A total of 15 species are currently recorded in marine algal flora of Korea (Lee and Kang 1986, 2002, Lee 2008, Bae 2010, Kim et al. 2013). During survey of indigenous species, two marine ulvalean species (Chlorophyta) were collected from the southern and eastern coasts of Korea. These two Korean entities were identified based on morphological and molecular analyses and are newly recorded in marine algal flora of Korea in the present study.
Samples for the present study were collected from Busan and Pohang, Korea, in 2014. All specimens were preserved in 5-10% formalin seawater, and pressed on herbarium sheets. A portion of the material was dried and preserved in silica gel for molecular analysis. Species identification was based on thallus morphology following the criteria of Bliding (1963, 1968) and Koeman and van den Hoek (1981). Sections of the thallus were mounted in 20% corn syrup for permanent preparation.
Total genomic DNA was extracted from silica-gel-preserved sample using the DNeasy Plant Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Before extraction, dried material was crushed with liquid nitrogen using a mortar and pestle. Concentrations of extracted DNA were assessed by using gel electrophoresis on a 1% agarose gel. Extracted DNA was used for amplification of the internal transcribed spacer (ITS) regions using published primers (Blomster et al. 1998). PCR amplifications were performed in a TaKaRa PCR Thermal Cycler Dice (TaKaRa Bio Inc., Otsu, Japan) with an initial denaturation step at 94℃ for 5 min followed by 35 cycles at 94℃ for 1 min, 56℃ for 1 min, and 72℃ for 2 min and a final extension at 72℃ for 7 min. The reaction volume was 20 μL, consisting of 20 ng of genomic DNA, 2 μL of 10x PCR buffer, 2 μL of 200 μM dNTP, 1 μL of each forward and reverse primer, and 0.5 units of Taq polymerase (TaKaRa Bio Inc.). Amplifications were examined using gel electrophoresis in a 1% agarose gel and amplified ITS region products were purified using a QIAquick Gel Extraction Kit (Qiagen). The PCR products were moved to Macrogen Sequencing Service for sequencing (Macrogen, Seoul, Korea). The PCR primers were also used for sequencing.
Sequences for the ITS region were aligned using BioEdit (Hall 1999). Phylogenetic analyses were performed using the neighbor-joining (NJ) and maximum-likelihood (ML) methods. Bootstrap values were calculated with 1,000 replications. ITS sequences of other species (excluding
