Acaiberry (
Acaiberry는 브라질 북부 아마존 열대지역의 늪지대에서 자생하는 야자수 나무의 열매로 지방산, 아미노산, 미네랄 등의 필수영양소와 안토시아닌 등의 플라보노이드계(flavonoid) 항산화물질이 풍부하게 함유되어 있으며1), 이러한 항산화 물질은 활성산소(reactive oxygen species, ROS)를 제거함2)으로써 신경보호3), 동맥경화 예방4), 항암효과5)를 나타낸다고 알려져 있다. In vitro 실험에서 acaiberry추출물은 cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), p38 mitogenactivated protein kinase (p38 MAPK), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), nuclear factor κB (NF-κB)의 활성을 억제하였고6), 동결 건조된 acaiberry 추출물은 lipopolysaccharide(LPS)로 유도된 ROS의 생성과 COX-1, 2 발현에 억제적 효과를 나타내었다1). 이러한 결과들은 acaiberry가 산화와 염증반응을 조절하는데 효과적임을 증명하였다. 천연물의 다양한 성분들은 주로 항산화와 관련된 물질의 분비를 조절하는 것으로 알려져 있고, 그 중 하나인 NOX4(nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate 4)는 세포막 단백질로 superoxide (O2-), hydroxy peroxide (H2O2), peroxitirite (ONOO-)와 같은 ROS을 생성하는 원인인자이다7). NADPH oxidase family에는 NOX1, NOX2, NOX3, NOX4, NOX5, dual oxide (DUOX) 1, DUOX2와 같은 7종류의 아형이 있으며, 모든 NOX family는 1개 이상의 세포막 또는 세포질단백질에 결합되어 있다고 보고되고 있다8). NOX4는 다양한 생리적 과정을 통해 활성화되며 신장에서 가장 높은 발현을 보이나 신체 대부분의 조직에서 중간 또는 낮은 발현을 보이며,9) 심혈관 질환, 당뇨 합병증, 섬유증의 질환에서 염증성 인자들을 중개하여 이러한 질환에 관여하는 것으로 보고된다10). 여러 병태생리학적 연구결과를 통하여 통증 및 염증과 NOX4의 연관성은 입증되고 있으나, 현재까지 악안면 통증 및 염증의 발생과 조절에 관여함을 입증한 증거는 없는 실정이다.
악안면 통증은 치아나 그 주위조직에서 주로 발생하며 일부 턱관절장애(temporomandibular joint disorder), 만성두통, 그리고 근육통증을 포함한다11). 통증의 완화를 위해 사용되는 약물로는 acetaminophen, 근육이완제, 항우울제, 비스테로이드성 항염증제(nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, NSAIDs), opioid계 약물 등이 처방되고 있으나12) 부작용과 약물 독성에 대한 문제로 인해 보다 효과적이고 안전한 천연물에 대한 관심이 증대되고 있는 추세이다. Formain으로 유도된 악안면 통증모델에서 항산화물질인 vitamin E, curcumin 등의 주입으로 실험동물의 통증행위 반응이 효과적으로 감소되었다는 보고가 있으며13,14), 본 연구실에서도 최근 천연물로 구성된 사물탕의 투여로 인한 악안면 통증 경감을 보고하였다15). 이러한 결과들은 천연물의 항산화 작용이 통증발생과 전도를 조절함에 있어서 중요한 역할을 할 수 있음을 증명한다. 