Sericinus montela Gray (or Sericinus telamon Donovan), a species of swallowtail butterfly (Collins and Morris, 1985), is known for the beauty of its wing phenotype. The unique wing morphology is characterized by a pair of slender tails elongated from each hindwing in the M3 vein region; therefore, it is called the “tailed butterfly” (Ackery, 1975; Kim and Lee, 1992). Swallowtails typically include all members of the Papilionidae family (Collins, 1991). In general, swallowtails are not only famous for large, colorful, and glamorous wings, but some species also have diverse hindwing tail types (Ackery, 1975). A variety of butterfly specimens, especially swallowtails, have been on display all over the world, and live butterflies are exhibited in indoor gardens and museums for educational and aesthetic purposes.
A representative flight mode of butterflies is fluttering, which is conspicuous because of large flamboyant wings. In addition, the wing couple is attached to the second and third thoraces, but it is not hooked together. This characteristic and the lack of bristles allow their flight to be more elegant. Possible correlations between flight performance and wing shape in swallowtails have been suggested, which might explain the wide range of complex flight patterns (Betts and Wootton, 1988). Field observations of S. montela have described fluttering with slow, full strokes when flying upward or climbing (Shin, 1974; Kim and Lee, 1992). However, the downward flight and landing mode utilize gliding without fluttering. S. montela spreads its wings when basking or landing instead of folding them vertically (Nam et al., 1998). Therefore, the distinct flight of S. montela adds celestial imagery to the beauty of the wings, and this is likely due to its large forewings and particularly long hindwing tails.
Approximately 20,000 butterfly species belong to a small part of the insect order Lepidoptera, which also contains the moth group that is ten times larger (Collins, 1991). Butterflies are divided into five families that are predominantly found in the tropics, but a few species extend to cool temperature latitudes in both hemispheres (Collins, 1991). Most swallowtails are distributed in extremely limited areas rather than widespread areas that are sensitive to habitat and environmental changes. S. montela is one of the over 500 species in Papilionidae (Munroe and Ehrlich, 1960), which is endemic to some countries of northeastern Asia, including Russia, China, and Korea (Ackery, 1975; Collins and Morris, 1985). Geographical forms from the northern region (e.g., ssp. greyi Fixs.) as well as the central and southern regions (e.g., ssp. koreana Fixs.) have been assigned to the subspecies found in Korea (Kim and Hong, 1991). However, extensive research on this species has been published mostly in Japan following introductions from Korea as recent as the late 1970s (Kim and Hong, 1991; Kim and Lee, 1992; Kumon, 1996).
S. montela feeds exclusively on Aristolochia contorta Bunge (Aristolochiaceae), which is a source of aristolochic acids in plants (Mix et al., 1983). Aristolochic acids, which can be toxic to humans via inhalation or contact with skin (Merk index), protect S. montela caterpillars and adults from predators via sequestration in the body (Omura et al., 2006). For instance, larvae secrete odoriferous fluid from their defensive glands (osmeteria), which contain five of the eight aristolochic acid compounds found in the host, A. debilis (Nishida, 1995). S. montela is dimorphic at the adult stage, which is characteristic of primitive insects. In the wild, it is simple to distinguish males and females by the color of their wings. Male wings are bright beige, whereas females have dark brown wings that are described as a melanized pattern (Nam et al., 1998), which has not yet been proven. Like most other butterflies, S. montela adults are solitary in behavior. Females lay clutches containing dozens to a hundred eggs on the stems or leaves of the host plant (Shin, 1974). After 5–8 d, larvae hatch from the eggs in a group and pass through five instars with a total developmental time of 16–21 d, depending on the ambient thermal environment and availability of host plants in Korea. Adults survive for about two weeks after pupae metamorphogenesis, which takes 10–12 d unless they enter diapause for overwintering. Taken together, adult emergence takes approximately one month, and completion of the full life cycle lasts up to about 50 d in the field. However, Russian subspecies take 16–19 d for the adult to develop at 20–25°C in the laboratory (Monastyrskiy and Kotlobay, 1995). Therefore, S. montela is multivoltine, emerging two or three times a year on average in Korea (Shin, 1974; Kim and Lee, 1992; Nam et al., 1998).
