This study was conducted to develop an efficient control method for water foxtail in the field sowing barley and wheat seeds before rice harvesting. When thifensulfuron-methyl (75%) was applied 0, 5 and 10 days after rice harvesting, little phytotoxicity was observed on both barley and wheat. Percent of water foxtail control with thifensulfuron-methyl (75%) was more than 88% at three different application timing. When butachlor (5%) was applied 5 days before barley and wheat sowing, phytotoxicity on barley and wheat was severe. However, no phytotoxicity was observed on barley and wheat 5 and 10 days after rice harvesting. Percent of water foxtail control with butachlor 0 and 5 days after rice harvesting was 85-89%. However, it dropped to 74-80% when applied 10 days after rice harvesting. In the thifensulfuron-methyl treatment, the dry matter of barley and wheat was 96-108% and 100-108%, respectively when compared with untreated control. While, in the butachlor treatment, the dry matter of barley and wheat was 53-73% and 106%, respectively when compared with untreated control. Therefore, we recommend thifensulfuron-methyl (75%) 0-10 days after rice harvesting or butachlor (5%) 5 days after rice harvesting to provide efficient water foxtail control and safe barley and wheat production.
사료맥류의 벼 수확 전 입모중 파종 재배는 벼 수확과 맥류 파종 작업의 경합 회피와 파종노력의 생력화 및 적기 파종으로 인한 생산 안정화를 기할 수 있는 재배방법이다. 또한 파종기인 10월에 강우로 인한 벼 수확이 지연되거나 논 토양의 과습으로 인한 기계파종이 불가능할 경우에도 적기에 파종할 수 있는 재배방법이다. 벼 수확 10일 전에 보리를 21 kg/10a 파종하고 벼 수확 후 볏짚 피복 후 질소 추비를 50% 증비(135 kg ha-1)시 관행 산파재배와 수량이 대등하다고 했다(Ju et al., 1993). 사료용 호밀을 벼 입모중 25 kg/10a 파종은 파종 비용을 60% 절감할 수 있다고 하여(Ryu et al., 1988) 벼 입모중으로 맥류 파종패배가 벼 수확 후 산파보다 생력적인 재배방법임을 구명하였다. 이러한 벼 입모중 사료맥류 파종 재배 시 가장 문제가 되는 것은 동절기 논에서 초우점 잡초인 뚝새풀이다. 벼 수확 전 입모중 보리, 밀 파종 재배 시 발생된 잡초 중 뚝새풀이 95% 정도로 가장 많다(Kim et al., 1996, Ahn et al., 1997). 뚝새풀은 벼 수확 전에 대부분 발생하여 작물과의 경합력이 매우 크며, 답리작에서 맥류 재배시 가장 피해가 큰 잡초라고 하였다(Chin et al., 1977; Kim et al., 1975; Im et al., 1998). 1980년대에도 보리와 밀 재배지에서 최우점 잡초이며(Ha et al., 1983), 또한 1990에도 논과 밭에서 우점도가 매우 높은 잡초라고 하였으며 (Chang et al., 1990), Im et al. (2004)의 조사에서도 전체 밭작물 포장 및 동계작물 재배포장에서 최 우점 잡초는 뚝새풀이라고 하여 최근에도 동계 작물 재배지에서 가장 문제 잡초임을 확인하였다.
뚝새풀은 보리 재배 논에서 지속적으로 문제가 되고 있는 잡초임을 보여주고 있다. 이러한 뚝새풀은 15°C 부근에서 발아가 가장 잘되고, 생육에는 인산이 절대적으로 필요하다고 하며(Im et al., 1994, 1998), 실온에서 습윤상태로 2개월 정도 경과하면 휴면이 타파된다(Kim et al., 1996). 또한 뚝새풀은 볏짚 추출물에 의하여 발아 등 초기 생육이 억제되며(Lee et al., 1998), 벼와 콩 등 답전윤환 재배로도 발생이 현저히 감소한다고 했다(Yoo et al., 1995). 과원에서 뚝새풀의 초생재배로 다른 잡초의 발생을 억제시킬 수도 있다고 하는(Jung et al., 1998) 등 생리 생태에 대한 연구도 꾸준히 진행되어 왔다. 벼 수확동시 맥류 파종재배의 경우 뚝새풀의 방제는 밀 재배 시 butachlor +glyphosate 처리로 92% 이상(Kim et al., 1998), 보리 재배시 thifensulfuron-methyl의 처리로 90% 이상(Im et al., 2005) 뚝새풀을 방제할 수 있다고 했다. 또한 보리 재배시 후기에 광엽잡초는 bentazone의 처리로 광엽잡초를 방제할 수 있다고 하여(Chang et al., 1990) 보리 재배 시 잡초방제 체계를 확립하려는 연구는 꾸준히 이루어 졌다.
