This study was carried out on freshwater chlorococcal green algae in ponds, swamps, reservoirs, lakes and rivers (290 sites) from May 2012 to January 2014. The family Radiococaceae was identified and classified into 3 genera, 12 species and 1 variety at 23 sites. These taxa were Eutetramorus. nygaardii, E. tetraporus, E. planctonicus, E. fottii, E. globosus, E. polycoccus, Coenocystis planctonica, C. planctonica var. hercynica, C. micrococca, C. subcylindrica, Gloeocystis baneergattensis, G. papuana, and G. polydermatica. These taxa may or not had remnants of the cell wall in the colonial gelatinous envelope for a short time. Of these, 2 taxa are newly recorded in Korea from this study: 1) C. micrococca and 2) G. polydermatica.
A great diversity of algal is expected to exist in the inland waters of Korea, but the freshwater algal flora has not been sufficiently investigated yet. The published check lists on the freshwater algal flora in Korea is include those of: Chung (1968, 1975, 1976, 1979, 1993), Chung et al. (1972a, 1972b), Chung and Lee (1986), Jeon and Chang (1995), Kawamura (1918), Kim (1996, 2013a, 2013b, 2013d, 2013e), Kim and Chung (1993), Kim and Chang (1997), Kim et al. (1998), Shin et al. (2013), and Wui and Kim (1987a, 1987b).
Few studies have reported on the family Radiococcaceae in Korea, but a few taxa have been reported on the family Palmellaceae:
This study investigates chlorococcal algal flora and adds a few taxa of the family Radiococcaceae Chlorococcales, Chlorophyceae as a new recorded species from the swamps, ponds, reservoirs, lakes and rivers in Korea. I present the taxonomic information, illustration, classification, reference, synonym, basionym, and distribution in Korea.
The samples of chlorococcal green algae were collected at 290 sites including ponds, swamps, reservoirs, lakes and rivers from May 2012 to January 2014. 12 species and 1 variety in these three genera were identified and classified from 23 sites (Table 1). Sampling sites are located throughout the country. All samples were collected using 10- or 20-µm mesh-sized plankton nets with vertical and/or horizontal towing, or submerged benthic or soil algae with spoid or brush. Chlorococcal green algae samples were immediately fixed with Lugol’s iodine solution (0.5%) for immobilizing the cells to facilitate microscopic examination. To examine the fine structures and cellular shapes, and to identify and classify species of the chlorococcal green algae, a temporary slide was made using the following steps: 1) the phytoplankton samples (chlorococcal green algae) were mixed with glycerin in micro tubes; 2) the mixed samples were placed, drop-wise on a slide glass, and were fixed in position with cover slides. Permanent slides were made using the following steps: 1) the phytoplankton samples (chlorococcal green algae) were mixed with liquid glycerol gelatin for mounting histochemical slides (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA); 2) the mixed sample was placed drop-wise on a slide glass and was fixed in position with a cover slide; 3) it was cemented to the margin of a cover glass with manicure (Thecashop, Seoul, Korea). The temporary and permanent slides were observed at ×200 to ×1,000 magnification using light microscopy (LM) ( Axioskop 20 and Axio Imager A2; Carl Zeiss, Jena, Germany) with an attached digital camera (Axiocam HRc; Carl Zeiss) being used to capture images. Specimens numbers are listed on the National Institute of Biological Resources (NIBR). The asterisk (*) mark indicates a newly recorded species in Korea.
[Table 1.] Sampling sites of the genus Euteramorus, Coenocystis and Gloeocystis from 2012 to 2014
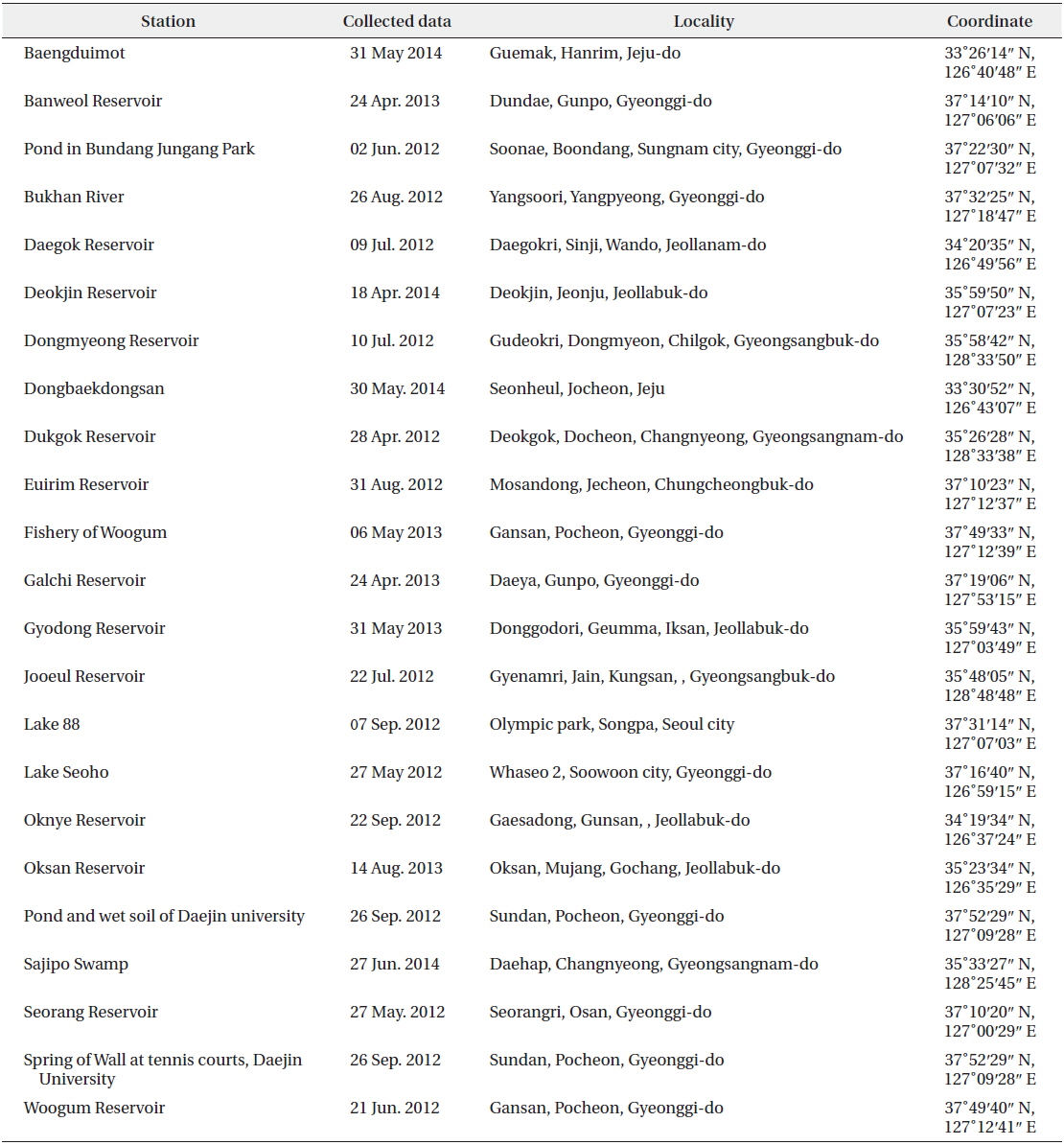
Sampling sites of the genus Euteramorus, Coenocystis and Gloeocystis from 2012 to 2014
At each site, physical and chemical factors of water were recorded during the sampling periods. Water temp. (Water temperature, ℃) and EC (electric conductivity) were measured in situ using a portable thermometer and EC meter (Orion 5-star; Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) and pH was measured in situ by using a pH meter (Ultrabasic-5; Denver Instrument, Bohemia, NY, USA). The data of total nitrogen (TN) and total phosphate (TP) concentrations at each sampling site were referred in the water information system of the Ministry of Environment (NIER 2013).