The habitat of S. montela in the Gwangneung area, one of the most important sites for insect conservation in Korea, was investigated for a long period of time from 1932 to 2004 (Shin, 1974; Byun et al., 2005). Swallowtail emergence was observed three times a year from 1960 to 1962 (Shin, 1974). Since then, the population has decreased rapidly until only a single male was observed in April 2004, despite the presence of 148 species (67.0% of the S. Korea butterfly fauna) listed in Gwangneung Forest (Byun et al., 2005). As a part of the ecosystem, the world’s human population has continuously increased, and it predominantly occupies most of the earth while simultaneously destroying or fragmenting natural habitats, which threatens worldwide biodiversity (Fahrig, 2003; Kim, 2010). Global warming caused by the greenhouse effect is a pernicious threat to swallowtails (Collins and Morris, 1985; Collins, 1991), and many species, including S. montela, are facing environmental challenges or further threats. Particularly, because S. montela habitats are intimately associated with human-occupied areas, the species is exposed to additional dangers. Therefore, the butterfly has disappeared near hiking trails, fields, and stream banks where it was previously observed (Kim, 2010). Special attention should be paid to the development of strategies to protect them (Collins and Morris, 1985; Collins, 1991). Since 2005, Hyundai Motor Company has made efforts to reconstitute natural environments that are optimal for S. montela by establishing eight ecology laboratories (the so-called “The Ecology Learning Center”) in five cities as one of the social responsibilities of the company (http://www.hyundai-green.com). Physiological and ecological research on S. montela should not only be conducted to provide butterfly habitats and guidelines for introducing them into the field, but it should also support the maintenance of optimal habitats and population control in the ecosystem.
In insects, their physiological processes, behaviors, and survival are susceptible to environmental variations. Temperature, which is one of the parameters, significantly affects gene expression, body size, and color during development, and it can also affect the natural habitats and generation times of species (Blau, 1981; Smith, 1991; Nylin and Gotthard, 1998; Hazel, 2002; Pateman et al., 2012; Kvist et al., 2013). For that reason, a long-standing issue in biology has been the impact of ambient temperature on physiological processes in the biosystem. As many studies of insects have documented, the growth rate increases with increasing temperature to a maximum point, after which increases in temperature result in larval death (Howe, 1967; Guppy, 1969; Poston et al., 1977; Rawlins and Lederhouse, 1981).
In the beginning of the S. montela physiological study, we set out to investigate its developmental characteristics and the effects of ambient thermal environments on embryonic and larval development throughout all developmental stages. Our study focuses on an examination of developmental durations and survival rates of eggs, larvae, and pupae under varying temperatures, with the expectation of discovering the most favorable conditions for laboratory rearing.
Native S. montela individuals were collected from Pyeongtaek, in Gyeonggi province, South Korea to establish a rearing system in the laboratory. The butterflies were then maintained for further investigation in the Division of Applied Entomology at the National Academy of Agricultural Science. They were grown at 25 ± 1°C and 50 ± 10% relative humidity with a photo regime of 16 L: 8 D, and experiments were conducted after two generations to minimize maternal effects. All S. montela adults and larvae fed on A. contorta plants. The larvae were kept under the following conditions: a small Petri dish (35 mm in diameter and 10 mm in height; 35 mm × 10 mm) for the first stage; a large Petri dish (60 mm × 10 mm height) for the second and third stages; and a large Petri dish (100 mm × 40 mm height) for the final stage.
Female butterflies were placed individually in a box, and were hand-mated in order to obtain eggs (Platt, 1969). Each male was removed from the box after mating, allowing the female to lay eggs on A. contorta. The female was then released from the cage, and the number of eggs adhering to the stem was counted. The eggs were distributed into chambers set at nine temperature regimes (15.0, 17.5, 20.0, 22.5, 25.0, 27.5 30.0, 32.0, and 35°C) with 50 ± 10% relative humidity and a 16 L: 8 D photoperiod. Each temperature-specific chamber contained 30 eggs in triplicate. Survivorship and developmental durations from eggs to larvae and larvae to pupae were recorded on a daily basis. On the initial experimental day, the newly hatched larvae grown at 25.0°C were distributed into various temperatures (15.0, 20.0, 25.0, 30.0 and 35.0°C). The food was replenished regularly each morning after examining larval development. When the fifth instar larvae stopped eating, each individual was placed into a separate large Petri dish (100 mm × 40 mm) where they were allowed to pupate. In addition, when larvae that were consistently reared at 25.0°C reached a pupal stage, they were distributed into 15.0, 20.0, 25.0, 30.0, and 35.0°C temperature regimes to investigate pupal development and adult eclosion. The duration of the each stadium (until pupation) as well as the survival rate was recorded to the nearest day.
