Abalone Haliotis species, a marine gastropod of aquacultural importance, has a worldwide distribution. Aquaculture of abalone has now become one of the fastest growing sectors of the global seafood industry, and the quality of aquacultural nutrients requires attention to further improve abalone production and the value of the product. Many studies have addressed the nutritional values of a variety of feeds (Britz et al., 1994; Naidoo et al., 2006) in efforts to optimize financial returns, and improvements in abalone quality would add value to the product. One simple manner by which quality can be improved is to use seaweed feeds containing valuable secondary metabolites (such as phlorotannins), thus transferring the materials to abalone flesh (foot muscle tissue).
The brown seaweed Eisenia bicyclis is a common kelp found in waters of Korea and Japan. The kelp is abundant in the subtidal zone of Dokdo, Korea, especially at depths of 2–10 m. The average length and wet weight of kelp were 34 cm and 227 g, respectively (Kang et al., 2001). E. bicyclis has been reported to contain high levels of marine polyphenols called phlorotannins (Kim et al., 2013), which are found only in brown seaweeds. Phlorotannins, polymers of phloroglucinol, are synthesized via the acetate–malonate pathway (Ragan and Glombitza, 1986) and exhibit a variety of physiological activities, including antioxidant (Yoon et al., 2011), antidiabetic (Okada et al., 2004), antimicrobial (Eom et al., 2011), anti-inflammatory (Jung et al., 2013; Kang et al., 2013), and antihypertensive (Jung et al., 2006) properties; they inhibit melanogenesis (Heo et al., 2009), metalloproteinases (Kim et al., 2006), and reverse transcriptase (Ahn et al., 2004), induce quinine reductase (Yoon et al., 2013), and exert depressive effects on the central nervous system (Cho et al., 2012). However, E. bicyclis has a bitter tannin-rich taste; it is also tough in texture and is thus unappetizing. Abalone grazing is known to be inhibited by polyphenolic compounds from brown seaweed (Winter and Estes, 1992). Thus, we changed the abalone feed to E. bicyclis after 4 d of starvation. After feeding the seaweed, we measured the levels of representative phlorotannins in abalone flesh, abalone growth rates, phlorotannin distributions in abalone tissues, reductions in phlorotannin levels over time, and the enzymatic degradation rates of such phlorotannins.
The brown seaweed E. bicyclis (Kijillman) Setchell (Laminariaceae) was collected from Dokdo (37°14′29′′N, 131°52′1′′E), Korea, in 2012 and 2013. A voucher specimen has been deposited in the laboratory of one author (Y.K. Hong). Seaweed thalli were thoroughly dried for 1 week at room temperature and stored at 4℃ until used as feed. Commercial dry thalli of Saccharina japonica, commonly used in abalone aquaculture, were used as a control feed.
The aquacultured abalone Haliotis discus hanai (initial mean wet weight 52 ± 6 g and mean shell length 7 ± 1 cm) were purchased from a local fish market, transferred to an aquarium (200 L) fitted with a semi-closed circulation and filtering system, and acclimatized for 7 d with feeding of S. japonica thalli. Flow-through seawater (3 L/min) was supplied and the temperature was maintained at 20 ± 1℃. A 12 h/12 h light/dark photoperiod was instituted. Fecal matter was removed from the filter daily, and 30% of the seawater was renewed 1 h before feeding.
Prior to conduct of the feeding trials, the abalone were starved for 4 d. Thirteen abalone were maintained in individual plastic containers (10 cm long, 8 cm wide, and 5 cm high) with slits on all sides, allowing water flowthrough but preventing egress of seaweed thalli. Each abalone was fed 0.8 g seaweed at 17:00 daily over the 20 d of the feeding trial. To quantify seaweed consumption, thalli remaining after daily feeding were collected, dried at room temperature, and weighed. Thalli treated under identical conditions but in the absence of abalone served as controls for dry matter loss for reasons other than abalone grazing. Abalone seaweed consumption was expressed as [weight of reference thalli] minus [weight of thalli remaining after grazing]. Each abalone relative growth rate (%) was calculated as: [(final weight minus initial weight)/initial weight] × 100.