벼 수확 전 입모중 맥류 파종 재배 시 제초제처리에 의한 뚝새풀의 방제 연구도 오래 전부터 진행되었으며, 벼입모중 보리 파종 재배 시 벼 출수 후 20-30일에 butachlor 처리에서 벼 수량 영향 없고 뚝새풀 방제효과 양호하다고 하였고(Lee et al., 1975), 벼 수확 전 입모중 호밀 파종 재배 시도 파종 후 5일에 butachlor처리에서 뚝새풀 방제효과가 양호하며(Shin and Jung, 1987), 파종 후 5-10일에 thiobencarb 및 butachlor처리에서 잡초발생이 85-89% 정도 억제됨(Ryu et al., 1988).
따라서 벼 입모중 사료작물 파종 재배에 의한 조사료의 생산성은 뚝새풀의 발생 및 방제 정도에 따라 크게 영향을 받는 경우가 많아 이에 대한 연구를 수행하였다.
벼 수확 전 사료맥류 입모중 파종재배 잡초방제 시험은 전남 장성군 남면 농가 포장에서 실시하였다. 벼는 동진1호를 5월 25일에 이앙하여 10월 21일에 수확하였다. 사료맥류 청보리(영양보리)와 밀(금강밀)은 벼 수확전 3일인 10월 18일에 25 kg 10a-1을 입제 비료살포기로 각각 파종하였다. 비료는 N, P2O5, K2O를 9.1, 7.4, 3.9 kg 10a-1를 시용하였으며, 질소는 기비와 추비를 40:60으로 분시 하였고, 인산과 칼리는 전량 기비로 시용하였다. 벼 수확 전 사료맥류 입모중 파종 재배 시 뚝새풀의 방제를 위하여 thifensulfuron-methyl (75%) 입상수화제를 벼 수확 직후, 수확 후 5일, 수확 후 10일에 7 g 10a-1 씩 처리하였으며, butachlor (5%) 입제를 파종 전 5일, 벼 수확 직후, 수확 후 5일, 수확 후 10일에 3 kg 10a-1 씩 처리하였다.
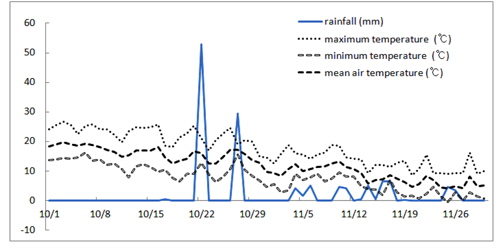
시험 년도의 시험 전 후 기상(Fig. 1)에서와 같이 수확 직후 처리 후 1일에 55 mm, 수확 후 5일처리 1일 29.5 mm 정도의 상당한 강우가 있었으며, 이후 11월 중에는 소량의 잦은 강우가 있었으며, 이러한 기상은 입모중외 일반적인 즉 벼 수확 후 맥류파종 재배는 어려운 기상이었다. 시험구배치는 난괴법 3반복으로 하였으며, 입모율은 무처리 대비 입모수를 조사하여 환산하였다. 사료맥류에 대한 처리 제초제의 약해는 생육 억제 정도(0-9)를 달관으로 조사하였다. 잡초는 월동 후 보리 재생기인 3월 14일에 50*50 cm의 격자를 이용하여 조사하였다. 뚝새풀 방제에 따른 사료맥류의 생초 및 건초 수량은 맥류의 황숙기에 수확하여 조사하였다. 기타는 농촌진흥청 표준재배법에 준하여 실시하였다.