Differences in the developmental period of egg, larval, and adult stages were tested by analysis of variance (ANOVA). If significant differences were detected, multiple comparisons were made using Tukey’s HSD multiple range test (p = 0.05).
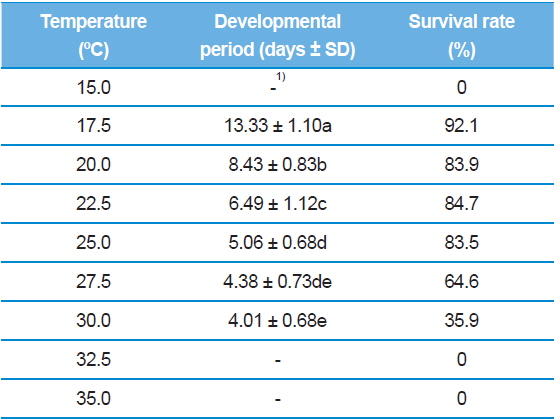
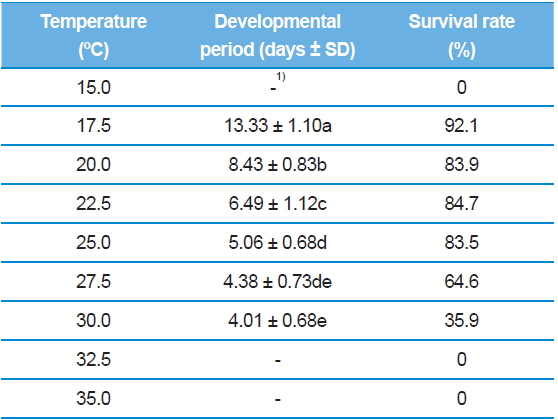
As shown in Table 1, the developmental duration of S. montela eggs decreased with increasing temperature within the range of 17.5–30.0°C. At the extreme ends of the test temperatures, 15.0°C and 35.0°C, embryonic development did not proceed, thus representing zero percent survival rates. The longest period was 13.33 ± 1.10 d at 17.5°C, and the shortest was 4.01 ± 0.68 days at 30.0°C. Our data revealed that developmental time exponentially decreased with increasing temperature from 17.5°C to 30.0°C. In the range of 25.0–30.0°C, no significant decreases were observed in developmental durations (from 5.06 ± 0.68 to 4.01 ± 0.68 d). Overall, the development of S. montela eggs at higher test temperatures takes a significantly shorter time than at lower temperatures, indicating that S. montela embryonic development is temperature-dependent. Further, eggs maintained at 17.5°C had the highest survival rate (92.1%), while the survival rates at higher temperatures, 27.5°C and 30.0°C, abruptly decreased to 64.6% and 35.9%, respectively. The eggs in the range of 20.0–25.0°C successfully hatched with high survival rates of 83.5–84.7%. Taken together, the temperature range of 20.0–25.0°C was observed to be optimal for embryogenesis of S. montela individuals with relatively short developmental periods and high survival rates. Representative morphology of S. montela eggs while embryogenesis proceeded at 25.0°C is shown in Fig. 1, and the color of the eggs darkened until hatching.