Chlorococcal algal identification was mainly based on Komarek and Fott (1983), John and Tsarenko (2002), Hindak (1977, 1980, 1984, 1988), Prescott (1962), Hirose and Yamagishi (1977), and Yamagishi and Akiyama (1984–1997).
This study has identified and classified the collected algae into 3 genera, 12 species and 1 variety based on Komarek and Fott (1983), Hindak (1977, 1980, 1984, 1988), John and Tsarenko (2002), and Komarek and Jankovska (2001). 11 taxa of this family are recorded in Korea by Kim (2013c):
This study described the taxonomic information, illustration, classification, reference, basionym, synonym, and distribution of new recorded species of these families.
Class Chlorophyceae
Order Chlorococcales
Family Radiococcaceae
Subfaimily Radiococcoideae
>
Genus Eutetramorus
Synonym
Basionym:
Synonym:
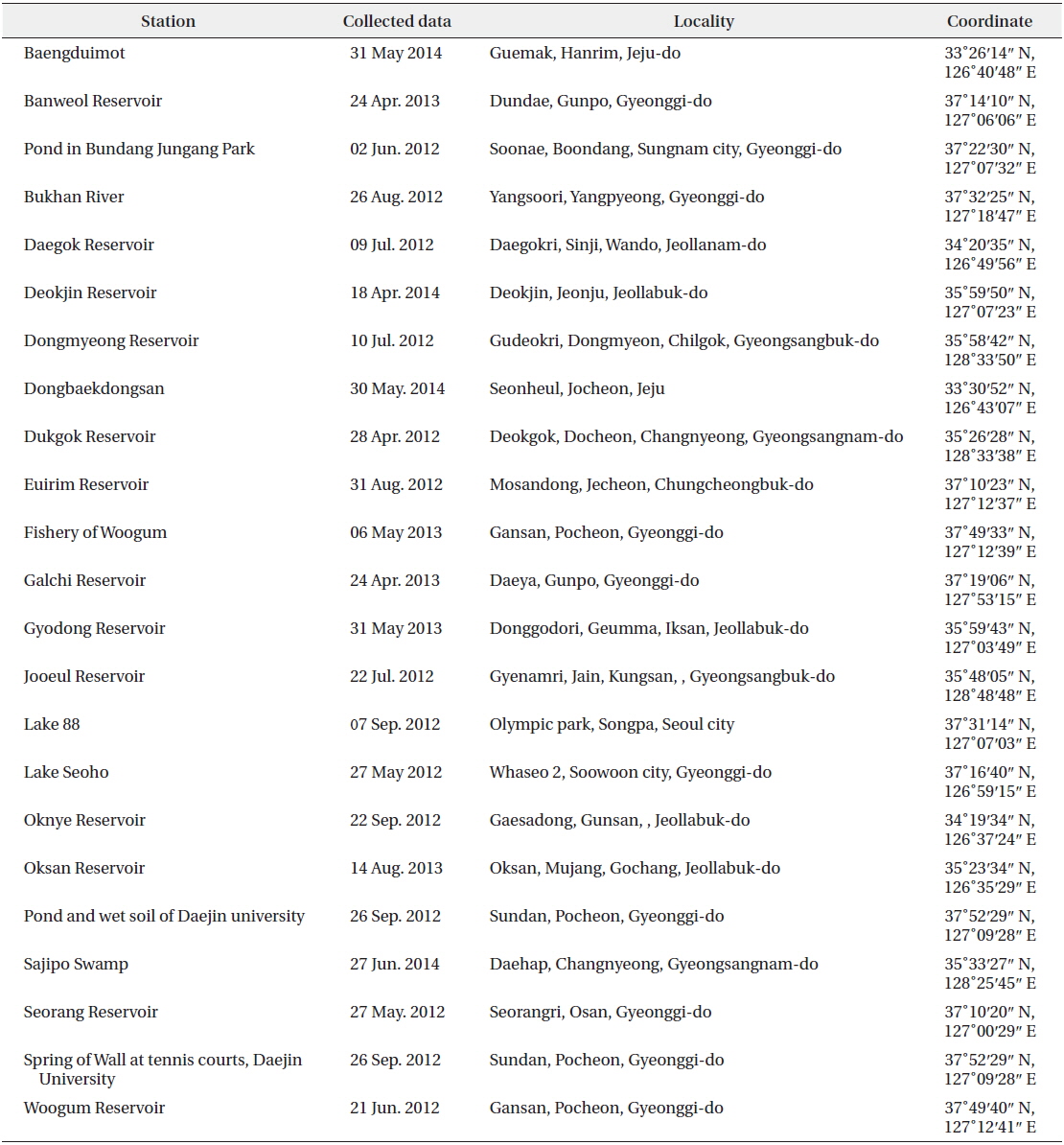
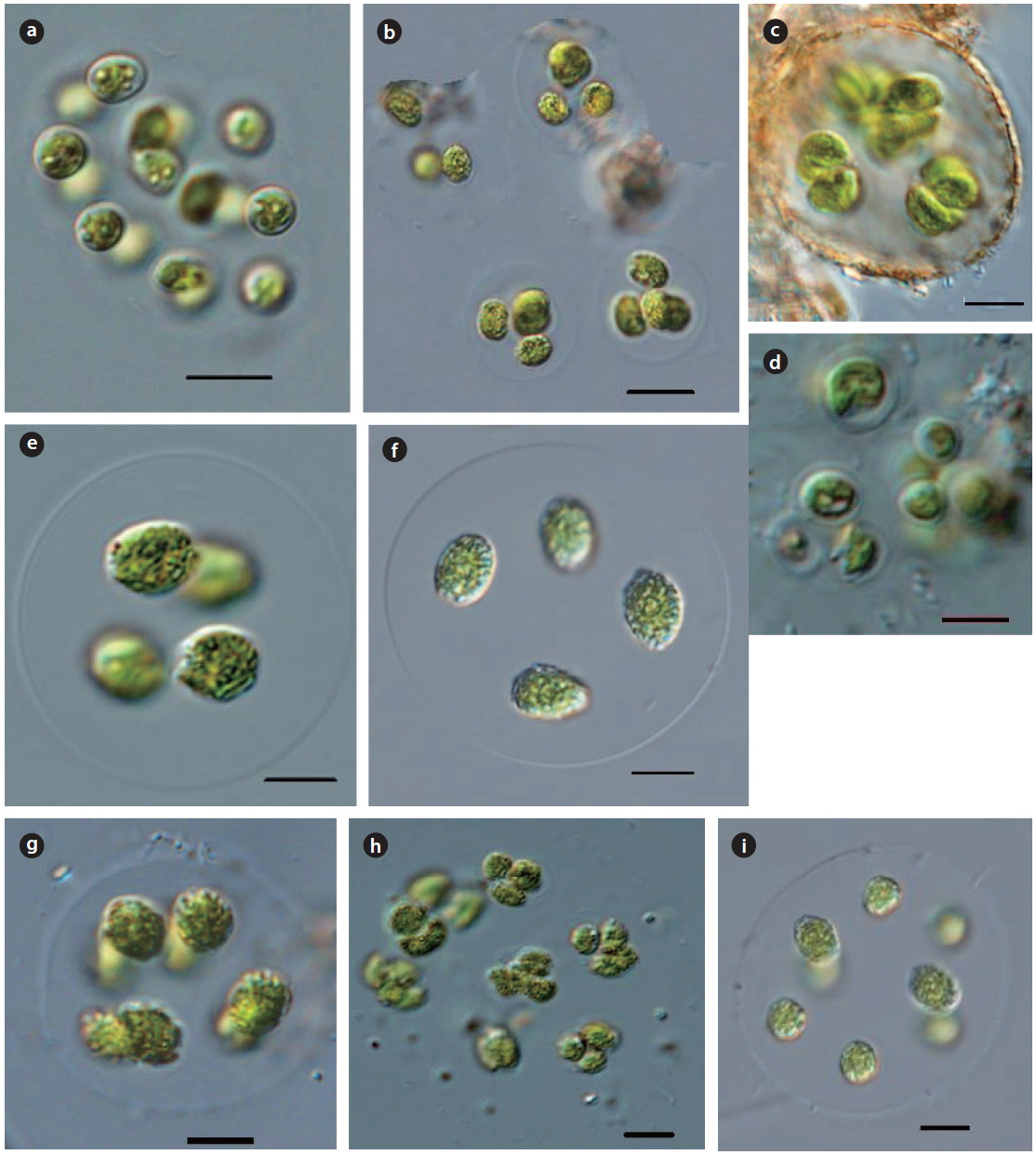
Illustration: Colonies consist of 4−8 or16 cells, sometimes with 4 cells in spherical 2−4 groups enclosed within spherical mucilaginous envelope. Cells or colonies arrange in spherical to tetrahedral form with a distance from each other. Cells are spherical, and parietal, with a pyrenoid. Autospores in the mother cell wall are released by gelatinization of the mother cell wall. Cells are 7−10 µm in diameter, colonies are 30−100 µm in diameter.
