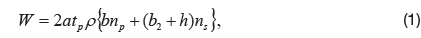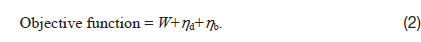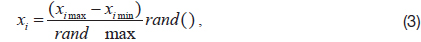For laminated Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer (CFRP) composites, optimization of the stacking sequences, and of the dimensions of the structures is essential, because of their strong anisotropic properties. Miki [1] and Fukunaga [2] both proposed a graphical optimization method using the lamination parameters. For practical laminated CFRP structures, however, the available fiber angles are usually limited to a small set of fiber angles, because of a lack of experimental data. In addition, multiple constraints on the fiber angles exist from specific empirical rules, such as the four-contiguous-ply rule, to prevent large matrix cracking. These facts make the optimization of the stacking sequences a combinatorial optimization problem, with combinatorial constraints.
For optimization of the stacking sequence of laminated CFRP composites, Genetic Algorithms (GAs) have been adopted in many research programs [3-15]. Narita proposed a layer-wise optimization method for stacking sequence design [16].
In previous research, we proposed a fractal branch and bound method (FBB), for optimizing the stacking sequence of laminated carbon fiber composites [17, 18]. This method employs a quadratic polynomial for the response surface using the lamination parameters, such as the buckling load, to approximate the objective functions. The method involves low computational costs, and a practical optimal result can be obtained in milliseconds, by means of a deterministic process. This method has been successfully applied to the problem of establishing the maximization of the buckling load of a laminate [17, 18], and for determining the maximization of the flutter speed limit [19] with constraints.
For a stiffened panel made from a laminated CFRP structure, the dimensions of the stiffener and panel have to be simultaneously optimized, in addition to optimizing the stacking sequences of the panel and stiffeners. We have published papers that deal with the modified efficient global optimization method using a multi-objective GA [20]: the improvement in the objective function, and the possibility of satisfying the constraints are treated as two objective functions.
To optimize, while preventing any fracture of a laminated CFRP composite structure, it is difficult to obtain an approximate surrogate model to predict the fracture load, when checking the fracture constraints. When a quadratic polynomial was used to predict the fracture of the CFRP laminate, the surrogate model provided poor estimates for this condition. In a previous paper, this problem was solved using the Kriging response surface [21]. This means that the FBB method cannot be applied to the fracture constraint, because it requires a response surface approximation of a quadratic polynomial. We proposed a new response surface technique to approximate the warping thermal deformation caused by the curing process [22], although the method was limited to the fixed dimensions of a blade stiffened composite structure.
In the present study, therefore, a GA is adopted to simultaneously optimize the stacking sequences and dimensions of a target composite structure, without using the FBB method. To optimize the number of plies for the GA, intron genes that represent the empty position of a chromosome have been proposed in [8]. To simplify the implementation, the intron genes were not used here. Therefore, a new simple crossover operation between chromosomes of different lengths is proposed. The main objective of this paper is to investigate the effectiveness of the response surface approximation of the warping thermal deformation for the blade stiffened composite structures, against the various dimensions of the stiffener. For the optimization process in the present study, the buckling load and warping of the thermal deformation of the target stiffened laminated composite structure are treated as given constraints. Here, the objective function of the GA is reduction in the weight of the laminated composite structure with the two constraints.
