This research includes the identification and cultivation of aerial algae from 33 sites located in Mt. Gwanggyo of Gyeonggi-do, Korea, from March 2011 to August 2012. The ecological factors of aerial algae were analyzed and a total of 29 taxa were identified in 4 phyla, 5 classes, 11 orders, 15 families, 19 genera, 28 species and 1 variety; 12 taxa of cyanophytes, 8 taxa of chrysophytes, and 9 taxa of chlorophytes were found. As for newly recorded cyanophytes of Korea, Komvophoron jovis, Microcoleus steenstrupii, and Nostoc edaphicum appeared. Komvophoron jovis, previously known to grow on rocks and boulders, appeared in soil. Microcoleus steenstrupii, reported to appear in desert soils, appeared on the wet surface of the soil after rain. Nostoc edaphicum, in symbiosis with fungi, appeared on tree bark as the lichen. Thus, there are a total of 99 reported taxa of Korean aerial algae, including 3 species that were discovered in this study.
Aerial algae have been found in a vast range of environments, including soils, rocks, tree barks and surfaces of buildings. Aerial algae contributes to carbon and nitrogen fixation, the release of organic material, and the coalescing of soil particles (Goyal 1997, Graham et al. 2009). In order to adapt to land environments, aerial algae display simplified shapes, such as globular, oval and filaments (Hoffmann 1989). Consequently, understanding the minute differences in form and alterations of shape is required to identify aerial algae based on morphology (Neustupa and Skaloud 2010).
Overseas, studies on distribution of soil algae have been performed in Texas (King and Ward 1977), North-Eastern Italy (Zancan et al. 2006), and Egypt (Mansour and Shaaban 2010). Research on the distribution of algae on tree barks has been done in India (Mikter and Shukla 2006), Singapore (Neustupa and Skaloud 2010), and Brazil (Lemes-Da-Silva et al. 2010). Studies on distribution of aerial algae in specific locations and on the walls of buildings have been done in Latin America (Gaylarde and Gaylarde 2000), Europe (Rindi and Guiry 2004), India (Samad and Adhikary 2008), Spain (Macedo et al. 2009) and the USA (Khaybullina et al. 2010). Domestically, with regard to aerial algae, research on distribution of soil algae in Seoul, Gyeonggi-do, Chungcheong-do has been done (Chang et al. 1998). In addition, studies by Klochkova et al. (2006), Lim and Lee (2008a, 2008b), and Kim et al. (2010, 2011) on aerial algae in Korean stone cultural heritages sites have been performed. In Korea, a total of 96 taxa, including 39 taxa of cyanophytes, 14 taxa of chrysophytes, and 43 taxa of chlorophytes have been found (Chung 1968, 1993, Chang et al. 1998, Lim and Lee 2008a, 2008b).
The current study aims to add newly recorded species of aerial algae, investigate the environmental factors of their habitats, and clarify the distribution of species in Mt. Gwanggyo of Gyeonggi-do, Korea.
Aerial algae were collected from a total of 33 sites—5 soil sites, 14 tree bark sites, and 14 rock sites—in Mt. Gwanggyo from March 2011 to August 2012. Basic environmental factors such as air temperature, surface temperature, humidity, and intensity of illumination were analyzed when collecting the aerial algae. Testo 625 (Testo, Lenzkirch, Germany) was used to measure temperature and humidity, Testo 830-T1 (Testo) for surface temperature, and LX-1108 (Lutron, Taipei, Taiwan) for illumination.
The samples were collected using a soft brush and sterilized spatula. All samples were collected and transported to the lab in sterilized distilled water in dark bottles (Crispim et al. 2004). Unialgal culture of aerial algae was done by separating it on agar medium using a pasteurpipette. For culture media, Bold 3N medium (Bold and Parker 1962), Bold basal medium (Bold and Wynne 1978), WEES medium (Kies 1967), and M chu No. 10 medium (Chu 1942) were used. An appropriate culture medium was used to culture aerial algae by manipulating factors such as[ph] (Stein 1979). The aerial algae increased a cell number for three to five days in the algae culture room with a temperature of 25°C, photoperiodic control of 16:8, and intensity of illumination of 40 μm m−2 s−1.
Species were identified using optical microscope (BX41; Olympus, Tokyo, Japan) under ×400-1,000 magnification. Pictures of cells’ outer shape were captured by a digital camera (C-5060; Olympus) attached to the microscope. A drawing attachment (BX40F4; Olympus) was used for drawing of the morphologies. Prescott et al. (1972, 1977, 1981, 1982), Prescott (1973), Hirose et al. (1977), Chung (1993), John et al. (2002), and John and Robert (2003) were used as references for each taxonomic group that appeared.
The ecological conditions of Mt. Gwanggyo, where the aerial algae were found, were measured (Table 1). Air temperature ranged from 3.8°C to 28.5°C and surface temperature ranged from 0°C to 31.5°C at the time of collection. Intensity of illumination ranged from 524 to 62,600 lux, and humidity ranged from 15.2% to 100% at the collection sites.
