The three populations of Climacostomum virens were collected from brackish water (salinity 10) of the Taehwagang river (35°32′51″N, 129°17′36″E) with mud debris in Taehwa-dong, Jung-gu, Ulsan, South Korea on 31 Jan 2008; brackish water (salinity 2) in Geowugae tidal pool (33°19′ 24″N, 126°50′46″E), in Pyoseon-ri, Pyoseon-myeon, Seogwipo-si, Jeju-do on 24 Feb 2012; and freshwater with dead leaves and debris in a small stream on Mt. Deoksoongsan in Sacheon-ri, Deoksan-myeon, Yesan-gun, Chungcheongnamdo, South Korea on 14 May 2010 (36°39′55″N, 126°37′10″ E). Fabrea salina was collected from saline water (salinity ~200) in a small artificial waterway in front of Gomso saltern, Gomso-ri, Jinseo-myeon, Buan-gun, Jeollabuk-do on 9 Oct 2012 (35°35′41″N, 126°37′03″E). Samples were delivered to a lab and transferred to petri dish (87 mm in diameter). Transferred samples were maintained at room temperature during one to five days without nutrient supply.
Live specimens were observed under a stereo microscope (Olympus SZH10; Olympus, Tokyo, Japan) and an optical DIC microscope (Axio Imager A1; Carl Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany) at low (50-400×) to high (1,000×) magnifications. Live images were prepared using a CCD camera (Axio Cam MRc; Carl Zeiss). The silver impregnated specimens were examined by protargol method (Wilbert, 1975; Foissner, 1991). Terminology and taxonomic classification followed Foissner et al. (1992), Lynn (2008), and Shazib et al. (2014).