Phlorotannins were prepared from seaweed powder using the method of Chowdhury et al. (2011). Briefly, E. bicyclis powder (10 g) was shaken in a mixture of methanol (40 mL) and chloroform (80 mL), and partitioning was next triggered by adding deionized water (30 mL). The upper layer was collected and extracted with ethyl ether (30 mL). The ether was evaporated to dryness and the crude phlorotannin residue was dissolved in methanol (1 mg/mL). Phlorotannins were quantified using reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC).
To quantify abalone phlorotannins, tissues detached from shells were thoroughly cleaned in distilled water, chopped into small pieces, and ground into paste by hand over 5 min. All procedures were performed on ice to prevent enzymatic degradation of phlorotannins. The paste was stored at –20℃ prior to analysis. Crude phlorotannins were extracted from paste using the method of Chowdhury et al. (2011), with some modifications. Paste (2.5 g) was immersed in methanol (10 mL) and shaken (180 rpm) for 3 h at room temperature. Chloroform (40 mL) was added, and the mixture was next homogenized by shaking for 5 min, followed by filtration through defatted cotton. The mixture was then subjected to partitioning by adding deionized water (7.5 mL) with shaking (5 min), followed by centrifugation (5 min, 4,000 g). The upper water layer (the non-lipid fraction) was collected and extracted twice with ethyl ether (7.5 mL). The ethyl ether fractions were combined and evaporated to dryness under a nitrogen stream (G-4510E; Domnick Hunter Ltd., Dukesway, England). The crude phlorotannins were dissolved in 300 μL of methanol, and 200 μL was injected into the HPLC apparatus. Individual compounds were isolated on a C18 column (250 × 10.0 mm; Altech Associates Inc., Deerfield, IL). The HPLC system was fitted with a 486 Tunable Absorbance Detector (Waters Associates Inc., Milford, MA). HPLC elution was performed at a flow rate of 1.0 mL/min using a linear gradient of 30–100% (v/v) methanol over 40 min. The UV detector was set to 290 nm. All compounds were isolated on the basis of retention times. Phlorotannin content was assessed by measuring the dimensions of HPLC peaks and comparing these with those of standard curves for each purified compound. Calibration plots of peak height (y cm) versus pure compound level (x mg) in methanol yielded straight lines. The regression equation for the P1 compound was y = 49.7x – 0.98; that for 7-phloroeckol was y = 38.8x – 0.82, and that for eckol was y = 16.6x – 0.14. The correlation coefficients (the r2 values) were 0.95, 0.95, and 0.93, respectively.
Compounds initially isolated as described above were dissolved in methanol and individually repurified via HPLC. Compounds thus prepared were analyzed by [1H] nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy on a JNM-ECP 400 NMR spectrometer (JEOL, Tokyo) after dissolution in methanol-d (CD3OD). Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC-MS) spectra were obtained on a GC-MS-QP5050A instrument (Shimadzu, Kyoto). Infra red (IR) spectra were measured on a Perkin-Elmer (Wellesley, MA) spectrophotometer. Each compound was identified by comparison with previously published spectral data (Kim et al., 2009; Yotsu-Yamashita et al., 2013).
To prepare a crude enzyme extract from abalone muscle, the abalone were fed E. bicyclis or S. japonica (control) for 20 d. Muscle tissue (2.5 g) was ground in 3 mL of distilled water and centrifuged (3,000 g, 15 min); then the enzymecontaining supernatants were collected. The crude enzyme solution (400 μL) was mixed with 300 μL solutions of each pure phlorotannin and incubated at 30℃ for 4 h. Two hundred microliter amounts of each reaction mixture were periodically removed and injected into the RP-HPLC apparatus to determine the residual amounts of each phlorotannin. Degradation rates (in mg/mL/h) were calculated by measuring the slope of the level of each phlorotannin over time.