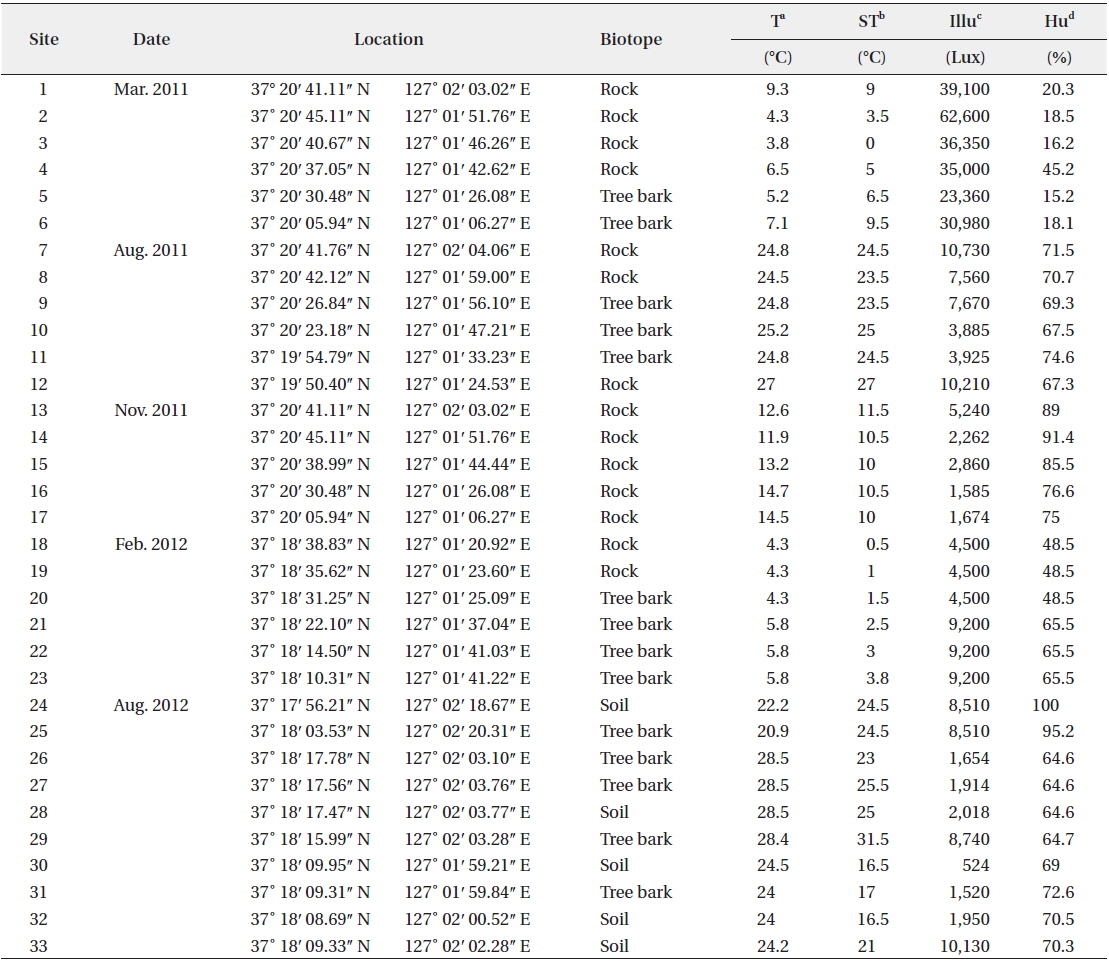
The 33 sampling sites and ecological factors in Mt. Gwanggyo of Gyeonggi-do, Korea, from March 2011 to August 2012
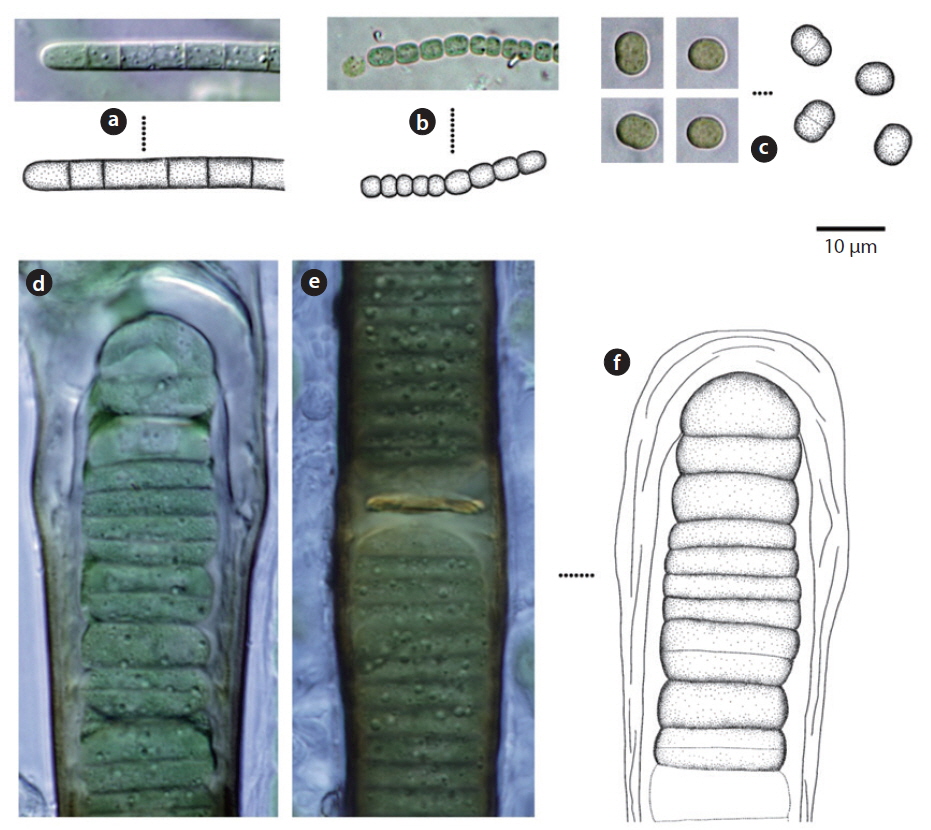
A total of 29 taxa were identified, with 4 phyla, 5 classes, 11 orders, 15 families, 19 genera, 28 species and 1 variety. Among the taxa