Key Reference: Komarek (1979).
Specimens: KOSPCL0000105967, KOSPCL0000106193.
Information on sampling sites: Spring of wall at tennis courts, Daejin University (26 September 2012; no data), Dongmyung Reservoir (10 June 2012; water temp. 28.7℃, pH 7.3, EC 240.3 µS cm-1, TN 2.321 mg L-1, TP0.046mg L-1), Bukhan River at Yangsoori (26 August 2012; water temp. 30.2℃, EC 238 µS cm-1), Oknyu Reservoir (22 September 2012; water temp. 25.2℃, pH 9.0, EC 572 µS cm-1, TN 0.855 mg L-1, TP0.194mg L-1), Euirim Reservoir (30 August 2012; water temp. 28.2℃, pH 7.6, EC 138 µS cm-1), Jooeul Reservoir (22 September 2012; water temp. 22.7℃, EC 267 µS cm-1), Pond in Bundang Jungang Park (02 June 2012; water temp. 26.3℃, pH 8.2, EC 407 µS cm-1), Lake 88 in Olymphic Park (07 September 2013; water temp. 29.8℃, EC 572 µS cm-1), Fishery of Woogeum (01 August 2013; water temp. 29.8℃, EC 193 µS cm-1), and Deokjin Reservoir (17 July 2014; water temp. 30.2℃, EC 342 µS cm-1).
Remarks: This species is widespread throughout the world as planktonic in lakes, ponds, slow flowing rivers and swamps. This species was first reported from ultra−oligotrophic lakes in Arctica (Groenlandia meridionalis, Narssaq) by Komarek (1979). It was also reported from oligotrophic lakes at South Greenland by Komarek and Fott (1983).