All data are presented as means ± SE of data from at least 4 independent replicates. Statistical comparisons of means were performed using analysis of variance (ANOVA), followed by application of Duncan’s multiple test. SPSS software (version 10.1; SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL) was used in all analyses. Mean values indicated by different letters are statistically significantly different (P < 0.05).
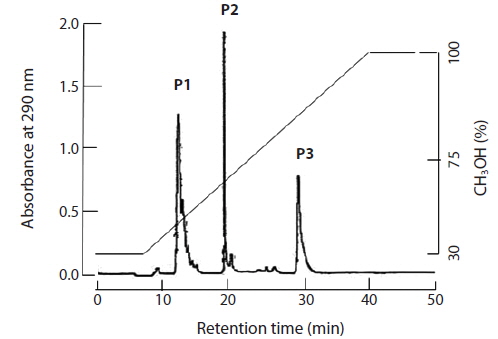
The brown seaweed E. bicyclis contains several phlorotannin compounds. MS and [1H]-NMR revealed that some matched known compounds, and that the chemical structures were confirmed. Separation of the E. bicyclis extract yielded seven peaks: the unidentified P1 compound, 7-phloroeckol, eckol, dieckol, the 974B compound, the 974A compound, and phlorofucofuroeckol-A. The RP-HPLC retention times were 13, 20, 28, 32, 34, 37, and 39 min, respectively. A water extract (obtained by boiling for 5 min) yielded five peaks: the unidentified P1 compound, 7-phloroeckol, eckol, dieckol, and phlorofucofuroeckol-A. The RP-HPLC retention times were 13, 20, 28, 32, and 39 min, respectively. P1 compound has not been clearly identified but is presumed to be a halogenated phloroglucinol-related derivative. It exhibited maximum absorbance at 272 nm. In the IR spectrum, the major characteristic bands were at 3,429 cm–1 for the phenol O–H stretch, 1,633 cm–1 for the alkenyl C=C stretch, 611 cm–1 for C–Cl, and 480 cm–1 for C–I/Br functional groups. The yields of crude phlorotannin extracted using solvent or hot water were approximately 3 and 418 mg/g dry tissue. After solvent extraction, the yields of the major three peaks (P1 compound, 7-phloroeckol, and eckol) were 0.2, 0.7, and 1.5 mg/g dry seaweed, respectively. After hot-water extraction, the respective yields were 0.6, 1.7, and 0.7 mg/g dry seaweed.
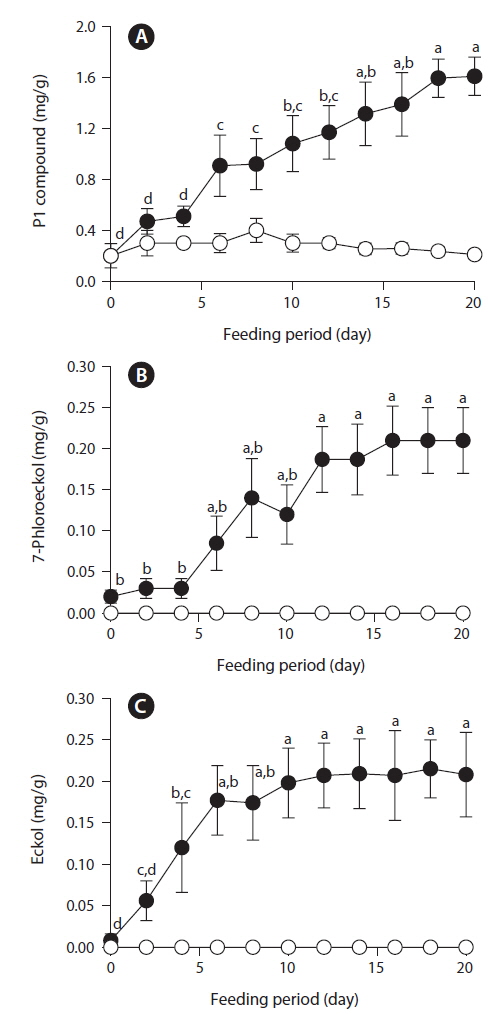
After feeding of E. bicyclis for 20 d, abalone foot muscle tissue was chopped and ground, and the tissue paste [92% (w/w) moisture] subjected to phlorotannin extraction. Based on RP-HPLC, under the conditions described above, the solvent extract exhibited three major peaks: the unidentified P1 compound, 7-phloroeckol, and eckol, at retention times of 13, 20, and 28 min, respectively (Fig. 1). The water extract exhibited two peaks: P1 and another unidentified compound, at retention times of 13 and 18 min, respectively. When the phlorotannin patterns of the solvent