identified, there were 12 taxa of cyanophytes including 3 newly recorded species for Korea, 8 taxa of chrysophytes and 9 taxa of chlorophytes. In soils, a total of 10 species—
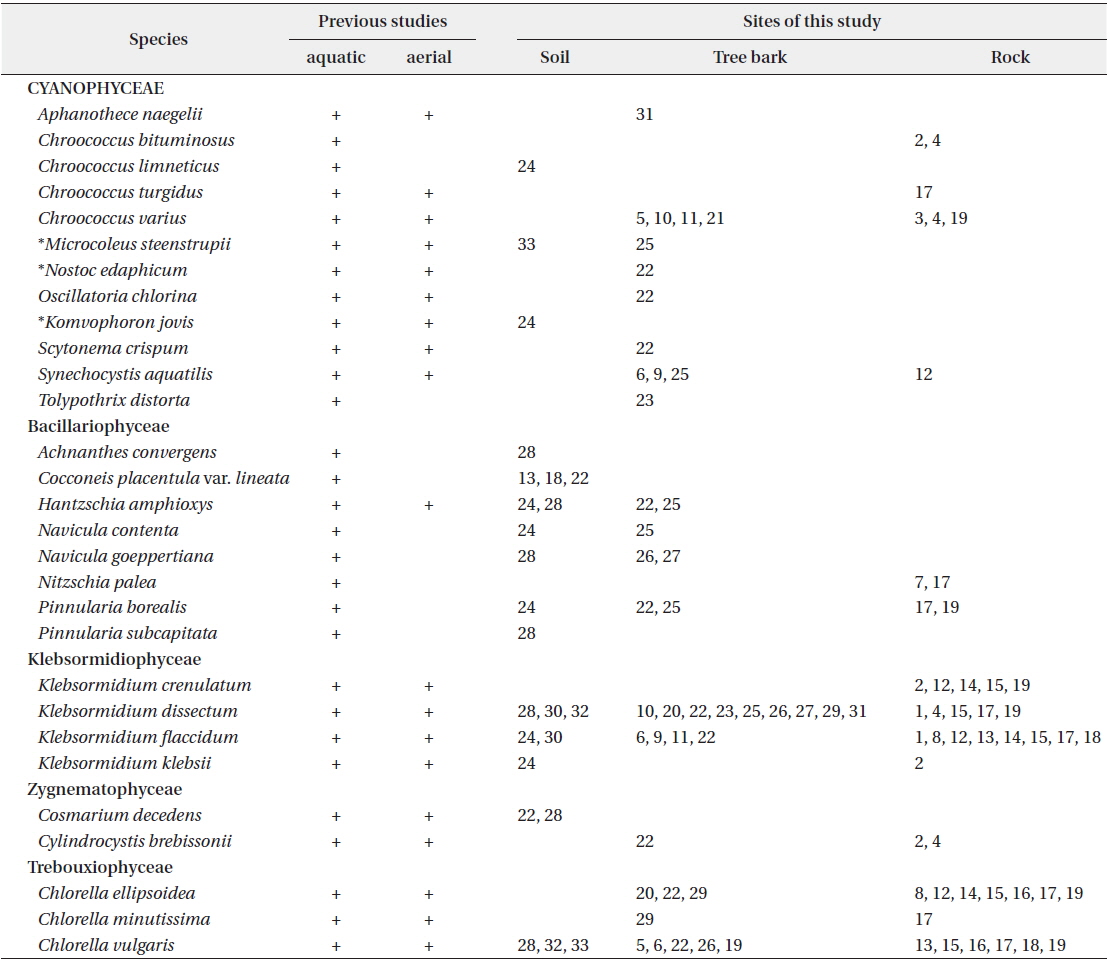
The biotope types of the aerial algae appeared at Mt. Gwanggyo of Gyeonggi-do in Korea, from March 2011 to August 2012
1.