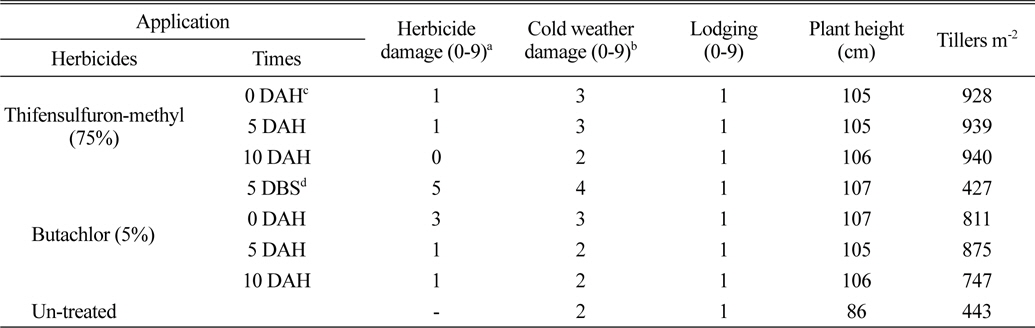
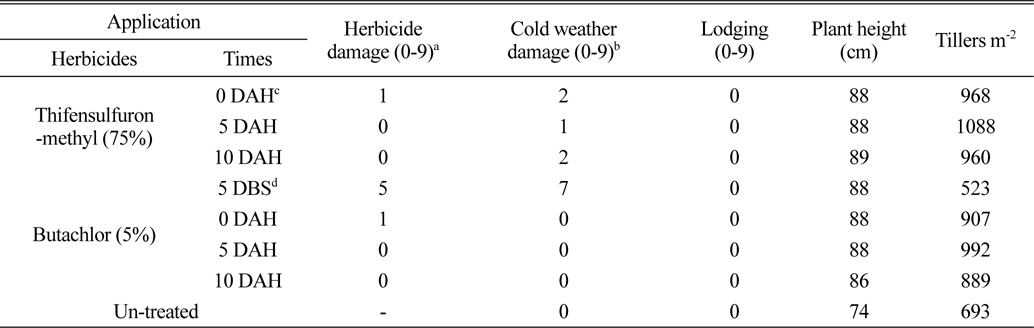
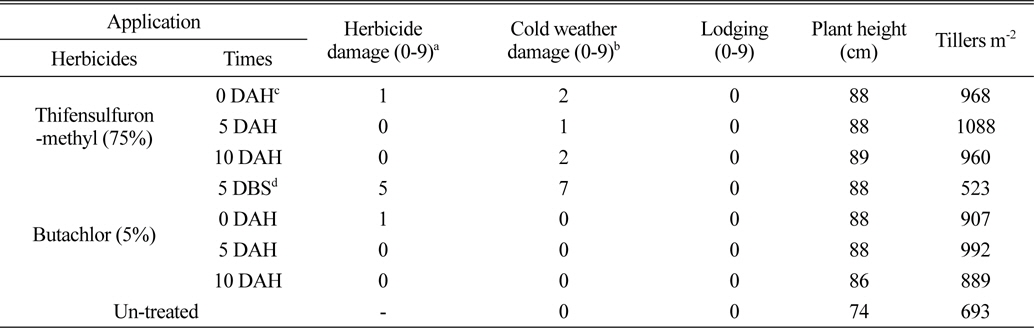
벼 수확 전에 입모중 조사료용 보리와 밀을 파종 한 후 3일에 벼를 수확 한 후 뚝새풀의 방제를 위하여 thifensulfuron-methyl (75%) 입상수화제를 벼 수확 직후, 수확 후 5일 및 10일에 처리한 결과(Table 1, 3), 보리 및 밀에 대한 약해는 없거나 아주 경미하였다. Butachlor (5%) 입제를 파종 전 5일과 수확 직후, 수확 후 5일, 수확 후 10일에 처리한 결과 파종 전 처리는 보리, 밀 모두 약해가 심했으며, 벼 수확 후 처리는 보리에서는 수확 직후 약해가 심한 경향이었으나, 밀에서는 수확 직후, 수확 후 5일, 10일처리에서 약해가 거의 없었다. Butachlor (5%) 처리는 파종 전 5일부터 파종 직후 보리에 대한 약해가 큰 경향이었다. 이는 벼 입모중 호밀 재배 시 처리시기가 빠를수록 약해가 심하다(Shin and Jung, 1987)는 보고와 유사한 경향이었으며, 또한 파종 직후 보리와 밀에서도 차이가 있는 것은 이것이 강우와 관련된 것인지 약제의 특성인지는 더욱 검토가 필요하다고 여겨지며, 또한 작물 간 즉 보리와 밀에 대한 약해의 차이와 Pyon and Kim (1983)은 보리 품종 간에 제초제에 대한 반응이 다르다고 하여 품종간의 차이도 더욱 검토가 필요하다고 생각된다.