and water extracts were compared, the former clearly contained both 7-phlorotannin and eckol. Both compounds are water-soluble and were likely partitioned into the water layer because the tissue paste per se had high water content. Thus, phlorotannins were extracted from abalone using a solvent-water partition process. After feeding of control S. japonica, little P1 compound, no 7-phlorotannin, and no eckol were detected in abalone tissue. After feeding of E. bicyclis, abalone accumulated phlorotannins in muscle tissue. To quantify the levels of such compounds, RP-HPLC was performed with the aid of a C18 column. Three major phlorotannins (approximate retention times: 13, 20, and 28 min) were evident in the solvent extract of muscle paste, and the levels were calculated based on comparisons of HPLC peak dimensions with those of standard curves. P1 compound accumulated during feeding to a maximum of 1.60 ± 0.15 mg/g dry weight of abalone tissue after 18 d. Control S. japonica-fed abalone accumulated about 0.2 mg/g of this compound (Fig. 2a). 7-Phloroeckol accumulated to a maximum of 0.21 ± 0.04 mg/g dry weight of abalone tissue after 16 d. Control S. japonica-fed abalone did not accumulate the compound (Fig. 2b). Eckol accumulated to a maximum of 0.22 ± 0.04 mg/g dry weight of tissue after 12 d. Control S. japonica-fed abalone did not accumulate the compound (Fig. 2c). The total weights of seaweed consumed by individual abalone during the 20-d feeding trial were 1.8 g for E. bicyclis and 2.3 g for L. japonica. Daily feed consumption levels were similar, 13% and 15% for E. bicyclis and S. japonica, respectively. During the 20-d trial, the relative growth rates of abalone fed E. bicyclis and S. japonica were also similar (Fig. 3). After abalone became adapted to the E. bicyclis feed after 4 d of starvation, the relative growth rate attained approximately 0.75% within 14 d. Thus, E. bicyclis had no effect on feed preference or growth rate compared with S. japonica. To know the distribution of phlorotannins in different tissues, all abalone were killed after feeding of E. bicyclis (0.8 g/d) for 20 d, and each of the foot muscle, heart, gonad, and gut tissues was chopped and ground into paste on ice. Table 1 shows the levels of phlorotannins that accumulated in each tissue type. The edible foot muscle contained the highest levels of the P1 compound, 7-phloroeckol, and eckol (1.61 ± 0.16, 0.21 ± 0.12, and 0.26 ± 0.05 mg/g dry tissue, respectively).