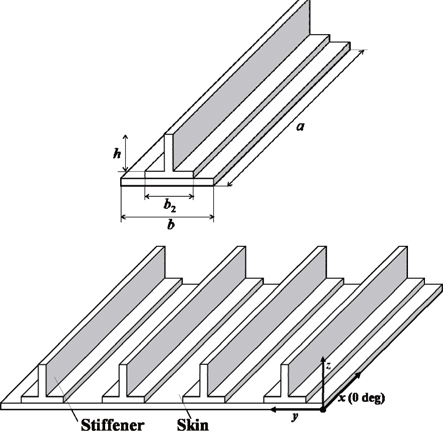
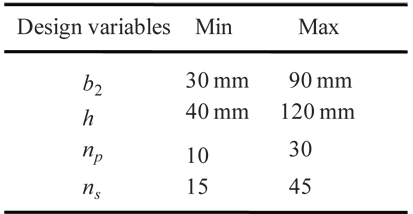
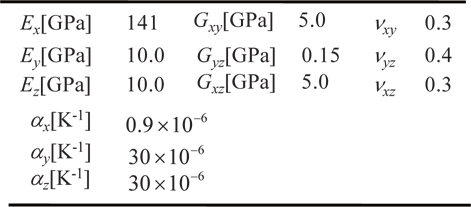
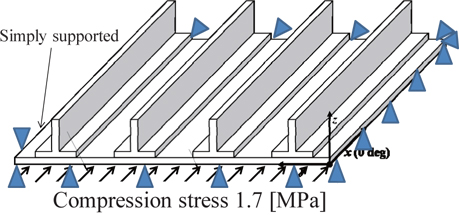
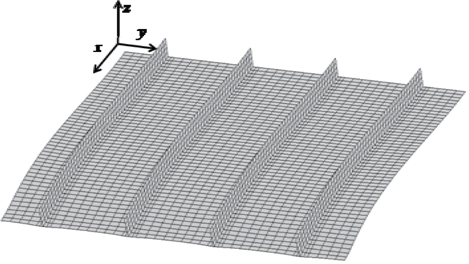
In the present study, a blade-stiffened laminated composite panel is dealt with, as shown in Fig. 1. The blade stiffened composite structure consists of four unit structures. The design variables and the material properties are shown in Tables 1 and 2, respectively.
[Table 1.] Range of design variables
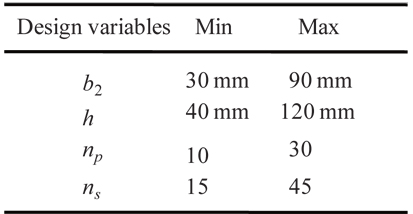
Range of design variables
[Table 2.] Material properties
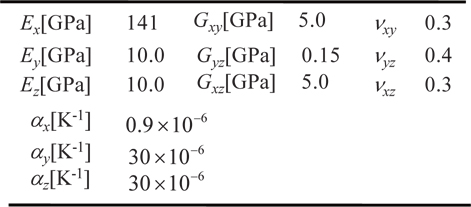
Material properties
The objective function of the optimization problem is the weight of the unit structure of the blade stiffened composite panel. Because the composite plates are thin, the weight of the unit composite structure can be calculated approximately, as follows:
where,
For the analysis of thermal deformation and the buckling load, the commercially available FEM code ANSYS ver.12 was used. Linear laminated structural shell elements were adopted for the analyses. The total number of elements was 4,160. Fig. 2 shows the boundary condition for the buckling analysis. The reference compression stress of 1.75 MPa was applied along the panel edge, as shown in Fig. 2. The composite panel had a simply supported boundary. As a buckling constraint, a buckling stress smaller than 1.75 MPa must be avoided.
For the warping analysis caused by thermal deformation, the displacement and rotation of the bottom center node of the plate was fixed. The applied temperature change was ΔT=−228℃, which came from the curing process. The maximum affordable thermal warping deflection was set to 2 mm. The change in the stacking sequence of the stiffener and panel causes a mismatch of the linear thermal expansion coefficients. A thermal expansion mismatch may cause a large thermal deformation of the target structure; from a fabrication point of view, this should be prevented.
