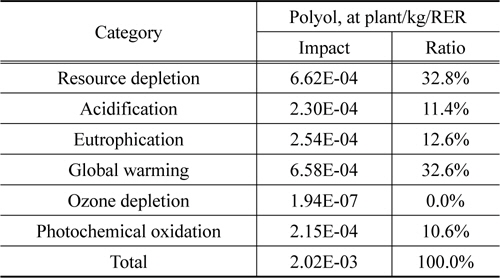
신재 폴리올 1 kg 생산 시 잠재적인 환경영향을 주요 범주 별로 살펴보면, 지구온난화 범주에서 온실가스 발생량이 3.64E+ 00 kg CO2으로 나타났다. 또한 자원소모의 경우 1.65E-02 kg Anitimony eq이며, 광화학산화물생성은 2.21E-03 kg C2H4, 오존층 파괴는 7.89E-09 kg CFC11으로 나타났다.
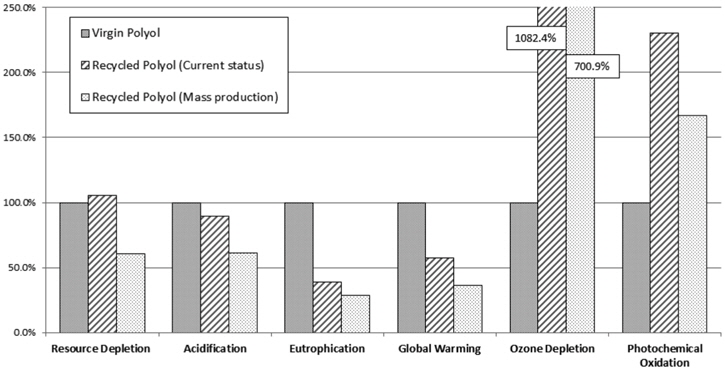
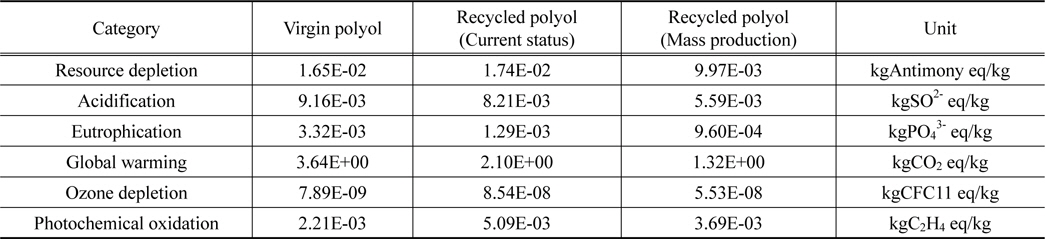
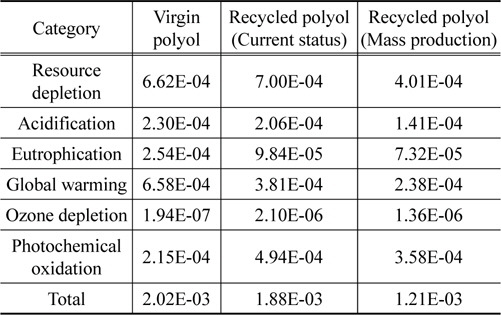
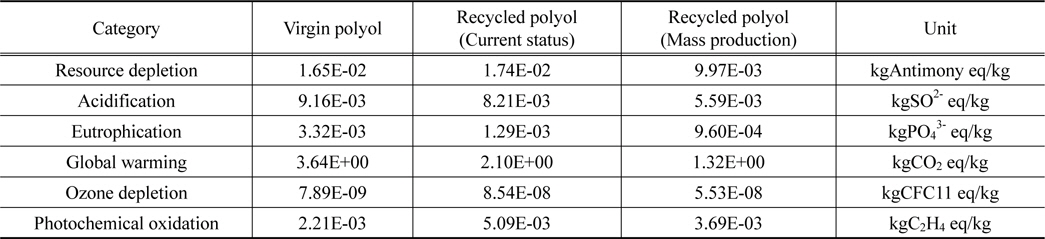
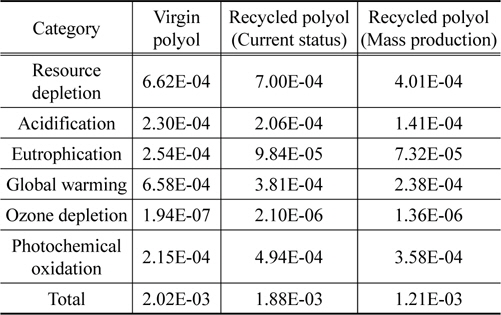
폴리올 1 kg 생산에 대한 신재와 양산 단계 예상 수준 재생기술에 대한 전과정 특성화 값을 비교한 결과, 자원소모, 산성화, 부영양화, 지구온난화 범주에서 재생 폴리올이 산재 폴리올에 비해 낮은 잠재적인 환경영향을 나타내었다. 영향 범주 별로 살펴보면 신재 폴리올에 비해 재생 폴리올의 환경영향이 자원소모 60%, 산성화 61%, 부영양화 29%, 지구온난화 36%로 나타났다. 신재 폴리올과 재생 폴리올의 현재단계 기술 수준 및 양산 단계의 기술에 대한 환경영향 범주 별 특성화 결과 비교는 Figure 4와 Table 9에 나타내었다.