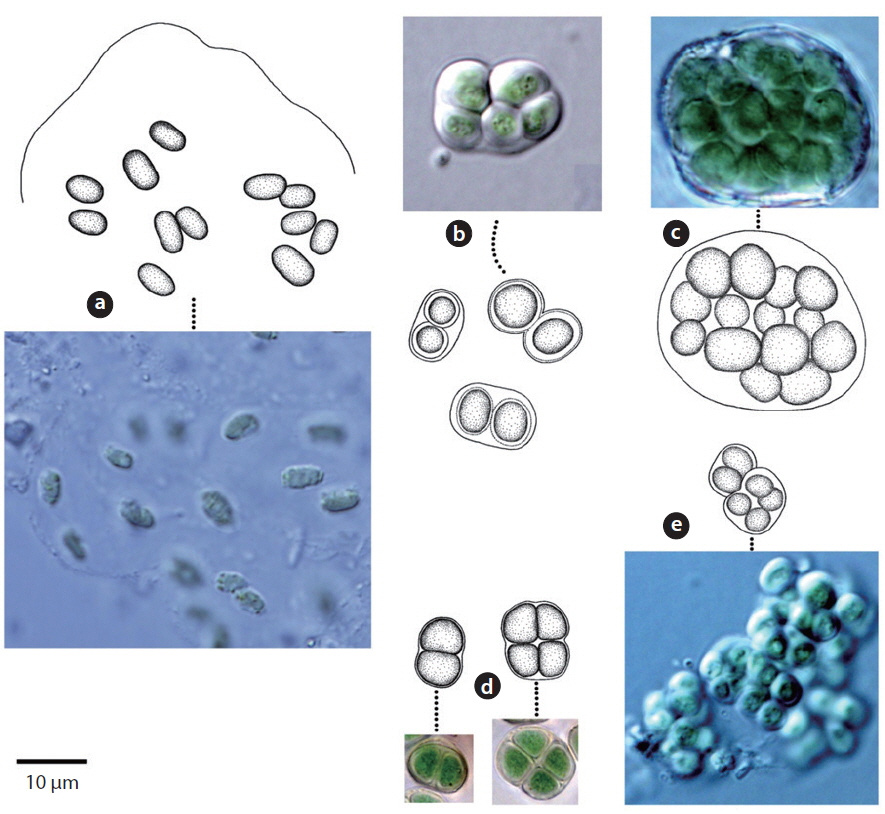
Colony microscopic; cell spherical to ovoid, irregularly arranged in a mucilage (Chung 1993), 5-7 μm long, 3-4 μm wide.
This species, which has been reported to inhabit streams and moist rocks, and to symbiose with bryophytes (Tilden 1901, 1902, MacCaughey 1917, 1918a, 1918b, Chung 1993), appeared on tree bark (Site 31; see Table 1 for site number hereafter) in this study.
2.
Colony containing 2-8 cells. The sheath contains 1-8 cells (Chung 1993). Cells 2-4 μm excepting the sheath.
This species has been reported to inhabit streams (Chung 1993), and appeared on rocks (Sites 2, 4) in this study.
3.
Colony ovoid or irregular, cells occurring within the mucilage. Outer margin of the colony usually distinct, mucilage colourless. Cells subspherical, 8-10 μm.
In previous studies, this species has been reported to inhabit streams (Chung 1993), and appeared on the surface of the soil (Site 24) in this study.
4.
Synonym:
Colony microscopic, usually 2-4 cells, with the outermost sheath layer forming the margin of the colony. Bluegreen or yellowish-green cells (John et al. 2002). Cells spherical or subspherical, 10-18 μm in diameter including the sheath. In previous studies, this species has been reported to inhabit streams, caves, rocks, and soil, and to symbiose with bryophytes (Chung 1993, John et al. 2002).
It appeared on rock (Site 17) in this study. Although the cell diameter of
5.
Colony microscopic, but forming large gelatinous groups of 2-4 cells embedded in mucilage. Mucilage colorless and the sheath displays a layered structure. Cells spherical or subspherical, 2-4 μm excepting the sheath, 4-8 μm including the sheath.