많은 연구들이 악안면 영역에서의 염증성 통증 발생과 조절에 관여하는 기전을 밝혀왔으며, 특히 염증성 통각신호 전달에 중요한 역할을 담당하는 것 중에 MAPK를 꼽을 수 있다. MAPK는 p38 MAPK, extracellula signal-regulated protein kinase (ERK), c-JUNN-terminal kinase/stress-activated protein kinase (JNK/SAPK)로 구성되며, 세포내 신호전달을 통해 염증, 스트레스 반응, apoptosis 등에 관여하는 것으로 알려져 있다16). 특히 interlukin-6 (IL-6), TNF-α, growth factor와 같은 염증성 매개물들에 의해 활성화되어 통증의 신호전달에 핵심적 역할을 하며, 미토콘드리아에서 생산된 ROS에 의해 인산화된 p38 MAPK는 핵 내 전사인자인 NF-κB을 활성화시키고, 이로 인해 COX-2, induceble nitric oxide synthase (iNOS)와 같은 pro-inflammatory cytokine의 발현을 증가시켜 염증성 통증을 초래한다고 알려져 있다17,18). 다양한 실험동물의 통증모델에서 p38 MAPK의 억제제인 SB203580의 투여는 이질통을 감소시켰고19,20), seasamin과 cinammon 등의 천연물 또한 p38 MAPK의 유의한 억제 효과를 나타내었다21,22). 이러한 내용은 악안면 영역의 염증성 통증발생에 p38 MAPK가 중요하게 관여함을 보여주었으며, 선택적인 억제제의 투여와 마찬가지로 천연물의 적용을 통해서도 악안면 통각 조절이 가능함을 제시하였다.
이상의 내용들을 종합하여 본 연구에서는 실험동물의 수염부에 formalin을 주입함으로써 악안면 통증을 유발하고, 이러한 통증발생과 조절에 항산화 물질이 풍부하게 함유된 acaiberry의 효능을 확인하고자 하였다. 또한, acaiberry의 항산화 효과를 입증하기 위하여 NOX4의 발현을 단백정량 분석법으로 확인하였고, 끝으로 통증전도에 주요인자인 p38 MAPK 활성변화에 acaiberry가 미치는 영향을 평가하고자 하였다.
실험동물은 Sprague-Dawley계 수컷 흰쥐(240∼280 g)를 효창 사이언스(Daegu, Korea)에서 공급받아 사용하였다. 12시간 주/야 순환주기 및 23∼24℃의 일정한 환경을 유지하면서 물과 사료는 자유로이 공급하였다. 행동적인 억압 등에 의한 실험 전 스트레스를 가능한 최소화하였다. 본 연구는 의식이 있는 동물의 실험에 관한 통증연구학회의 윤리적 규정에 따라 수행하였다.
Acaiberry는 아마조니아 유기농 acaiberry 동결건조분말(브라질산 유기농 acaiberry 동결건조 분말 99.9%, 유기농 아세로라분말 0.1%)을 0.9% normal saline에 각각 16, 80, 160 mg/kg의 농도로 희석하여 복강투여(intraperitoneal injection, i.p.)하였다. Acaiberry 적용 30분 후 5% formalin을 악안면에 주입하여 통증행위반응을 관찰하였다. 단, 단백정백분석은 80 mg/kg의 농도에서 시행하였다. 분말은 ㈜렉스진바이오텍(Cheongwon, Korea)에서 생산한 제품으로 보관방법에 따라 냉장 보관하였으며 사용직전 희석시켜 사용하였다.
3. 악안면 통증 발현 및 acaiberry의 영향 평가
실험동물(n=6)의 오른쪽 수염부 피하에 5% formalin (50μl)을 인슐린 주사기(0.25 mm [31G]×8 mm)를 이용하여 주입하였고, 주입 직후부터 5분 단위로 누적하여 총 45분간 행위반응을 관찰하였다. 약물이 주입된 악안면 부위를 문지르거나 긁는 행위를 통증 지표로 간주하였다23). 각 실험군은 formalin 주입군, 9% normal saline 투여 후 5% formalin 주입군, acaiberry (16, 80, 160 mg/kg) 투여 후 5% formalin 주입군으로 분류하였다.
