Colonial ascidian, Eusynstyela monotestis (Tokioka, 1953), is newly reported from Korean waters. The specimens of E. monotestis examined in this study were collected at subtidal zone of Beomseom, Munseom, Seopseom and Chagwido in Jeju-do by SCUBA diving. The genus Eusynstyela Michaelsen, 1904 is also new to Korean waters and it is distinct from other genera by having branchial sac with folds, longitudinal stigmata, hermaphrodite gonads on both sides, 1-2 male follicles in each gonad and body wall with endocarps. Eusynstyela monotestis is distinct from other species by having gonad with only single male follicle. In this paper, detailed descriptions and photographs of Eusynstyela monotestis (Tokioka, 1953) are provided.
The family Styelidae Sluiter, 1895 is large family with 536 species either colonial or solitary. Up to date, 19 species of 7 genera in this family have been reported in Korean waters (Rho, 1966, 1975, 1977; Rho and Heo, 1984; Rho and Lee, 1989, 1991; Rho and Park, 1998; Rho and Cole, 1999). The genus
The specimens of
The systematic scheme of ascidians was adopted from Gittenberger (2014). Specimens are deposited in Natural History Museum, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea (EWNH MAS 4-12).
Order Stolidobranchia Lahille, 1887 Family Styelidae Sluiter, 18951*Genus Eusynstyela Michaelsen, 1904
1*Eusynstyela monotestis (Tokioka, 1953) (Fig. 1) Polyandrocarpa (Eusynstyela) monotestis Tokioka, 1953: 247-248, fig. XLVIII.
Material examined. One colony, Korea, Jeju-do, Beomseom, 5 Sep 2013, Seo SY (EWNHMAS4), 25 m deep by SCUBA diving; 1 colony, Jeju-do, Seopseom, 4 Aug 2011, Song JI (EWNHMAS12); 1 colony, Jeju-do, Chagwido, 17 Aug 2001 (EWNHMAS5); 2 colonies, Jeju-do, Chagwido, 8 Jun 2001 (EWNHMAS6-7); 1 colony, Jeju-do, Chagwido, 23 Feb 2001 (EWNHMAS8), 25 m deep by SCUBA diving; 1 colony, Jeju-do, Munseom, 7 Nov 2000, Song JI (EWNHMAS9), 18 m deep by SCUBA diving; 1 colony, Jeju-do, Chagwido, 6 Nov 2000 (EWNHMAS10), 20 m deep by SCUBA diving; 1 colony, Jeju-do, Munseom, 13 Aug 1985, Song JI (EWNH MAS11).
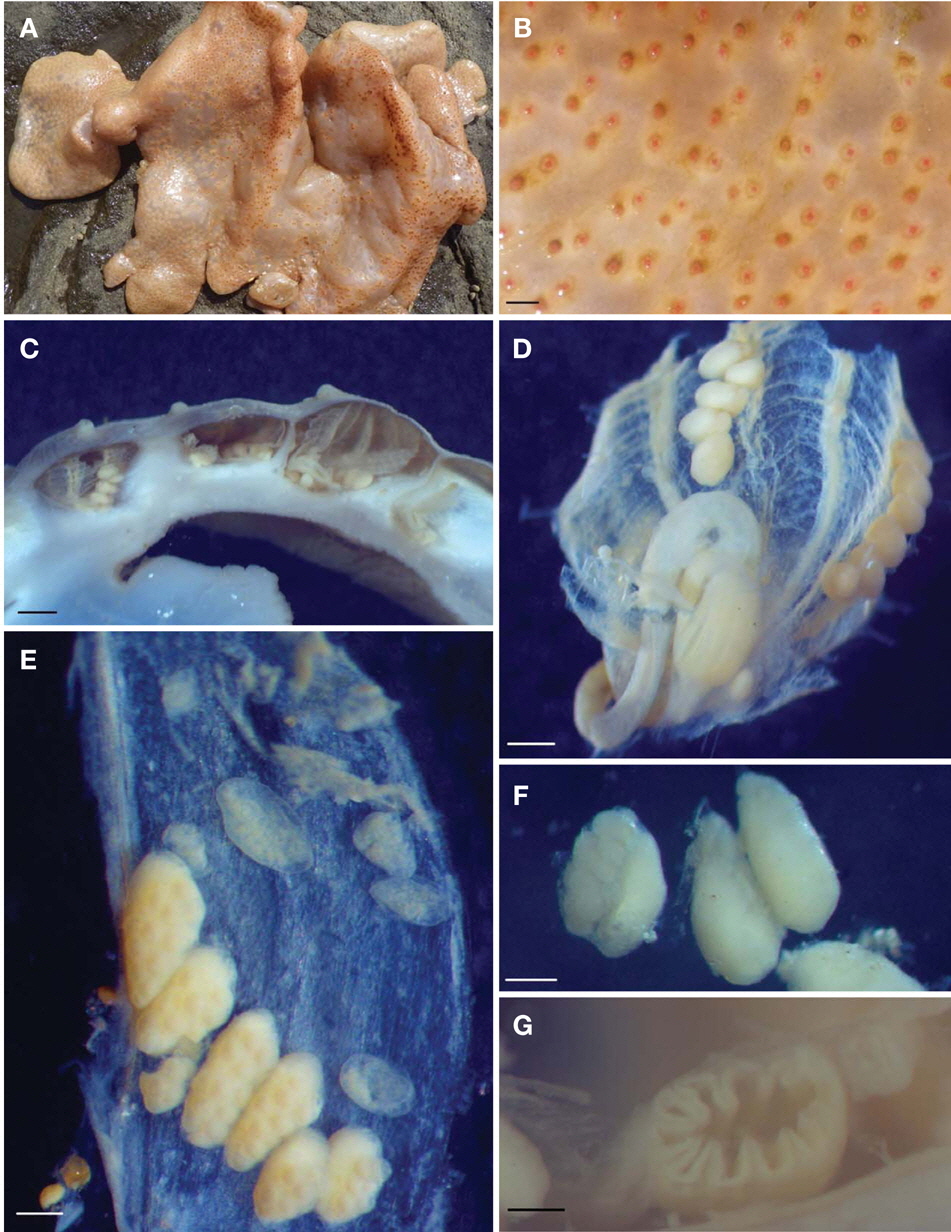