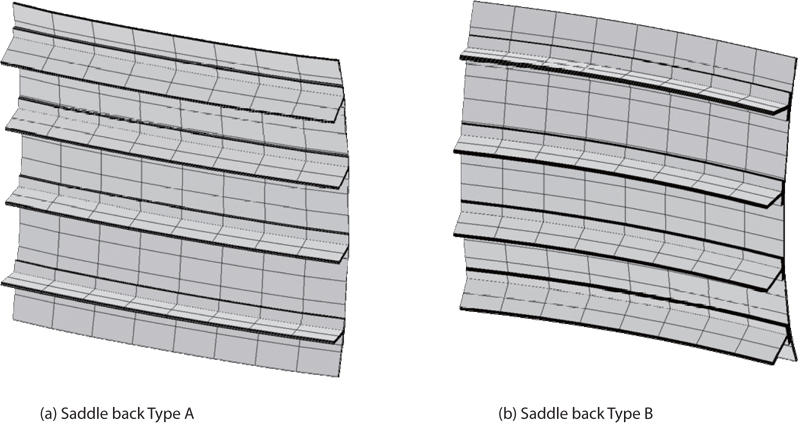
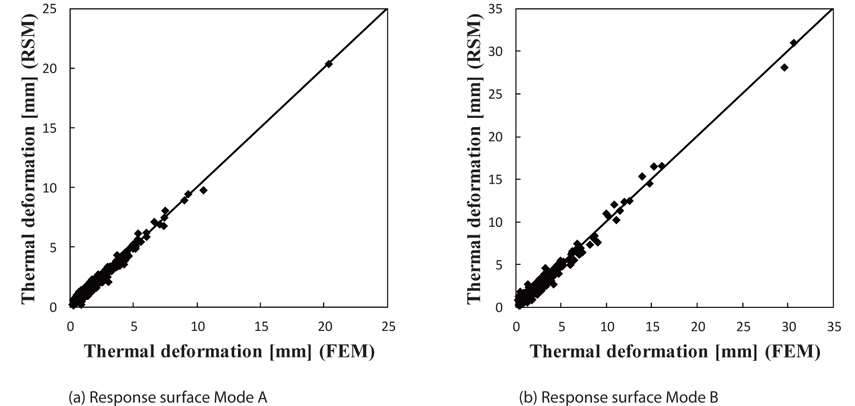
Thermal deformation was checked using quadratic response surfaces. The process for using the response surfaces to check the thermal deformation constraint is described in detail in [22]. Although all dimensions of the composite structure are fixed in [22], the dimensions are variables in this study, which is one of the original points of the study. Thermal deformation is classified into two types, as shown in Fig. 3. Quadratic polynomial responses surfaces were made for the two types of deformation modes.
We considered the case where the
It can be readily concluded that the small differences in the linear thermal expansion coefficients of the plate and stiffener are easily warped. Thus, the simple extension mode was neglected in this study.
After the classification of the thermal deformation mode, two types of response surfaces were made, using the lamination parameters, linear thermal expansion coefficients of the plate and stiffener, and the dimensions of the design variables in Table 1. This means that
To create a response surface of the buckling stress for plates with various numbers of plies, it was not sufficient to use a simple quadratic polynomial response surface, because the buckling stress was significantly affected by the plate thickness. Let us consider a simply supported rectangular plate, subjected to a single axial compression stress. The buckling stress is proportional to the square of the plate thickness. This means that a response surface can be made, when the buckling stress is divided by the square of the thinner thickness of the blade stiffened composite structure. In this study, the buckling stress factor
The buckling stress factor
The GA used was a general simple GA, but the crossover was a modified new one. The violation of the constraints on thermal deformation and the buckling stress ratio were implemented in the objective function of Equation (1) as penalties. When the composite structure violated the two constraints calculated from the response surfaces, penalty values were added into the objective function. In this study, constraints calculated from the response surfaces, penalty values were added into the objective function. In this study, the penalty factors were
For a real number of design variables, the real number was used as a chromosome. When the random number function (
where,
For a stacking sequence, an array of the same length as the number of plies was used. For example, (0,2,1,1) meant [0/90/45/-45]s. The recessive gene-like repair method is described in [4]. When the number of genes was decreased in the mutation process for the number of plies, the inner plies were deleted until the number of plies is satisfied, to prevent a large change in the bending lamination parameter. When the number of genes was increased in the mutation process, the innermost ply was added. The mutation of the number of plies was limited to one ply in this study.
