구강점막질환은 구강점막, 혀, 구개, 협점막에서 나타나는 감염성 질환 중 하나이며1), 세균, 바이러스, 전신질환, 영양장애, 스트레스에 의한 감염 등 다양한 원인으로 인해 발생하게 된다2,3). 구강점막질환이 발생되는 원인 중 하나는 기회 감염으로, 기회 감염은 일반적으로 건강한 사람에게는 쉽게 발생하지 않으나, 숙주의 면역체계가 비정상적이거나 손상된 면역체계를 가진 경우 진균 감염은 구강이나 다른 전신질환으로 쉽게 이환될 수 있다. 또한, Candida albicans는 기회감염을 일으키는 대표적인 원인균으로서 구강, 식도, 생식기와 손톱 등에 쉽게 이환되어 나타난다4). 더욱이 면역체계가 손상된 환자에게서는 전신적인 캔디다증을 유발하여5), 전신에 있어 병적 상태를 유발하거나 기회 감염으로 인하여 사망에 이르게 될 가능성이 있다6). 구강 캔디다증은 구강에 있어 가장 흔한 진균 감염의 형태로서 나타난다7). 캔디다 균은 현재 20개 이상의 종류가 알려져 있으며, 구강점막 질환을 일으키는 가장 일반적이며 널리 알려진 진균은 C. albicans이다8). 또한, 구강점막질환이나 구강 내 진균 감염을 일으키는 가장 대표적인 원인균으로 알려져 있다. 구강 캔디다증은 주로 어린 아이, 질병에 감염된 환자, 노인 등 면역이 제 기능을 발휘하지 못하는 층에서 흔히 발생하게 된다9). 대부분 구강 캔디다증을 치료하기 위하여 흔히 항생제, 스테로이드나 구강 소독제를 사용하게 되는데 장기간 사용시 정상 세균총의 균형을 무너뜨려 2차 질환인 균교대증이 발병할 수 있는 위험이 있다.
플라즈마란 액체, 고체, 기체와 함께 ‘제4의 상태’라고 불리고 있으며 이온화된 기체로서 활성종인 하전 입자, OH radical, 이온, 자유 라디칼 등을 발생시킨다. 또한 이러한 활성 산소들은 동물 세포와 박테리아에 영향을 미치고 있음이 지속적으로 보고되고 있다10). 이렇듯 기존에 발표되는 플라즈마 관련 논문들에서는 동물의 조직이 아닌 주로 membrane 등에 박테리아를 처리하여 사멸효과를 발표하고 있으며, Streptococcus mutans 등의 구강 내 박테리아나 암세포에 있어 매우 효과적임이 보고되고 있다. 진균의 특성상 빠른 번식력으로 인하여 효과적으로 사멸시키기 어려워 약제 사용시의 다양한 부작용이 보고되고 있는데, 본 연구에서는 아르곤 가스를 이용한 jet type의 저온 상압 플라즈마 장치를 이용하여 구강 내에서 발생하는 진균성 구강 병원균인 C. albicans 균주를 마우스 조직에 적용시켜 플라즈마를 처리하여 짧은 시간 내에 보다 효과적인 사멸 방법을 제시하고자 한다.
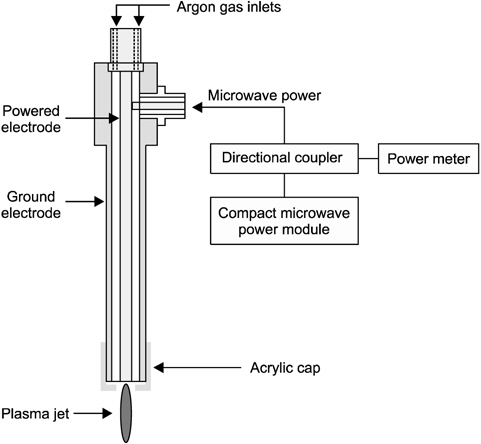
대기압 저온 상압 플라즈마는 in vivo와 in vitro 내에서 박테리아 살균을 위해 사용되었다. 플라즈마 장치는 손바닥 크기의 전원 모듈에서 900 MHz, 2.5 W의 마이크로파 전력으로 아르곤 플라즈마 제트를 생성시킬 수 있도록 설계되었다11,12). 입력전원을 측정하기 위해 RF power meter (EPM-441A; HP, Georgia, USA)를 이용하였다. 본 연구에서 사용한 플라즈마 장치의 아르곤 가스 유량은 분당 3 리터(liter per minutes)이며, 플로우 미터기(Ar-05; KOFLOC, Tokyo, Japan)로 가스 유량을 측정하였다. 플라즈마 장치의 끝은 아크릴 캡을 이용하여 직경 4 mm의 구멍을 낸 후 플라즈마 장치에 씌울 수 있도록 설계하였다. 저온의 상압 플라즈마 장치에 아크릴 캡을 씌운 후 플라즈마는 큰 변화 없이 발생되는 것을 확인하였으며, 마우스 조직과 플라즈마 장치의 거리는 10 mm로 유지하여 시행하였다(Fig. 1).
