A newly recorded species of gammaridean amphipod, Cryptodius kelleri (
The family Odiidae Coleman and Barnard, 1991 is a small group, characterized by the compressed body, smooth dorsal pereonites, propodochelate gnathopod 1 and subchelate gnathopod 2. The family contains five genera (
Order Amphipoda Latreille, 1816 Suborder Gammaridea Latreille, 1803 1*Family Odiidae Coleman and Barnard, 1991 2*Genus Cryptodius Moore, 1992
Type species.
Diagnosis. Body compressed laterally; pereonites dorsally smooth; pleonites carinate; rostrum well developed; antennae 1 and 2 short; mandible styliform, accessory setal row well developed, molar small, triturative; maxillipedal palp article 2 broad, expanded medially, palp article 4 elongate; coxa 1 tapering distally; gnathopod 1 feeble, linear; gnathopod 2 subchelate, broader than gnathopod 1, carpus lobate; Pereopods 5-7, basis without posterior process; epimera 2-3 pointed posterodistally; uropod 3, outer ramus more than half length of inner ramus; telson entire.
Species composition.
Material examined. 32♀♀, Gajin, Goseong-gun, Korea, 25 Feb 2005, Kim YH.
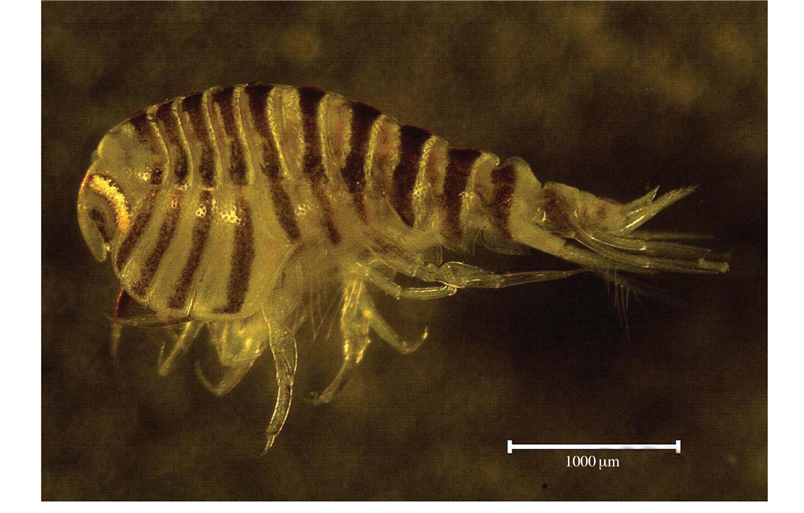
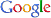
Coloration. Body light yellow; pereonites to pleonites including coxae 1-7 with brownish striped patterns which rapidly disappearing in alcohol (Fig. 1).
Description. Female (cat no. DKU 201302): Body (Figs. 1, 2A) round, medium, about 6.6 mm long, pereonites ovate, pleonites compressed in dorsal view, coxae 1-4 deeper than their pereonites, gradually increasing in width and depth ventrally; head (Fig. 2B) subequal in length to pereonites 1-2 combined; rostrum well developed, pointed, tapering distally, extending far beyond end of peduncular article 1 of antenna 1; antennal sinus deeply concave; lateral cephalic lobe subangular; eye large, curved, subreniform, brown in alcohol; mouthparts well developed, conical.
Antenna 1 (Fig. 2C) gradually decreasing in thickness distally, slightly longer than head; peduncle less setose, 1.25 times as long as flagellum, length ratio of peduncular articles 1-3=1.00 : 0.68 : 0.39, accessory flagellum (Fig. 2D) minute, uniarticulate, with 1 penicillate and 2 simple setules; flagellum 7-articulate, with tufted aesthetascs posterodistally, proximal article elongate, about 1.2 times as long as peduncular article 3.
Antenna 2 (Fig. 2E) shorter than antenna 1; peduncular article 4 rectangular, about 1.7 times as long as article 3, with 4 penicillate setae posteriorly, peduncular article 5 about 0.8 times as long as article 4; flagellum short, 6-articulate, subequal in length to peduncular article 5, proximal article elongate, as long as following articles 2-3 combined.
Maxilla 1 (Fig. 2F), inner plate slender, with 2 pinnate setae apically; outer plate attenuate apically, medial inclined margin serrate, with 3-4 rows of short setae, subapical margin with 10 dentate spine-teeth; palp small, slender, elongated isosceles triangular in form, uniarticulate, with 1 simple seta apically, surrounded by pubescence.