In previous studies, this species has been reported to inhabit streams and building walls (Samad and Adhikary 2008). It appeared on tree barks (Sites 5, 10, 11, 21), and rocks (Sites 3, 4, 19) in this study.
6.
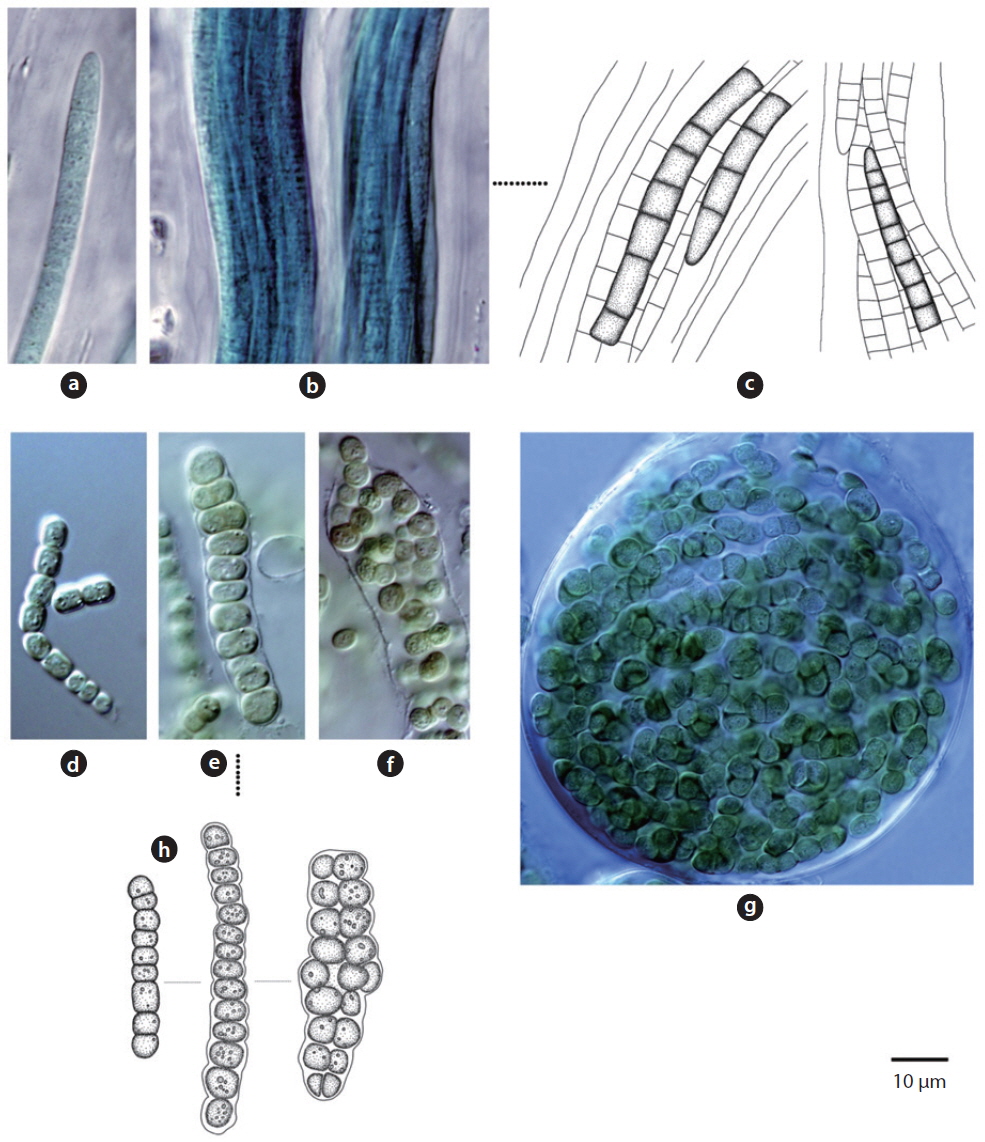
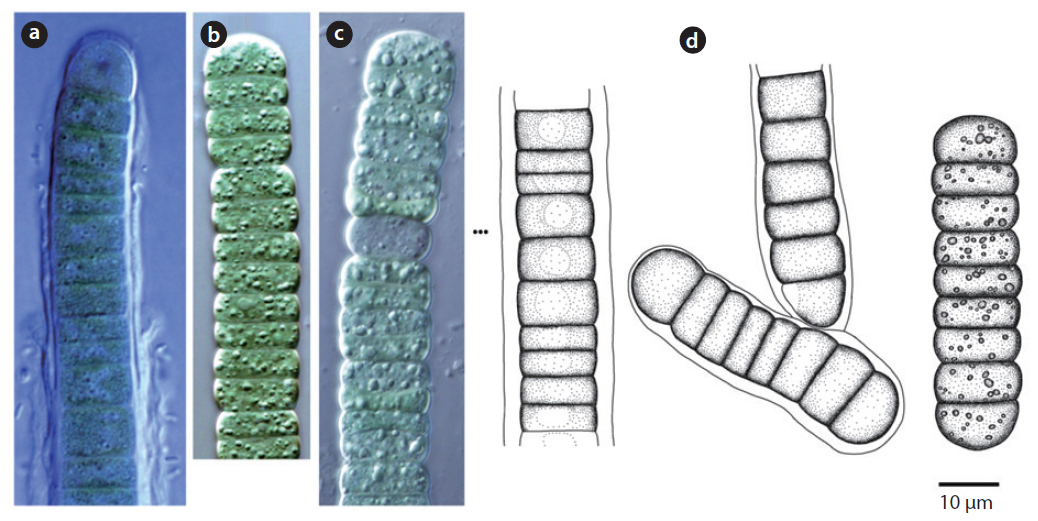
Trichomes loosely arranged with many filaments per sheath. Trichomes bright blue-green, tapering toward end, indistinctly constricted at the cross-walls. End cell not capitate, rounded-conical. Sheaths colourless. Cells 3-8 μm long, 3-5 μm wide.