Nuclear DNA was extracted using the RED Extract-N-Amp Tissue PCR Kit (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Universal primers of forward EukA and reverse EukB were used to amplify the small subunit (SSU) rRNA gene (Medlin et al., 1988). PCR products were checked by electrophoresing on 1.2% agarose gels and sequenced directly on an ABI 3730 automatic sequencer using the same sequencing PCR primers (Macrogen Inc., Seoul, Korea). Sequences were checked and analyzed using Geneious ver. 6.1.6 (http://www.geneious.com/) and deposited to the GenBank database.
Phylum Ciliophora Doflein, 1901
Class Heterotrichea Stein, 1859
Order Heterotrichida Stein, 1859
Family Climacostomidae Repak, 1972
Genus Climacostomum Stein, 1859
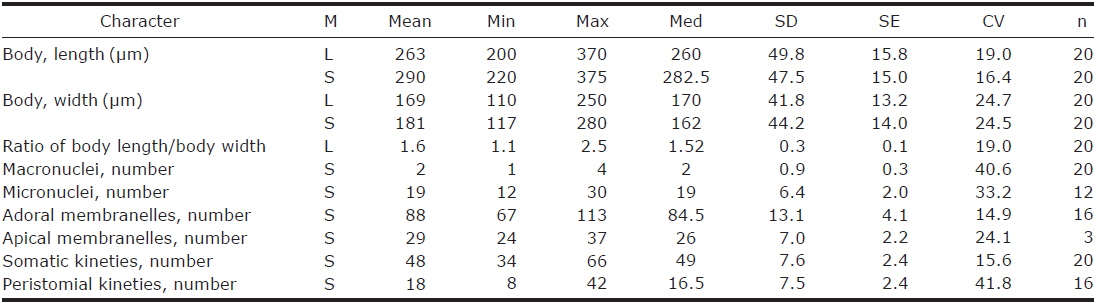
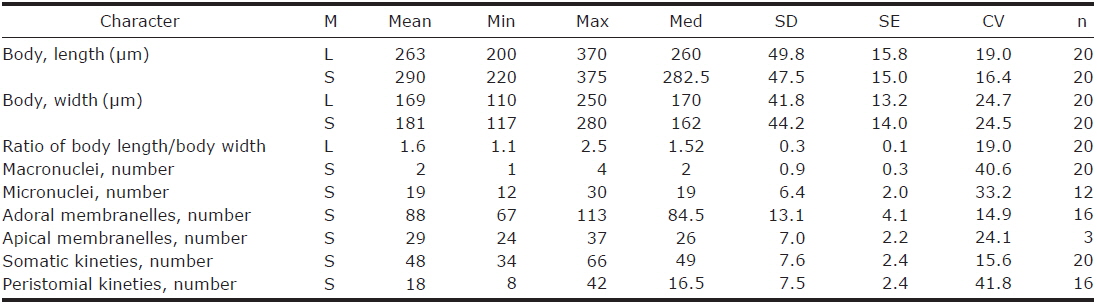
1. Climacostomum virens (Ehrenberg, 1838) Stein, 1859 (Table 1, Figs. 1, 2)
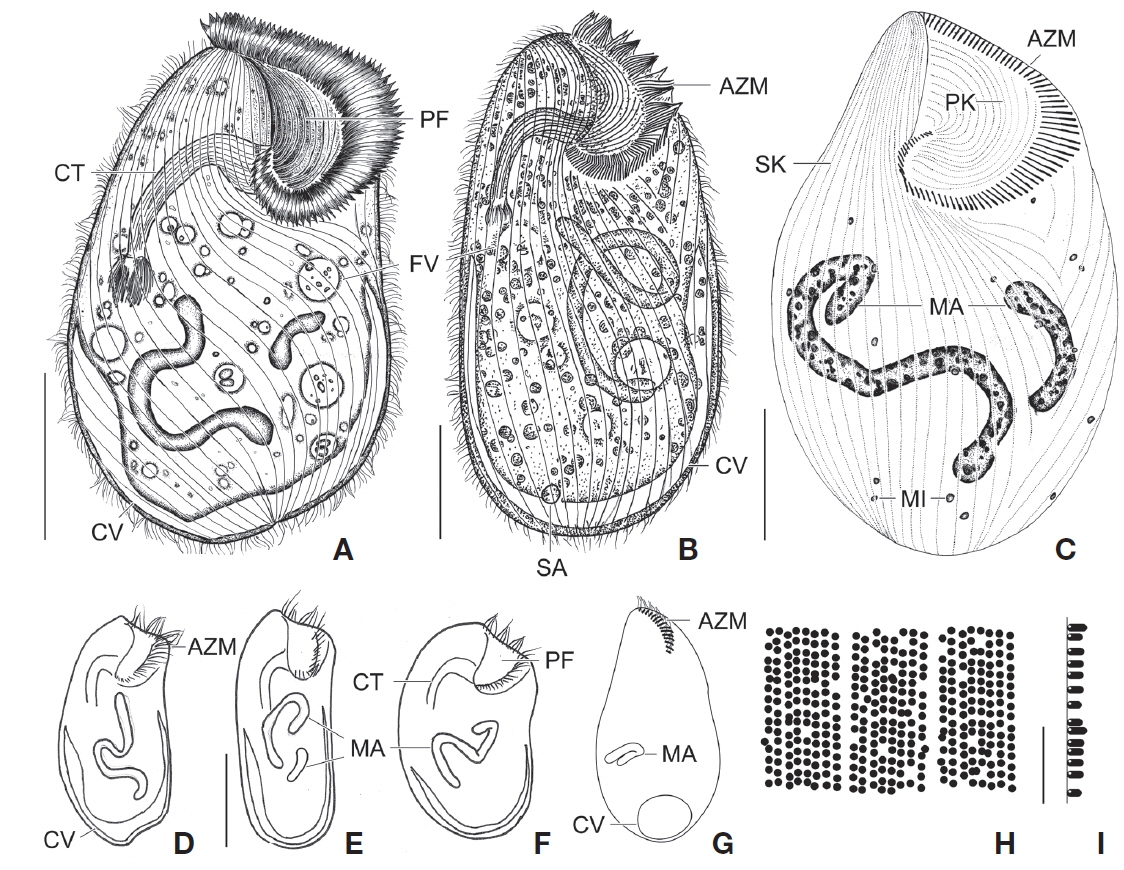
[Fig. 1.] Climacostomum virens from life (A, B, D-I) and after protargol impregnation (C). A, Typical body shape of brackish water specimen; B, Ventral side view of freshwater specimen with symbiotic algae; C, Ventral view to show macronuclei, somatic, and oral ciliature; D-F, Various body shapes; G, Swarmer stage cell; H, Arrangement of cortical granules; I, Lateral view of ellipsoidal cortical granules. AZM, adoral zone of membranelles; CT, cytopharyngeal tube; CV, contractile vacuole; FV, food vacuole; MA, macronuclei; MI, micronuclei; PF, peristomial field; PK, peristomial kinety; SA, symbiotic algae; SK, somatic kinety. Scale bars: A-C=50 μm, E=100 μm, I=5 μm.
