오랜 기간 동안 유기합성 제초제는 저렴한 비용과 높은 제초활성 등의 이유로 다양한 종류의 잡초를 제거하기 위해 사용되어 왔다. 하지만 세계적으로 환경에 대한 관심이 높아지면서, 종래에 사용하던 유기합성 제초제를 이용한 잡초관리에 대한 부정적 의식이 증가하는 추세이다. 또한 제초제 연용에 의한 저항성 잡초의 출현 빈도가 늘어나 이를 대체 할 수 있으며 낮은 인축독성과 생분해가 가능하고 선택성이 높은 친환경 제초제에 대한 관심이 커지고 있다(Hoagland, 1990). 특히 미생물이 생산하는 제초활성 물질의 경우 효율이 높고(Duke et al., 1996, Lydon et al., 1999) 환경친화적인 특징을 지녀 연구재료로써 뿐만 아니라 산업적 응용분야에서도 큰 관심을 받고 있다.
미생물 기원의 제초활성 물질은 세균이나 곰팡이, 또는 방선균으로부터 분비되는 생리활성 물질 중 하나로 식물독소(phytotoxin)로 분류된다. 대표적인 미생물 유래의 식물독소 또는 제초활성 물질의 예로 세균으로는 Pseudomonas syringae가 생산하는 phaseolotoxin, syringomycin, tabtoxin (Bender et al., 1999)등이 있으며, 곰팡이의 경우는 Colletotrichum gloeosporioides (Templeton et al., 1984), Phytophthora palmivora, Morenia adorata (Misra, 2005) 등이 알려져 있고, C. gloeosporioides와 M. adorata는 미국에서 상품으로도 개발된 바 있다(Misra, 2005).
Streptomyces 속을 포함하는 방선균은 균사형태로 생장하는 그램 양성 토양미생물로서, 500가지 이상의 속으로 분류되며 세균 속에서도 가장 큰 그룹을 형성하고 있는데, 제초제 등의 항생물질뿐 아니라 다양한 종류의 유용한 2차 대사산물을 합성하기 때문에 학문적으로나 산업적 응용측면에서 연구자들의 관심을 끌고 있다(Joseph et al., 2012). 지금까지 방선균에서 생산하는 2차 대사산물을 활용한 제초활성 물질의 예로는 Streptomyces saganonensis가 생산하는 herbicidin과 herbimycin (Chang et al., 2006; Li et al., 2003), Streptomyces actinomycetes가 생산하는 anismycin, 그리고 Streptomyces viridochromogenes가 생산하는 bialaphos (Bayer et al., 2004; Duke et al., 1996), Streptomyces albus subsp. chlorinus NRRL B-24108가 생산하는 albucidin (Hahn et al., 2009), Streptomyces viridichromogenes와 Streptomyces hygroscopicus에서 분리된 glufosinate-ammonium (Hoerlein, 1994) 등이 있다. 방선균은 이 외에도 많은 종류의 2차 대사산물을 합성하며 그 중에서 일부(bialophos, ansamitocins 등)는 상업화 되어 있다. 그러므로 방선균은 지금까지 알려지지 않은 전혀 새로운 작용기작을 갖는 제초활성을 발현하는 생리활성물질을 생산할 가능성이 있으며, 이러한 가능성은 기존 제초제 작용기작과는 다른 메커니즘으로 살초력을 발휘할 수도 있을 것이다(Saxena et al., 2001).
본 연구는 한국생명공학연구원 미생물 자원센터로부터 분양받은 약 3,000 여종의 방선균 배양액을 대상으로 바랭이에 대한 살초활성 평가를 통해 후보 균주를 선발하고 염기서열 분석을 하여 균을 동정하였다. 또한, 주요 문제 잡초와 난방제 잡초에 대한 온실 및 포장조건에서의 제초 활성 평가를 통해 보다 친환경적이며 효율적인 잡초 관리를 위한 천연물 제초제로의 개발 가능성을 검토하였다.