실험동물 20% urethan (1.5 ml)으로 복강마취 후 경동맥을 차단하여 뇌로 가는 혈류를 차단하였다. 두개골을 절개하여 연수를 적출하고 이어 복부를 절개하여 부신을 적출하였다. 균질화 전까지 -70℃에 보관하였다가 꺼내어 사용하였다. 적출한 연수와 부신 조직에 lysis buffer (PROPREPTM protein extraction solution kit; Intron Biotechnology, Seongnam, Korea)를 첨가하여 4oC에서 homogenizer (Intron Biotechnology)를 이용하여 각각의 조직을 균질화하였다. 균질화 이후 centrifuge (Hanil Science, Incheon, Korea)로 4℃, 13,000 rpm에서 10분간 원심분리하였다. 세포 찌꺼기를 제거한 상층액을 X-ma spectrophotometer (Human Co., Seoul, Korea)로 595 nm에서 단백질 흡광도를 측정하였다. 단백질 농도는 bovine serum albumin (BSA)를 표준화하여 Bio-Rad Protein assay kit(Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA)를 사용하여 정량하였다. 정량된 단백질과 distilled water (DW), sample buffer (125mM Tris [pH 6.8], 20% glycerol, 4% sodium dodecyl sulfate [SDS], 2% β-mercaptoethanol, 0.04% bromophenol blue, DW)를 혼합하여 10분간 95℃에서 heating시키고 2분간 -20℃에서 보관, 원심 후 vortex로 다시 혼합하였다. 준비된 단백질 sample은 12% SDS-polyacrylaminde gel에 18.5 μl로 loading 후 70 V, 100 V, 110 V에서 각각 30분, 1시간 30분, 1시간 40분으로 전압을 조절하면서 running하였다. Gel에서 nitrocellulose membrane으로 단백질을 옮기기 위해 100 V로 2시간 동안 transfer하였고, 전체 단백질 패턴을 확인하기 위해 Ponceau 용액으로 확인 후 DW에 10분간 세척하였다. 교반기(WISD, SHO 2D; Daihan, Wonju, Korea) 위에서 blocking buffer (1×phosphate-buffered saline with Tween 20 [PBST], 탈지분유, sodium azide)로 2시간 blocking하고 7분간 5회에 걸쳐 1×PBST(10×PBST, DW, 0.1% Tween 20)로 수세 후 NOX4, p38, β-actin, anti body (Ab)를 4℃에서 overnight시켰다. 수세 후 2차 Ab를 교반기 위에서 2시간 실온 부착하였고 발현은 ECL (Amersham Pharmacia Biotech, Buckinghamshire, UK)을 이용하여 분석하였다. 1차 Ab는 p38 MAPK rabbit mAb, NOX4와 β-actin monoclonal Ab (Cell Signaling Technology Inc., Danvers, MA, USA)를 각각 1:2,000, 1:500, 1:20,000의 비율로 5% skim milk에 희석하여 사용하였고, p38 MAPK와 NOX4의 2차 Ab인 anti-rabbit immunoglobulin G (IgG; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA, USA)와 b-actin의 2차 Ab는 horseradish peroxidase-conjugated anti-mouse IgG를 각각 1:8,000, 1:3,000, 1:10,000의 비율로 sodium azide를 제외한 5% skim milk에 희석시켜 사용하였다. Vision Works Image Software (UVP Llc., Cambridge, UK)를 이용하여 발현 정도를 나타내었다.
실험결과의 통계 분석에 사용된 프로그램은 SPSS 12.0 K (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA)와 sigmaplot 2001 (SPSS Inc.)이며, 다중 그룹에서 반복측정자료의 분산분석법과 least significant difference (LSD) post-hoc test를 이용하였다. 통계적인 비교를 위해 통계적 유의성의 표준값은 p<0.05로 설정하였다. 모든 결과는 평균±표준 오차(standard error of mean)로 표시하였다.
