This study examined the effects of the dietary inclusion of
양식어류의 생산성 향상과 어체의 품질 또는 면역성 향상을 위한 다양한 사료첨가제가 개발되고 있으나 이들 사료첨가제의 효과는 어종, 사료 조성, 첨가제 형태(추출 방법), 첨가제 농도 또는 사육실험 조건 등에 따라서 다르게 나타난다(Lindsay et al. 1984; Shiau and Yu 1999; Park et al. 2003; An et al. 2012). 최근 해산 어류용 사료첨가제로서 한약제(Kim et al. 1998, 2000),
조피볼락은 넙치와 더불어 국내 어류양식을 대표하는 중요한 양식대상어종으로서 2012년 조피볼락 양식생산양은 222,351톤에 이르지만(KOSIS 2013) 연중 양식에서 빈번하게 발생하는 질병의 발생이나 사육환경의 급변화에 따른 양식어류들의 대량폐사가 지속적으로 발생하고 있기 때문에 이러한 대량폐사를 줄이기 위한 다양한 사료첨가제의 개발은 지속적으로 필요하다.
해조류, 특히 김(
본 연구에서는 김과 다시마 추출물과 분말 첨가가 조피볼락치어의 성장, 사료이용성, 체조성 및 혈액성상학적 변화에 미치는 영향을 조사 하였다.
실험어는 일정한 크기의 조피볼락 치어를 경남 남해에 위치한 개인양어장에서 구입하여 운반하였으며, 사육실험을 시작하기 전에 1주간 사육환경에 적응시킨 후 실험어로 이용하였다. 적응기간 동안에는 상업용 부상사료(수협사료: 조단백질 함량 52%, 조지질 함량 7%)를 1일 2회 공급해 주었다. 실험에는 총 840마리를 이용하였으며, 40마리의 치어(시작시 평균 무게±SD: 5.0± 0.01 g)를 21개의 180 L 원형 유수식 FRP수조(수량: 150 L)에 무작위로 각각 분산 수용하였으며, 이때 수조당 환수량은 5.8 L/min이었다. 실험기간 동안 사육수온은 16.4-23.4℃ 범위(평균수온±SD: 21.1±1.96℃)이었다.
김 추출물은 건조 김 분말 40 kg을 대용량 추출용기에 넣고 증류수 1톤에 침지한 후 실온에서 3시간 동안 교반하면서 추출한 다음, 여과하여 상층액을 취해 3배 부피의 에탄올을 첨가하고 침전된 물질을 여과기로 제거한 뒤 여액을 취해 감압 농축하였다. 완전히 농축하여 에탄올과 수분을 제저한 시료에 다시 증류수를 첨가하여 용해시킨 다음 이를 김 추출물로 사용하였다.
다시마 추출물은 건조 다시마 분말 600 g을 대용량 추출용기에 넣고 증류수 15 L에 침지하였다. 실온에서 6시간 동안 교반하면서 추출한 다음, 5,000 rpm 4℃에서 20분간 원심분리하여 상층액을 취해 3배 부피의 에탄올을 첨가하고 침전된 물질을 뷰흐너 깔대기로 제저한 뒤 여액을 취해 감압 농축하였다. 완전히 농축하여 에탄올과 수분을 제저한 시료에 다시 증류수를 첨가하여 용해시킨 다음 이를 다시마 추출물로 사용하였다.