실험에 사용한 방선균은 충청북도 청원군 대청호 주변 산림 토양으로부터 HV한천(Humic acid-Vitamin agar) 배지(0.1% humic acid : dissolved in 0.2N NaOH, 0.05% Na2HPO4, 0.171% KCl, 0.005% MgSO4, 0.001% FeSO4·7H2O, 0.002% CaCO3, 50 ppm cycloheximide, 10 ppm nalidixic acid, thimine-HCl을 비롯한 8종 및 2% agar) (Hayakawa et al., 1987)를 사용하여 분리하였다. 분리한 방선균의 보존을 위한 배양은 Bennett’s medium (1% glucose, 0.1% yeast extract, 0.2% Bacto-peptone, 0.1% beef extract)에서 이루어 졌다(Hesseltine et al. 1954). 또한, 방선균의 제초 활성 평가를 위한 배양은 28∘C에서 GSS 배지(1% soluble starch, 2% glucose, 2.5% soybean meal, 0.1% beef extract, 0.4% yeast extract, 0.2% NaCl, 0.025% K2HPO4 and 0.2% CaCO3)를 이용하였다(Kim et al., 1989).
방선균 유전체는 Qiagen사의 DNeasy Blood & Tissue kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany)을 사용하여 제조사에서 제공하는 방법에 따라 순수분리하였는데, 5 mL Bennett’s media 에서 1일 배양한 세균을 1.5 mL 튜브로 옮겨 원심분리하여 상징액을 제거하였다. 남아 있는 세균 덩어리를 enzymatic lysis buffer (20 mg mL-1 lysozyme, 2 mM EDTA, 1.2% Triton X-100, and 20 mM Tris-Cl, pH 8) 180 μl에 현탁하여 37°C에서 1시간동안 방치한 뒤 제조사에서 제공하는 AL buffer에 proteinase K를 첨가하고 56°C에서 30분간 반응시켰다. 이 후 200 μl의 에탄올을 첨가하고 키트에 포함된 컬럼을 이용하여 순수 분리하였다. 최종적으로 분리된 DNA는 AE(제조사 제공) buffer에 용리(elution)하여 냉장 보관하였다.
방선균 유전체로부터 16S rRNA를 암호화하는 유전자를 PCR로 얻어낸 뒤 서열분석을 하고((주)제노텍, 대전, 대한민국), 밝혀진 유전자 서열은 BLAST를 통해 NCBI의 데이터베이스의 염기서열과 비교하였다. 염기서열 비교결과로 얻은 후보군 중에서 유사도가 높은 후보군 20종의 서열을 clustal w (1.6)를 이용하여 정렬하고, 유사도가 매우 높은 부분을 제외한 나머지 서열을 트리밍한 뒤, Neighbour-Joining method (PHYDIT program version 3.0)을 통해 phylogenetic tree를 작성하였다.
방선균 배양액의 살초력을 평가하기 위하여 원예용 상토를 충진한 350 cm2 사각 플라스틱 폿트에 바랭이를 포함한 화본과 잡초 5종과 까마중을 포함한 광엽 잡초 5종을 파종하여 온실(30/20±5°C, Light/Dark=14/10h)에서 토양처리용은 1일, 경엽처리용은 12일 동안 생육시켰다. 이때, 토양처리는 원예용 복합비료가 첨가된 사질 양토를 사용하였다. Bennett’s media에서 1주일간 배양한 방선균 배양액(Tween-20®, 0.1%)을 폿트당 14 ml량으로 분무처리하고 동일한 온실에서 관리 후 토양처리는 14일, 경엽처리는 7일 후에 외형적인 증상 및 약효를 기준표에 의해 달관조사(0; 효과 없음, 100; 완전고사)하였다.
상기 배양조건에서 배양한 S. scopuliridis KR-001 균주 배양액(1 L)을 감압농축기(EYELA SB-1200, EYELA Shanghai CO., LTD)를 이용하여 농축한 후(45°C, 70 rpm), 헥산, 에틸아세테트, 부탄올 및 물 층으로 분획하였다. 각 용매 분획물을 다시 동일한 조건으로 감압 농축하여 용매를 완전히 건조시킨 후, 사용할 때까지 -20°C 냉동고에 보관하였다.