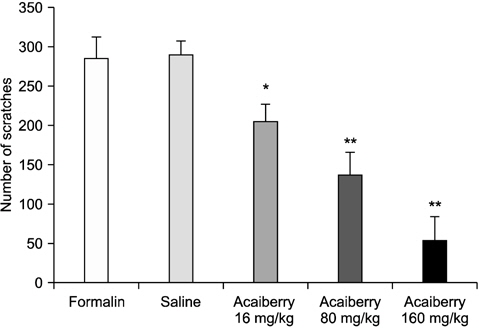
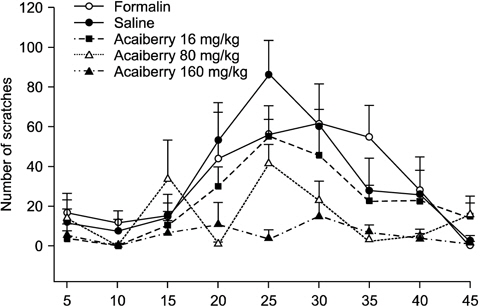
Formalin으로 유도한 악안면 통증에서 acaiberry의 통증행위반응 조절효과를 Fig. 1에 나타내었다. Formalin의 주입에 의한 악안면 부위의 통증행위 반응은 286±26.0회로 나타났으며, 용매로 사용된 saline의 복강투여군에서는 290±17.4회로 이러한 악안면 통증행위반응의 변화에 영향을 미치지 못했다. 하지만 acaiberry (16, 80, 160 mg/kg)의 복강투여는 각 205.3±21.8, 137.8±21.8, 53.5±30.2회로 나타나 농도 의존적으로 통증행위반응을 감소시켰다. 이러한 통증행위반응은 시간의 경과에 따라 변화를 나타내었고, acaiberry의 시간에 따른 통증행위반응의 조절효과는 Fig. 2에 나타내었다. Formalin의 주입으로 인한 통증행위반응은 15분 이후부터 증가하여 25분, 30분에 가장 높게 나타났으며 40분까지 지속되다가 45분에 감소되었다. Acaiberry의 복강투여는 15∼40분에서 formalin에 의해 증가된 통증행위반응을 현저하게 감소시켰다.
2. Acaiberry가 NOX4의 발현에 미치는 영향
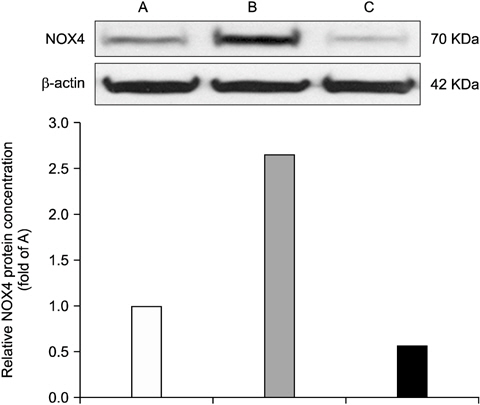
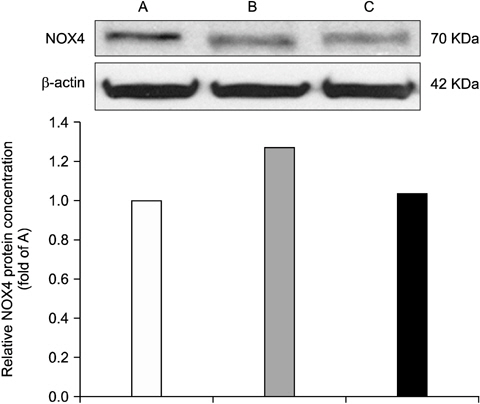
Acaiberry의 항산화 효과를 확인하기 위하여 연수와 부신에서 NOX4의 발현의 변화를 관찰하였다. Fig. 3은 formalin 주입 후 연수에서의 NOX4의 발현을 관찰한 것이다. 실험동물의 수염부에 formalin을 주입한 그룹은 아무것도 처치하지 않은 군에 비해 NOX4의 발현이 증가되었고, 이것은 acaiberry (80 mg/kg)의 복강투여에 의해 유의하게 감소됨을 보여주었다. Fig. 4는 부신에서의 NOX4 발현의 변화를 보여주고 있으며, 동일 농도의 acaiberry의 주입으로 formalin 주입에 따른 증가된 NOX4의 발현이 현저히 감소됨을 보여주었다.