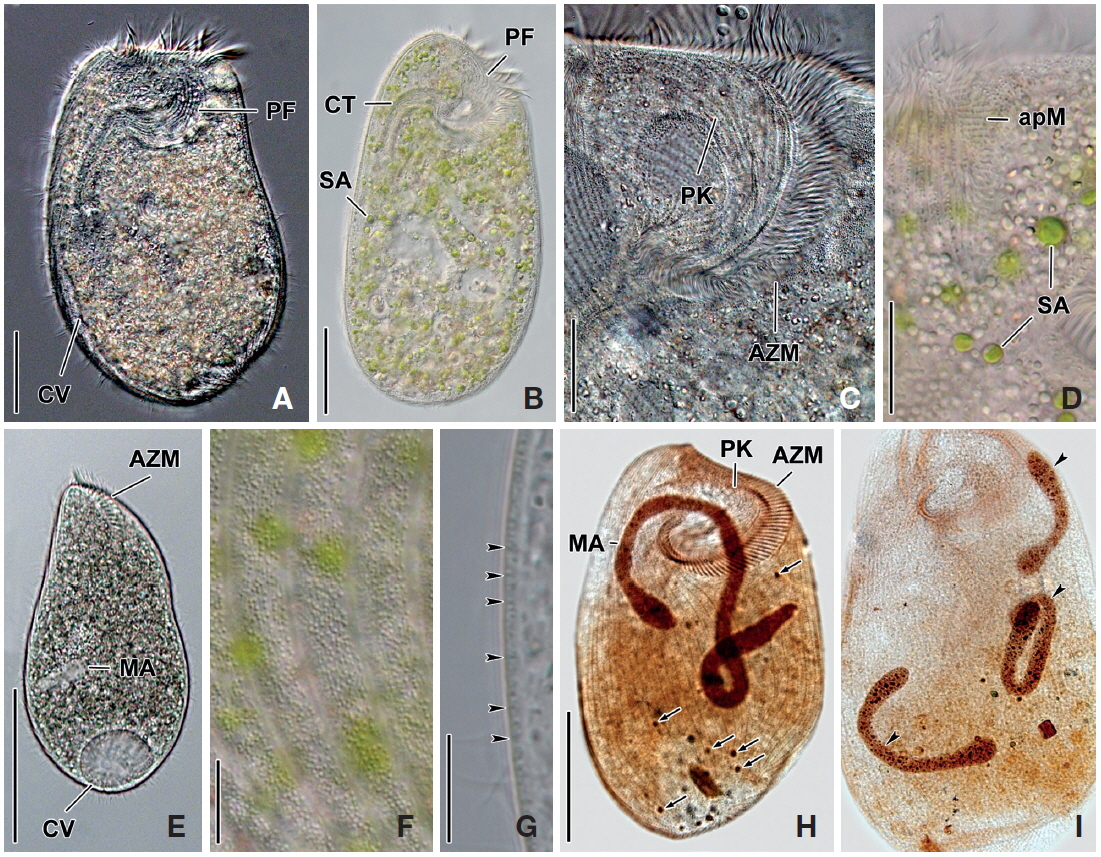
[Fig. 2.] Photomicrographs of Climacostomum virens from life (A-G) and after protargol impregnation (H, I). A, Ventral side view of brackish water specimen with contractile vacuole; B, Ventral side view of freshwater specimen with symbiotic algae and cytopharyngeal tube; C, Oral apparatus to indicate peristomial field and adoral zone of membranelles; D, Apical membranelles and symbiotic algae; E, Swarmer specimen with spherical contractile vacuole and small macronucleus; F, Arrangement of cortical granules in between somatic kineties; G, Lateral view of ellipsoidal cortical granules (arrowheads); H, Whole body to show macronucleus, micronuclei (arrows), somatic and oral ciliature; I, Three macronuclei (arrowheads) of brackish water specimen. apM, apical membranelles; AZM, adoral zone of membranelles; CT, cytopharyngeal tube; CV, contractile vacuole; MA, macronuclei; PF, peristomial field; PK, peristomial kinety; SA, symbiotic algae. Scale bars: A, B=50 μm, C, D=20 μm, E, H=100 μm, F, G=10 μm.
Spirostomum virens Ehrenberg, 1838: 332.
Climacostomum virens (Ehrenberg, 1838) Stein, 1859: 55; Repak, 1972: 417; Peck et al., 1975: 368; Dubochet et al., 1979: 218; Chen et al., 2011: 920.
Climacostomum (Spirostomum) virens: Kahl, 1932: 459.