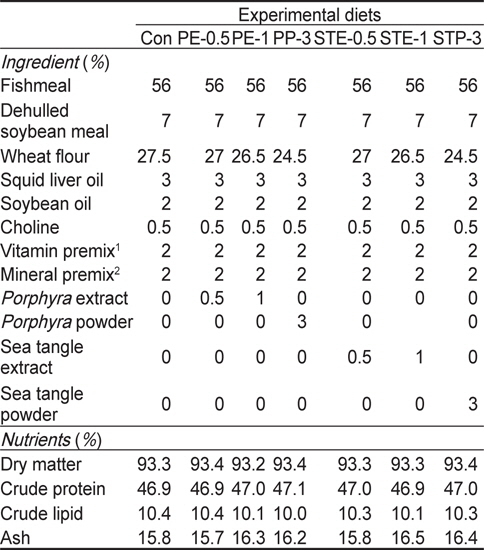
실험에 이용된 실험사료는 총 7종류의 실험사료[대조구(Con)-무첨가구, 김 추출물 0.5% 첨가 사료(PE-0.5), 김 추출물 1% 첨가 사료(PE-1), 김 분말 3% 첨가 사료(PP-3), 다시마 추출물 0.5% 첨가 사료(STE-0.5), 다시마 추출물 1% 첨가 사료(STE-1), 다시마 분말 3% 첨가 사료(STP-3)]를 준비하였으며(Table 1), 각 실험구는 3 반복구를 두었다. 김과 다시마의 추출물과 분말은 동일한 양의 소맥분 대신에 첨가해 주었다. 실험사료는 어 분과 대두박을 주요 단백질원으로 이용하였으며, 소맥분을 탄수화물 및 오징어간유와 대두유를 지질원으로 각각 이용하였다. 실험사료 원료는 3:1의 비율로 물과 섞어 펠렛제조기를 이용하여 실험사료를 제조하였다. 제조한 실험사료는 실온에서 건조시킨 후 -20℃ 냉동고에 보관하면서 필요시 마다 소량씩 사용하였다. 모든 실험어는 1주일에 7일간 1일 2회(07:00, 17:00)씩 매일 손으로 만복시까지 사료를 공급하여 주었으며, 사육실험 기간은 총 8주간이었다.
[Table 1.] Ingredient and chemical composition (%, DM basis) of the experimental diets
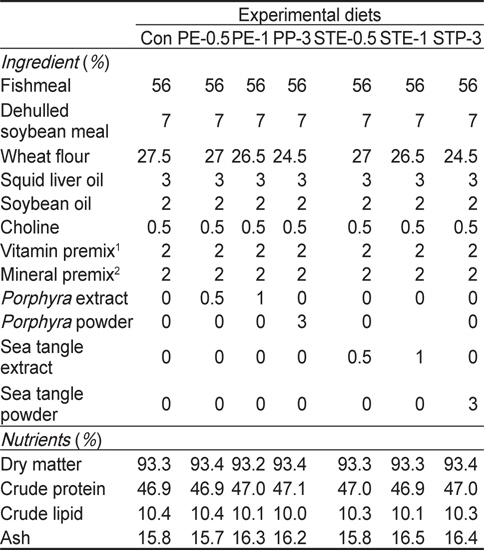
Ingredient and chemical composition (%, DM basis) of the experimental diets
일반성분 분석을 위하여 8주간의 사육실험 종료 후 생존한 조피볼락을 각 실험구에서 5마리씩 무작위로 샘플하여 전장과 무게를 측정하여 비만도(Condition factor, CF)를 계산하였으며, 간을 분리한 후 무게를 측정하여 간체장지수(Hepatosomatic index, HSI)를 계산하였다. 또한 각 실험구에서 3 마리를 무작위로 샘플하여 전어체의 일반성분분석을 AOAC 표준방법(1990)에 따라 분석하였다. 조단백질은 Kjeldahl method으로 조지방은 ether-extraction method으로 분석하였으며, 조회분은 550℃의 회화로에서 4시간 동안 태운 후 정량하였고, 수분은 105℃에서 24시간 동안 건조시킨 후 측정하였다.
8주간의 사육실험 종료 후 각 실험구에서 생존한 조피볼락을 무작위로 5마리씩 추출하여 미부정맥에서 채혈하여 3000 rpm에서 10분간 원심분리하여 혈장을 분리하였다. 실험어는 채혈 전 24시간 동안 절식시켰다. 분리된 혈청은 -70℃의 냉동고에 보관하여 분석에 사용하였으며, total protein, glucose, glutamate oxaloacetate transminase (GOT), glutamate pyruvate transminase (GPT), cholesterol, triglyceride는 자동혈액 분석기(Vitros DT60 II, Vitros DTE II, DTSC II Chemistry System, Johnson and Johnson Clinical Diagnostics Inc., New York, USA)로 분석하였다. 또한 혈액중의 IGF (Insulin-like growth factor)-1 activity의 측정하기 위해 Human IGF-1 EIA kit (Komabiotech, Korea)를 사용하여 분광광도계(Ultraspec 2001 pro. Amersham Phamacia Biotech, England)로 450 nm 에서 흡광도를 측정하였다.
One-way ANOVA와 Duncan's multiple range test (Duncan 1955)로서 SAS version 9.2 program (SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA)을 이용하여 각 실험구간의 유의성을 검정하였다.