When two chromosomes with a different numbers of plies were selected for the crossover operation, a new normalized coordinate method was adopted, to implement the crossover between the two different-length chromosomes. The normalized coordinate was defined for the stacking sequence. We assume that all the stacking sequences can be normalized by the number of plies. For example, a laminate [0/90/0/90]s has 0°-ply from 0.0 up to 0.25, and 90°-ply from 0.25 up to 0. 5. In the present study, the crossover operation was performed using this normalized coordinate. Let us consider the case in which a four-ply laminate ([0/90/0/90] s)and six-ply laminate ([45/-45/45/-45/90/0]s) were selected as parents, and the child was a five-ply laminate. The five-ply laminate had five gene loci: 0-0.2, 0.2-0.4, 0.4-0.6, 0.6-0.8 and 0.8-1.0. The coordinate of the gene locus was the midpoint of the segment. For example, 0.1 was the gene locus of the first segment. For the fiber angle of the gene locus, a gene from the parents at the same gene locus was selected with a 50 % probability. If the four-ply laminate was selected as the first ply, 0°-ply was set to the first gene locus of the child. The rest of the gene loci were decided similarly.
A two-stage optimization process was adopted. In the first stage, the dimensions of the composite structures were decided. In the second stage, a stacking sequence optimization was performed, to obtain the best performance of the fixed dimensions, taking into account the constraints. For both processes, the GA was adopted. In the second optimization process, however, to obtain the best stacking sequences, nearby laminates in the lamination parameter design space were searched, using the same method as in [23]. This means the GA used here was not a pure simple GA, but included searching of the adjacent laminates. The optimizations were performed five times, to prevent errors based on probability.
Figures 4 (a) and (b) show the results of the response surface of the warping thermal deformation. The abscissa gives the FEM results, and the ordinate is the estimated results, using the response surface. The adjusted coefficient of the determination is 0.97 for Mode A, and 0.98 for Mode B. These high values for the adjusted coefficient of the determination indicate that both response surfaces provided extremely good approximations, similar to those shown in [22]. Even when the dimensions were variables, the response surfaces using quadratic polynomials provided very good approximations.
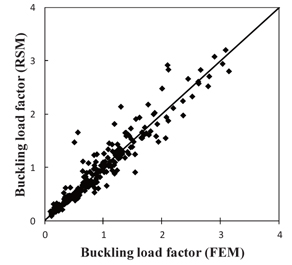
The cross validation of the Kriging response surface is shown in Fig. 5. The cross validation is different from that in Fig. 4. As the Kriging response surface gives exactly the same value as that given in the training data, this study used cross validation for the Kriging response surface. In the cross validation, one item of data was deleted, and a Kriging response surface was made. Using the Kriging response surface, the deleted item of data was estimated. The estimation, therefore, was a new case of the estimations, which is why the Buckling stress Kriging response surface looks worse than the warping thermal deflection response surface. The Kriging response surface, therefore, gives an affordable response approximation.
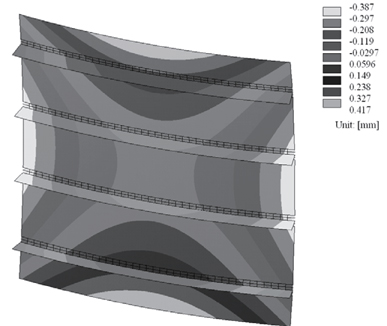
The optimal results obtained here are shown in Table 3. The buckling mode of the optimal composite structure is shown in Fig. 6. The warping thermal deformation mode of the optimal result is shown in Fig. 7. As mentioned in the optimization process, the optimization method includes adjacent searching, to confirm the optimality in the lamination parameter design space. The result obtained is the approximately true optimal result. The results are confirmed using FEM analyses.
[Table 3.] Optimal blade stiffened composite structure

Optimal blade stiffened composite structure
The present study investigated the warping thermal deformation constraint for various dimensions, using blade stiffened composite structures. Lamination parameters, linear thermal coefficients and dimensions of the composite structures were used as variables of quadratic polynomials. As a result, the response surfaces gave very good approximations, and the warping thermal deformation was evaluated using the response surfaces. The GA was adopted, to obtain the optimal composite structures with the buckling stress, and the warping thermal deformation constraints. The optimization successfully obtained the optimal result.