3. Acaiberry가 p38 MAPK의 발현에 미치는 영향
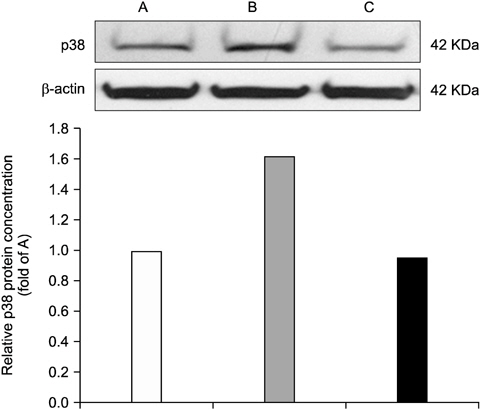
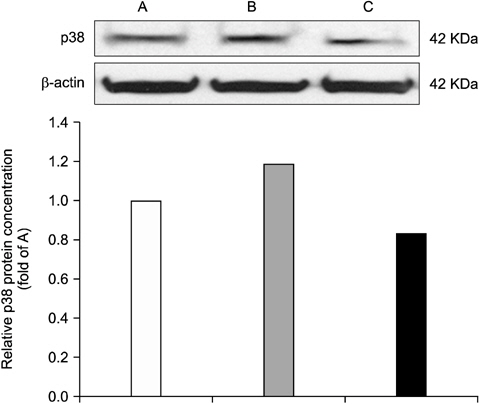
Acaiberry의 복강투여가 염증성 통증 신호의 조절에 미치는 영향을 확인하기 위하여 연수와 부신에서 p38 MAPK의 발현의 변화를 관찰하였다. Fig. 5는 연수에서 p38 MAPK의 발현의 변화를 관찰한 것이다. Formalin을 주입한 그룹은 아무것도 처치하지 않은 군에 비해 연수 p38 MAPK의 발현이 증가되어 나타났고, 이것은 acaiberry (80 mg/kg)의 복강투여에 의해 유의하게 감소됨을 확인하였다. Fig. 6은 부신에서 p38 MAPK발현의 변화를 나타내며, 동일 농도의 acaiberry의 복강 투여로 formalin의 주입에 따른 증가된 p38 MAPK의 발현이 현저히 감소됨을 보여주었다.