Description. Body size in vivo 200-370×110-250 μm with an average 263×169 μm, size of protargol preparations inflated 5-15% compared to live cells, ratio of body length/body width about 1.6/1 in vivo (Table 1). Body oval and pouch-like to kidney-like shape, slightly curved to left, dorsoventrally flattened about 1 : 3, anterior end truncated to leftward, posterior end broadly rounded (Figs. 1A, B, D-F, 2A, B). Lateral view dorsally convex, ventrally flattened. Macronucleus coiled freely, elongated rod-like or ribbonlike shape, number of macronuclei one to four (Table 1, Figs. 1A, B, D-F, 2H, I). Micronuclei scattered in whole body, oval to ellipsoidal shape, 12-30 in number, diameter 1.5-2.5×1-2 μm (Table 1, Figs. 1C, 2H, I). Contractile vacuole located posterior with two long canals, crescent or arched shape (Figs. 1A, B, D-F, 2H, I). Cortical granules transparent and colorless, ellipsoidal shaped, densely embedded into whole cortex, regularly arranged 3-10 rows in between two somatic kineties, size 1-1.5×0.4-0.5 μm (Figs. 1H, I, 2F, G). Cytoplasm basically transparent, dark gray to dark brown colored on low magnification, spherical food vacuoles, some specimens filled by symbiotic algae, and symbiotic algae diameter of 3-5 μm in freshwater population (Table 1, Figs. 1A, B, 2A, B, D). Movement by crawling on bottom, relatively slow. Swarmer pyriform, no peristomial field, contractile vacuole spherical shape, macronucleus sausage-like shape (Figs. 1G, 2E).
Somatic kineites arranged obliquely from right side of oral field to posterior end, some of the somatic kineties started from the lower part of the adoral zone of membranelles and constructed a small suture on left postoral part of ventral side (Figs. 1A-C, 2H).
Adoral zone of membranelles located left side of ventral side, formed hook-like shape, curved rightward, started from the right side of the oral field, continued to cytopharynx (Figs. 1A-F, 2A, B). Adoral membranelles about 88 in number, each membranelle consisted of two longer and one shorter rows of kinetosomes (Table 1, Figs. 1A-C, 2H). Peristomial kineties located on peristomial field, arched about 18 kineties in parallel, commenced from anterior right side of peristomal field, with some of the kineties running into a cytopharyngeal tube (Table 1, Figs. 1A-C, 2C, H). Cytopharyngeal tube positioned right and lower part of the peristomal field, curved downward, internal kineties connected to some of the peristomial kineties (Figs. 1A, B, D-F). Cytopharyngeal filiament linked to terminal part or cytopharyngeal tube, brush-like form (Figs. 1A, B, 2A). Apical membranelles located in the anterior right side inner wall of the peristomial field, arranged horizontally, and composed of 24-37 membranelles (Table 1, Fig. 2D).
Voucher specimen. One voucher slide of silver-impregnated specimens is deposited in the National Institute of Biological Resources (NIBR), Incheon, South Korea, with registration number KOSPPRO0000104455.
Gene sequence. Accession number of the SSU rRNA gene sequence of Climacostomum virens (Jeju, Korea) population is registered as KJ651814 in the GenBank database. The sequence size is 1,591 bp and GC contents 48.52%.
Distribution. Austria, Austrailia, China, Czech, England, Germany, Korea, Mexico, Russia, Spain, and USA.
Remarks. The populations of Climacostomum virens lived in both freshwater and brackish water. The macronucleus is usually single and ribbon-like shaped in freshwater population but there are two or more macronuclei were observed in the brackish water population. Symbiotic algae are also one difference between the populations. Symbiotic algae are common in freshwater populations but no symbiotic algae are found in brackish water populations. However, the presence of symbiotic algae is not a constant character, even in freshwater populations. Repak (1972) and Foissner et al. (1992) mentioned that some specimens from freshwater habitats have been described without symbiotic algae. Therefore, we conclude that the characters, which are the presence of symbiotic algae and number of macronuclei, are not species specific.
The descriptions of Climacostomum virens were similiar with original and subsequent populations in body shapes, oral structures, number of somatic kineties, and shape of contractile vacuole. However, adoral membranelles in our populations are more numerous than previous studies, and the macronucleus was described as singular in previous descriptions. In addition, the pattern of cortical granules is slightly different in populations described by Augustin and Foissner (1992) and Foissner et al. (1992) in shape (spherical vs. ellipsoidal in these populations) and number of cortical granule rows in between kineties (3-5 vs. 8-10) (Ehrenberg, 1838; Stein, 1867; Kahl, 1932; Repak, 1972; Peck et al., 1975; Dubochet et al., 1979; Foissner et al., 1992). The present population is similar to the Chinese population in the description (Chen et al., 2011). Climacostomum virens is different from C. emarginatum (Stokes, 1885), because C. emarginatum has a smaller body size and notched posterior end of body (Kahl, 1932). In addition, C. patulum is different from ours in terms of body size, body shape, present or absent symbionts (Kahl, 1932; Foissner et al., 1992).