>
Ulva flexuosa Wulfen 1803: xxii
Korean name: Yeon-gal-pa-rae nom. nov. (신칭: 연갈파래)
Specimens examined: NIBRAL0000143269, PKNU0000134878 (Cheongsapo: 17 May 2014).
Habitat: Epilithic near the lower intertidal.
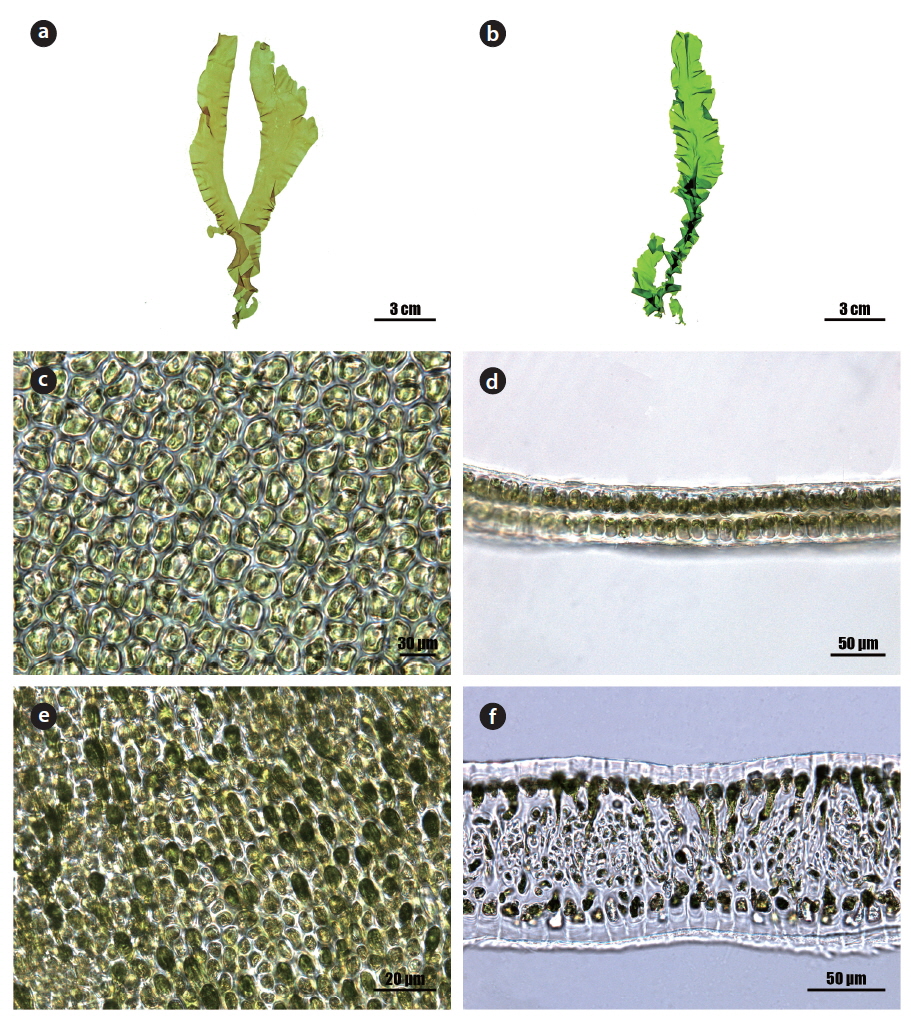
Morphology: Thalli 15-25 cm high (Fig. 1a and 1b), erect, membranous, distromatic, usually unbranched or little branched conical to ligulate shape, light to dark green in color, soft in texture, attached by a small holdfast (<5 mm) on rocks near the lower intertidal; frond ribbon-shaped, with a spirally twisted basal portion, usually undulate at the margin, 40-60 μm thick in the upper portion (Fig. 1d), 80-120 μm thick in the basal portion (Fig. 1f); cells usually arranged in pairs, rectangular to polygonal near the middle to upper portion (Fig. 1c), oval to rectangular with round corners near the basal portion in the surface view (Fig. 1e), transformed into rhizoidal cells near the base, 15-25 μm × 10-15 μm, with a length to width ratio of 1.6-1.8 in the transverse section; chloroplasts cap-like, parietal, with 1 (-2) pyrenoids (5-6 μm).
>
Ulva rigida C. Agardh 1823: 410
