A geostationary orbit (GEO) satellite or geosynchronous orbit satellite is a satellite that orbits around the Earth with the same period as the Earth rotation. Therefore, it appears on the same position from the viewpoint of a ground observer. However, in reality, it very slowly moves naturally or by human-designed operation, and the movement should be monitored by a ground station to keep the satellite properly operating. Several attempts have been made to observe GEO satellites by optical methods (Choi et al. 2009; Choi et al. 2010; Choi et al. 2011; Lee et al. 2004; Montojo et al. 2011; Nikolayev et al. 2011), but most of these methods are done by manual observations and manual data reduction. The optical wide-field patrol (OWL) system is capable of automatic observation using a pre-arranged observation schedule (Park et al. 2013); thus, if a method of automatic data reduction of GEO satellites is available, a fully automated GEO satellite monitoring would be possible.
In this paper, Section 2 describes the test observation for data acquisition to be used in a data reduction algorithm. Section 3 explains the details of the reduction algorithm. Section 4 provides the results and their discussion. Section 5 presents the summary.
2.1 Site, Telescope and Detector
The test observation was performed at the testbed site located in the Korea Astronomy and Space Science Institute (KASI), Daejeon, Korea. Table 1 lists the summary of the test environment information and the observation system specification.
[Table 1.] OWL test-bed specifications.
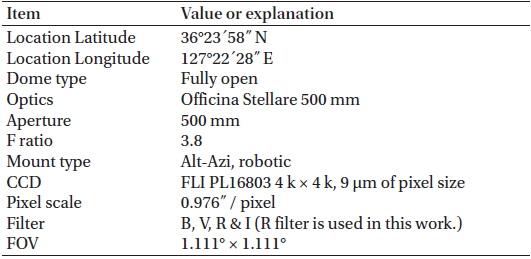
OWL test-bed specifications.
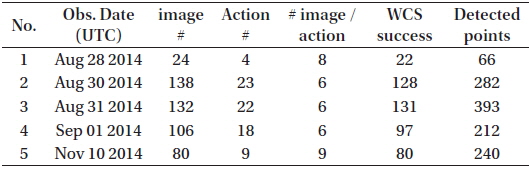
Table 2 lists the summary of the test observation run. All pointing directions of the telescope are within one square degree in the horizontal coordinates (expressed in azimuthal angle and elevation) because the target is just one GEO satellite, which is assumed to stay apparently fixed on the sky from the viewpoint of a ground observer. The observation sequences consist of “actions,” which include from six to nine images with just 1-s exposure time. The reasons for taking only 1-s exposure time are the following:
1. The night sky in the observation site is too bright; thus, the target and the stars are easily absorbed in the background noise. 2. With short exposure time, the number of available images can be increased.
[Table 2.] Summary of test observation night results.
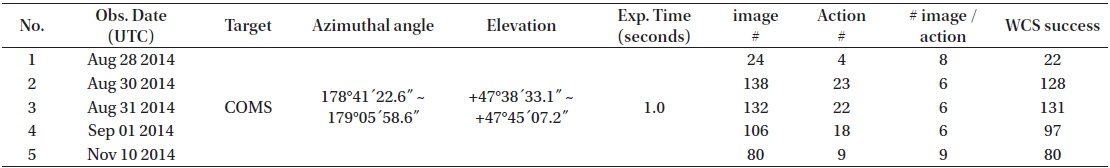
Summary of test observation night results.
Because of weather conditions, the rate of successful world coordinate system (WCS) solution varies daily. If one image fails in the WCS solution, it is excluded for further reduction steps.
The sequence of the data reduction steps is described as follows:
1. WCS solution calculationReference image selection 2. “Object” image generation using SExtractor 3. Image transformation to match the reference image 4. Transformed image combination 5. GEO detection in the combined image 6. Detection of the points nearest the GEOs in the original images
The
Obtaining the positions and brightness of the objects in the image using SExtractor (Bertin & Arnouts 1996; Bertin 2006).
Retrieving the stars in the corresponding sky area from the Guide Star Catalog (GSC) 1.1 (Jenkner et al. 1990; Lasker et al. 1990; Russel et al. 1990).
Matching the SExtractor output with the GSC stars using the triangle pattern matching algorithm (Groth 1986) with CCXYMATCH and CCMAP tasks in the Interactive Data Reduction and Analysis Facility (IRAF) (Valdes 1984).