본 연구에 사용한 C. albicans (KCTC 7965/ATCC 10231)의 균주는 한국생명공학연구원 생물자원센터(Daejeon, Korea)에서 분양받아 사용하였다. 균주의 배양은 YM broth(BD Difco Laboratories, Maryland, USA) 배지를 이용하여 1∼2차 계대 배양 후 37℃ CO2 incubator를 이용하여 배양하였다.
중앙 실험동물(Seoul, Korea)에서 공급받은 5주령 된 수컷 hairless mouse-2 (HRM-2) 마우스를 이용하였으며, 사육장에서 1주일간 적응을 시키고 물과 음식은 자유로이 섭취시켰다. 동물 실험실의 환경은 실내온도 23±2℃, 습도 55±5%로 유지하였고, 12시간씩 명암을 조절하였다. 본 실험은 동물실험수행을 하기 위하여 양산부산대학교병원 동물실험윤리위원회에서 승인(IRB No. 2012-0033)을 받았으며, 동물 실험 시 모든 실험 과정에서 PNU-IACUC의 규정에 따라 동물실험에 관한 윤리 과정을 준수하여 연구를 진행하였다.
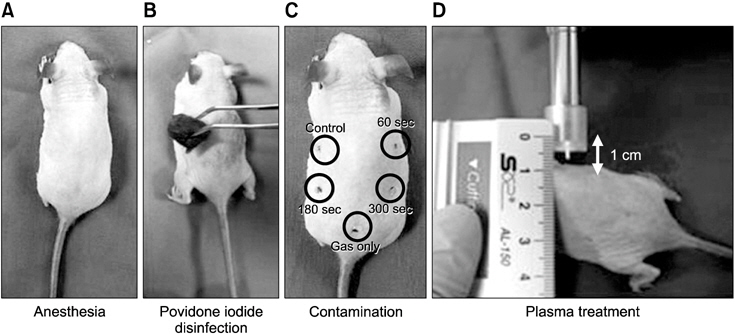
실험군의 마우스에 70∼100 mg/kg ketamine (hydroxide zoletil 50; Virbac, Sao Paulo, Brazil)과 10∼20 mg/kg xylazine (Rumpun; Bayer, Shawnee Mission, KS, USA)을 복막 주사하여 마취하였다. 마우스를 마취시킨 후 C. albicans 균을 처리할 마우스 dorsal 부위에 표시하여 포비돈으로 소독 후 알코올로 닦아내었다. 실험할 마우스 dorsal 부위에 약 6×10 colony forming units (CFU) 농도의 C. albicans 균을 5 μl를 접종 후 상온에서 5분간 건조시켰다. 플라즈마와 마우스 조직과의 거리는 1 cm로 조정하였다. 플라즈마 처리 시간은 0초, 60초, 180초, 300초씩 C. albicans로 오염된 마우스 조직에 처리하였다. 마우스 조직에서의 사멸률을 확인하기 위해 C. albicans 균주를 마우스 조직에 처리 후 1∼3회 반복처리하였다. 마우스 조직에 플라즈마 처리 후 멸균된 면봉으로 표본을 채취하여 1 ml의 phosphate buffered saline에 처리하여 100 μl씩 agar plate에 10-fold serial dilution하여 도말하였다. 처리한 agar plate는 37℃의 incubator에서 24시간 동안 배양시킨 후 미생물 수를 CFU 방법을 이용하여 측정하였다.