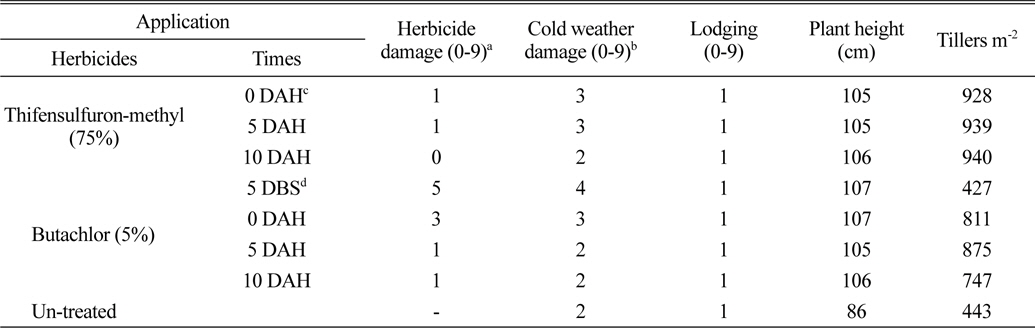
Damage and growth according to application times of thifensulfuron-methyl and butachlor in the field sowing barley seeds before rice harvesting.
Damage and growth according to application times of thifensulfuron-methyl and butachlor in the field sowing wheat seeds before rice harvesting.
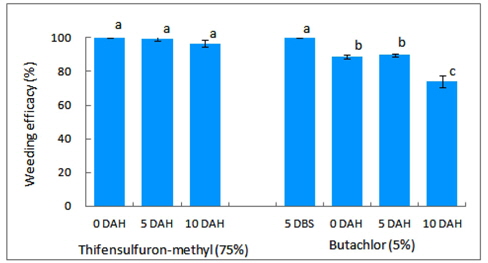
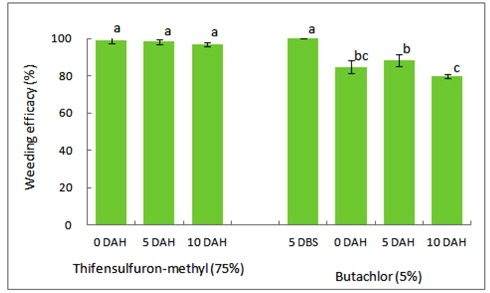
벼 수확 전에 입모중 조사료용 보리와 밀을 파종 한 후 3일에 벼를 수확 한 후 뚝새풀의 방제를 위하여 thifensulfuron-methyl (75%) 입상수화제를 처리한 결과, 뚝새풀의 방제가는 보리 재배 논에서는 벼 수확 직후, 수확 후 5일 및 10일에 처리에서 모두 96 이상의 높은 방제효과를 보였다(Fig. 2). 밀 재배 논에서도 97 이상의 방제효과를 보였으며(Fig. 3), 보리, 밀 재배 논 모두 방제효과 차이는 적지만 처리시기가 빠를수록 방제효과가 높은 경향이었다. 이는 벼 수확동시 보리파종 재배 논에서 thifensulfuron-methyl (75%) 입상수화제 처리시 파종 후 3일부터 이듬 해 보리 재생기까지 처리시기가 빠를수록 잡초방제 효과가 높았다는 보고와 일치하는 경향이었다(Im et al., 2005). Thifensulfuron-methyl은 뚝새풀에 대한 경엽처리 효과가 높으나, 엽기가 진전됨에 따리 방제효과가 낮이지는 경향으로 작물에 대한 약해와 뚝새풀에 대한 방제효과를 고려하여 보면, 벼 수확 전 입모중 사료맥류 파종 재배 시에는 벼 수확 이후에서 월동 전까지 처리하는 것이 안전할 것으로 사료된다.