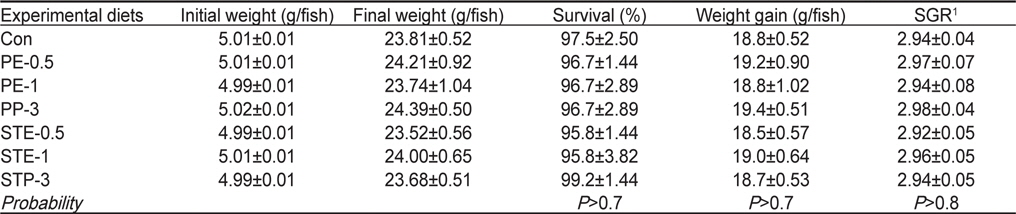
8주간의 사육실험 결과 조피볼락 유어의 생존율, 어체중 증가 (Weight gain) 및 일일성장율(Specific growth rate, SGR)은 모든 실험구간에 유의적인 차이가 나타나지 않았으며, 본 실험에 사용된 해조류의 형태(분말 또는 추출물) 및 첨가량에 따른 차이를 보이지 않았다(
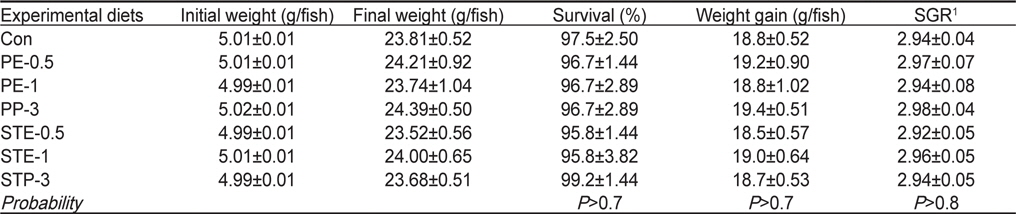
Survival (%), weight gain (g/fish) and specific growth rate (SGR) of Korean rockfish Sebastes schlegeli fed the experimental diets containing Porphyra extract (PE) and powder (PP), and sea tangle Laminaria japonica extract (STE) and powder (STP) for 8 weeks
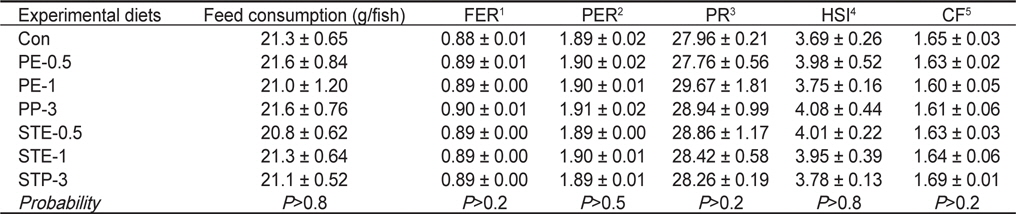
조피볼락 유어의 사료섭취량(g/fish), 사료전환효율(Feed efficiency ratio, FER), 단백질전환효율(Protein efficiency ratio, PER), 단백질축적율(Protein retention, PR), 간체장지수(Hepatosomatic index, HSI)와 비만도(Condition factor, CF)는 8주간의 사육실험 종료시 실험사료에 따른 유의적인 차이는 나타나지 않았다(
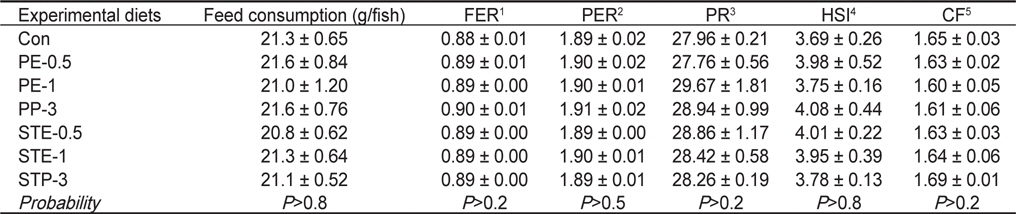
Feed consumption (g/fish), feed efficiency ratio (FER), protein efficiency ratio (PER), protein retention (PR), hepatosomatic index (HSI) and condition factor (CF) of Korean