Comparison of characterization result between virgin polyon and recycled polyol in terms of impact categories
[Table 10.] Normalization result of virgin polyol at current status in terms of impact categories
Normalization result of virgin polyol at current status in terms of impact categories
3.1. 2. 정규화 결과
신재 폴리올 생산에 대한 LCI 데이터베이스의 전과정 영향 평가 정규화 결과 값을 살펴보면, 자원소모(32.8%)와 지구온난화(32.6%)의 2가지 범주에서 환경영향 비율이 높게 나타났다.
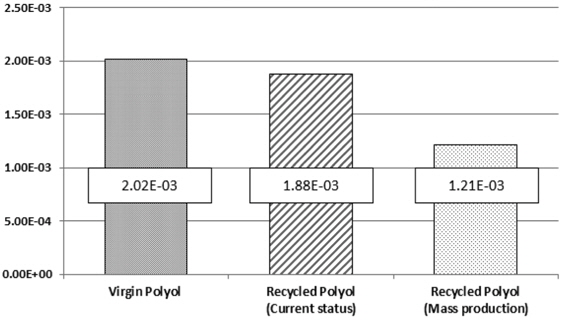
폴리올 1 kg 생산에 대한 신재와 현재 기술 수준 및 양산 예상 단계 기술 수준의 재생재의 정규화 값 비교 결과 신재생산에 비해 현재 기술은 환경영향이 93.1% 수준으로 나타났고, 양산 단계는 59.9%로 낮아지는 것을 확인할 수 있다. 폴리올 신재와 재생 폴리올의 현재 기술 수준 및 양산 단계의 예상 수준에 대한 환경영향 범주 별 정규화 결과는 Figure 5와 Table 11에 나타내었다.
Comparison of normalization result of virgin and recycled polyol in terms of impact category
신재 폴리올과 재생 폴리올의 환경영향 비교를 현재 재활용 기술 개발 단계와 양산 예상 단계 수준으로 구분하여 수행한 결과, 현재 단계는 신재의 93%, 양산 예상 단계는 신재의 60%로 나타났다. 폴리우레탄 폼 스크랩을 재활용하여 재생하는 폴리올이 환경적으로 우수하다는 결과를 보여주고 있다. 더하여 기존 폐기물의 소각으로 인한 추가적인 환경 부하와 재생 폴리올 자체의 제품 가치를 고려한다면 재생 폴리올은 환경 및 경제적으로 보다 높은 가치로 평가될 수 있을 것이다.
양산 예상 단계의 비교 내용을 영향 범주로 살펴보면 지구온난화(36%), 자원소모(61%), 부영양화(29%), 산성화(61%)는 재생 폴리올의 환경영향이 작으나, 오존층 파괴(701%)와 광화학적산화물생성(167%)은 재생 폴리올의 환경영향이 큰 것으로 평가되었다. 재생 폴리올의 전 공정에서 알킬렌옥사이드의 투입으로 인한 환경영향(자원소모 75%, 지구온난화 60%, 오존층 파괴 83%)이 가장 크게 나타났다. 재활용 기술의 환경 성능을 보다 향상시키기 위해서는 알킬렌옥사이드의 투입량을 줄여나가거나 스팀의 환경영향을 저감시키는 노력이 요구된다.