Specimen: NIBRCY0000000450.
This species has been found to be distributed in desert soils (Komárek and Anagnostidis 2005). In this study, it was found at the surface of wet soil after rainfall (Site 33) but was not found in dry soils. Moreover, it was found in tree barks that had humidity of approximately 90% (Site 25). Thus, this species showed low distribution in dry conditions.
7.
Colony irregularly arranged in the mucilage. Filaments commonly flexuous, loosely entangled. Cells spherical or subspherical, 2-4 μm, blue-green or brownish-green (Komárek 2013). Heterocyte usually many.
Specimen: NIBRCY0000000448.
This species appeared as an irregular colony surrounded by mucilage when collected, but appeared as a single strand colony in the culture medium. In previous studies, this species was reported to be a Cyanolichen—a lichen containing blue-green algae (Syiem et al. 2011). In this study, they were found as lichen in tree bark (Site 22).
8.
Colony yellowish-green and blue-green (Hirose et al. 1977). Trichomes straight, cross-walls not narrowed. Filaments 6-9 μm long, 4 μm wide.
This species has been reported to inhabit Brackish waters and the surface of moist soil (Hirose et al. 1977). It appeared on tree bark (Site 22) in this study. From the data, with humidity of 65.5% and appearance on tree bark with a water distance of 5 m,
9.
Synonym:
Trichomes lacking a mucous sheath, straight or loosely flexuous. End cell thin, spherical or conical (Komárek and Anagnostidis 2005). No cell granule, 3.4-4.2 μm wide.
Specimen: NIBRCY0000000449.
This species was first published in Anagnostidis and Komárek (1988), and was reported as inhabiting rocks, boulders, and roadside paths as
10.
Synonym:
Colony brown or blue-green, often spread out. Filaments firm with false branches, mostly arranged in pairs. Sheath colourless or yellowish-brown . Heterocyte oval or square, single or many (Chung 1993). Cells 12-25 μm wide, 3-7 μm long. Cross-walls narrowed.
This species has been reported to inhabit the surfaces of buildings after rainfall (Samad and Adhikary 2008), and appeared on tree bark (Site 22) in this study.
11.
Unicellular or colonial (2-4 cells) and spherical 3-7 μm cells.
This species has been reported as inhabiting fresh and brackish waters (John et al. 2002) and highly weathered sand stone (Makandar and Bhatnagar 2010). It appeared on tree barks (Sites 6, 9, 25) and rock (Site 12) in this study.
12.
Colony a mat or spread, blue-green or brown. Filaments repeatedly branched, false branches often deeply or sharply erect (John et al. 2002). Cells 5-7 μm long, 12-15 μm wide. Heterocyte single.
In previous studies, this species has been reported as living in attached or free-floating form in ponds and shallow lakes (John et al. 2002). It appeared on tree bark (Site 23), humidity of 65.5%, in this study. Although the shape of
13.