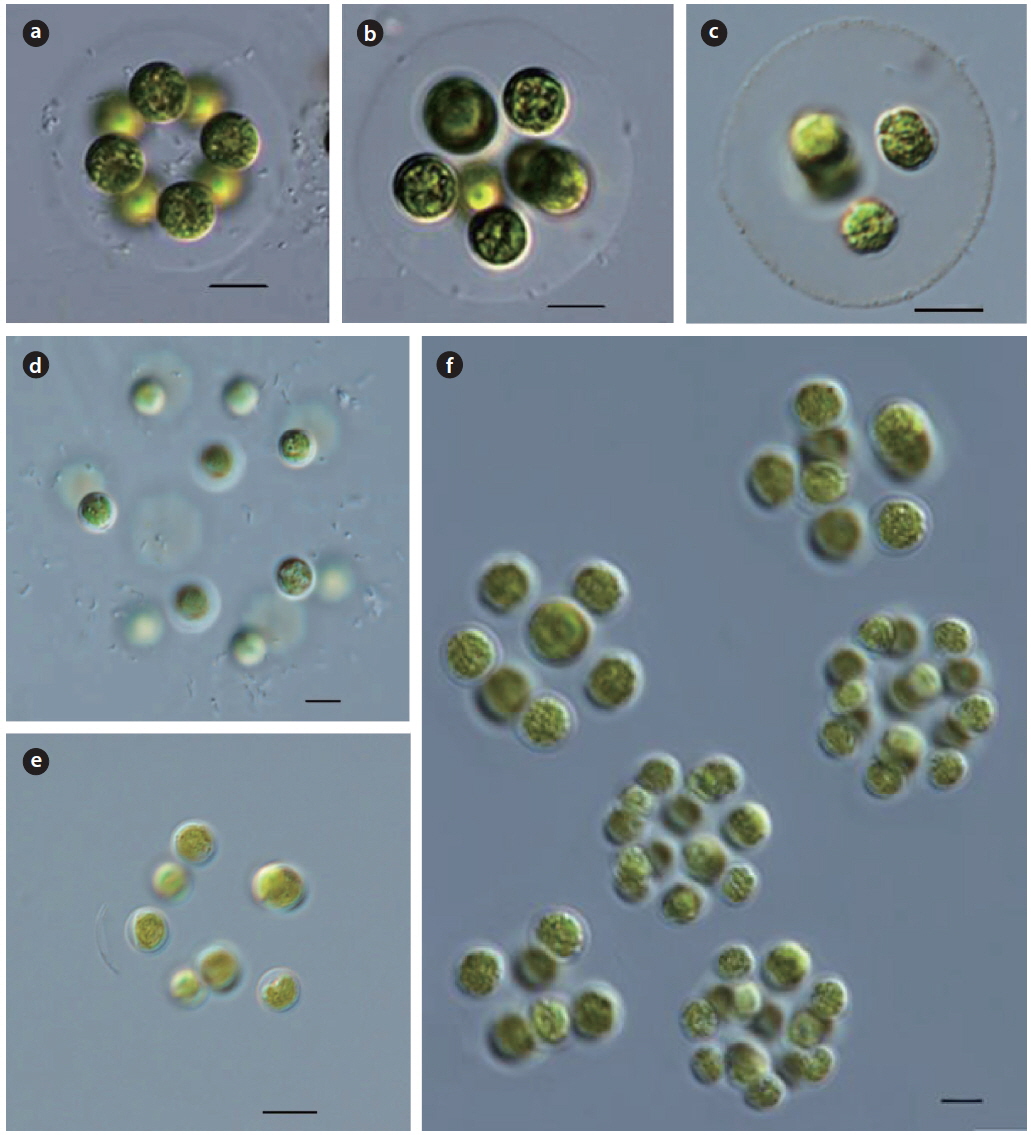
Illustration: Colonies are spherical, or tetrahedral, consisting of 4−8 or 16 tetrahedrally cells. Cells are spherical, with a distance from each other. Cells are parietal, with a pyrenoid, consisting of 4−8 autospores within the mother cell wall, released by gelatinization of the mother cell wall. Cells are 5−10 µm in diameter, colonies are 30−100 µm in diameter.
Key Reference: Komarek (1983)
Specimens: KOSPCL0000106035, KOSPCL0000108484.
Information on sampling sites: Daegok Reservoir (09 July 2012; water temp. 24.0℃, pH 7.4, EC 151 µS cm-1), Spring of wall at tennis courts, Daejin University (26 September 2012; no data), Dongmyung Reservoir (10 July 2012; water temp. 28.7℃, pH 7.3, EC 240.3 µS cm-1, TN 2.321 mg L-1, TP 0.046 mg L-1), the Bukhan River at Yangsoori (26 August 2014; water temp. 30.2℃, EC 238 µS cm-1), Euirim Reservoir (30 August 2012; water temp. 28.2℃, pH 7.6, EC 138 µS cm-1), Jooeul Reservoir (22 September 2012; water temp. 22.7℃, EC 267 µS cm-1), Lake 88 in Olymphic Park (07 September 2013; water temp. 29.8℃, EC 572 µS cm-1), and Galchi Reservoir (24 April 2013; water temp. 23.4℃, pH 6.9, EC 143.2 µS cm-1).
Remarks: This species is widespread throughout the world as plankton in eutrophic lakes, ponds, slow flowing rivers, and swamps. This species was first reported from Ciudad de la Habana (Zoological Garden, eutrophic pool), province Habana (El Dique, eutrophic basin), Cuatro Caminos and Tapaste, Cuba, by Komarek (1983). It was reported from the artificial lakes at the municipality of Goiania from Brazil by Nogueira and Oliveira (2009).
Basionym:
Illustration: Colonies consist of 4−16 or 32 or more cells, arranged in dense and irregular tetrahedrons within a spherical, ellipsoidal or irregular mucilaginous envelope. Cells are spherical, wide and ovoid, with a smooth wall. Chloroplast is cup-shaped, with a pyrenoid. Often 4−8 or sporadically 2 autospores are densely arranged in the mother cell walls, subsequently distributed at a distance from each other, and released by gelatinization of the cell wall. Cells are 5−10 µm in diameter, colonies are 30−100 µm in diameter.
Key Reference: Bourrelly (1966).
Specimens: KOSPCL0000102451, KOSPCL0000107294.