rockfish Sebastes schlegeli fed the experimental diets containing Porphyra extract (PE) and powder (PP), and sea tangle Laminaria japonica extract (STE) and powder (STP) for 8 weeks
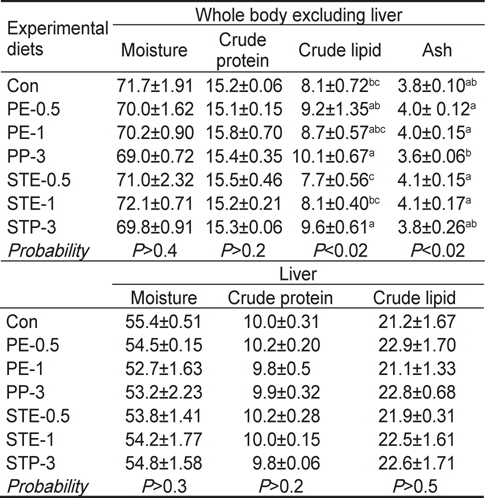
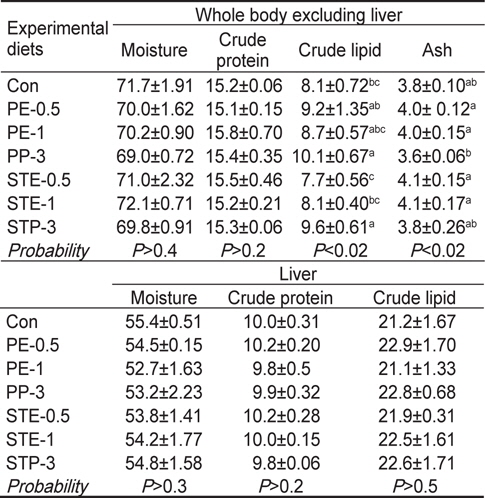
Chemical composition (%, wet weight basis) of the whole body excluding liver and liver of Korean rockfish Sebastes schlegeli at the end of the 8-week feeding trial
조피볼락의 간을 제외한 전어체와 간의 일반성분분석 결과 전어체의 수분과 조단백질 함량 및 간의 수분, 조단백질 및 조지질 함량은 실험사료에 따른 유의적인 차이를 보이지 않았다(
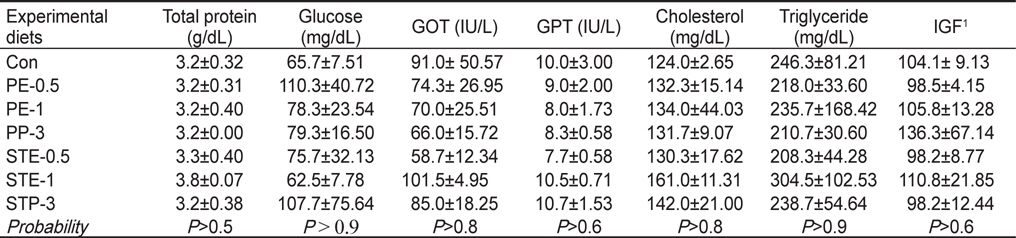
8주간 사육실험 종료시 생존한 조피볼락의 혈액성상학적 분석 결과 총단백질(total protein), glucose, GOT, GPT, cholesterol, triglyceride와 IGF는 사료내 김과 다시마의 첨가에 따른 유의적인 차이가 나타나지 않았으며(
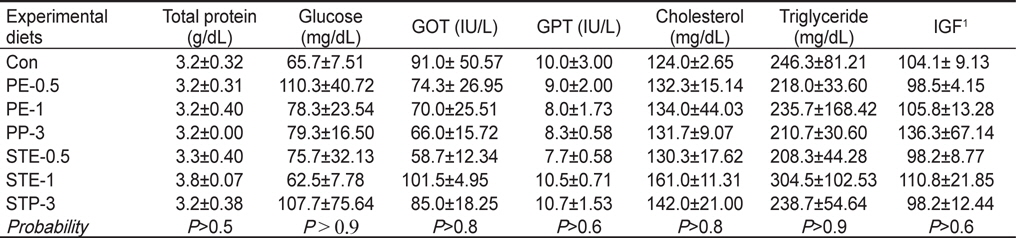
Plasma chemical composition of Korean rockfish Sebastes schlegeli at the end of the 8-week feeding trial
이상의 결과를 고려할 때 본 실험의 조건하에서 조피볼락 치어를 이용하여 사료내 김과 다시마의 추출물 또는 이들의 분말 공급시 조피볼락의 성장, 사료 이용성, 체조성 및 혈액성상학적 변화에 크게 영향을 미치지 않는 것으로 사료된다.