용매 분획의 살초력을 평가하기 위하여 표면적 38.5 cm2 polystyrene 컵에 원예용 상토를 충진한 후 바랭이 종자를 10~15립씩 파종하여 온실에서 관리하다가 파종 9일 후에 각 용매 분획 농축물을 약제 조제액(아세톤 50%, 0.1% Tween-20®)으로 8, 16, 32, 63, 125, 250 및 500 μg ml-1 농도가 되도록 희석 조제하여 폿트당 5 ml씩 처리하였다. 처리 5일 후에 약효 기준표에 의해 살초력 정도를 달관 조사하였다.
용매 분획물 중 에틸아세테트 분획물에서 바랭이에 대한 살초력이 가장 우수하였으므로, 에틸아세테트 분획물의 토양 및 경엽처리 효과를 평가하였다. 배양액의 살초활성 평가방법과 동일하게 주요 잡초를 파종하고 온실조건에서 1일(토양처리)과 9일(경엽처리) 동안 생육시킨 후, 에틸아세테트 분획물을 약제 조제액으로 62.5, 125, 250, 500, 1,000 및 2,000 μg ml-1 농도가 되도록 희석 하여 폿트당 14 ml씩 처리하였다. 토양처리는 14일, 경엽처리는 7일 후에 약효 기준표에 의해 달관 조사하였다.
온실조건에서 주요 잡초에 대한 살초력을 확인한 에틸아세테트 분획물의 적용확대 평가를 위해 2011년 10월 중하순경에 대전광역시 유성구 지역에서 환삼덩굴, 쑥, 쇠뜨기, 클로버가 자생하고 있는 지점을 선정하여 수행하였다. 처리 구획은 1×1m로 하였으며, 에틸아세테트 분획물의 최종 처리농도가 2,000 및 4,000 μg ml-1가 되도록 조제하여 처리구당 200ml씩 분무 처리하였다. 처리 후 환삼덩굴은 5, 10, 15일후, 쑥과 쇠뜨기는 5, 8, 10일 후, 클로버는 4, 8, 12일 후에 육안으로 살초효과를 달관 조사하였다.
최근 환경부가 환경위해잡초로 지정할 정도로 심각한 문제가 되고 있는 가시박에 대한 에틸아세테트 분획물의 방제효과를 온실 및 포장조건에서 평가하였다. 온실조건에서 3엽기까지 생육시킨 가시박에 에틸아세테트 분획물 을 약제 조제액으로 최종처리 농도가 1,000 및 2,000 μg ml-1 이 되도록 조제하여 폿트 당 10 ml씩 처리하여 7일 후 에 방제효과 정도를 달관 조사하였다. 한편, 포장조건에서 의 가시박 방제력을 확인하기 위해 경기도 양평군 앙덕리 남한강변 주변에 가시박이 자연 발생된 지점을 선정하여 1×1m로 구획하여 에틸아세테트 분획물을 1,000 및 2,000 μg ml-1 농도로 처리하여 5, 8, 14일 후에 달관 조사하였다. 이 때, 가시박의 생육정도는 12~16엽기이었으며, 전장의 길이 는 약 2~3 m 내외였다.
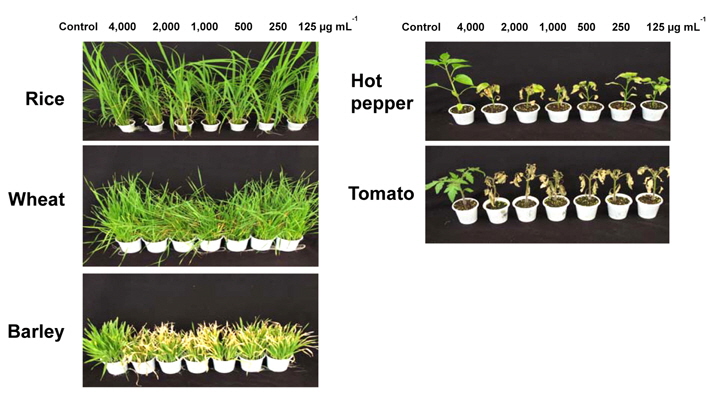
에틸아세테트 분획물의 주요 작물에 대한 약해 정도를 평가하였다. 대상작물은 벼, 밀, 보리 등 화본과 작물 3종과 고추 및 토마토 등 광엽작물 2종이었으며, 처리 당시 각 작물의 생육상황은 벼 3.5엽, 밀 1.2엽, 보리 1엽, 고추 7.3엽, 토마토 4.4엽이었다. 처리농도는 125, 250, 500, 1,000, 2,000 및 4,000 μg ml-1이었고, 처리 14일 후에 약해 정도를 육안으로 달관 조사하였다.