Mapping the matched objects and calculating the solution.
3.2 Selecting the Reference Image
Before creating a combined image, a reference image should be selected first. The rest of the images in an “action” are geometrically transformed to match this reference image in the horizontal coordinate system (expressed in azimuth and elevation). The condition for the reference image is described as follows:
1. Its WCS solution calculation is successful. 2. The seeing, expressed in the mean full width at half maximum (FWHM) value of the stars in the image, is the smallest among those of all the images in the “action.”
3.3 Generating “Object” Images Using SExtractor
In the WCS solution calculation step, a quick photometry of the celestial objects in the image is performed using SExtractor to obtain the
3.4 Transforming Images to Match the Reference Image
Before combining the “object” check images, they must be geometrically transformed to match the reference-object check image to compensate the slight displacement and rotation due to time difference and telescope-pointing error. Because the purpose of the combination is to retain only the GEO candidates, the transformed and the reference images should have the same horizontal coordinate system (expressed in azimuthal angle and elevation). The steps of this procedure are described as follows:
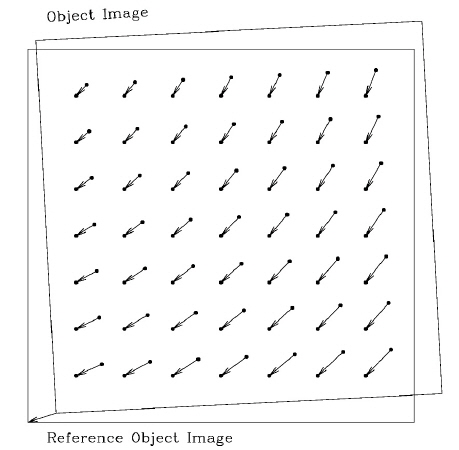
1. We generate equally spaced grid points on the object image. In this case, 7 × 7 = 49 grid points located at every 512 pixels are used (Fig. 3). 2. Using the WCS solution of the object image, we obtain the J2000 right ascension and declination coordinates. 3. We convert these coordinates to geocentric (CIRS) position at the observation date and time. 4. We obtain the topocentric azimuthal angle and elevation at the observation date and time from step 3. 5. We calculate the right ascension and declination at the date and time of the reference image from step 4. 6. From step 5, we obtain the J2000 right ascension and declination. 7. Using the WCS solution of the reference image, we calculate the X and Y coordinates of the grid points transformed to match the reference image. 8. Now, we have 49 mapped ensemble pairs of {(X, Y) object, (X, Y) reference object}. Using these pairs, we calculate the geometric mapping formula. In this step, the GEOMAP task of IRAF is used. 9. We transform the image using the GEOTRAN task of IRAF (Valdes 1984).
In the above steps, a traditionally developed code that uses functions of the International Astronomical Union Standards of Fundamental Astronomy (IAU SOFA) library (version 11, Nov. 2013) is applied in steps 3 and 4 for coordinate transformation and correction of precession and nutation.
3.5 Combining Transformed Images
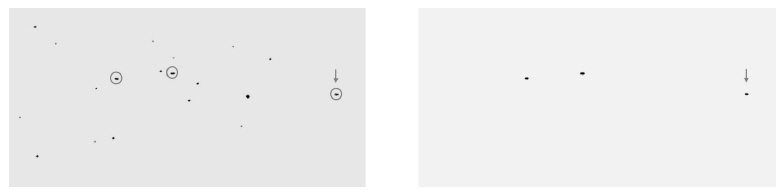
The geometrically transformed check images, including the check image of the reference image, are median-combined to a single image. This combined image has the same coordinate system as the reference image, but all have zero pixel values except the area of the possible GEO objects (Fig. 4) because all other background stars are in different positions due to sidereal movement.
3.6 Detecting GEOs on the Combined Image
The positions of geostationary objects are extracted using SExtractor. The resultant positions are possible GEO objects detected in the reference image. Using the WCS solution of the reference image, the J2000 equatorial right ascension and declination coordinate values of the possible GEO objects at the time the reference image is taken are calculated.