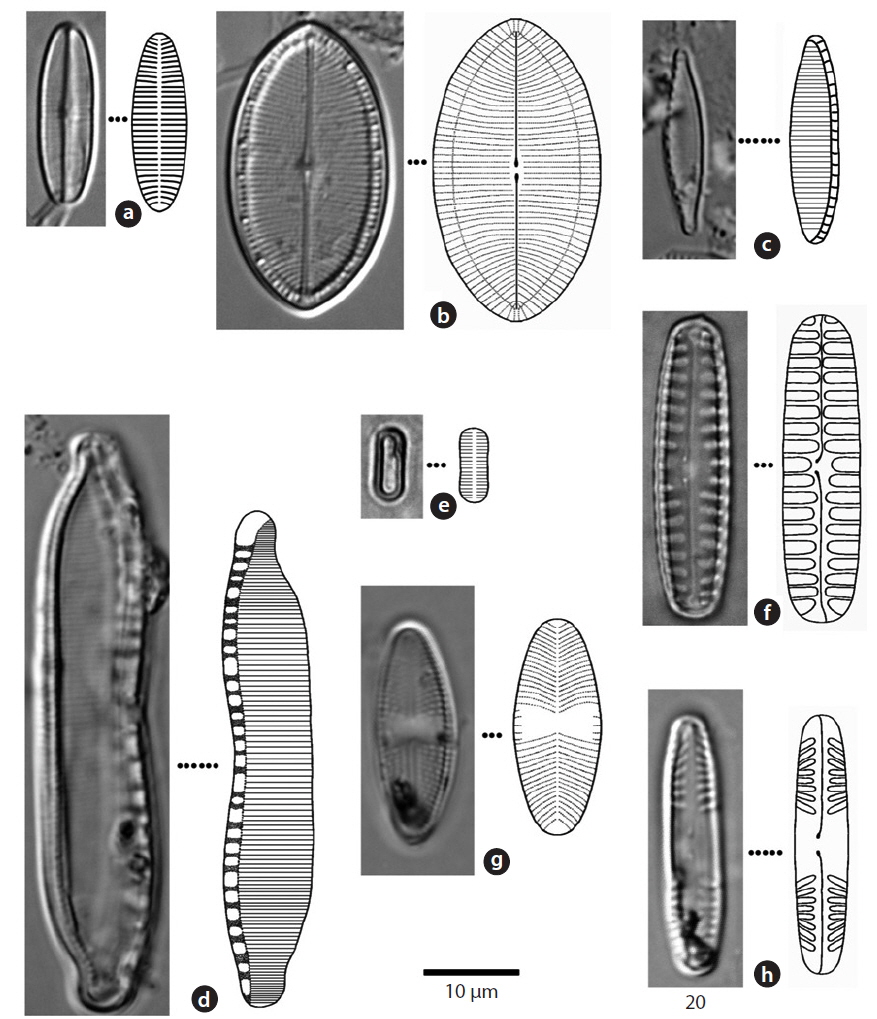
Valve broadly linear, with simple rounded or slightly protracted ends. Striae in the central area parallel or radial in both valves (Chung 1993). Striae of raphe valve 15- 18 rows within 10 μm in the central area and 35-40 rows at the terminal ends. Valves 10-15 μm long and 4-4.5 μm wide.
This species appeared in soils (Site 28) in this research.
14.
This species appeared in soils (sites 13, 18, 22) in this research.
15.
Apical plane of valve asymmetry, arch-shaped. Fibulae 4-11 rows within 10 μm, striae 11-28 rows in 10 μm. Valve 40-60 μm long, 8-10 μm wide. The length of this species has been found to be up to 300 μm at the longest (Chung 1993), but in this study, a maximum length of 60 μm was found.
The species has been reported to grow both under water and in soil (Chung 1993, John et al. 2002, Lin et al. 2013). In this research, it was found in soils (Sites 24, 28) and tree barks (Sites 22, 25).
16.
Valve ellipsoidal. The central area of the valve flattened, both ends broad and rounded. Striae parallel or slight radial, striae of the terminal area inverse radial, 25-40 rows within 10 μm (Chung 1993). Valve 6-10 μm long and 2-4 μm wide.
This species appeared in soil (Site 24) and tree bark (Site 25) in this research.
17.
Synonym:
Valve ellipsoidal or narrow ellipsoidal, with terminal ends sharp or round (Chung 1993). Median ends of the raphe turned slightly to one side. Central area broad, striae punctate, about 15 rows within 10 μm. Valve 10-30 μm long, 4-10 μm wide.
In this research, this species appeared in soils (Site 28) and tree barks (Sites 26, 27).
18.
Valve narrow sharp or linear, apices of valve round or rostrate-capitate (Chung 1993). Fibulae 9-17 rows in 10 μm, striae 20-40 rows in 10 μm. Valve 15-70 μm long, 2.5-5 μm wide.
This species appeared on rocks (Sites 7, 17) in this research.
19.
Valve broad linear, terminal ends rounded. Median ends of the raphe turned slightly to one side, axial area narrow. Striae usually parallel, 4-6 rows in 10 μm (Chung 1993). Valve 30-40 μm long, 8-12 μm wide.
This species appeared in soil (Site 24), and on tree barks (Sites 22, 25) and rocks (Sites 17, 19) in this research.
20.
Valve linear with capitate to subcapitate ends. Axial area narrow, central area rounded or elliptical (Chung 1993). Striae somewhat radiating at the center of the valve, convergent at the ends. Striae, 12-13 in 10 μm; toward the center of the valve, sometimes 10 in 10 μm. Valve 24-42 μm long, 4-6 μm wide.
This species appeared in soil (Site 28) in this research.
21.