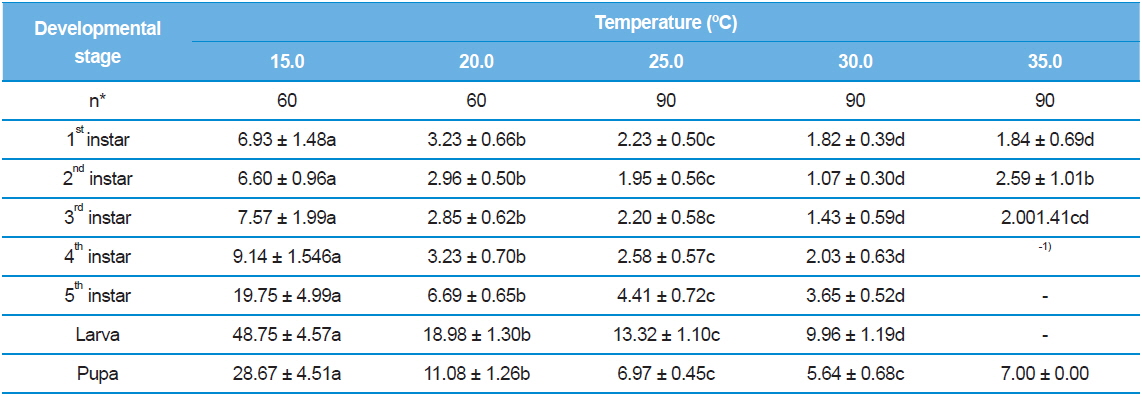
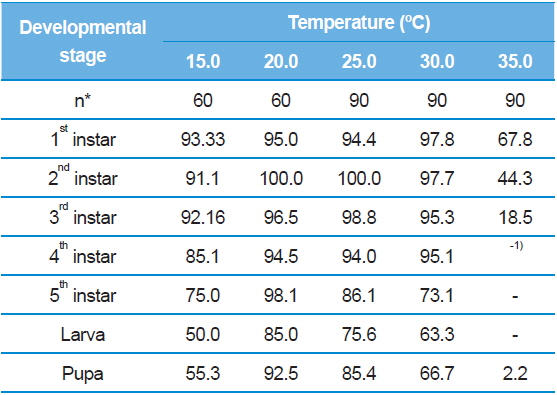
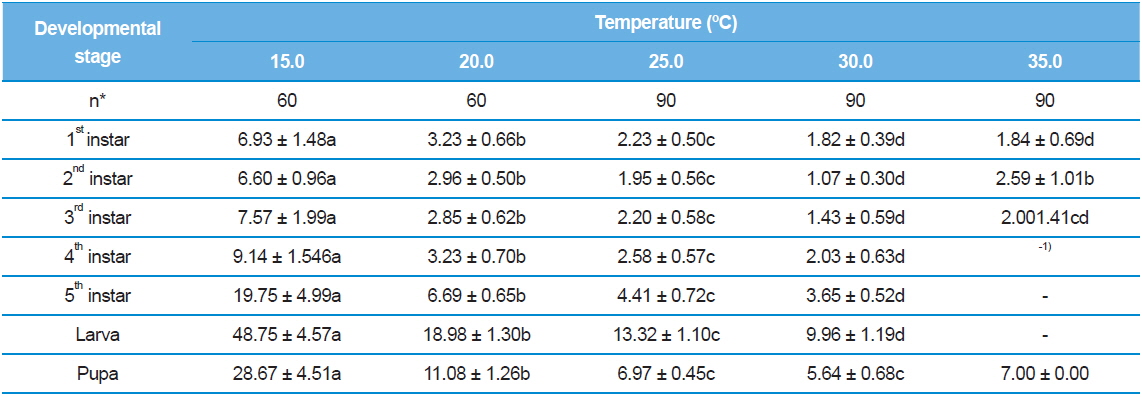
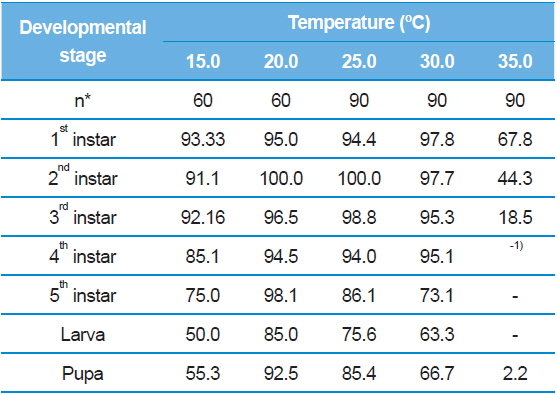
Inevitably, we observed S. montela adults eclosed from the pupae across all test temperature ranges from 15.0°C to 35.0°C (Table 2). The duration became shortest (5.64 ± 0.68 d) when the temperature increased to 30.0°C, and it again increased to 7.00 days at 35.0°C with a 2.2% survival rate instead of a die-off (Table 3). Interestingly, larval development completed even at the lowest temperature of 15.0°C, at which embryonic development ceased (Table 1). In addition, survival rates of the larvae and pupae at 15.0ºC were not particularly low at 50.0% and 55.3%, respectively (Table 3). However, developmental durations of the larvae (48.75 ± 4.57 d) and pupae (28.67 ± 4.51 d) were especially long at 15.0ºC compared to those surviving at higher test temperatures. Our results indicate that unlike eggs, S. montela larvae and pupae can fully develop at lower temperatures despite extremely slow growth.