3.7 Detecting Points Nearest to the GEOs in the Original Images
The positions of the GEO candidates on the combined image are the same as those on the reference image. Now reversing the coordinate conversion procedure from steps 2 to 7 in Section 3.4, the positions of the GEO candidates on the images other than the reference image can be calculated. For each image in one action, the quick photometry results are already waiting. Using these results, the nearest points to the GEO candidates are selected. The final results are arranged in the text format of observation time and right ascension and declination expressed in degrees.
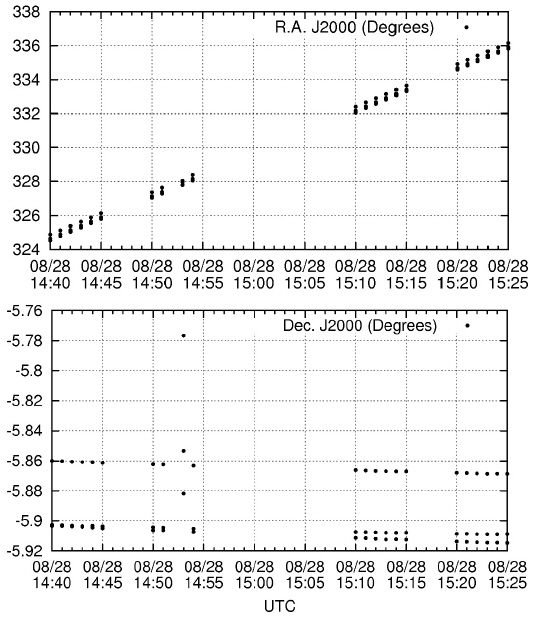
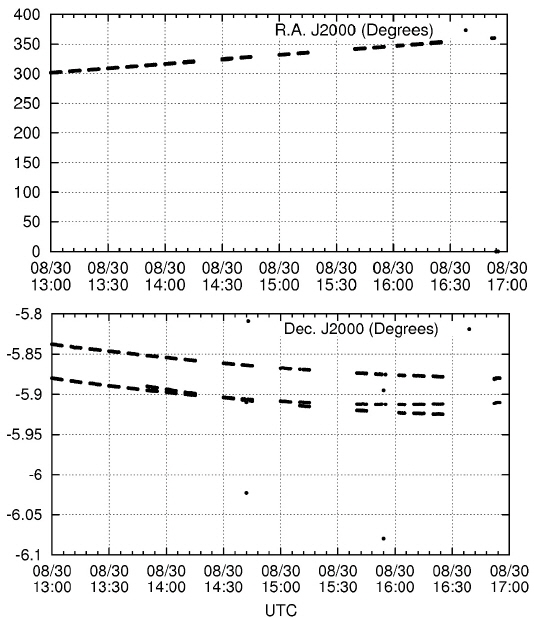
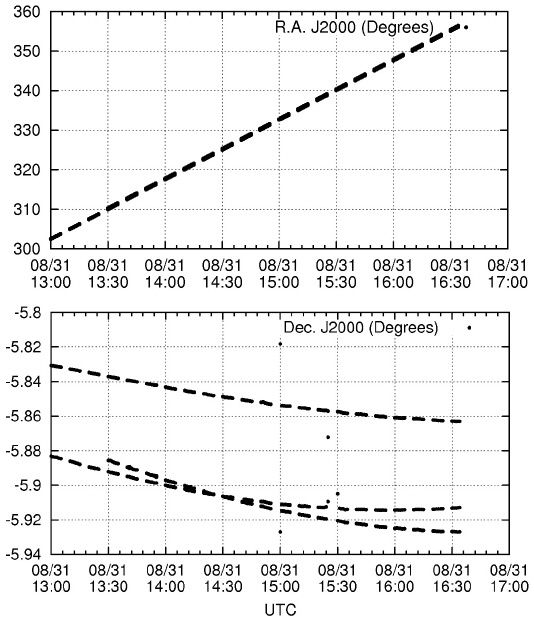
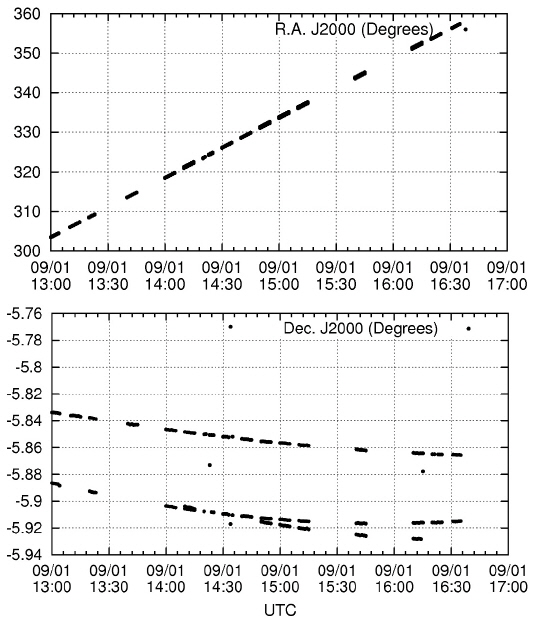
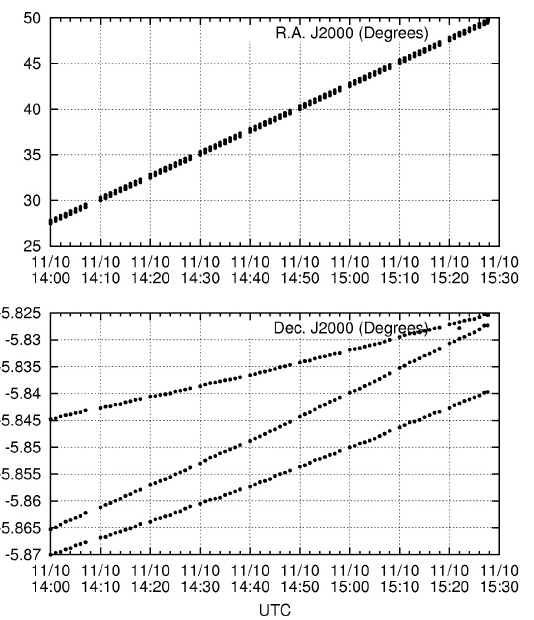
The final reduced product is a sequence of UTC time and J2000 right ascension and declination. Table 3 lists the summary of the observation and reduction results. Figs. 5-9 show the time series plots of the GEO objects observed during the campaign. In both right ascension and declination plots, the celestial positions with observation times of all three GEO objects (including the COMS and two Japanese GEO satellites) are detected and traced. The equinox of the right ascension and declination is 2000.0, in reference to the GSC catalog.
[Table 3.] Number of detection times―coordinate data points.
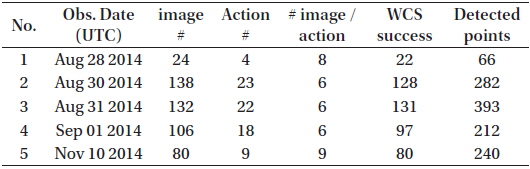
Number of detection times―coordinate data points.
The weather condition on August 29, 2014, was worst among the five nights of observation. The automatic observation system of OWL cancels the schedules during bad weather; thus, only a few data points were produced (24 images were taken, 22 images were successful for WCS solution calculation, and 