Korean name: Gyeong-gal-pa-rae nom. nov. (신칭: 경갈파래).
Specimens examined: NIBRAL0000143268, PKNU 0000134875, PKNU 0000134879 (Duhodong: 3 July 2014).
Habitat: Epilithic near the subtidal.
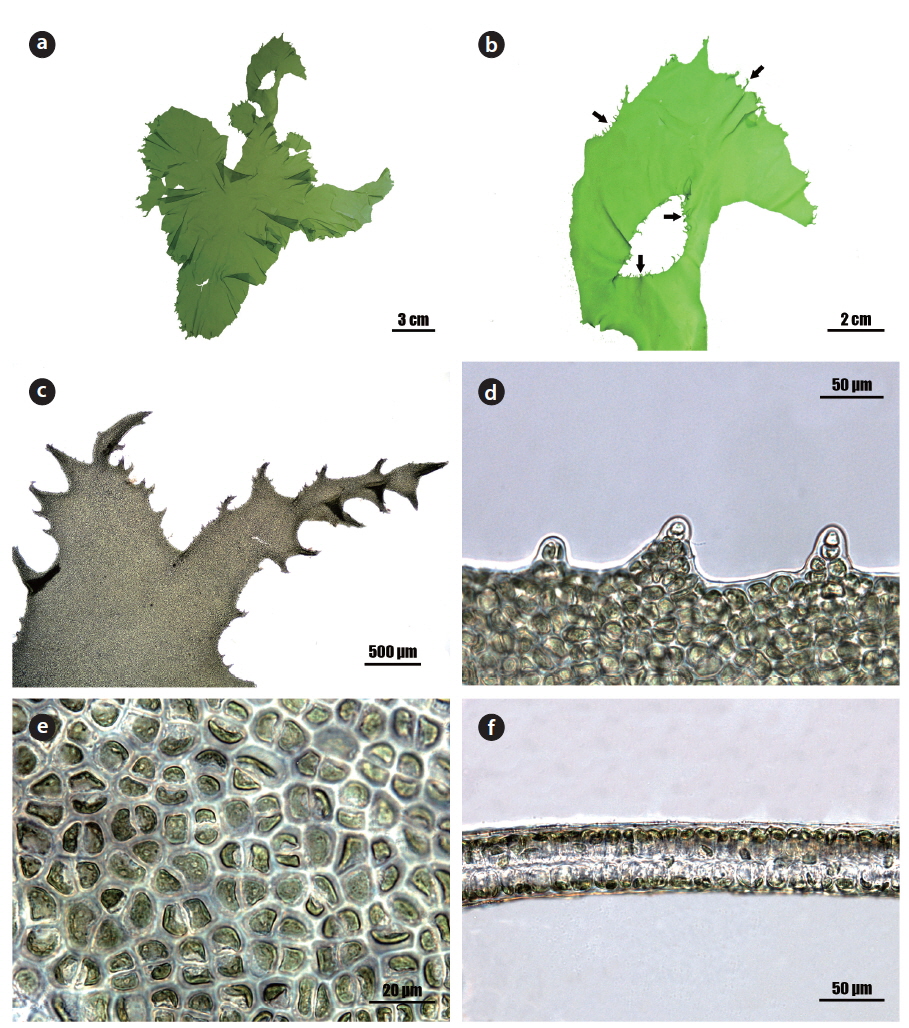
Morphology: Thalli 20-30 cm high (Fig. 2a), membranous, distromatic, irregular in shape, light to dark green in color, stiff in texture, attached by small holdfast on rocks near subtidal; frond irregular in shape, usually undulate and dentate at the margin (Fig. 2d), with small macroscopic denticulations along the margin (Fig. 2b), 40-60 μm thick (Fig. 2f); denticulations usually branched (Fig. 2c); cells usually arranged in pairs, rectangular to polygonal with round corners in the surface view (Fig. 2e), 5-15 μm × 5-10 μm, with length to width ratio of 1.2-2.0 in the transverse section; chloroplasts cap-like, parietal, with (1-) 2-3 pyrenoids (2-3 μm).
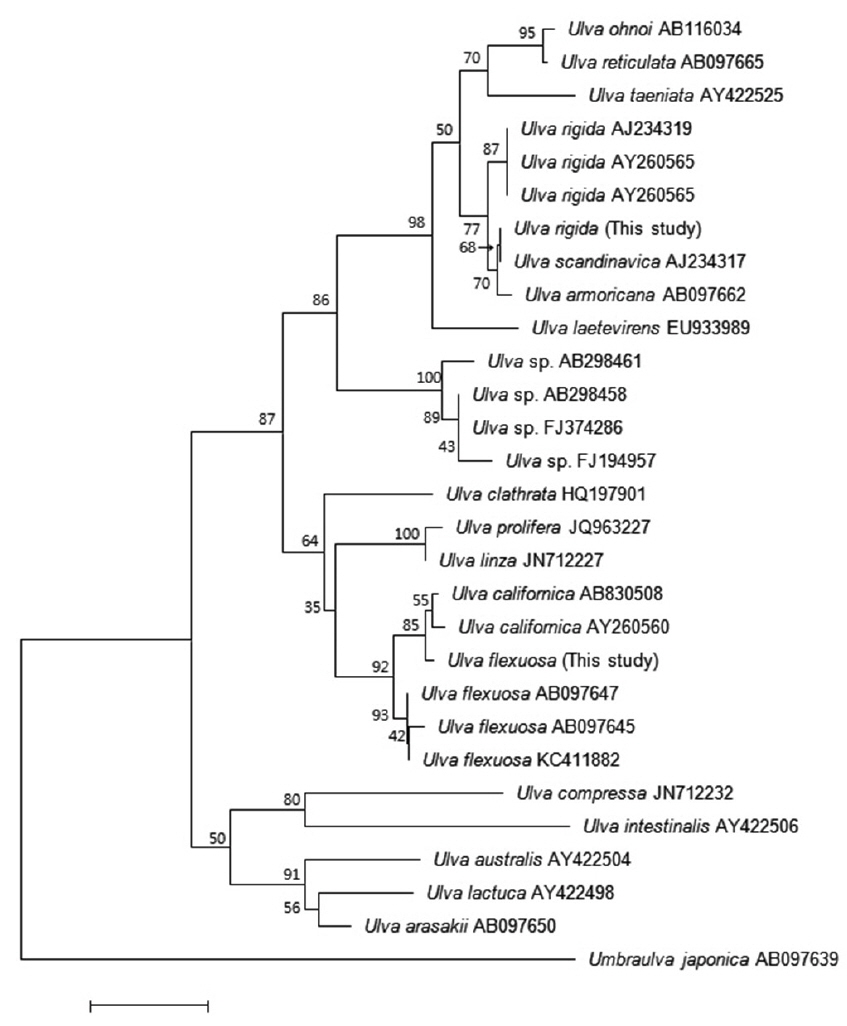
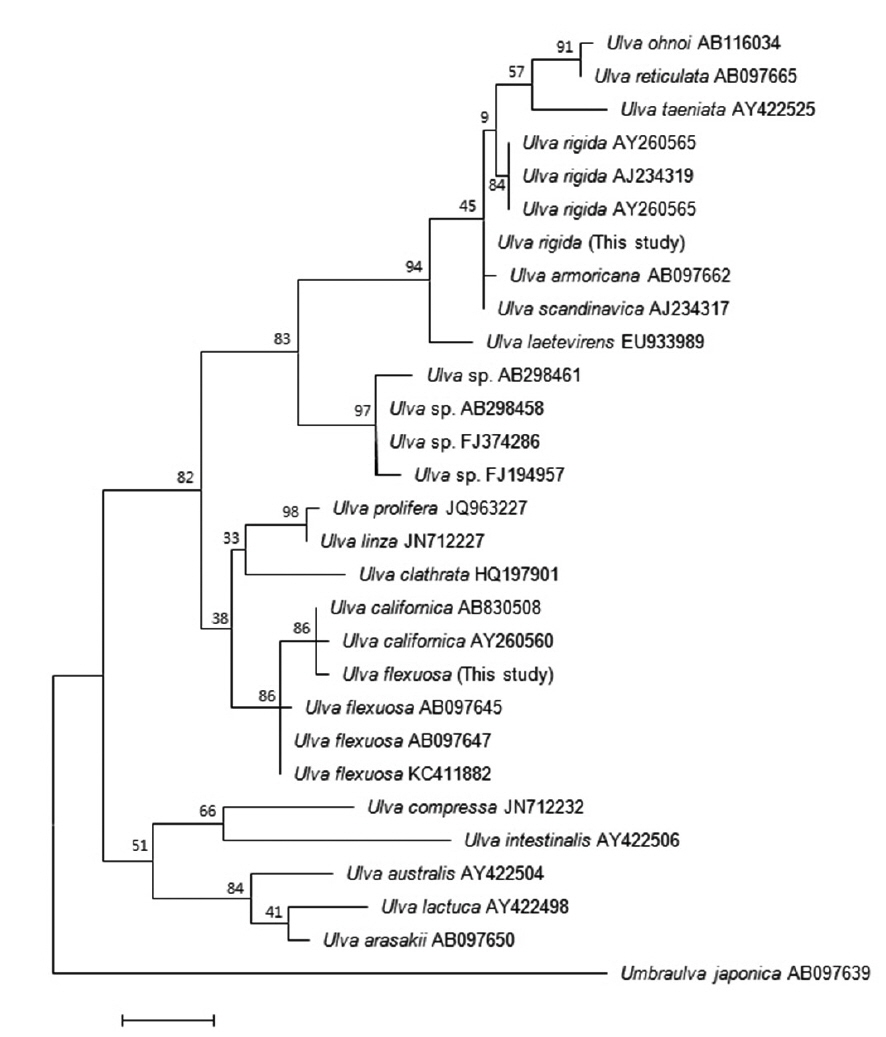
Many studies have used the ITS region to analyze the phylogenetic relationships among
The second Korean entity nests in the same clade with
Based on these morphology and molecular data, our Korean entities are identified as