Up to now, three SSU rRNA gene sequences of Climacostomum virens have been deposited in GenBank from Chinese (accssion No. EU583990) by Miao et al. (2009), Korean (accssion No. KJ651832) (Shazib et al., 2014), and German (accssion No. X65152) (Hammerschmidt et al., 1996) populations. Gene lengths (nucleotides number) and percentage of GC contents of each population are as follows: Chinese 1,713 nucleotides (nt), GC content 48.34%; Korean 1,591 nt, 48.52%; and German 1,711 nt, GC content 47.45%, respectively. Length difference of sequence is caused by exclusions of primers and uncertain sequences of 3′ and 5′ regions, especially in the Korean population. Nucleotide difference and similarity in overlapped sequences in these populations are 4 nt (i.e., 4 substitutions), 99.75% (4/1591 positions) in pairwise comparisons between Korean and Chinese; 31 nt (i.e., 2 uncertain, 6 indel, and 23 substitutions), 98.05% (31/1593 positions) between Korean and German; and 35 nt (i.e., 2 uncertain, 6 indel, and 27 substitutions), 97.96% (35/1715 positions) between Chinese and German populations. Chinese and German populations were collected from freshwater, while the Korean population was collected from brackish water. In terms of SSU rRNA gene sequence, species identity of the German population has uncertainty compared to those of the Korean and Chinese populations.
Family Fabreidae Shazib, Vd’ačný, Kim, Jang & Shin, 2014
Genus Fabrea Henneguy, 1890
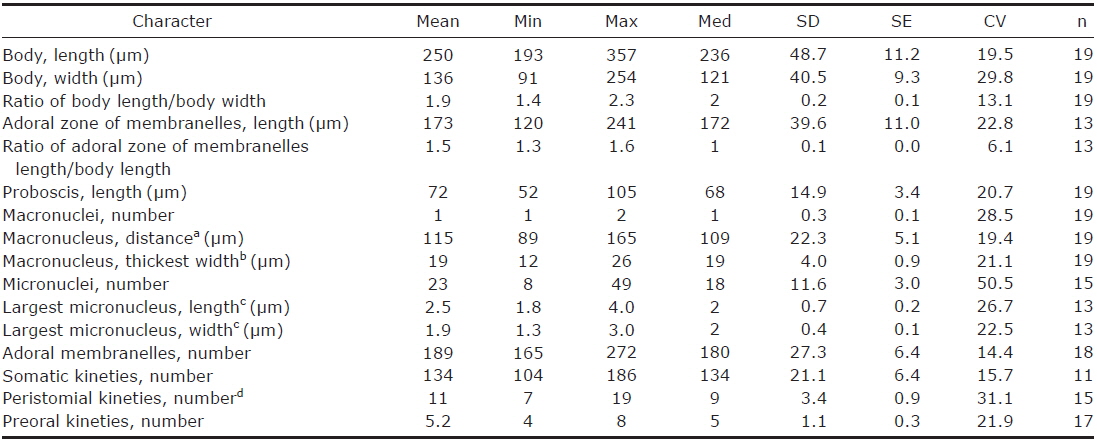
2. Fabrea salina Henneguy, 1890 (Table 2, Figs. 3, 4)
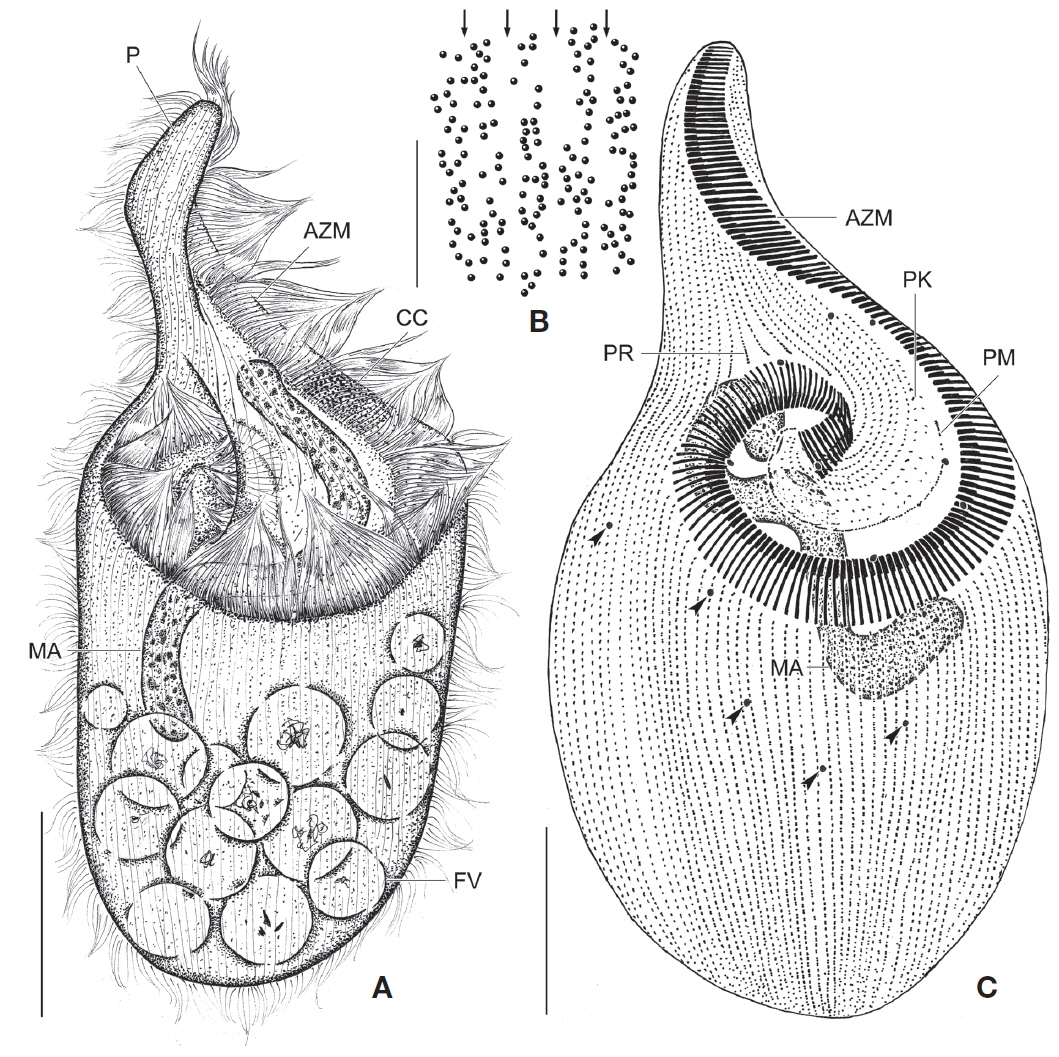
[Fig. 3.] Fabrea salina from life (A, B) and after protargol impregnation (C). A, Typical body shape; B, Arrangement and pattern of cortical granules, arrows indicate each somatic kineties; C, Typical impregnated specimen to show macronucleus, micronuclei (arrowheads), somatic and oral ciliature. AZM, adoral zone of membranelles; CC, part of condensed cortical granules; FV, food vacuole; MA, macronucleus; P, proboscis; PK, peristomial kinety; PM, paroral membrane; PR, preoral kineties. Scale bars: A, C=50 μm, B=5 μm.