Information on sampling sites: Spring of wall at tennis courts, Daejin University (26 September 2012; no data), Lake 88 in Olymphic Park (07 September 2013; water temp. 29.8℃, EC 572 µS cm-1), Euirim Reservoir (30 August 2012; water temp. 28.2℃, pH 7.6, EC 138 µS cm-1), Jooeul Reservoir (22 September 2012; water temp. 22.7℃, EC 267 µS cm-1) and Sajipo swamp (27 June 2014; water temp. 32.0℃, EC 364 µS cm-1).
Remarks: This species was firstly reported from Distrio Kharkivska, cerca de Lyubotina, Ukraine by Bourrelly (1966). It has been reported from several regions: in a swamp at Escaleras de Jaruco and Zapata pennisula throughout Cuba (Komarek 1983), reservoir at Hrinova from Central Slovakia (Hindak 1977) and in ponds, lakes and cannal throughout British Isles (John and Tsarenko 2002). This species was recorded in the report of the investigation and excavation of the native species by Kim (2013c), but Kim (2013a) reported
Basionym:
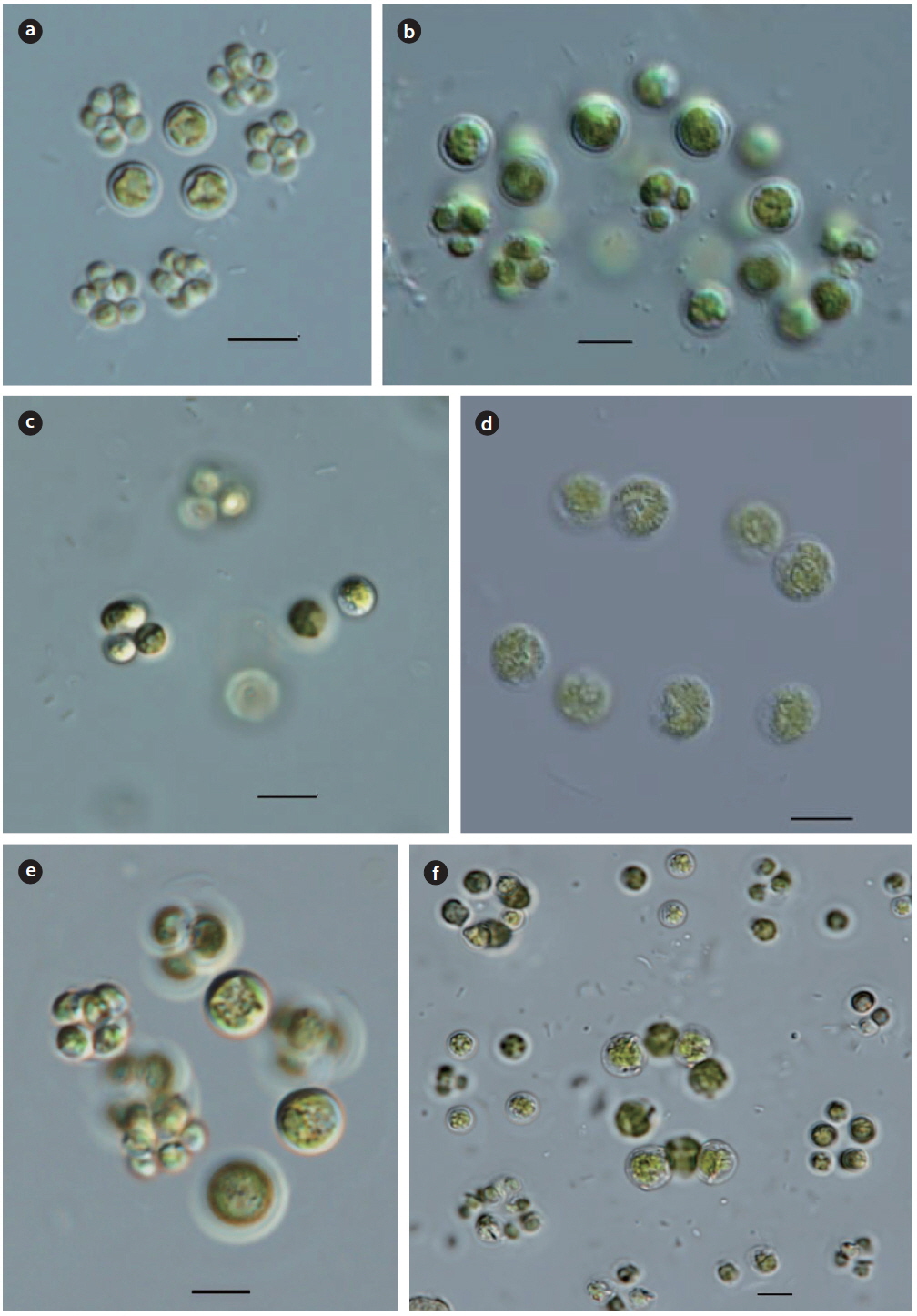
Illustration: Colonies consist of 4−8 cells, arranged in a tetrahedron, and enclosed a spherical, or irregular, colorless mucilaginous envelope. Cells are cup-shaped with a pyrenoid. dense 4−8 or 16 autospores in the mother cell wall, subsequently distributed a distance from each other, and released by gelatinization of the mother cell wall. Cells are 5−8 µm in diameter, colonies are 30−100 µm in diameter.
Key Reference: Komarek (1979).
Specimens: KOSPCL0000105096, KOSPCL0000105962
Information on sampling sites: Dukgok Reservoir (28 April 2012; water temp. 18.1℃, pH 9.2, EC 162.8 µS cm-1), Dongmyung Reservoir (10 July 2012; water temp. 28.7℃, pH 7.3, EC 240.3 µS cm-1, TN 2.321 mg L-1, TP0.046mg L), Bukhan River (26 August 2012; water temp. 30.2℃, EC 238 µS cm-1), Euirim Reservoir (30 August 2012; water temp. 28.2℃, pH 7.6, EC 138 µS cm-1),and Pond in Bundang Jungang Park (02 June 2012; water temp. 26.3℃, pH 8.2, EC 407 µS cm-1)
Remarks: This species was first reported
Illustration: Colonies consist of 4−8 or 16 cells, arranged flattened or in a tetrahedral form, and enclosed in a spherical, colorless, homogeneous mucilaginous envelope. Cells are spherical, arranged at a distance from each other, densely with 4−8 or 16 autospores in the mother cell wall, and subsequently a distance from each other, and released by gelatinization of the mother cell wall. Chloroplast is cup-shaped, with a pyrenoid. Cells are 5−10 µm in diameter, colonies are 30−100 µm in diameter.