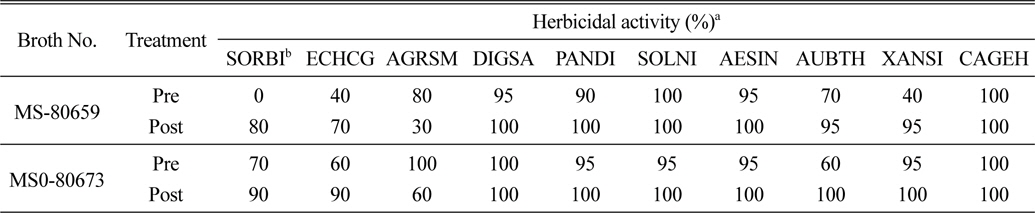
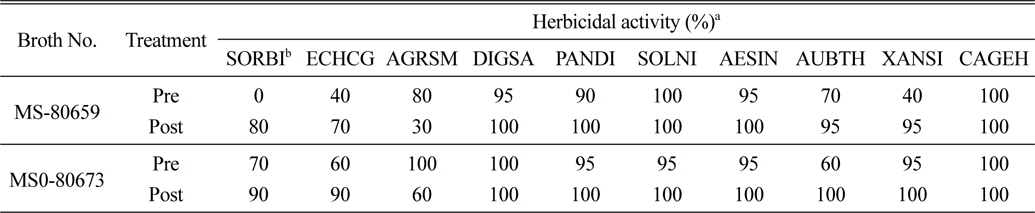
한국생명공학연구원으로부터 약 3,000여 종의 토양 방선균 배양액을 분양받아 바랭이(Digitaria sanguinalis)를 대상으로 제초활성 정도를 평가하였는데, 완전고사(100%) 수준의 살초력을 나타내는 50여 종의 후보 방선균을 선발하였다(자료 미제시). 선발된 후보 방선균 중 2종의(Code No. MS-80659, MS-80673) 배양액에서 토양처리 효과는 물론 특히 경엽처리에서 강력한 살초력을 발현하는 것을 확인하였다(Table 1). 두 균주 배양액은 살초력의 발현이 매우 속효성이며 약효 지속효과도 상당히 길게 유지되는 살초특성을 확인하였다. 경엽처리의 경우 24시간 후부터 외형적인 살초증상이 발현되기 시작하여 3일 후에 대부분의 잡초를 고사시켰으며, 처리 10일 이후에도 효과가 지속되었다. 외형적으로 발현되는 주된 증상은 고사(burndown) 이었으며, 일부 초종에서는 괴사(necrosis)증상도 발현되었다.
방선균은 의약용 항생제를 비롯하여 다양하고 유용한 생리활성물질을 생성하는데, Streptomyces hygroscopicus가 분비하는 2차 대사산물로부터는 bialaphos가 천연물 제초제로 개발되었으며(Tachibana et al., 1986), Streptomyces 속에서 유래한 methoxyhygromycin도 천연 제초활성 후보소재로의 가능성이 보고되어 있다(Lee et al., 2003). 따라서 제초활성 평가를 통해 선발한 2종의 토양 방선균 배양액도 제초활성을 발현하는 대사물질을 생성할 가능성이 매우 높을 것으로 판단하였다.