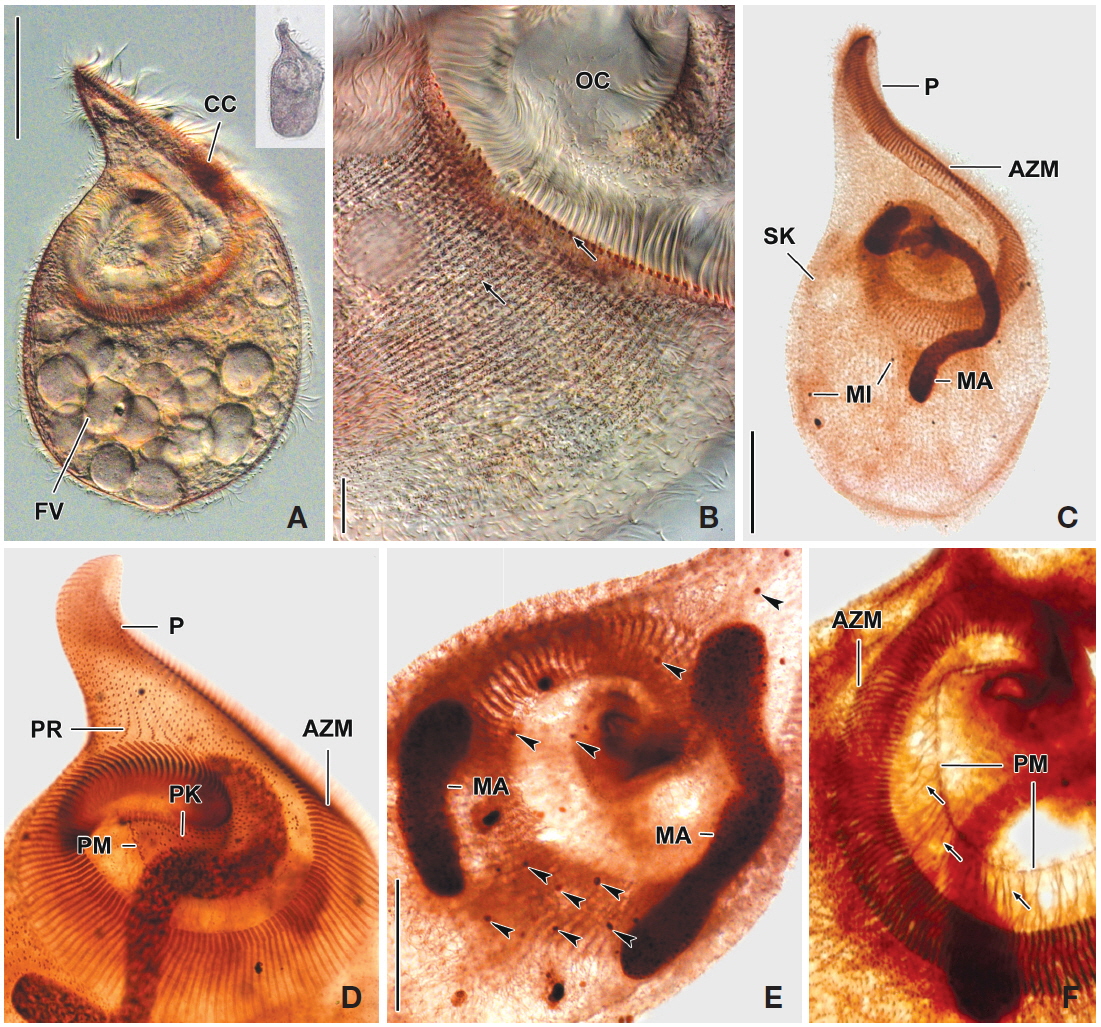
[Fig. 4.] Photomicrographs of Fabrea salina from life (A, B) and after protargol impregnation (C-F). A, Scoop-like shaped ventral view and additional figure shows original shape in low magnification (×50); B, Arrangement and pattern of cortical granules, brownish pink colored in photomicrographs but grayish green colored to the unaided eye; C, Whole body to show macronucleus, somatic and oral ciliature; D, Detail of oral ciliature and related apparatus; E, Two macronuclei and micronuclei (arrowheads); F, Detail of fibrillar myoneme connected with paroral membrane. AZM, adoral zone of membranelles; CC, part of condensed cortical granules; FV, food vacuole; MA, macronucleus; MI, micronuclei; OC, oral cavity; P, proboscis; PK, peristomial kinety; PM, paroral membrane; PR, preoral kineties; SK, somatic kineties. Scale bars: A, C=50 μm, B=10 μm, E=30 μm.
Fabrea salina Henneguy, 1890: 118; Song & Packroff, 1997: 338; Chen et al., 2011: 921.
Description. Body size in vivo 190-240×100-145 μm with an average 213×120 μm, size of protargol preparations inflated about 10% greater than live cells, ratio of body length/body width about 1.8/1 in live and 1.9/1 in protargol preparations (Table 2). Body scoop-like shape, ventrally concave, posteriorly pouch-like convex, proboscis located left part of anterior and obliquely curved rightward with length 60-90 μm in vivo (Figs. 3A, 4A). Lateral view usually cylindrical but flattened in starved cells. Macronucleus located anteriorly and elongated from proboscis to ventral side, ribbon-like shape, usually one but rarely two, longest distance approximately 115 μm, widest width approximately 19 μm (Table 2, Figs. 3A, C, 4C, E). Micronuclei scattered in whole body, oval to ellipsoidal shape, 8-49 in number (Table 2, Figs. 3C, 4C, E). Contractile vacuole absent. Cortical granules grayish green colored to the unaided eye but brownish pink colored in photomicrographs, spherical shape, regularly arranged 2-3 rows in between somatic kineties, some cortical granules partly concentrated on middle part of adoral zone of membranelles, 0.2-0.3 μm in diameter (Figs. 3B, 4B). Cytoplasm transparent to slightly grayish but basically colorless, scrambled eggs-like cytoplasmic filling with many spherical food vacuoles (Figs. 3A, 4A). Movement free swimming, fast, rotated around body axis.