Key Reference: Walton (1918).
Specimens: KOSPCL0000105891, KOSPCL0000106162.
Information on sampling sites: Euirim Reservoir (30 August 2012; water temp. 28.2℃, pH 7.6, EC 138 µS cm-1), Pond in Bundang Jungang Park (02 June 2012; water temp. 26.3℃, pH 8.2, EC 407 µS cm-1), and Jooeul Reservoir (22 September 2012; water temp. 22.7℃, EC 267 µS cm-1).
Remarks: This species is widespread throughout the world as plankton in eutrophic lakes, ponds, slow flowing river and swamps. This species was first reported from Mirror Lake (a small pond on the campus of the State University at Columbus) Ohio, USA, by Walton (1918). The other researcher has reported from mesotrophic lakes in Austria (Komarek and Fott 1983).
Basionym:
Synonym:
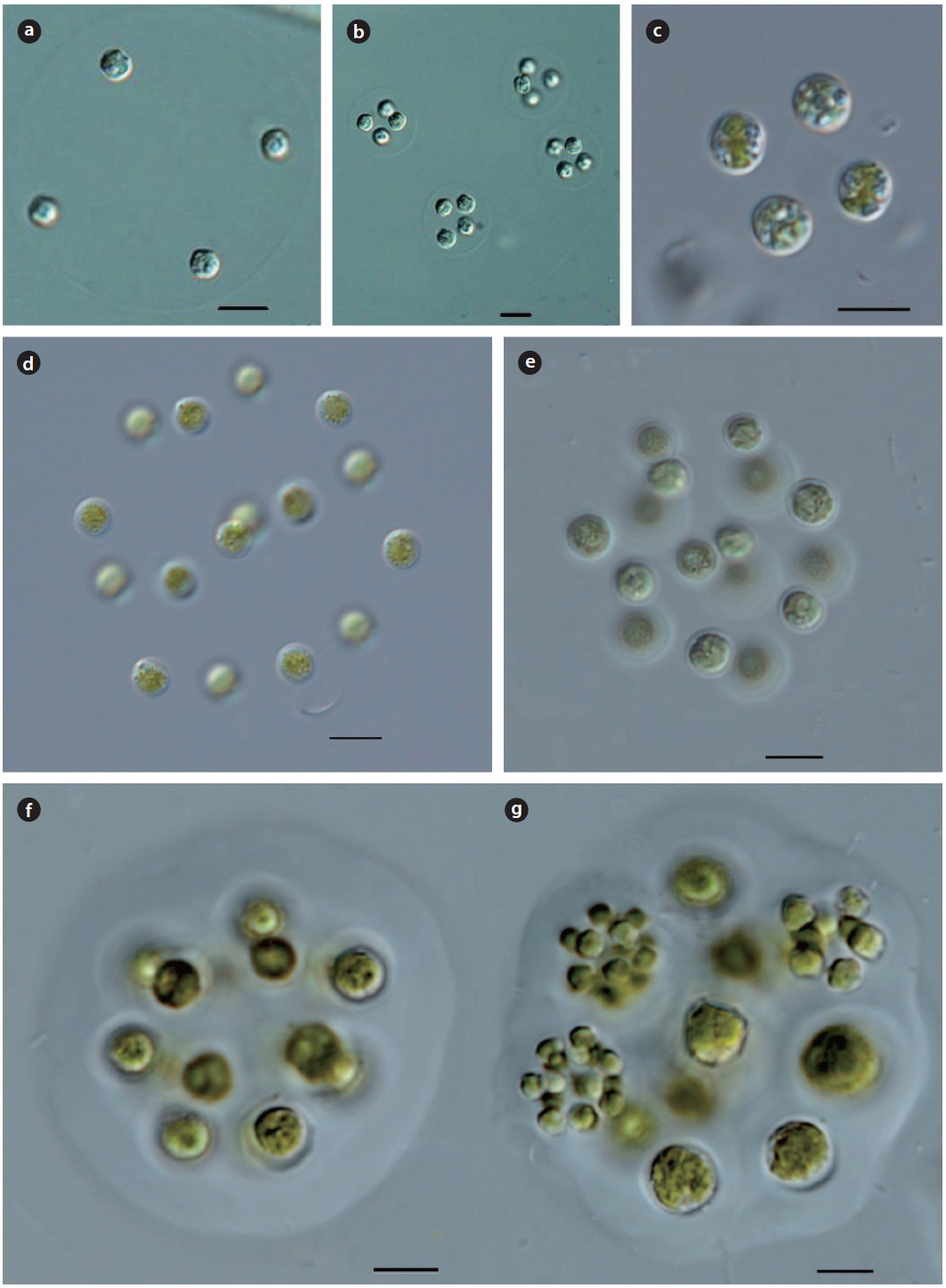
Illustration: Colonies consist of 4−8 or 16 cells, enclosed in a spherical or irregular mucilaginous envelope. Cells are spherical, with a smooth wall, and arranged at a distance from each other. Chloroplast is cup−shaped, with 2 or more pyrenoids. 4−8 or 16 autospores are in the mother cell wall and released by gelatination of the mother cell wall. Cells are 5−10 µm in diameter, colonies are 30−100 µm in diameter.
Key Reference: Komarek (1979).
Specimens: DJWG20120621.
Information on sampling sites: Woogeum Reservoir (21 July 2012; water temp. 27.8℃, pH 8.9, EC 123 µS cm-1) and Gyodong Reservoir (31 May 2013; water temp. 25.4℃, EC 204 µS cm-1)
Remarks: This species was first reported from Northern Europe; Russia (Silva 1996−to date) by Komarek (1979). This species was reported from eutrophic lakes, rivers, ditches, and ponds throughout the British Isles (John and Tsarenko 2002), in inundation lakes of Morava from Western and Southern Slovakia (Hindak 1977), and in lakes throughout Europe (Austria, Romania, Switzeland, Ukraina) and in Washington, USA (Komarek and Fott 1983).