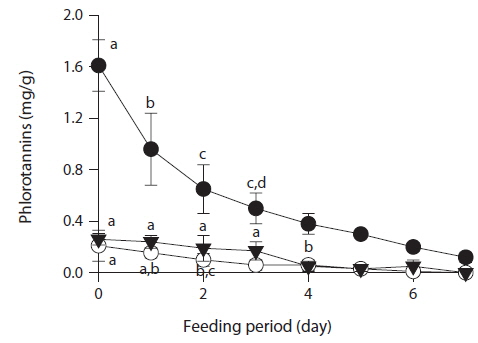
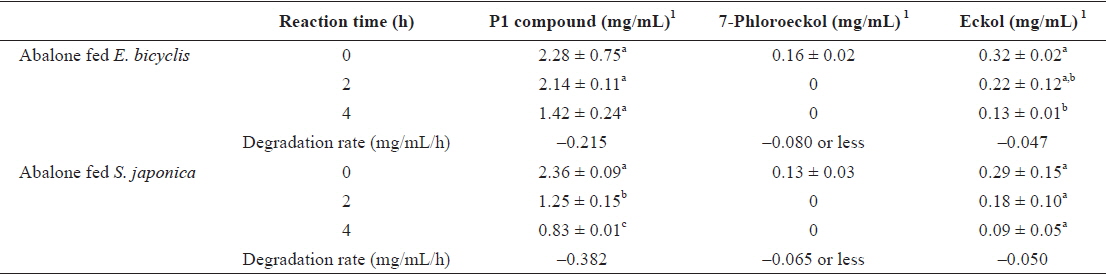
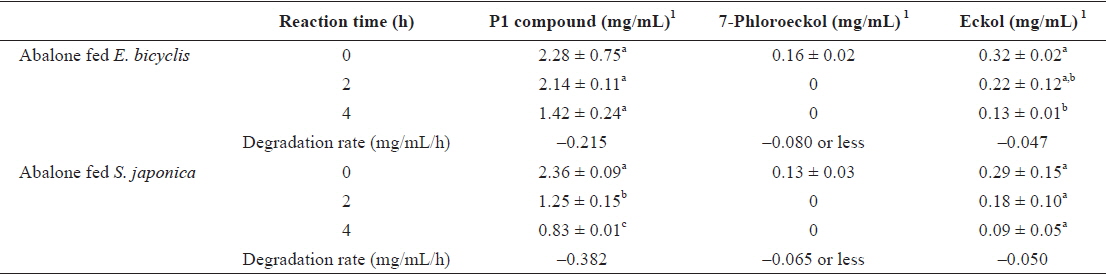
To determine whether phlorotannin levels in muscle tissue would fall when the phlorotannin-rich feed was changed, abalone were first fed E. bicyclis for 20 d to allow phlorotannin accumulation, and the feed was then switched to S. japonica for the following 7 d. The levels of all phlorotannins decreased after E. bicyclis feeding ceased (Fig. 4). Reduction to the half-maximal accumulation levels of the P1 compound, 7-phloroeckol, and eckol occurred 1.5, 1.9, and 3.4 d, respectively, after S. japonica feeding commenced. The abalone lost the P1 compound, 7-phloroeckol, and eckol from muscle tissue at mean rates of –0.18, –0.03, and –0.04 mg/g dry tissue per day, respectively. When abalone were starved, the pattern of decline in the level of each compound was similar to that noted upon S. japonica feeding (data not shown). To confirm enzymatic degradation of phlorotannins in abalone tissue, aliquots of muscle paste from abalone fed for 20 d with E. bicyclis or S. japonica were analyzed enzymatically. Both tissues contained enzymes degrading the P1 compound, 7-phloroeckol, and eckol (Table 2). S. japonica contained no phlorotannins, but tissue of abalone fed with this material could also degrade the P1 compound, 7-phloroeckol, and eckol, at –0.38, –0.06 or less, and –0.05 mg/mL/h, respectively. Thus, it appeared that phlorotannin-decomposing enzymes were constitutively produced. Abalone fed E. bicyclis, thus exposed to phlorotannins, exhibited slower degradation rates than abalone fed S. japonica. Phlorotannins may perhaps inhibit or suppress certain enzymes involved in phlorotannin degradation.