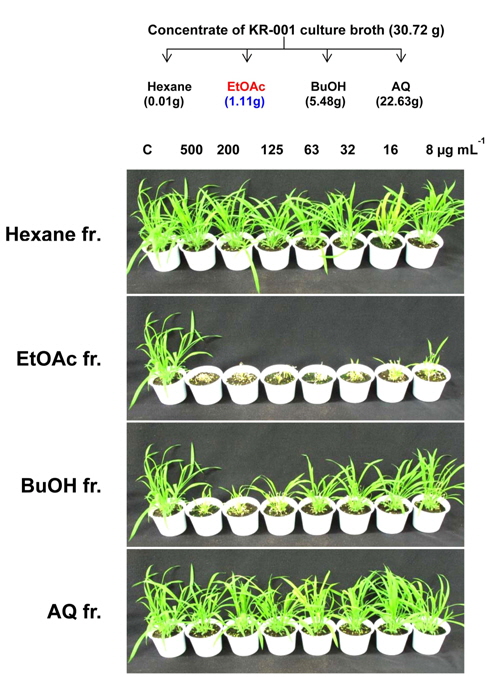
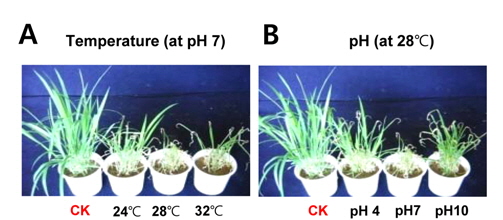
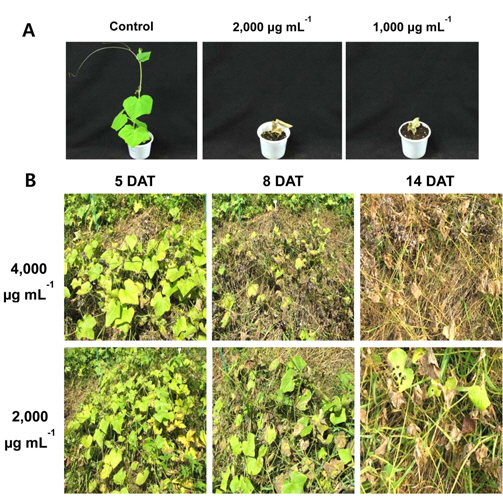
강력한 제초활성을 발현하는 2종 후보 방선균의 최적배양 조건을 확립하였고, 최적 배양조건에서의 살초력 정도를 평가하였다. 두 균주의 최적 배양조건은 배양온도 28°C, pH 7, 배양기간은 4-6일로 일반적인 방선균의 배양조건과 비슷하였으며, 이렇게 확립한 최적 배양조건에서 배양한 배양액의 바랭이에 대한 살초력도 가장 우수하였다(Fig. 1A and B).
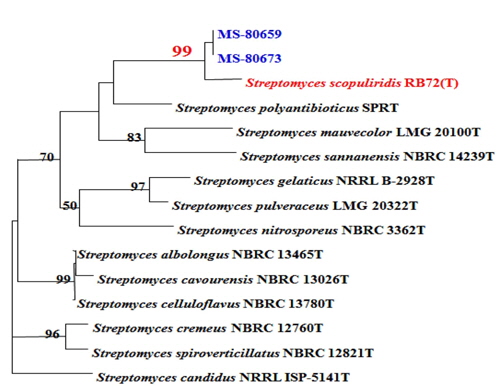
강력한 살초력을 발현하는 두 균주 동정을 위해 16SrDNA의 유전자 서열 약 1.4 kb를 확보하여 이 전체 서열을 BLAST를 통해 NCBI 데이터베이스와 비교한 결과 두균주 모두 Streptomyces scopuliridis RB72와 99% 이상의 상동성을 나타내어 가장 유사한 속이라 판단되었다(Fig. 2). BLAST의 결과로 얻어낸 유전자서열 유사도가 높은 후보군 중에서 13종의 후보군 서열을 대상으로 PHYDIT 프로그램을 통해 계통분류학적 조사를 수행한 결과, MS- 80659와 MS-80673이 S. scopuliridis RB72와 가장 유연관계가 높음을 확인 할 수 있었다(Fig. 2). 따라서 MS-80659 와 MS-80673 두 균주는 모두 S. scopuliridis의 아속으로 분류 할 수 있으며, 두 균주 중에서 살초력이 상대적으로 높은 MS-80673을 Streptomyces scopuliridis KR-001로 명명하고 한국생명공학연구원 생명자원센터(Korea Culture Type Collection; KCTC)에 기탁하였다(KCTC 12156BP). 이후 연구 과정에서는 S. scopuliridis KR-001을 대상으로 실험을 진행하였다.
