We prepared antibodies from insect glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) and assayed the titer. Nine polyclonal antibodies against insect GAGs were raised for development of an ELISA in biological fluids (mice serum). The 3th booster collection of antiserum of BALB/c mice as a primarily antibody was assayed for titer determination by ELISA method. In sandwich ELISA of GAGs derived from Isaria sinclairii or other insects, antiserum from insect GAGs gave satisfactory results for so potent antibody(100: 1∼1000:1) raising (manufacturing) agent in range of 10 ng/ml.
The necessity of developing antibodies for autoimmune diseases has recently increased due to the outbreak of new virus such as avian influenza (AI) and foot-and-mouth disease. In the development of antibody treatment, immunological and pathological importance of N-glycosylation of immunoglobulin glycoprotein (IgG), composed of two heavy chains and two light chains, has been recognized. Because all N-glycosylation phenotype of mice is not identical to human’s, antibody production from mice has been difficult. It has been devoted to develop antibodies that are humanized with containing N-glycosylation of a mouse IgG2b hinge region, more resistant to the attack of protease and providing a high level of complement fixation. Major saccharides found in human glycoprotein are xylose (pentose); fucose, galactose, glucose, mannose, N-acetylgalactosamine and N-acetylglucosamie (hexose); and N-acetylneuramic acid (nonose) (Kim
GAGs are polysaccharides linked between glyco, amino and glycan by glycosidic linkage. It is a type of carbohydrate molecules making up the blood vessel inner walls and is known to influence directly and indirectly on various functions such as metabolism of low density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, blood coagulation and the formation of cellular matrix. Such GAGs have structurally various and complex form through partial changes in biosynthetic pathway. This research of GAGs derived from insects showed, unlike other GAGs, the effects of significance on the subjects (mice) with chronic inflammation reproducibly in the 3rd repeat animal testing (Ahn
>
Purification of insect GAGs in insect shell residue
Fresh insects (1. male silkworm pupae 2. clony shell of
>
Purification of polysaccharides in insect extracts
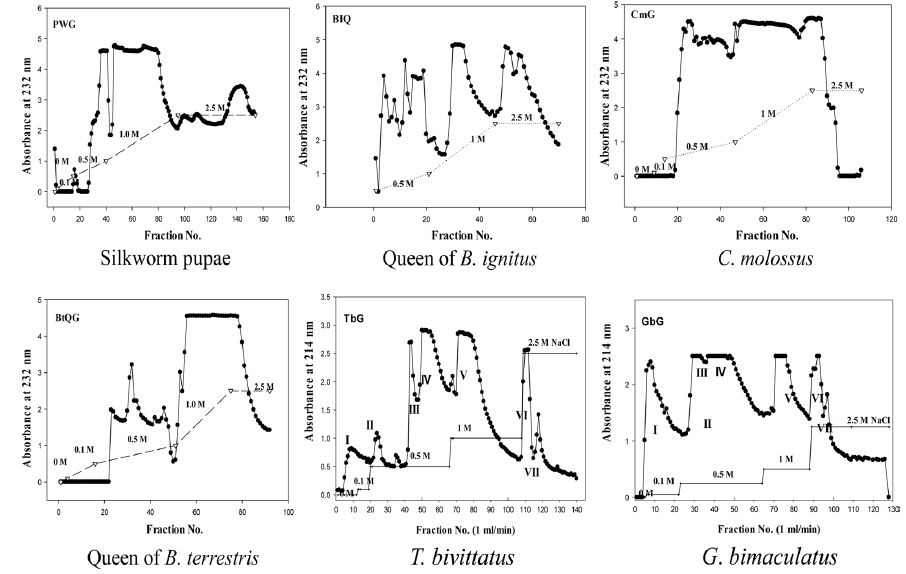
After dissolving crude GAGs in water and removing substances insoluble in water by centrifugation, 5% cetylpyridinium chloride was added to 1/4 volume and the mixture was deposited. The precipitate was purified by dissolving in 2.5 M sodium chloride by centrifugation and depositing with alcohol. Polysaccharides were purified by freeze drying after dialyzing by dissolving the purified sample in a small amount of water. Through the repetition of the process, each insect GAG fraction was prepared by collecting sugar acid fraction to determine the purity by electrophoresis; purifying more with a salt gradient (0, 0.1, 0.5, 1, 2.5M NaCl in phosphate buffer) via ion exchange chromatography (Sephadex DEAE A-25); and collecting the fraction containing uronic acids.