Maxilla 2 (Fig. 2G), inner plate shorter than outer one (86 %), with row of 10 simple or denticulate stout setae; outer plate with 2 rows of 18 setae; both plates pubescent.
Mandible (Fig. 2H) elongate, tapering apically; incisor narrow, with 10 small blunt teeth; molar placed medially, columnar, prominently produced, truncate and triturative; accessory spine row with 17 denticulate spines; palp attached behind molar, slender, triarticulate, length ratio=1.00 : 3.51 : 4.00, distal article with 4 multicuspidate setae medially, 1 multicuspidate and 2 simple setae apically, posterior margin with patch of pubescence.
Maxilliped (Fig. 2I), inner plate elongate, extending well beyond half length of outer plate, medial margin with row of 13 pinnate setae, apical margin with 2 spines and 4 setae, surrounded by patch of pubescence; outer plate broad, tapering apically, not extending beyond palp article 3, medial margin straight, with blunt setae and row of 10 simple setae subapically; palp (Fig. 2J) 4-articulate, length ratio=1.00 : 1.30 : 1.28 : 0.68; article 2, medial margin swollen roundly, with 14 simple setae; article 3 subrectangular, roundly produced distoposteriorly, about half as wide as article 2, surrounded by simple setae subapically; distal article present, slender, spiniform.
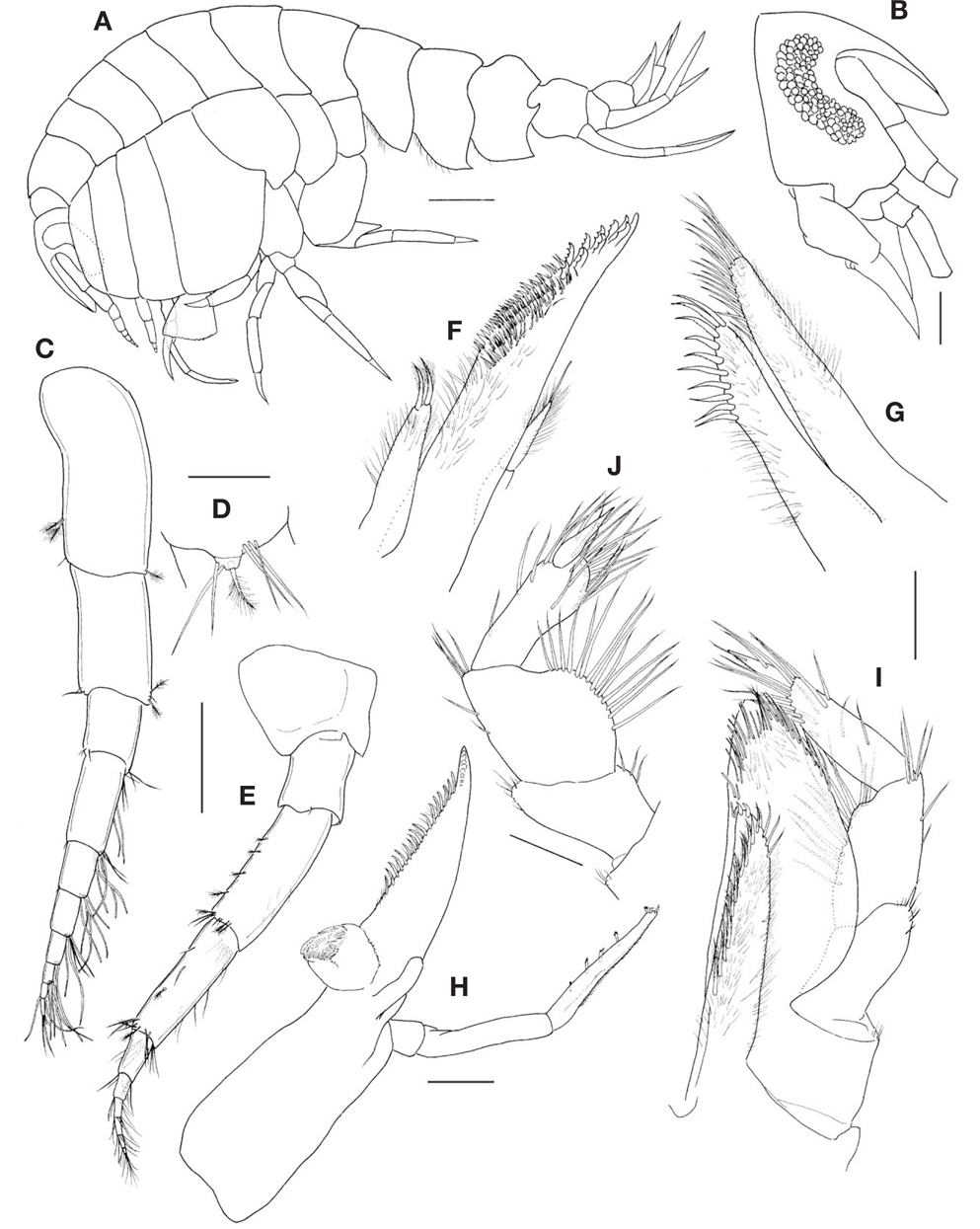
Gnathopod 1 (Fig. 3A) propodochelate; coxa narrow, distally pointed, unarmed; basis subrectangular with rounded posterior margin, with 15 plumose setae anteroproximally, 3 plumose setae and 3 setules posterodistally; ischium subrectangular, protrudent anterodistally; carpus slender, unarmed, slightly longer than propodus; propodus slender, uniform in width to carpus, concave posteriorly; dactylus subacute, slightly extending beyond end of propodus, with 2 simple and 4 pinnate setae.