벼 수확 전에 입모중 보리와 밀 재배 시 butachlor (5%) 입제를 파종 전 5일, 벼 수확 직후, 수확 후 5일, 수확 후 10일에 처리한 결과, 뚝새풀의 방제효과는 벼 수확 직후 및 수확 후5일 처리까지는 보리, 밀 모두 88 이상이었으나, 벼 수확 10일 후 처리는 80 이하로 방제효과가 낮은 경향이었다(Fig. 2, 3). 이는 벼 입모중 호밀 재배 논에서 벼 수확 후 5일부터 15일 까지 butachlor 입제를 처리한 결과 수확 10일 이후 처리는 72% 이하의 방제효과를 보인다는 결과(Shin and Jung, 1987)와 유사한 경향으로 수확 전 처리는 1엽 이하의 어린 상태로 butachlor에 민감하게 반응하기 때문이며, 또한 뚝새풀은 보리 파종 전에 대부분 발생되어 있는 상태에서 파종 후 복토에 의한 새로운 출현으로 제초제 처리 층에서 반응하여 수확 후 10일 즉 복토 후 10일까지의 처리는 토양처리 효과를 보이 것으로 사료된다. 그러나 10일 이후 처리에서 방제효과가 낮은 것은 발생된 뚝새풀이 복토 위에 노출되어 있거나 생육 즉 엽수 진전에 의한 토양처리 효과를 보이지 못하였기 때문으로 사료된다. 따라서 벼 수확 전에 입모중 사료맥류 재배 시 butachlor 입제 처리에 의한 뚝새풀의 방제는 보리, 밀 모두 수확전의 처리는 약해가 심하여 어려울 것으로 사료되며, 보리는 약해와 방제효과를 고려하여 더욱 검토가 필요하며, 밀은 약해가 거의 없어 수확 직후부터 10일 이내에 처리하는 것이 효과적일 것으로 판단된다.
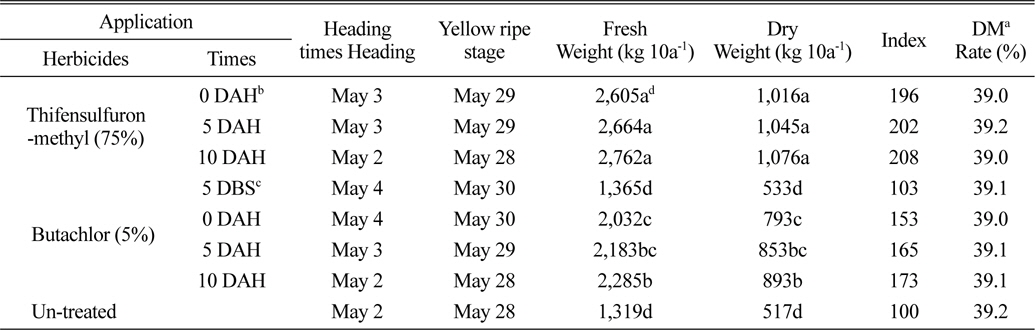
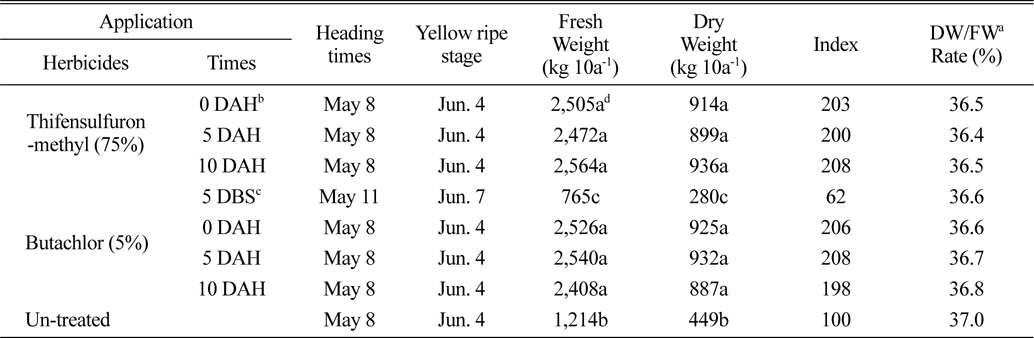
벼 수확 전에 입모중 조사료용 보리와 밀을 파종 한 후 3일에 벼를 수확 한 후 뚝새풀의 방제를 위하여 thifensulfuron-methyl 입상수화제 및 butachlor 입제 처리에서 생육 및 조사료 수량을 보면 다음과 같다. 보리는 수확 직후부터 10일 후 처리까지 모두 5월 2-4일에 출수하여 5월 28일-5월 30일 경에 황숙기가 되었으며, 초장은 105cm, 경수는 928-940개/m2이었다(Table 1). 