천연물 혹은 식품 등에 함유되어 있는 다양한 항산화물질은 생체 내에서 산화 및 노화에 주요 원인으로 여겨지는 ROS의 생성을 억제하는 것으로 알려져 있다. 최근, 피토케미컬의 항염증, 항산화 및 항암 등의 약리적 효능에 관심이 증대하고 있고, 이러한 피토케미컬을 이용한 많은 연구결과들을 통해 생체 내 적용되는 다양한 기전들을 밝혀주었다. 실험동물의 염증성 통증 모델에서 tart cherry의 주요 성분인 안토시아닌의 전신 또는 중추 투여는 통증행위반응을 억제하였다24). 또한 항산화 식품에 많이 함유되어 있는 vitamin E 역시 formalin test에서 통증행위반응을 감소시켰다13). 마찬가지로 본 연구에서 acaiberry의 복강투여는 formalin에 의해 유도된 통증행위반응을 농도 의존적으로 감소시켰음을 관찰하였다. 이와 같은 사실은 acaiberry와 천연에서 유래한 여러 식물성분이 통증의 조절에 관여한다는 것을 증명하며 악안면의 통증조절에도 유용할 것이라고 사료된다. 통증 신호전달과정에는 다양한 세포 내 염증성 인자들의 활성 및 발현과 관련되는데 acaiberry와 같은 천연식물들은 통증을 매개하는 여러 염증성 인자들을 조절한다고 알려져 있다. 포도에서 추출한 안토시아닌은 관절염유발 실험동물의 대식세포로부터 분비되는 염증성 사이토카인의 분비를 억제하였다고 보고되었다25). 또한 acaiberry 추출물은 다양한 염증 모델에서 pro-inflammation cytokine과 산화스트레스에 의한 발현되는 단백 효소들의 조절을 통해 항염증작용과 항산화 작용을 나타낸다고 보고되고 있다4,26,27). Acaiberry 추출물의 경구투여는 cigarette smoke의 흡입에 의해 유도된 페염증 모델에서 내재성 산화효소인 myeloperoxidase, superoxide dismutase, catalase, glutathione peroxidase activities와 TNF-α, nitrites와 같은 염증인자의 조절하여 염증을 완화시켰으며26), acaiberry로부터 추출한 velutin은 LPS로 유도된 NF-kB/p38 MAPK 경로의 활성을 저해시켜 TNF-α와 IL-6의 유전자발현을 감소시켰다고 보고되었다27). 이러한 결과와 마찬가지로, 본 연구에서도 acaiberry의 주입은 formalin으로 유발된 악안면 통증행위반응을 유의하게 감소시켜 천연물이 악안면 통증의 발생과 조절에 관여함을 증명하였다.
본 연구에서는 복강으로 투여된 acaiberry가 통증의 신호전달 경로에서의 다양한 염증성 인자들 중에서 세포 내 산화효소들의 생성을 유도하는 ROS의 생성과정에 주요 원인으로 알려져 있는 NOX4를 조절함을 보여주었다. NOX4는 세포막에 함께 위치한 p22phox의 조절에 의해 활성화되며, NOX1, NOX2, NOX5가 O2-를 생성하는 것과 달리, NOX4는 주로 O2-에 전자를 운반하여 H2O2를 생성하는 것으로 보고되고 있다8). 또한 산화적 스트레스 환경에서 NOX4는 H2O2의 과잉생산을 유도하며28), H2O2에 의한 축삭의 수초 이형성은 신경세포의 이소성 탈분극과 기계적 이질통을 유발한다는 연구결과가 있다9,29). 이러한 내용은 ROS의 생성을 촉진하는 NOX4 경로가 통증의 발생과 조절에 관여한다는 것을 시사하며, 이는 동물실험을 통해 확인되고 있다. 실험동물의 뒷다리에 주입된 O2-와 OHOO-와 같은 ROS는 열성과민반응 및 기계적 이질통을 유도하였으며, ROS scavenger는 이러한 통증을 완화시켰다30). 또한 척수신경 결찰에 의한 신경병증성 통증모델에서 NOX4 결핍 mice는 정상군에 비해 기계적 이질통이 완화되었다고 보고되고 있다31). 이와 같이 NOX4의 통증신호의 전달에 관한 일부의 보고는 밝혀져 있으나 악안면 영역에서 염증성 통증반응 조절에서 NOX4의 역할에 관한 연구는 거의 없다. 본 연구를 통하여 formalin의 주입으로 NOX4 발현의 증가된다는 것을 관찰하였고, acaiberry의 복강투여는 NOX4 발현을 감소시켰다. 이러한 결과는 acaiberry가 NOX4경로의 조절함으로써 항산화 효과를 나타내고, 이를 통해 악안면 염증성 통증 발생과 전도에 관여하는 것으로 사료된다.