가장 유사한 모델 균주인 S. scopuliridis RB72는 항생제인 bacteriocin을 생합성하며 세균과 곰팡이에 대한 길항능력은 갖고 있는 것으로 알려져 있으나(Farris et al.,2011), 아직까지 식물에 대한 길항능력이나 제초활성물질의 분비능력에 대한 보고는 없다(Choi et al., 2012a). 따라서 본 연구를 통해 밝혀진 S. scopuliridis KR-001은 16SrDNA 서열만으로 비교했을 경우에는 S. scopuliridis RB72와 가장 유사한 것으로 나타나지만 특별한 생리활성을 나타내는 새로운 타입의 아속(subspecies)일 가능성도 고려해야 할 것으로 판단되었다.
S. scopuliridis KR-001 균주 배양액 농축물의 헥산, 에틸아세테트, 부탄올, 물의 용매 분획물 중 헥산과 물 분획물에서는 제초활성이 전혀 없었고, 에틸아세테트와 부탄올 분획물에서 활성이 발현되었는데 특히 에틸아세테트 분획물에서 가장 강력한 살초력을 보였다(Fig. 3). 에틸아세테트 분획물 8, 16, 32, 63, 125, 250 및 500 μg mL-1 농도에서의 바랭이에 대한 살초력은 각각 80, 90, 95, 100, 100, 100 및 100%이었다. 이때, 각 용매 분획별 활성물질의 수율은 헥산 분획물 0.03%, 에틸아세테트 분획물 3.61%, 부탄올 분획물 17.87%, 물 분획물 73.67%이었다. 따라서 S. scopuliridis KR-001 배양액이 나타내는 살초성분 중 주요 제초활성을 발휘하는 물질은 에틸아세테트 분획물 내에 존재할 것으로 생각되어 이후 연구는 에틸아세테트 분획물을 농축하여 수행하였다.
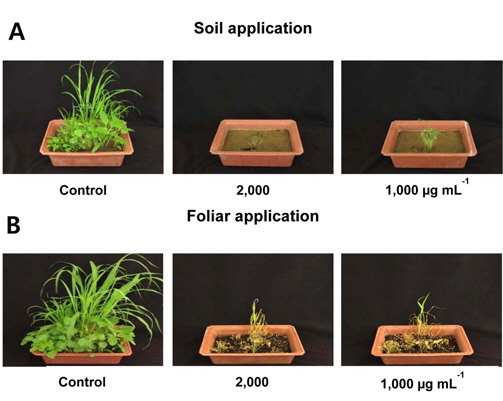
처리방법에 따른 살초활성의 특징을 살펴 보기 위해 에틸아세테트 분획물을 토양 및 경엽처리로 구분하여 10종(까마중, 어저귀, 자귀풀, 도꼬마리, 메꽃, 미국개기장, 돌피, 수수, 바랭이, 개밀)의 잡초를 대상으로 활성 정도를 비교하였다. S. scopuliridis KR-001 배양액 에틸아세테트 분획물은 토양처리와 경엽처리 모두에서 우수한 활성을 나타냈는데, 토양처리 시 2,000 μg ml-1 농도에서는 대상잡초 10종에 대한 살초력이 95~100%이었으며, 1,000 μg ml-1 농도에서도 수수와 어저귀를 제외한 대상 전 초종에 대해 완전한 방제효과(100%)를 나타냈다(Fig. 4A). 또한, 경엽처리에서도 1,000 및 2,000 μg ml-1 처리농도에서 시험대상 잡초에 대한 살초력은 95~100%로 강력한 활성을 보였다(Fig. 4B).