조사료 건물수량은 thifensulfuron-methyl 입상수화제 처리에서 1,016-1,076 kg/10a 정도로 무처리에 비하여 96-108% 정도 높았으며, 수확 직후부터 10일 후 처리까지 처리시기 간에는 유의차가 없는 경향 이었고, 황숙기에 조사료의 건물율은 39% 정도 이었다(Table 2). 이는 thifensulfuron-methyl 입상수화제 처리에서 초기에 경미한 약해는 조사료 수량에 크게 영향을 미치지 않고 또한 뚝새풀의 방제효과가 거의 유사하게 높았기 때문으로 사료된다. Butachlor의 처리에서는 보리의 수량은 생육저해 등으로 인하여 수량이 낮았으나, 무처리에 비하여는 53-73% 정도 높은 경향이었다(Table 2). 밀은 5월 8일경에 출수하여 6월 4일경에 황숙기가 되었으며, 초장은 88 cm, 경수는 968-1088개/m2 이었다(Table 3). 황숙기에 조사료 건물수량은 thifensulfuron-methyl 입상수화제 처리에서 914-936 kg/10a 정도로 보리보다는 낮았으며, 처리시기 간에는 유의차가 없는 경향이었다. 또한 무처리에 비하여 100-108% 높았다(Table 4). Butachlor의 처리에서도 밀은 수확 직후에서 5일 후에 조사료 건물 수량이 887-932 kg/10a 정도이었으며, 수확 직후부터 10일 후 처리까지는 처리시기 간에 유의차가 없었다(Table 4).
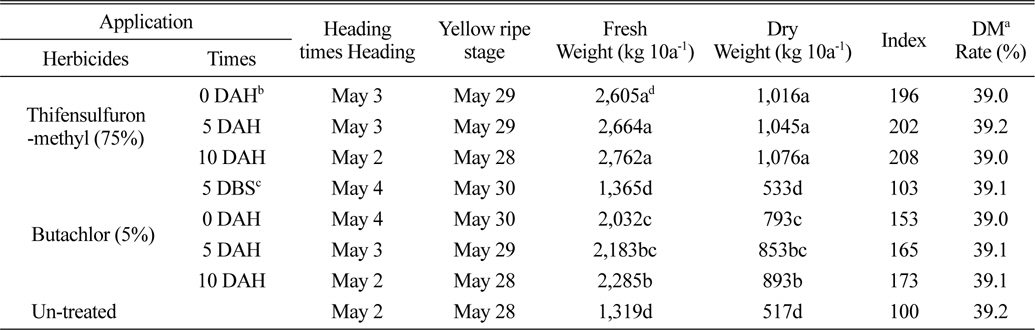
Heading stage, yellow ripe stage and amount of the roughage according to application times of thifensulfuron-methyl and butachlor in the field sowing barley seeds before rice harvesting.
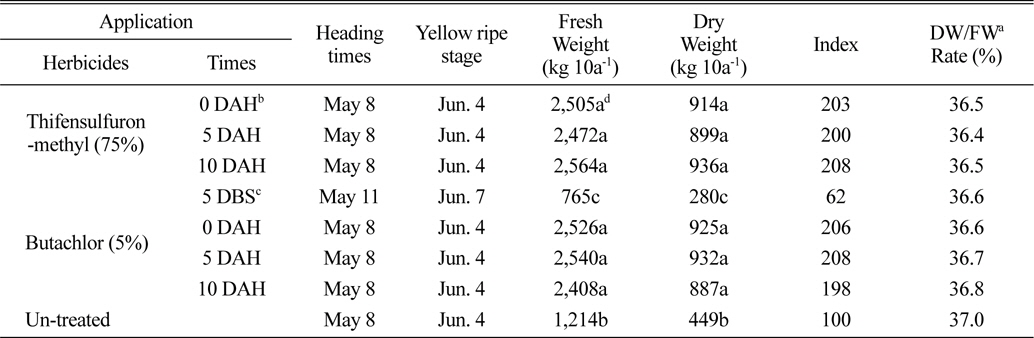
Heading stage, yellow ripe stage and amount of the roughage according to application times of thifensulfuron-methyl and butachlor in the field sowing wheat seeds before rice harvesting.