Gnathopod 2 (Fig. 3B), coxa subrectangular, 0.39 times as wide as long, unarmed; basis gradually broadened distally, anterior and half of posterodistal portions with feeble plumose and simple setae; ischium rectangular, with 6 slender spines posteriorly; merus produced posterodistally, about 1.3 times as long as ischium, with 7 spines posteriorly; carpus short, carpal lobe elongate, with cluster of simple and unipinnate setae distally; propodus subtriangular, widening distally, with 6 short setae anteriorly, palm transverse, slightly convex, serrulate marginally, palmar corner delimited by 2 spines; dactylus falcate, fitting palm, about 0.6 times as long as propodus, with tiny accessory tooth on inner margin.
Pereopod 3 (Fig. 3C), coxa and basis similar to those of gnathopod 2; ischium to dactylus linear and slender; length ratio of articles 2-7=1.00 : 0.39 : 0.58 : 0.43 : 0.58 : 0.33.
Pereopod 4 (Fig. 3D) similar to pereopod 3, except coxa 4 longer and wider than coxa 3, excavate posteroproximally, midposterior margin pointed, expanded backward; length ratio of articles 2-7=1.00 : 0.45 : 0.56 : 0.45 : 0.60 : 0.37.
Pereopod 5 (Fig. 3E), coxa subovate, about 1.1 times as long as wide, bilobate, posterior lobe roundly expanded downward, with numerous setules ventrally; basis moderately broad, posterodistal lobe roundly expanded ventrally; merus overhanging and tapering posterodistally, nearly reaching end of carpus; propodus rectangular, with row of 8 pairs of spines anteriorly; length ratio of articles 2-7=1.00 : 0.33 : 0.72 : 0.41 : 0.68 : 0.35.
Pereopod 6 (Fig. 3F) similar to pereopod 5, but coxa 6 subquadrate, smaller than coxa 5, anterior margin slightly concave, with feeble plumose setae; basis, posterodistal lobe reaching distal end of ischium.
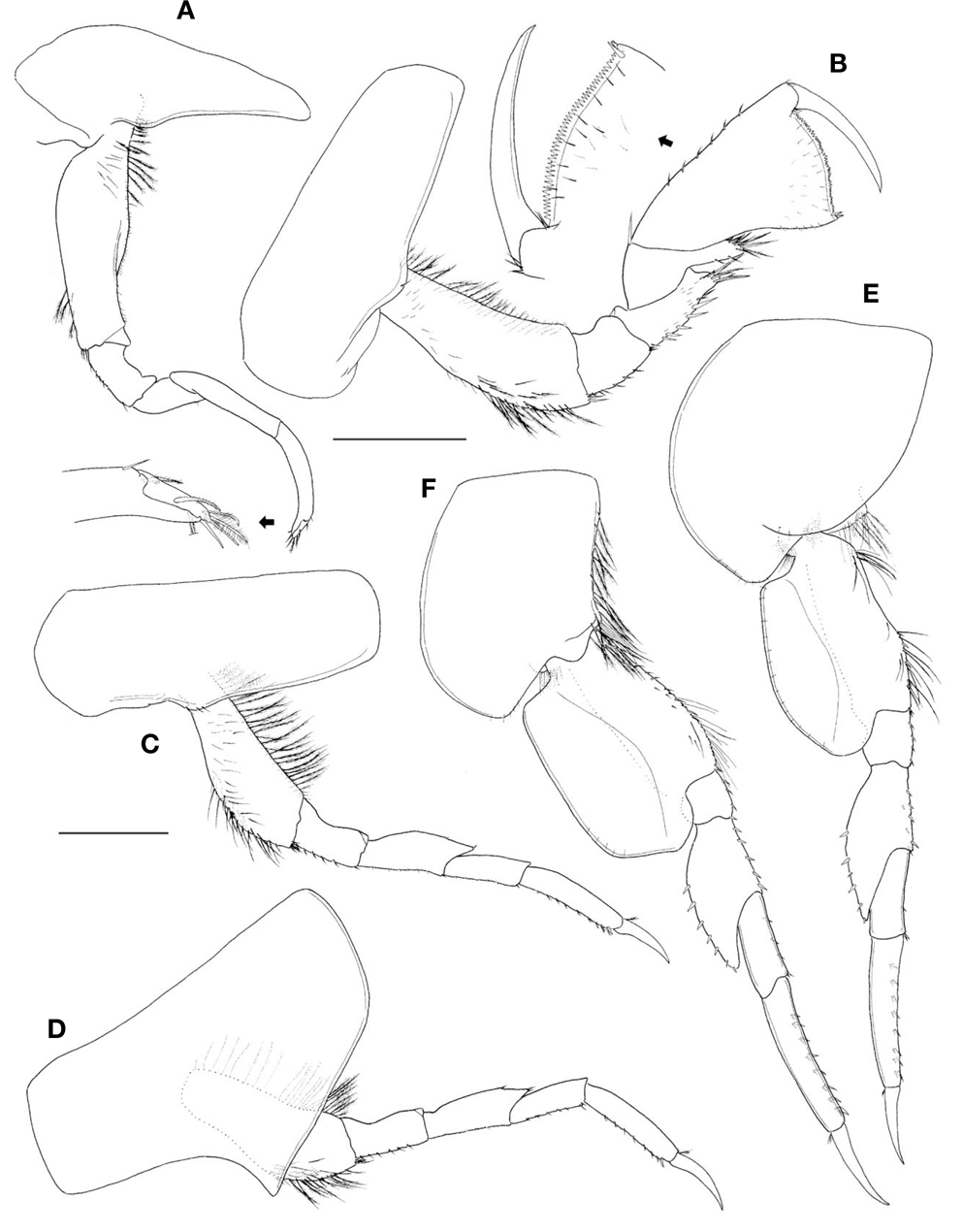