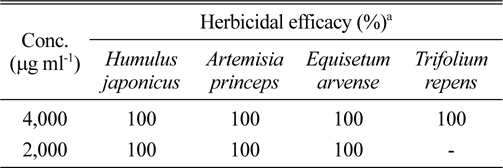
S. scopuliridis KR-001 균주 배양액 에틸아세테트 분획 물은 환삼덩굴이나 쑥과 같은 기존 제초제로서 방제하기 매우 까다로운 난방제 잡초에 대한 방제효과도 매우 우수했다(Table 2). 에틸아세테트 분획물은 환삼덩굴(Humulus japonicas)에 대해 뛰어난 방제효과를 나타냈는데, 2,000 밑 4,000 μg ml-1 농도에서 처리 5일 후에는 각각 30 및 40% 정도의 살초력을 보였다가 이후 급속하게 효과가 진 전되어 10일 후에는 각각 95와 100%, 15일 후에는 처리 농도 모두 100%의 살초력을 나타내었다. 또한, 처리 후 시간이 경과하면서 살초력이 계속 증가되어 처리 15일 이 후까지 살초력이 유지되어 약효지속효과가 지속되는 특성 을 보였다. 2,000 및 4,000 μg ml-1 농도에서 쑥(Artemisia princeps)에 대하여 완전한 방제효과를 나타내었는데, 처리 3일이 지나면서 효과가 발현되기 시작하여 5일 후에는 4,000 μg ml-1 농도에서는 완전하게 방제되었고, 2,000 μg ml-1 농도에서도 80%이었다가 8일 후에는 모두 100%로 완전 방제되었다. 쇠뜨기(Equisetum arvense)에 대해서는 약효발현이 매우 빨라서 처리 5일 후에 2,000 및 4,000 μg ml-1 농도에서 각각 90%와 95%의 살초력을 나타내었고, 8 일 이후에는 완전고사 되었다. 한편, 클로버(Trifolium repens) 의 경우에는 처리 4일이 지나면서 잎에 반점이 형성되어 진행되다가 8일 이후에 잎이 완전하게 고사되고 12일 이 후에는 줄기까지 고사되었다. 따라서 S. scopuliridis KR- 001 배양액 에틸아세테트 분획물에는 난방제 잡초를 효과 적으로 제어할 수 있는 제초활성물질이 포함되어 있음을 추측할 수 있었다.
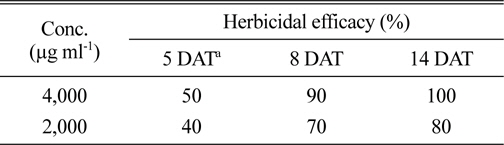
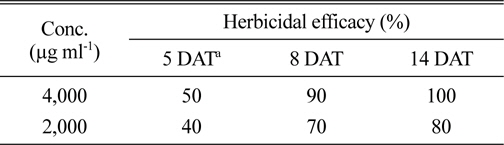
S. scopuliridis KR-001 균주의 에틸아세테트 분획물은 온실조건에서 가시박에 경엽처리 했을 때, 24시간이 경과하면서 외형적인 증상이 발현되기 시작하였고, 5일이 지나면서 1,000 μg ml-1와 2,000 μg ml-1 농도 모두 가시박이 완전하게 방제되었다(Fig. 5A). 포장조건에서는 4,000 μg ml-1 농도에서 처리 후 5일, 8일 및 14일의 가시박 방제효과가 각각 50, 90 및 100%이었으며, 2,000 μg ml-1 농도에서의 방제효과는 각각 40, 70 및 80%이었다. 또한, 처리 2주일 후에도 재생되는 개체가 없는 것으로 관찰되어 약효지속성이 우수한 특성을 보였다(Table 3, Fig. 5B). 가시박은 북아메리카가 원산지인 박과의 1년생 귀화식물로 환경부에서는 야생동식물보호법 시행규칙에 생태계교란 야생식물로 지정한 잡초이다(Choi et al., 2012b; Kang et al.,2011). 농경지에 발생하는 가시박은 linuron이나 simazine으로 일부 방제가 가능하고, 도로변이나 축사 등 비농경지에 발생하는 가시박은 glufosinate ammonium이나 glyphosate를 경엽처리하면 방제가 가능하다고 알려져 있다(Lee et al., 2007). 그러나 가시박의 주된 발생지가 수원지, 강변, 도로변 등 사람들의 생활과 밀접한 곳에 있기 때문에(Moon et al., 2008) 유기합성 제초제를 이용한 방제에는 한계가 있다. 따라서 농경지 이외 지역에 발생하는 가시박을 방 제하기 위해서는 천연물 유래의 친환경적인 소재를 활용하는 것이 가장 이상적인 수단이 될 수 있을 것이다. 본 연구에서 발굴한 토양 방선균 S. scopuliridis KR-001 배 양액은 온실 조건뿐만 아니라 실제 포장에서 발생한 가시 박을 매우 효과적으로 방제하고 있음을 확인한 바, 향후 제형 연구 등을 통해 약효를 증진시키고, 실용화를 위한 대량생산 기술이 확립된다면 천연물 유래의 친환경적인 가시박 방제용 후보소재로의 활용 및 개발에 좋은 재료가 될 수 있을 것으로 판단하였다.