Similar to embryonic development, the stage-specific development time of S. montela larvae significantly decreased with increasing temperatures up to 30.0°C (Table 2). At 35.0°C, the stagespecific durations slightly increased as predicted (Howe 1967; Guppy, 1969; Poston et al., 1977; Rawlins and Lederhouse, 1981), implying a maximum growth rate at 30.0°C among the test temperatures. The durations in the range of 20.0–35.0°C were significantly shorter compared to those at 15.0°C until the third instar stage. Caterpillars accomplished development from the first to the third instars at all the temperatures with high survival rates (over 90%), except at 35.0°C (Table 3). During the early developmental period until the third instar stage, larval survival rates substantially decreased from 67.8% to 18.5% at 35.0°C. No further development proceeded at the later stages, resulting in zero percent survival rates for both the fourth and fifth instars at 35.0°C. The fourth and fifth instar larvae still showed decreases in the developmental duration at temperatures from 20.0°C to 30.0°C, which was identical to the patterns of the earlier instars. The fourth instar showed high survival rates of 85.1% to 95.1%. By contrast, the survival rates were relatively low (73.1–86.1%) at the fifth stage compared to the four earlier stages, with the exception of the 20.0ºC treatment. The results suggest that S. montela larval development is more susceptible to temperature at later stages, especially after the third larval stage. We also demonstrate that full development of S. montela cannot occur at 35.0°C (and probably above 30.0°C).
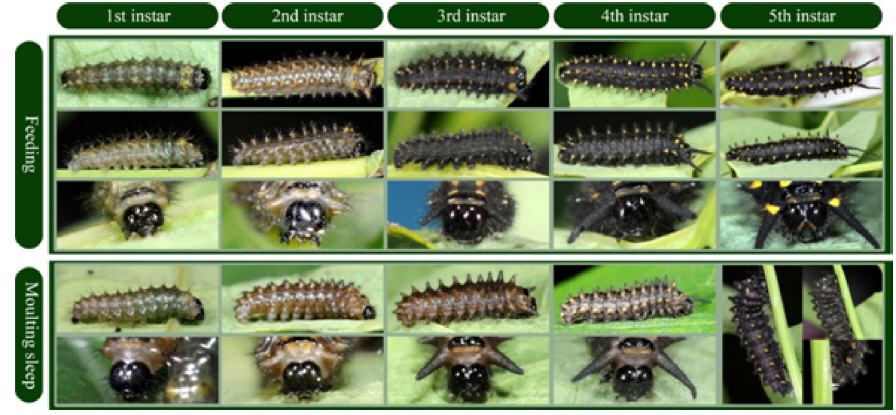
The representative larvae of S. montela at all developmental stages are shown in Fig. 2. A larva feeding on the host plant at each stage is presented in the upper panel, and the sleep-like state of a larva before molting is displayed in the lower panel. The colors of the third, fourth, and fifth larval instars became darker as development proceeded, whereas the first and second exhibited lighter colors. A pair of osmeteria in the prothoracic segment started to protrude at the first instar stage, and became long and thick.