본 연구에서는 통계분석을 위해 PASW Statistics 18.0 (IBM Co., Armonk, NY, USA)을 이용하였다. 마우스 조직에서 반복적으로 플라즈마를 처리시 나타나는 살균효과를 알아보기 위하여 one-way ANOVA를 실시하였다(p<0.05).
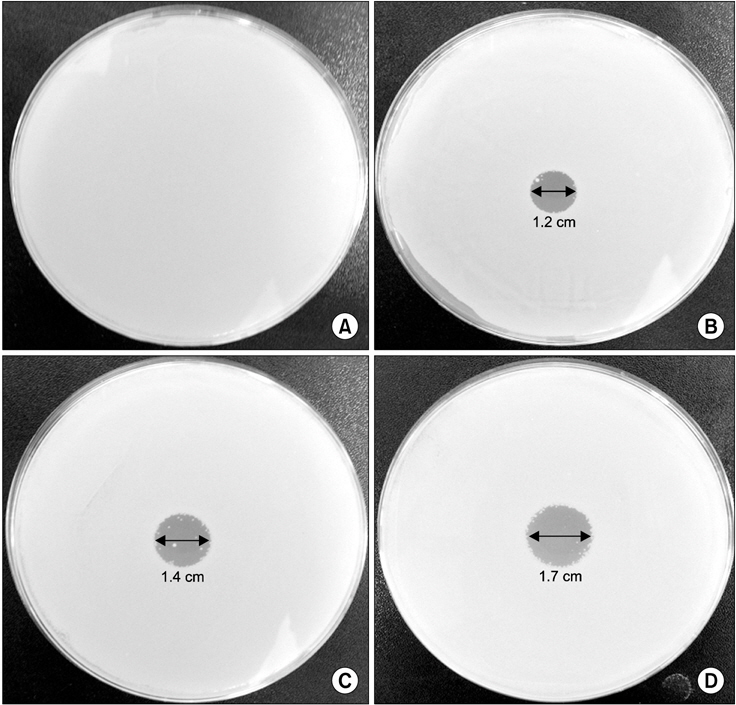
저온 상압 플라즈마 장치의 박테리아 사멸효과를 알아보기 위해 먼저 agar plate 표면에 C. albicans 균을 처리 후 플라즈마를 0초, 60초, 180초, 300초 동안 조사하였다. 그 결과 C. albicans 균은 저온 상압 플라즈마 처리시 시간 의존적으로 균의 억제 구간에 있어 0초(Control) 처리시 변화가 없음을 확인하였으며(Fig. 2A), 60초 처리시 1.2 cm (Fig. 2B), 180초 처리시 1.4 cm (Fig. 2C), 300초 처리시 1.7 cm (Fig. 2D)로 박테리아 억제 구간이 증가되는 것을 확인하였다.
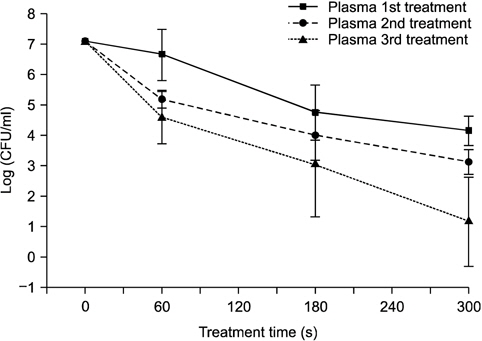
C. albicans 균주에 대한 살균효과를 알아보기 위해 마우스 조직 표면에 저온 상압 플라즈마 장치를 조사하였다(Fig. 3). 앞선 agar plate 실험 결과를 통해 60초간 플라즈마를 처리하였을 때보다 300초 동안 플라즈마 처리시 살균력에 효과적인 것을 확인하였다. 이를 바탕으로 C. albicans 균을 마우스 조직에 처리하여, 상온에서 건조시킨 후 플라즈마 장치를 0초, 60초, 180초와 300초간 조사하였으며, 사멸 효과를 증진시키기 위하여 1∼3회간 반복하여 10분 간격으로 플라즈마를 조사하였다. 처리 결과 플라즈마 장치를 300초 동안 1회 처리시 2 log CFU/ml, 2회 처리시 3 log CFU/ml, 3회 반복 처리시 6 log CFU/ml의 박테리아 사멸률 감소 효과를 보였다. 본 연구 결과 플라즈마의 처리 시간을 증가시키고 플라즈마 반복 처리시의 박테리아 살균효과에 유의한 차이(p<0.05)가 있음을 확인하였다(Fig. 4).