>
Genus Coenocystis
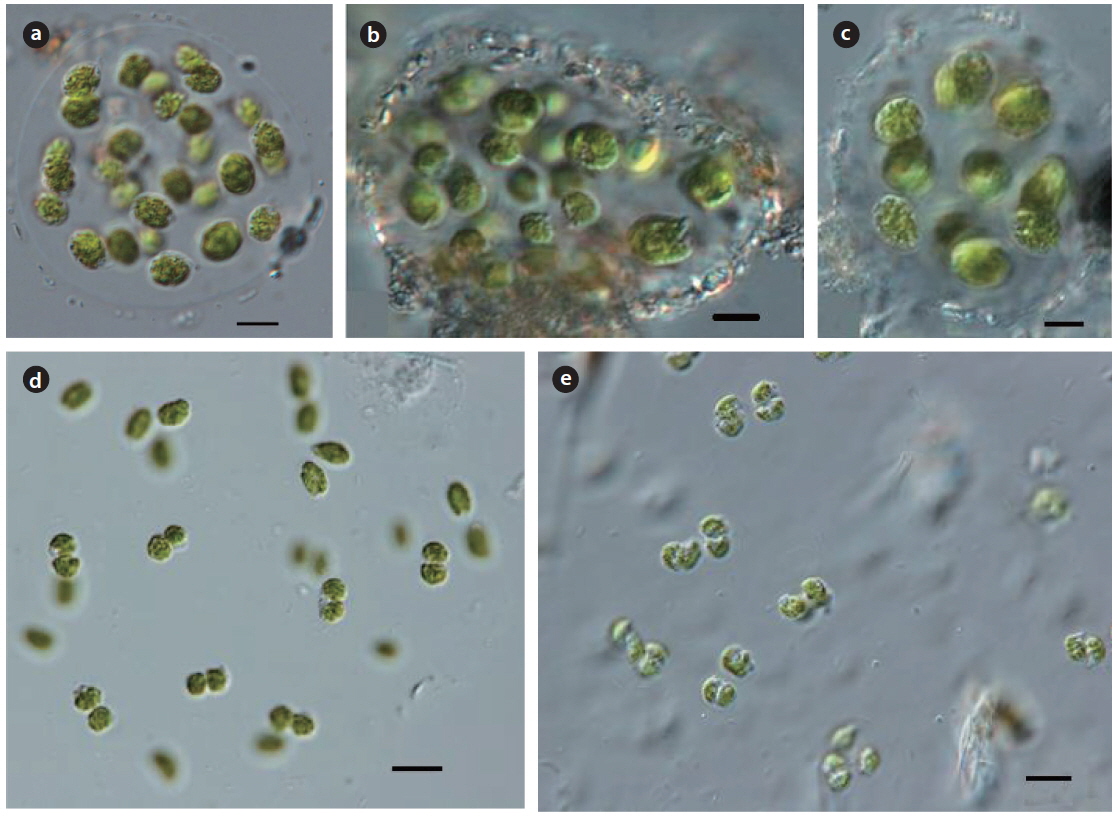
Illustration: Colonies consist of 4−8 or 32 cells, sometimes 4 or 8 cell groups, enclosed by colorless, irregular mucilaginous envelope. Cells are wide and ovoid, slightly asymmetrical or spherical, with a thin gelatinous layer around the cells. Reproduction is by 4−8 or 16 autospores, arranged parallel in the mother cell wall, and released by gelatinization of the mother cell wall, with no visible remnants of the mother cell wall. Chloroplast is cup-shaped, with a pyrenoid.
Key Reference: Komarek (1983).
Specimens: KOSPCL0000106052.
Information on sampling sites: Dongmyung Reservoir (10 July 2012; water temp. 28.7℃, pH 7.3, EC 240.3 µS cm-1, TN 2.321 mg L-1, TP0.046mg L), Euirim Reservoir (30 August 2012; water temp. 28.2℃, pH 7.6, EC 138 µS cm-1), Lake 88 in Olympic Park (07 September 2013; water temp. 29.8℃, EC 572 µS cm-1), and Banwoel Reservoir (24 April 2013; water temp. 19.1℃, pH 8.3, EC 267 µS cm-1).
Remarks: This species was first reported from Habana (Escaleras de Jaruco, swamp), province Mantanzas (Zapata peninsula, swamps), Cuba and swamps at Escaleras de Jarucp and Zapata throughout Cuba (Komarek 1983). This species was reported from eutrophic lake in Cuba (Komarek and Fott 1983) and the Bermejales reservoir in the Iberian Penisula from Cuba (Trevino et al. 2010).
Synonym:
Illustration: Colonies consist of 4 or 8 cells located towards the center of a spherical or ellipsoidal mucilaginous envelope, with an indistinct edge. Cells are spherical or ovoid, and symmetrical. Chloroplast is parietal, with a pyrenoid. Reproduction is by 4 or 8 autospores in the mother cell wall, released by the splitting of the mother cell wall. Cells are 10−15 µm in length and 8−10 µm in width. Colonies are up to 80 µm in diameter.
Key Reference: Korshikov (1953).
Specimens: KOSPCL0000104313, KOSPCL0000105264.
Information on sampling sites: Dongmyung Reservoir (10 July 2012; water temp. 28.7℃, pH 7.3, EC 240.3 µS cm-1, TN 2.321 mg L-1, TP0.046mg L), Euirim Reservoir (30 August 2012; water temp. 28.2℃, pH 7.6, EC 138 µS cm-1), and Lake 88 in Olympic Park (07 September 2013; water temp. 29.8℃, EC 572 µS cm-1).
Remarks: This species was first reported from Kharkov area, Lake Liman, Ukrainian, by Korshikov (1953). This species has been reported from lakes, rivers and ponds throughout the British Isles (John and Tsarenko. 2002), in lakes throughout Europe (Czech, Hungary, Poland, Ukraina) and America (USA, Canada, Cuba, Argentina) (Komarek and Fott 1983), and the inundation lakes at the Morava river into the Danube throughout Slovakia (Hindak 1984).
Basionym:
Synonym:
Illustration: Colonies consist of 4 or 8 cells located towards the center of a spherical or ellipsoidal mucilaginous envelope, with an indistinct edge. Cells are spherical or ovoid, symmetrical. Chloroplast is parietal, with a pyrenoid. Reproduction is by 4 or 8 autospores in the mother cell walls, released by the splitting of the mother cell wall. Cells are 10−20 µm in length and 8−15 µm in width.
Key Reference: Fott (1974).
Specimens: KOSPCL0000106081, KOSPCL0000106129.