66 data points were contained in four actions). The four visible packs of data points represent four observation actions. Three bad points between 14:50 and 14:55 and one bad point at about 15:21 UTC were observed, which appeared to be false detections and were excluded in the orbit determination.
In the night of August 30, 2014, the three detected GEO objects (including the COMS) were faint, and their brightness varied with time. Therefore, not all the images detected the three GEO objects. Among the 23 actions, 18 were successful, and the failed five actions did not detect any GEO objects. In the night of August 31, 2014, all 22 actions detected at least two GEO objects. In the night of September 1, 2014, the result shows similar behavior that on August 30, 2014. Out of the 18 actions, 16 detected at least one GEO object detected. The weather condition was the best at November 10, 2014. All actions of nine images detected three GEO objects (only one point was not detected).
An algorithm to automatically extract the coordinate and time information from optical observation data of GEO satellites has been developed. As a test observation campaign, the COMS1 satellite was observed for five nights from August to November 2014 with 1-s of exposure time and 1-min of interval. These images were grouped and processed into “action,” and each action was composed of six or nine successive images. Using coordinate transformation and combining all images in one action, the possible GEO candidates, including the COMS, were detected. The output shows that this data reduction algorithm can be used for full automation of the monitoring of GEO satellites by optical observation using OWL. However, this method suffers from the limitations of detectable brightness of the targets as well as from bad weather conditions.