건강한 성인의 구강 내의 30∼45%에서 진균인 C. albicans는 정상 세균총으로 발견되고 있다13). 그러나, 면역체계가 정상적이지 않고 면역력이 감소하게 되면 구강 내 존재하던 C. albicans 균의 수가 빠르게 증가하여 구각염 등의 구강질환이 발생하게 된다14). 특히, 구각염은 의치를 장착하고 있는 노인15), 불량한 구강위생이나 전신 질환자나 화학요법을 받은 암환자에서 흔히 나타나게 된다16). 의치의 경우 위생 상태가 불량할 경우 C. albicans 균이 의치 내에 증식하게 되며, 노인들의 구강에서 구내염을 일으키는 원인이 된다17). 최근 연구에 따르면 저온의 플라즈마 장치가 구강소독제에 비해 C. albicans 균의 살균력이 효과적이라는 것이 보고되고 있다18). 대부분의 구강 소독제는 장기간 사용시 흔히 균교대증, 약제 내성과 구강건조증을 야기시키는 부작용을 초래하게 된다.
본 연구팀에서 저온 상압 플라즈마 장치의 효과를 확인하기 위해 agar plate에 300초 동안 저온 상압 플라즈마 처리시 300초간 처리시 박테리아 억제구간이 0초, 60초, 180초간 처리했을 때보다 넓게 나타나는 것을 확인하였다. 즉, C. albicans 균의 수가 감소 효과를 증진시키기 위해서는 플라즈마 처리 시간을 300초간 처리하였을 때 진균의 수가 감소효과가 증가된다는 것을 확인하였다. 그러나, agar plate 표면에서 C. albicans 균의 수가 감소가 높게 나타났으나, 마우스 피부조직에서 플라즈마를 300초 동안 처리시 균의 수가 2 log CFU/ml로 낮은 감소효과가 나타나는 것을 확인하였다. 본 결과를 종합하여 볼 때 agar plate는 1차원적인 구조로 인해 플라즈마 조사시 처리 시간에 따라 균일하게 agar plate에 적용이 되지만, 마우스 조직은 3차원적인 구조로서 조직의 특성상 균일하게 처리되지 못함을 인지하였다. 그리하여 마우스 조직에서 C. albicans 진균의 사멸효과를 증대시키기 위하여 300초간 플라즈마 장치를 반복 처리하여 살균 효과를 확인하였다. 그 결과, 300초 동안 플라즈마 1회 조사 시 2 log CFU/ml, 2회 조사 시 3 log CFU/ml, 3 회 조사 시 6 log CFU/ml의 높은 균수 감소 효과를 나타내는 것을 확인하였다. 저온 상압 플라즈마 장치의 특성상 발생하는 이온, 자유전자, 활성 산소 등 다양한 radical 등이 발생하여 플라즈마가 직접 병소에 닿지 않더라도 활성종에 의한 사멸효과가 나타나므로, 치과 영역에서 응용하여 적절하게 사용시 구강 내 점막질환이나 더 나아가 접근이 어려운 근관 내에 존재하는 박테리아 사멸에 매우 효과적일 것으로 생각된다.
본 연구에서 사용한 플라즈마 장치는 실험을 위해 고안된 장비이며, jet type의 형태로 인해 구강 내 넓은 부위의 점막질환의 경우 한계가 있을 것으로 생각된다. 또한, 본 연구에서는 플라즈마를 이용한 박테리아 사멸효과에 대해서는 증명이 되었으나, 조직의 안정성 및 유해 효과를 모두 확인하지 못한 한계점을 지니고 있다. 그러므로, 후속 연구에서는 구강 내 적용하기 위한 조직에의 안정성에 대한 연구가 이루어져야 할 것으로 생각된다. 그러나 본 연구를 통해서 조직에서의 저온 상압 플라즈마 장치의 살균효과가 증명되었으며, 본 연구를 바탕으로 치과 영역에서의 저온 상압 플라즈마 장치의 응용연구가 지속적으로 이루어져야 할 것이다.