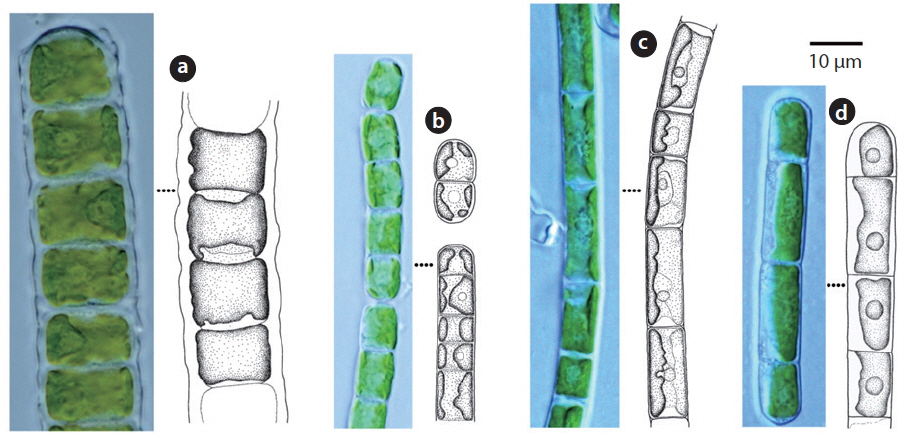
Cells cylindrical, walls thick. Chloroplast encircles up to about 80% of cell circumference (John et al. 2002). Cells 7-15 μm long, 10-14 μm wide, 0.5-2 times longer than wide.
This species has been reported to inhabit aquatic and subaquatic biotopes (John et al. 2002) and appeared on rocks (Sites 2, 12, 14, 15, 19) in this study.
22.
Filaments straight or slightly bent. Cell walls straight. Chloroplast encircling half to just over two-thirds of cell circumference. Cells 7-15 μm long, 5-8 μm wide.
This species has been reported as inhabiting aquatic and subaquatic biotopes (John et al. 2002) and appeared mostly in aerial biotopes in this study.
23.
Filaments long, bent or twisted. Cells cylindrical, walls thin, chloroplast encircles up to about two-thirds of cell circumference. Cells 8-20 μm long, 6.5-7 μm wide, 1 to 3 times longer than wide.
This species has been reported to inhabit aquatic and subaquatic biotopes (John et al. 2002) and appeared mostly in aerial biotopes in this study.
24.
Filament not branched. Chloroplast encircles about 50% of cell circumference. Cells 12-25 μm long, 5-6 μm wide.
This species has been reported to inhabit aquatic and subaquatic biotopes (John et al. 2002) and appeared in soil (Site 24) and on rock (Site 2) in this study.
25.
Cells twice as long as wide, medium-sized; median constriction shallow, the sinus open; semicells rectangular, the basal angles rounded, the lateral margins retuse to the apical angles, which are slightly more broadly rounded (John et al. 2002). Semicell 14-16 μm long, 13-15 μm wide, 11-12 μm Isthmus.
This species has been reported as inhabiting aquatic and subaquatic biotopes (John et al. 2002) and appeared in soils (Sites 24, 28) in this study.
26.
Cells cylindrical, apices rounded, 30-35 μm long, 20-23 μm wide. Chloroplasts star-shaped, a central spherical pyrenoid.
This species has been reported to inhabit aquatic and subaquatic biotopes (John et al. 2002) and appeared on tree bark (Site 22) and rocks (Sites 2, 4) in this study.
27.
Cells cylindrical-ellipsoidal, ellipsoidal or ovoid-ellipsoidal (John et al. 2002). Chloroplast trough-like or bandshaped, covering one half of cell, margins irregularly undulate and occasionally incised. An indistinct pyrenoid visible or invisible. Cells 5-7 μm long, 3-4 μm wide.
This species has been reported to inhabit aquatic and subaquatic biotopes (John et al. 2002) and appeared on tree barks (Sites 20, 22, 29), and rocks (Sites 8, 12, 14, 15, 16, 17, 19) in this study.
28.
Cells spherical, 1-2 μm. Chloroplast cup-shaped. Pyrenoid invisible.
In previous studies, this species has been reported as inhabiting aquatic and subaquatic biotopes (John et al. 2002). It appeared on tree bark (Site 29) and rock (Site 17) in this study.
29.
Cells spherical. Chloroplast broadly cup-shaped or band-shaped, filling one-half to three-quarters (Chung 1993). A pyrenoid visible. Cells 5-3 μm diameter..
This species has been reported to inhabit soil, tree bark, and rock, and to symbiose with lichen, according the studies by Aleksahina and Shtina (1984), Andreyeva (1988), Rindi and Guiry (2004), and Khaybullina et al. (2010). It appeared on tree bark (Site 23) in this study.
In total, including 3 species that were newly found in this study, there are reported to be a total of 99 Korean aerial algae taxa (Chung 1968, 1993, Chang et al. 1998, Lim and Lee 2008a, 2008b).