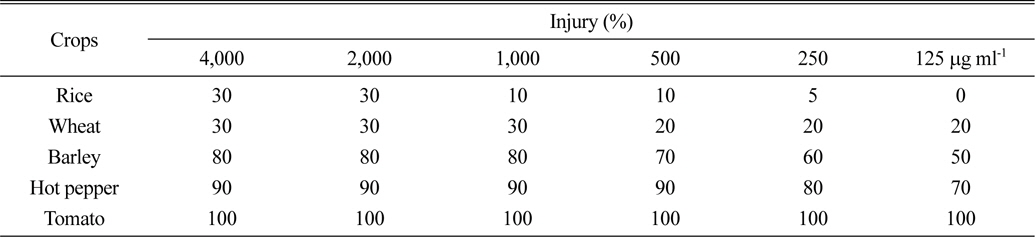
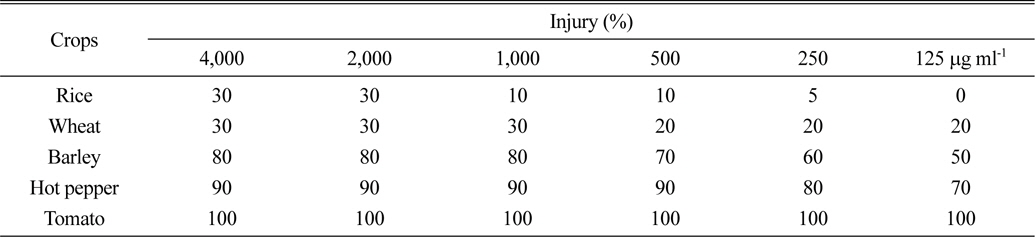
S. scopuliridis KR-001 균주 배양액은 대상작물 5종 모두 약해가 심하게 유발되어 작물 선택성은 없었다(Table 4 and Fig. 6). 특히 광엽작물인 고추와 토마토에서 심한 약해가 유발되었는데, 토마토의 경우에는 처리한 전 농도범위에서 100%의 약해가 발생하여 가장 심하였으며, 고추에서도 처리범위에서 70~90%의 약해가 관찰되었다. 화본과작물에서는 광엽작물에 비해 상대적으로 약해가 다소 낮았지만, 보리에서는 처리농도 범위에서 50~80%로 화본 과작물 중에서는 약해가 가장 크게 나타났다. 벼와 밀에서는 4,000 μg ml-1 농도에서 약해 정도는 30% 이하로 약간의 생장저해만이 관찰되는 수준이었고, 벼에서는 1,000 μg mL-1 이하 농도에서는 육안으로는 판단하기 어려운 수준이었다. 따라서 S. scopuliridis KR-001 배양액은 뚜렷한 작물선택성은 없었으며, 작물 종에 따라 약해 유발 정도의 차이가 있었다. 작물 종에 따른 약해 정도는 작물의 종류 및 종자 크기에 따라 차이가 있으며(Ibrahim et al., 2004; Lee et al., 2007), 이러한 원인은 식물에서 제초활성 물질의 활성기작이 작물 종에 따라 차이가 있을 수 있다고 하였다(Vaughn et al., 1993). 작물에 대한 약해 정도 평가로부터 본 연구에서 확보한 S. scopuliridis KR-001 배양액은 작물 선택성이 없기 때문에 비농경지, 강변, 생활주변 등에서 비선택성 경엽처리제로의 실용화를 검토해야 할 것으로 판단하였다.