In Korea Haliotis discus hanai is commonly cultured by feeding Undaria pinnatifida. To produce value-added abalone with flesh containing biologically active substances, we changed the feed to the brown seaweed E. bicyclis for a short time before harvest. E. bicyclis contains high levels of several phlorotannins, which exhibit diverse biological activities, including anti-oxidative properties (Yoon et al., 2011). Usually, polyphenolic compounds from brown algae have been considered to deter grazing by and growth of abalone (Winter and Estes, 1992). Abalone prefer to eat phenolic-poor rather than phenolic-rich seaweeds. Thus, we starved the abalone for 4 d before offering them phenolic-rich E. bicyclis as the sole feed source. After adaptation, abalone consumed this seaweed readily. Similar weight gains were evident upon feeding with phlorotannin-rich E. bicyclis and phlorotannin-poor S. japonica (Fig. 3), suggesting that a high level of phlorotannins may not affect weight gain, at least during the short 20-d feeding period that we used. Kubanek et al. (2004) reported significant enhancements in the survival and growth of amphipods upon adding purified phlorotannins to the feed. Some herbivores with basic or surfactant-rich digestive systems readily consume phlorotannin-rich seaweeds (Targett and Arnold, 1998). Herbivore digestive efficiency, or willingness to feed on seaweeds, may or may not be related to the phlorotannin concentration of such seaweeds (Denton and Chapman, 1991; Targett et al., 1995). Cronin and Hay (1996) have shown that starved animals can be less sensitive to the presence of secondary metabolites in food.
Accumulation of diet-derived compounds has been reported in many herbivores. Abalone previously fed Ulva lactuca accumulated more dimethylsulfoniopropionate than wild-collected abalone or those given manufactured feeds (Smit et al., 2007). The Caribbean sacoglossan Costasiella ocellifera fed the green seaweed Avrainvillea longicaulis accumulated the metabolite avrainvilleol (Hay et al., 1990). The sacoglossans Cyerce nigricans and Elysia sp. fed the green seaweed Chlorodesmis fastigiata accumulated the diterpenoid chlorodesmin (Hay et al., 1989). Furthermore, lactone-containing diterpenes related to acetoxycrenulide have been isolated from both the sea hare Aplysia vaccaria and the brown seaweed Dictyota crenulata (Midland et al., 1983). The sea hare sequestered secondary metabolites from chemically rich marine algae, particularly the red algal genera Plocamium and Laurencia, the brown seaweed family Dictyotaceae, and cyanobacteria (Paul and Pennings, 1991; Faulkner, 1992). Aplysia parvula, grazing on the red seaweed Delisea pulchra, accumulated halogenated furanone secondary metabolites of the seaweed (de Nys et al., 1996). The accumulated furanones were lost at a mean rate of –0.92 mg/g dry weight/day from A. parvula fed Ulva sp. (Rogers et al., 2000). Abalone lost phlorotannins at mean rates of –0.03 to –0.18 mg/g dry tissue/day, which generally had longer half-lives than furanones in abalone tissue. The uptake and retention of metabolites depend on their chemical properties and feed sources. 7-Phloroeckol from Ecklonia cava was taken up more rapidly, but eliminated more readily, compared to the same compound in E. bicyclis (Bangoura et al., 2014). The abalone may possess enzymes capable of degrading phlorotannins present in muscle. Tissues of abalone fed E. bicyclis exhibited lower phlorotannin degradation rates than tissues of abalone fed S. japonica, suggesting that the degradative enzymes were expressed constitutively, and may be subject to substrate inhibition or suppression by accumulated phlorotannins. Common dietary polyphenols also undergo extensive degradation in the small intestine and liver, facilitating elimination from the body (van Dorsten et al., 2010). In conclusion, our results indicate that E. bicyclis can be used as a feed source, and that maximum phlorotannin accumulation in abalone flesh occurs after 18 d of feeding. Moreover, our findings suggest that producing value-added abalone containing high levels of phlorotannins may be possible by simply changing the feed. Continuous feeding with phlorotannin-rich seaweed is necessary to maintain high phlorotannin levels in abalone flesh.





![Relative growth rates of abalone after feeding with Eisenia bicyclis and Saccharina japonica. Black circles, E. bicyclis feeding; white circles, S. japonica feeding (control). Abalone were fed 0.8 g seaweed daily. Relative growth rates (%) were calculated as: [(final weight minus initial weight)/initial weight] × 100 (n ≥ 6)](http://oak.go.kr/repository/journal/15854/E1HKAL_2015_v18n2_165_f003.jpg)