Information on sampling sites: Daejin Uiversity pond (26 September 2012; no data), Dongmyung Reservoir (10 July 2012; water temp. 28.7℃, pH 7.3, EC 240.3 µS cm-1, TN 2.321 mg L-1, TP0.046mg L), Euirim Reservoir (30 August 2012; water temp. 28.2℃, pH 7.6, EC 138 µS cm-1), Lake Seoho (27 May 2012; water temp. 30.4℃, pH 7.3, EC 569 µS cm-1), Oknyu Reservoir (22 September 2012; water temp. 25.2℃, pH 9.0, EC 572 µS cm-1, TN 0.855 mg L-1, TP 0.194mg L-1), and Lake 88 in Olympic Park (07 September 2013; water temp. 29.8℃, EC 572 µS cm-1).
Remarks:
Synonym:
Illustration: Colonies are spherical, oval, slightly irregular or several subcolonies, arranged parallel in 1 or 2 planes, slightly irregularly, with a distance from each other. Cells are widely ovoid or sometimes slightly asymmetrical shape. Chloroplast is parietal, massive, without pyrenoid. Reproduction is by autospores arranged in 1 or 2 planes in the mother cell wall, and released by gelatinization of the mother cell wall. Cells are 5−15 µm in length and 5−10 µm in width.
Key Reference: Korshikov (1953).
Specimens: KOSPCL0000105269.
Information on sampling sites: The Bukhan River at Yangsoori (26 August 2012; water temp. 30.2℃, EC 238 µS cm-1), Lake Seoho (27 May 2012; water temp. 30.4℃, pH 7.3, EC 569 µS cm-1), Woogeum Reservoir (01 August 2013; water temp. 29.8℃, EC 193 µS cm-1), and Lake 88 in Olympic Park (07 September 2013; water temp. 29.8℃, EC 572 µS cm-1).
Remarks: This species is widespread throughout the world as plankton in eutrophic lakes, ponds, slow flowing rivers and swamps. This species was first reported from the Gorkij-district, USSR, by Korshikov (1953). It has been recorded from the several regions in lakes throughout Europe (Czech, Hungary, Poland, Ukraina, and Germany), America (Canada, USA, Cuba, and Argentina), and New Zealand (Komarek and Fott 1983). Hindak (1988) reported this species at two different typical localities. He collected the sample at the outflow of the mountain Lake Rohacske at Western Tatras in Setember 1982 and at the eutrophicated water reservoir at Boleraz near Trnava throughout Slovakia in the summer 1986 (Hindak 1988). This species was also collected in the eutrophicated reservoir and lake in Korea.
*
Illustration: Colonies are spherical, oval, and irregular or 1-4 subcolonies, fine colorless, and with different gelatinous envelope. Cells are oval to widely oval, and old cells almost spherical. Autospores are ellipsoidal to oval, sometimes asymmetrical, and irregularly arranged from another. Chloroplast is single, parietal or cup shaped with a pyrenoid. Cells are 5 µm in length and 5−10 µm in width.
Key Reference: Komarek (1983).
Specimens: DJDB20140530.
Information on sampling sites: Dongbaekdongsan (30 May 2014; water temp. 32.0℃C, pH 6.9, EC 69.6 µS cm-1).
Remarks: Komarek (1983) collected the samples in the detritus eutrophic pool in Province Matanzas, Cuba, and reported a new species. This author collected the sample of this species from a swamp of Dongbaekdongsan in Jeju Island.
>
Genus Gloeocystis Nageli 1849: 65
Illustration: Colonies consist of 4−8 or 16 cells, and are enclosed by a colorless, concentric circular mucilaginous envelope. Cells are spherical, with a gelatinous sheath around each cell, chloroplast is cup shaped, with a pyrenoid. Reproduction is by 4 or 8 autospores, arranged in a tetrahedron form, within oval or spherical the mother cell wall. Cells are 8-15 µm in diameter
Key Reference: Iyengar (1971) in Komarek and Fott (1983).
Specimens: DJDM20120710, DJOS20130814.
Information on sampling sites: Dongmyung Reservoir (10 July 2012; water temp. 28.7℃, pH 7.3, EC 240.3 µS cm-1, TN 2.321 mg L-1, TP 0.046 mg L-1), Seorang Reservoir (27 May 2012; water temp. 30.4℃, pH 7.0, EC 294.6 µS cm-1), Oksan Reservoir (14 August 2013; water temp. 30.2℃, EC 342 µS cm-1), and Deokjin Reservoir (17 July 2014; water temp. 31.6℃, EC 110.0 µS cm-1)
Remarks: Iyengar (1971) collected samples from the pond at Bangalore in India, and identified it as a species of the genus
Basionym:
Key Reference: Ettl and Gärtner (1995).
Specimens: DJDM20120710, DJBD20120602.
Information on sampling sites: Dongmyung reservoir (10 July 2012; water temp. 28.7℃, pH 7.3, EC 240.3 µS cm-1, TN 2.321 mg L-1, TP 0.046 mg L-1), Pond in Bundang Jungang Park (02 June 2012; water temp. 26.3℃, pH 8.2, EC 407 µS cm-1), Woogeum Reservoir (01 August 2013; water temp. 27.8℃, pH 8.9, EC 123 µS cm-1), and Deokjin Reservoir (17 June 2014; water temp. 31.6℃, EC 110.0 µS cm-1).
Remarks: Watanabe (1977) collected the sample from the Papua, and reported a new species
*
Basionym :
Synonym :
Illustration: Colonies are amorphous, green mucilaginous, with scattered cells in a colorless gelatinous concentric envelope. Cells are composed with a single, pair or four, oval or ellipsoidal shapes. Cells are enclosed several concentric gelatinous sheaths around cells, chloroplast is parietal, with a pyrenoid. Reproduction is by 4 or 8 autospores, enclosed by an oval or spherical mother cell wall. Cells are 5−8 µm in length and 4−6 µm in width.
Key Reference: Hindak (1978).
Specimens: DJBD20140530.
Information on sampling sites: Baengduimot (30 May 2014; water temp. 31.7℃, pH 7.7, EC 91.3 µS cm-1).
Remarks:
This study was carried out on freshwater chlorococcal green algae in ponds, swamps, reservoirs, lakes and rivers (290 sites) from May 2012 to January 2014. The family Radiococaceae was identified and classified into 3genera, 12 species and 1 variety at 23 sites. These taxa were