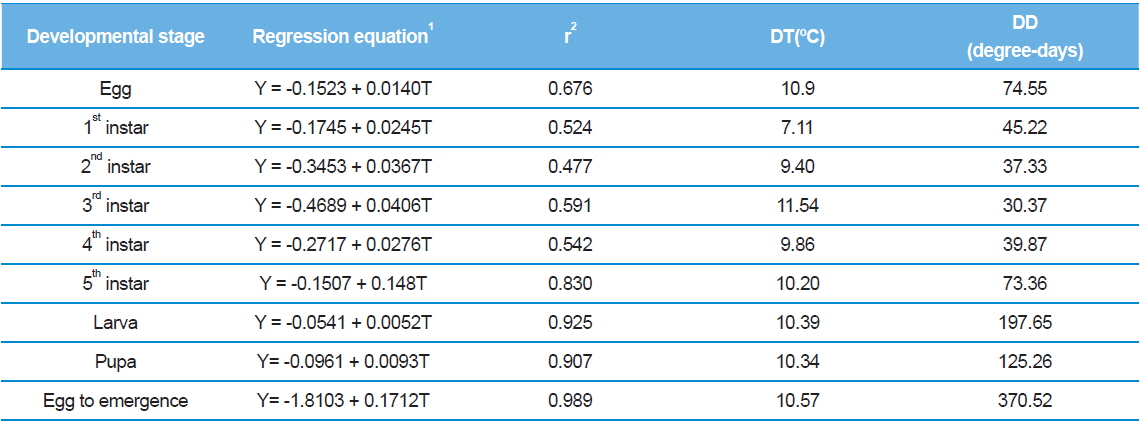
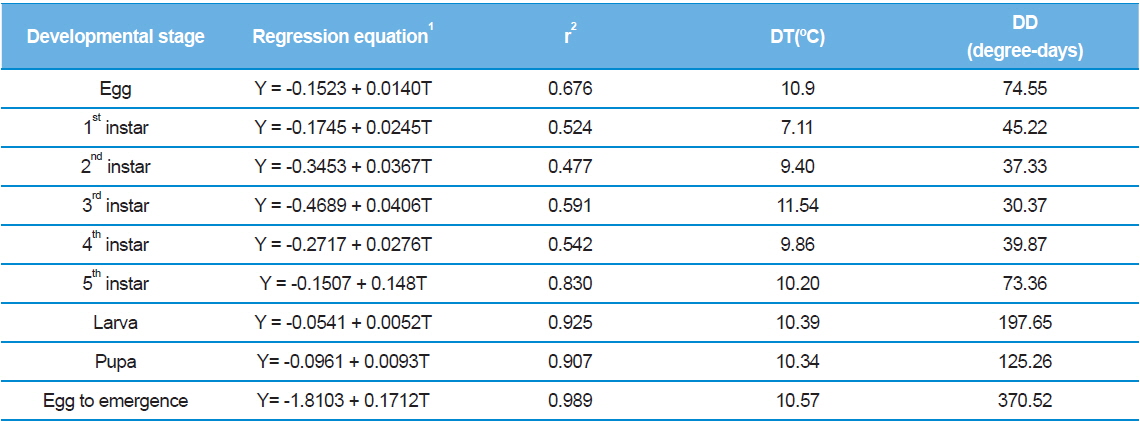
A linear model was used to determine the developmental thresholds (DTs) based on the temperature variable data found in Tables 1 and 2 (Table 4). At all stages, the estimated values were within approximately 7.0–12.0°C, which fell outside of the temperature range tested in our experiments. The lower thresholds for larvae and pupae were 10.4°C (p = 0.075) and 10.3°C (p = 0.093), respectively, and the threshold for full development was 10.6°C with high accuracy (p = 0.011). Therefore, the lower developmental threshold of S. montela from egg to adult that was determined by the linear method in our study is somewhat convincing. However, the hatching threshold showed the discrepancy between empirical data and the calculated value. The hatching threshold was 10.9°C(p = 0.324), which deviated significantly from the experimental data in Table 1 since we did not observe egg hatching at 15.0°C for quite a long period of time (unpublished data). A more accurate estimated value can be obtained if the threshold is determined by a non-linear method. Another possibility is that the survival rate may not be zero if the size of the egg population increases. We also cannot rule out the possibility that the eggs might endure low ambient temperature of 15.0°C much longer than we have observed.
In the present study, we have shown that varying thermal environments influence the duration and survival rates of S. montela development at all stages from eggs to pupae. Analysis of survival rates suggests that the eggs are able to complete all developmental processes until eclosion in the range of 17.5–30.0°C. Moreover, with analysis of developmental periods, our data have provided strong evidence that optimal development of S. montela occurs from 20.0°C to 25.0°C in an indoor rearing system. In the optimal range, both the developmental periods and survival rates of S. montela are not significantly affected by variations in temperature. An attempt to develop a method for rearing S. telamon under laboratory conditions in Russia identified similar data for embryonic and larval developmental durations at 20.0–25.0°C (Monastyrskiy and Kotlobay, 1995).
Although the optimal temperatures of S. montela development are in the range of 20.0–25.0°C, the larvae can survive at the lowest test temperature of 15.0°C. Total larval development time at the lowest temperature was measured at about 50 d (Table 2), which is exceedingly long and comparable to a whole generation time in the field (Shin, 1974). Therefore, we conclude that the larvae can endure low temperatures for a long period of time, achieving full larval development with delayed growth. Further, maximum egg hatching occurs at 17.5°C with the longest embryonic duration in our study. However, the eggs failed to develop at both test temperature extremes, indicating that embryogenesis of S. montela is more sensitive in response to the ambient thermal environment.