Pereopod 7 (Fig. 4A) similar to pereopod 6, except coxa 7 unilobate, smaller than coxa 6.
Pleonites (Fig. 4B) subequal in length to each other; epimeron 1 tapering ventrally, pointed, with row of setae anteroventrally; epimeron 2 similar to epimeron 1, but posteroventral corner with acute tooth; pleonite 3 with dorsal protrudent carina convexly, epimeron 3 with posterolateral upturned acute process and posteroventral corner with acute tooth. Urosomite 1 subrectangular, longer than urosomites 2-3 combined, with a low dorsal elevation.
Pleopod 1 (Fig. 4C), peduncle subrectangular, about 0.8 times as long as rami, with 2 retinaculae anterodistally and row of feeble plumose setae posteriorly; both rami subequal in length, 14-16 articulate, with plumose setae.
Uropod 1 (Fig. 4D) slender, elongate, peduncle slightly curved, about 1.2 times as long as outer ramus, with row of 26 dorsolateral and 6 dorsomedial spines; both rami subequal in length, with 2 rows of dorsal spines.
Uropod 2 (Fig. 4E), peduncle subequal in length to inner ramus, with 14 dorsolateral and 1 apicomedial spines; inner ramus about 1.3 times as long as outer one.
Uropod 3 (Fig. 4F) shorter than uropod 2, peduncle slightly longer than inner ramus, with 5 dorsolateral spines; outer ramus distinctly shorter, about 0.7 times as long as inner.
Telson (Fig. 4G) elongate, subtriangular, tapering distally, about 2.1 times as long as wide, with 2 pairs of short setae dorsolaterally, entire with 2 setules.
Remarks.
Distribution. Alaska, Bering Sea, Sea of Okhotsk, Korea (east coast), British Columbia.
>
Key to the species of Cryptodius
1. Epimeron 3 with dorsal carina and posterolateral process; urosomite 1 dorsally convex ∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙
Epimeron 3 without dorsal carina and posterolateral process; urosomite 1 dorsally flat ∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