The titer assay was conducted by preparing polyclonal antibodies for research on mass production techniques of the insect GAG antibodies. Polyclonal antibodies were prepared by mixing 10 mg/kg of the insect GAGs with the same amount of complete Freund’s adjuvant (sigma CO, USA) in the 1st immunization; injecting the homogenate emulsified for a day to BALB/c mice intraperitoneally; at 12-day intervals as the 2nd and the 3rd, mixing incomplete Freund’s adjuvant (sigma, CO., USA) with the same amount of the purified GAGs; injecting intraperitoneally after emulsifying for a day; and collecting serum after 2 wk. After taking the blood sample, antibodies in this research were prepared by preparing sodium citrate 3.8%; coating it in the syringe for 1/9 of the blood to enter; collecting blood; hardening fibrin by centrifugation; and diluting the serum with 1% FCS-tween to 1/10.
>
Antibody titer assay with sandwich ELISA
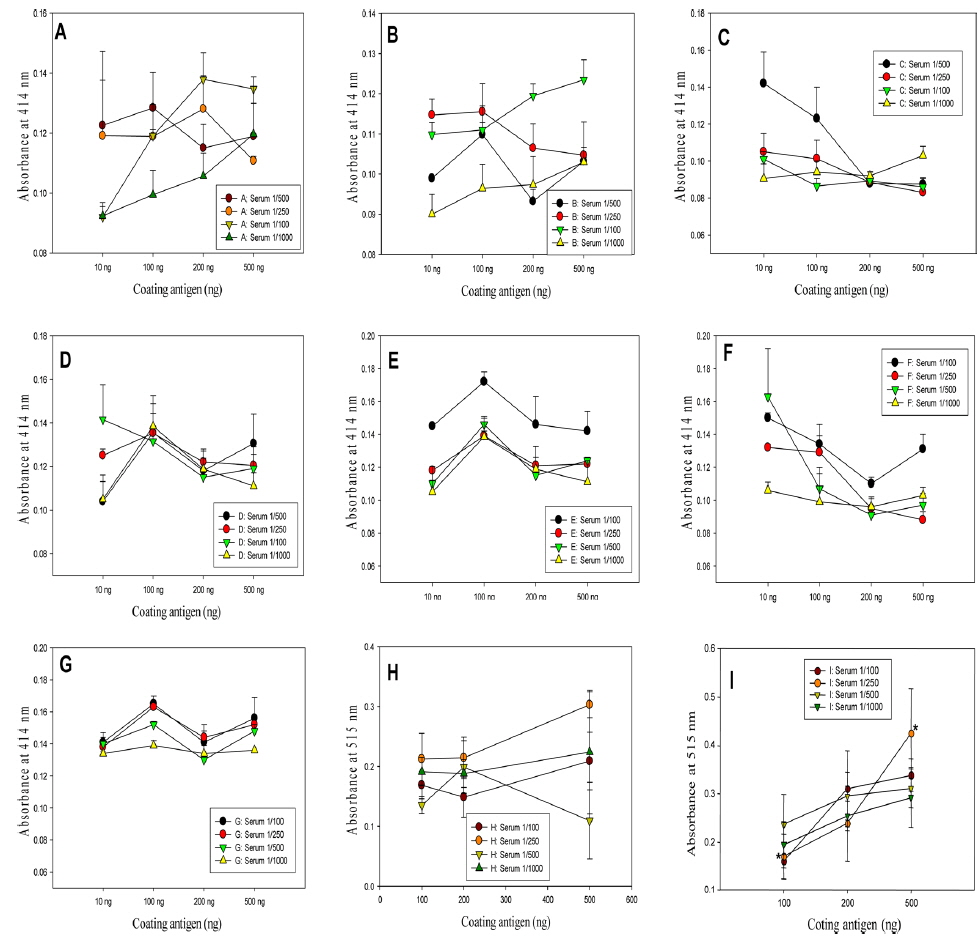
In the titer assay, the GAGs as an antigen were dissolved in 0.1 M coating buffer (1.593g Na2CO3, 2.93g Na HCO3) in a 96 well ELISA plate and coated overnight with 100, 200 and 500 ng and then the plate was washed two times with PBS-0.05% tween. The unattached impurities were incubated with PBS-0.05% tween buffer containing 1% fetal calf serum for an hour and dried to prevent antibodies from combining at nonspecific binding sites. Sandwich ELISA was performed after diluting the serum, containing the antibodies gained from immune induction by emulsifying the GAGs in the 1st to the 3rd with the complement and injecting intraperitoneally, 100-fold, 250-fold, 500-fold and 1000-fold and incubating at room temperature. Serum was put in a half of the ELISA plate as dilution ratio and bovine serum albumin (BSA), with serum-free, i.e. serum-immunoglobulinfree, from commercial sigma was put in the other half of the plate as the equal dilution ratio (100, 250, 500, 1000:1) as serum. The method to determine the antibody production was applied by comparing the both parts of the plate for coloring reaction at 414 nm. As measuring coloring reaction at 414 nm with antispecies (mouse) IgG alkaline phosphatase as 2nd antibodies and WesternBreeze Chromogenic from Invitrogen as the reagent, the WesternBreeze manual of Invitrogen (Carlsbad, USA) was applied to the ELISA plate (Choi
>
Insect collection, GAG purification
As seen in the Table 1, the insect GAGs of the nine species (1. male silkworm pupae 2. clony shell of
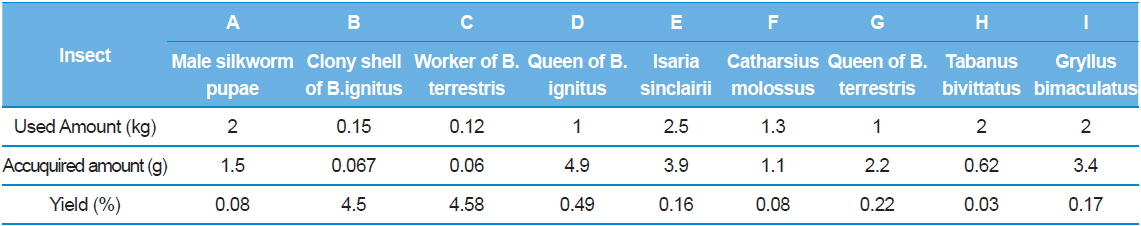
[Table 1.] Yield of purified insect glycosaminoglycan from each extract residue
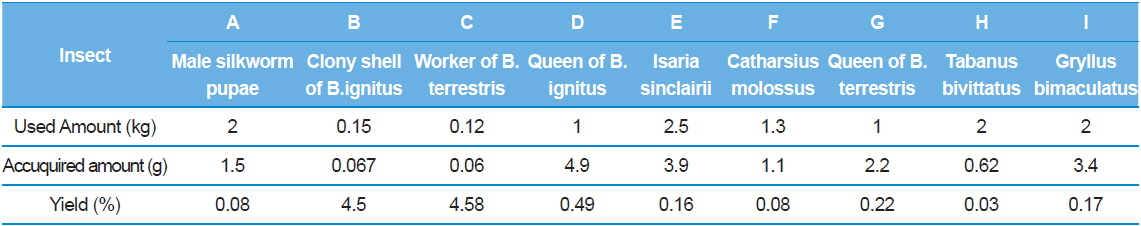
Yield of purified insect glycosaminoglycan from each extract residue
The insect shells left after the preparation of alcoholic extract from the nine species were dried to be utilized and 1.1 g(yield= approximately 0.1%) was obtained by drying each insect shell; removing protein by proteolysis with proteinases; and dialyzing with ethanol and distilled water after removing impurities by precipitation. In particular, the yield was gained with 4.9% from queen of
In the titer assay result of polyclonal antibodies, antibody production could be derived from a variety of insects. 1. PSG (male silkworm pupae GAG, Fig. 1 A): Significance was
In conclusion, if producing methods of antibodies derived from insect GAGs of the various species in this research further improve, it is considered to be possible to produce antibodies that are more stable form than the method producing antibodies derived from the GAGs of pigs with the possibility of contamination by infection. This is because it is injected into mammals or animal cells as safer replacement than heparin, GAG derived from pigs and the like with the possibility of having infectious diseases such as foot-andmouth disease.