Description. Colonial ascidians flat and incrusting form having zooids embedded in common tough opaque whitish tunic (Fig. 1A). Lower section of common tunic dotted with small, yellowish and fibrous grains. Largest colony 119×230 mm in extent and 3-17 mm in thickness. Color of zooid light yellowish orange (Pantone 149C) in living and brownish white (Pantone 468C) in preservative. Color of apertures dark brown and dark brownish orange (Pantone 160C, 165C) in living (Fig. 1B).
Zooids usually vertical in position, though sometimes horizontal in thin colony, attached to substrate by ventral region (Fig. 1C). Zooids 1.38-2.42 mm long excluding siphons and 2.85-3.64 width. Interval between zooids 0.73-2.98 mm. Both apertures on dorsal side, protrude as mammalian nipple, open on surface of colony without cloacal systems and 4 lobed. Interval between both apertures 1.2 mm on average, up to 1.69 mm. Branchial apertures with fine tentacles. Zooid’s mantle thin with endocarps (Fig. 1E).
Branchial sac with four folds consisting of 14-19 internal longitudinal vessels. Branchial formulae 1.38 mm: D0(4)0 (3)0(4)0(3)0E; 2.42 mm: D0(7)1(1)0(4)1(3)E. First and third folds fully developed. Branchial sac with about 18-24 stigmata rows of 50-60 longitudinal stigmata. Dorsal lamina thin membrane. Oesophagus short and stomach about 0.62 mm long with 12-14 plications (Fig. 1D, G). Gastric caecum conspicuously project into pole of gut loop. Gut loop simple, extending from one-third to one-fourth of length of branchial sac. Rectum long and atrial apertures have smooth border.
Hermaphrodite gonads arranged along fourth branchial fold on both sides of body. 4-8 gonads on each side of body (Fig. 1D). Each gonad contains only a single elongate male follicle and ovary with 8-16 oocytes (Fig. 1F). Gonad enclosed in a common membrane.
Distribution. Pacific Ocean: Korea (Beomseom, Munseom, Chagwido, Seopseom in Jeju-do), Japan (Miyose-no-takane, Kamegisho in Sagami Bay).
Remarks. The present specimens much resembles
But the zooids of this specimen are 1.38-2.42 mm long in contracted condition and are smaller than 5-9 mm of the original description of Tokioka. The present specimens were collected from subtidal zone at depth of 18-25 m, but the one of Tokioka (1953) was collected at the depth of 144 m.