The butterflies never completed development at 35.0°C in this study, which has been reported in some other species of Lepidoptera, including the armyworm (Guppy, 1969), the alfalfa butterfly (Sherman and Watt, 1973), and the tropical monarch (Rawlins and Lederhouse, 1981). However, the early instar larvae and pupae of S. montela accomplished development at 35.0°C, which is the highest temperature we tested (Table 2 and 3). In agreement with our results, it has been suggested that 37.0°C might be close to the maximum temperature that tiger swallowtails (Papolio glaucus) can endure on a continuous basis (Scriber and Lederhouse, 1983). Researchers have observed larval death and progressively poorer growth, although complete development can occur at some stages. Coincidently, our data have indicated that the developmental duration of S. montela larvae or pupae at 30.0°C significantly decreases to half the time compared to that at 20.0°C at the expense of low survival rates (Table 2).
The S. montela developmental threshold estimated in this study is quite similar to that of other butterflies and insects including 85 species in which developmental percentages of zero at a temperature of 11.0°C has been reported (Rawlins and Lederhouse, 1981). In contrast, the determined hatching threshold is much lower than the temperature resulting in no embryogenic progress, although the value is close to that of full development. There is an interesting review of the hatching threshold. It has been revealed that the eggs of most insects and mites can hatch with a high percentage at a constant temperature of 15.0ºC, and this can also be achieved even at temperatures 3–4°C lower if it varies (Howe, 1967). In addition, at constant temperatures within 2–3°C of developmental limits, the proportion of eggs hatching erratically varies and drops rapidly to zero. Therefore, from the discrepancy between the hatching threshold and empirical data in our study, we assume that longer incubation or larger population size at 15.0°C would disclose whether the eggs could stop embryonic development, or if the survival rate might be slightly higher than zero.
The lower temperature limit permitting development can determine the earliest and latest times of the year for insect emergence, as well as the highest latitude for distribution (Rawlins and Lederhouse, 1981). Korea is located in a temperate climate zone, and thus has four distinct seasons. The annual mean temperature ranges from 10°C to 16°C with the highest from 23°C to 27°C in August (Korea Meteorological Administration (KMA), http://web.kma.go.kr/eng/index.jsp). S. montela in Korea has been reported to emerge up to five times from April to the middle of October in the Ecology Centers, depending upon the weather in the cities during the year. Therefore, the plan for swallowtail restoration is fairly successful in comparison with observations of three generations from April to the end of September in the Gwangneung area (Shin, 1974).
Amongst many organisms in the animal kingdom, butterflies are considerably valuable as biological indicators for the monitoring of climatic changes and ecological trends (Collins, 1991). S. montela is likely one of them because it is monophagous, which primarily limits its habitat. Based on our results, this insect is sensitive to environmental temperatures in that it failed to emerge at 35.0°C. Therefore, the survival of this species could be significantly influenced by increasing global climate temperatures caused by the greenhouse effect. Due to their destruction of natural environments, many industrial companies are encouraged to realize natural threats. Hyundai, an exemplary company, has restored the optimal environment for S. montela, which is in danger of extinction. Furthermore, cooperative efforts between the government and companies should be made to restore or protect more endangered species in the ecosystem. In accordance with a plan for swallowtail conservation (Collins, 1991), the strategy for restoration of S. montela can be a good example of a species-oriented program. In the same context, some progress has been made in community-oriented conservation of fireflies in Muju and dragonflies in Gurye, which are critical faunal sites for those species in Korea. Furthermore, there are more beneficial or human-friendly insects in need of conservation such as beetles, crickets, dragon swallowtails, and so on. Since our work on S. montela has not yet advanced to provide a substantial amount of information, further research on this butterfly with various experimental approaches is necessary in the near future.
The results obtained in our study suggest optimum thermal environments to rear S. montela in the laboratory as well as in the field. A further study focusing on the development of substitutes for its natural food source has been conducted. In addition, more research on aristolochic acids and defense mechanisms is required. The results of this study will be of interest in the examination of whether or not there might be a certain effect of the acids on S. montela development. The influence of other developmental parameters of S. montela, such as photoperiod and nutrients, should also be studied. Photoperiod and temperature are important variables that induce diapause of pupae. Therefore, research on S. montela pupal diapause is essential for the development of methods to control the duration as well as to terminate diapause when necessary.