말초조직의 손상은 말초신경과 중추신경에서의 p38 MAPK을 유도하여 염증성 통증신호를 전달하여 통증을 나타내는 것으로 알려져 있다. Formalin은 다양한 부위에서 말초의 염증성 통증을 나타내었다. 예를 들어, 측두하악관절 염증모델에서 formalin은 통증행위반응의 증가와 함께 microglial p-p38 MAPK의 활성을 증가시켰고20), 실험동물의 수염부위에 formalin의 주입은 연수 후각에서의 p-p38 MAPK의 활성 조절을 통해 통증행위반응을 증가시켰다32). 또한 hind paw에 formalin의 주입은 신경염증성 통증행위 반응과 함께 척수후각의 p-p38MAPK의 발현을 증가시켰다33). p38 MAPK은 아미노산 배열에 따라 p38α, p38β, p38γ, p38δ의 네 가지 아형이 있으며, 그 종류에 따라 발현부위의 차이가 있다. p38α는 대부분의 조직에서 발현되며, p38β는 뇌, p38γ는 골격근, p38δ는 내분비선에 관여한다34). 본 연구에서 formalin의 주입에 의한 통증행위반응의 변화와 연수와 부신조직에서 p38 MAPK 활성의 변화를 관찰하였고, formalin 주입 후 유의하게 증가된 통증행위반응과 연수와 부신조직에서 증가된 p38 MAPK의 활성은 복강으로 주입된 acaiberry에 의해 농도 의존적으로 감소되었다. 이러한 결과를 통해 acaiberry가 p38 MAPK 경로를 조절함으로써 formalin으로 유발된 악안면 통증발생 및 전도에 관여함을 알 수 있다.
본 연구는 항산화, 항염증 효과를 가지는 acaiberry를 이용하여 악안면 통증의 조절능력에 대해 평가하고자 하였다. 실험동물의 악안면 통증유발모델에서 acaiberry는 통증의 주요전달경로인 p38 MAPK의 활성을 조절함으로써 통증의 완화효과를 나타내었다. 또한 산화적 스트레스 인자인 NOX4를 조절하여 항산화적 능력도 나타내었다. 이러한 acaiberry의 항염증, 항산화효과는 악악안면 통증조절에 유용하게 활용할 수 있을 것으로 생각된다.
본 연구에서는 formalin으로 유발된 악안면 염증성 통증 모델에서 acaiberry의 진통작용과 항산화작용을 확인하고자 하였다.
실험동물의 악안면 통증은 수염부에 5% formalin (50 μl)을 주입하여 유발하였고 45분간 행위반응을 측정하였다. Acaiberry의 통증행위반응 조절효과를 확인하기 위해 formalin주입 30분 전 실험동물에게 복강투여 하였다. Acaiberry의 통증행위반응조절에 대한 생리적 기전을 확인하기 위해 항염증과 항산화의 지표인 p38 MAPK의 활성 및 NOX4의 발현을 단백정량분석법을 통해 평가하였다.
Acaiberry (16, 80, 160 mg/kg)의 복강투여는 실험동물의 통증행위반응을 대조군(290±17.4)에 비해 농도 의존적(205.3±21.8, 137.8±21.8, 53.5±30.2)으로 감소시켰다. 이러한 통증행위반응은 시간의 경과에 따라 변화를 나타내었다. Formalin의 주입으로 인한 통증행위반응은 15분 이후부터 증가하여 25분, 30분에 가장 높게 나타났으며 40분까지 지속되다가 45분에 감소되었으며, 15∼40분에서 증가되었던 통증행위반응은 acaiberry의 복강투여로 인해 현저하게 감소되었다. 또한 acaiberry의 복강투여는 실험동물의 연수와 부신에서 p38 MAPK활성 및 NOX4의 발현을 감소시켰다.
Acaiberry은 포르말린으로 유도한 악안면 통증에서 실험 동물의 통증행위반응을 유의하게 감소시켰으며, 이는 p38 MAPK 및 NOX4 경로의 조절을 통한 항염증 및 항산화 작용에 의한 것으로 사료된다.