Somatic kineties arranged longitudinally from usually adoral zone of membranelles to posterior end (Figs. 3C, 4C, D). Ciliated somatic dikinetids arranged densely, cilia length about 15 μm in vivo.
Adoral zone of membranelles spirally curved and coiled about one and a half turns, started from anterior end of proboscis, running on ventral edge, terminated internal wall of oral cavity (Figs. 3A, C, 4C-F). Adoral membranelles ~190 in number, widest part approximately 20 μm, with each membranelle consisting of two longer and one shorter row of kinetosomes (Table 2, Figs. 3C, 4D). Preoral kineties were constantly located in the inner part of the proboscis, commenced from middle part of the proboscis, and terminated at the outer side of the adoral zone of membranelles, spaces of kinetosomes gradually dense, partly fragmented in some kineties, 4-8 in number (Table 2, Figs. 3C, 4D). Paroral membrane arranged on the inner side of the adoral zone of membranelles, commenced near the posterior end of the proboscis, terminated at the cytopharyngeal wall and irregularly fragmented, with each fragment connected with fibrilar myoneme (Figs. 3C, 4D, F). Peristomial kineties located on peristomial field, arranged 7-19 rows concentric parallel, curved spirally, loosely lined kinetosomes of two or three outer rows, commencing from the lower part of the proboscis, and terminating near the cytopharyx (Table 2, Figs. 3C, 4D).
Voucher specimen. One voucher slide of silver-impregnated specimens is deposited in Biodiversity Lab, Department of Biological Science, Colllege of Natural Sciences, University of Ulsan, Korea, with registration number 20121009 Kim00011.
Gene sequence. Accession number of the SSU rRNA gene sequence of Fabrea salina of Korean population is KJ651817 in the GenBank database, with a sequence size of 1,598 bp and GC contents 47.50%.
Distribution. China, France, Korea.
Remarks. The original description of Fabrea salina Henneguy, 1890 is similiar with our population in body size, body shape, color of cortical granule and oral apparatus. However, there is no variation in number of macronuclei in the original population (Henneguy, 1890), while two macronuclei rarely occurred in our population.
Our population of Fabrea salina is also similar with population of Song and Packroff (1997) in body size and shape, basic oral structure, number of somatic kineties, and number of adoral membranelles, but some of characters were different in color of cortical granules (grayish green vs. colorless), length of paroral membrane (shorter vs. longer), and micronuclei (present vs. no mentioned). The present population is also well matched with the population of Chen et al. (2011) in description and photomicrographs.
Fabrea salina is a monotypic family and the morphologically most similar family is Climacostomidae until now. Climacostomum virens, C. emerginatum, C. minimum, C. patulum, and C. salinarum were shown to have similar morphology in oral and perioral structure, shape of macronucleus, and presence of a proboscis-like protuberance. However, there are several morphological differences in body shape, color and distribution of cortical granules, cytoplasm and absence of paroral membrane (Kahl, 1932; Foissner et al., 1992).
Four SSU rRNA gene sequences of Fabrea salina have been deposited in GenBank from the Chinese (accession No. EU583991) by Miao et al. (2009); Korean (accession No. KJ651817) (Shazib et al., 2014); and Italian (accession Nos. DQ168805 and DQ168806) (Angeli et al., unpublished) populations. Gene lengths (nucleotides number) and percentage of GC contents of each population are as follows: Chinese 1,717 nucleotides (nt), GC content 47.29%; Korean 1,598 nt, 47.50%; and Italian 1,682 nt, GC content 47.15%, respectively. Nucleotides difference and similarity in overlapped sequences in these populations are 4 nt (i.e., 2 indel and 2 substitutions), 99.75% (4/1598 positions) between Korean and Chinese populations, 4 nt (i.e., 2 indel and 2 substitutions), 99.75% (4/1598 positions) between Korean and Italian populations, and 4 nt (i.e., 2 indel and 2 substitutions), 99.88% (4/1684 positions) between Chinese and Italian populations. Chinese and Korean populations were collected from marine and hypersaline water, while the Italian population was collected from freshwater. In terms of SSU rRNA gene sequence, these populations are identical species.