Pharmacopuncture therapy is a new acupuncture therapy to treat diseases based on herbal medicine, acupuncture & moxibustion medicine, and meridian theories [ 1 ]. Pharmacopuncture fluid is extracted from herbs and injected into acupoints or sore spots [ 2 ].Through a single procedure, it can achieve both the effects of acupuncture and herbal medicine [ 3 ].
The
The animals used in this study were 6-week-old SD rats. The mean weights were 185.4 - 209.0 g and 153.0 - 174.5 g for the male and the female rats, respectively, at the time of injection of the pharmacopuncture. Visual inspections were conducted for all animals; all animals were weighed using a CP3202S system (Sartorius, Germany). During 7 days of acclimatization, the general symptoms of the rats were observed at the end of the day. The weights of the rats were recorded on the last day of acclimatization. No abnormalities were observed. The temperature of the lab was 21.0 - 23.2°C, and the humidity was 40.9% - 59.4%. Enough food (Teklad Certified Irradiated Global 18% Protein Rodent Diet 2918C) and UV-filtered water were provided.
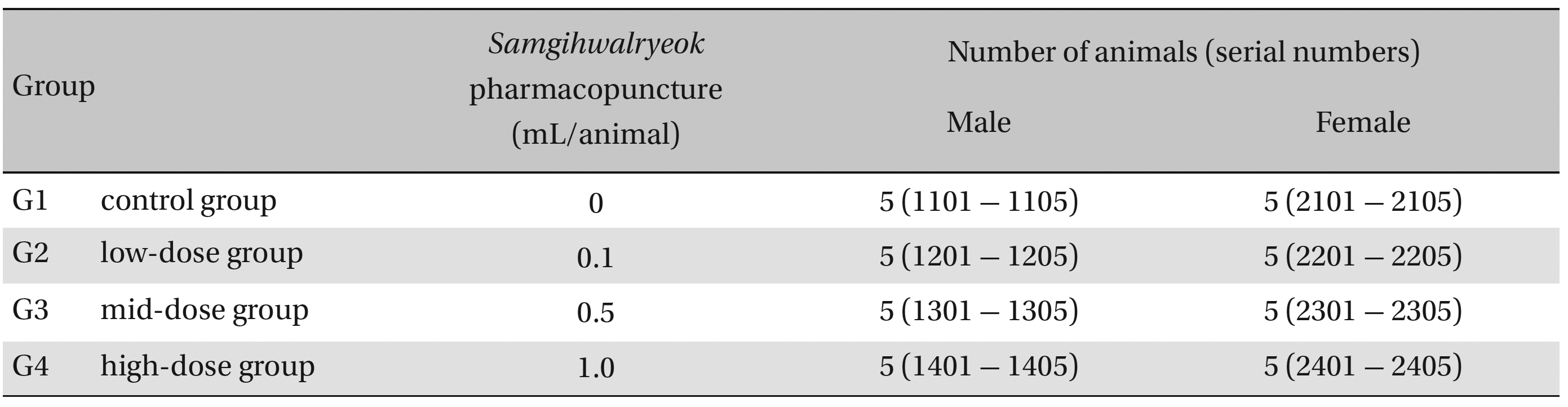
Group separations were done after 7 days of acclimatization. The animals were randomly distributed into 4 groups of 5 male and 5 female rats per group (Table 1 ): the control, low-dose, mid-dose and high-dose groups.
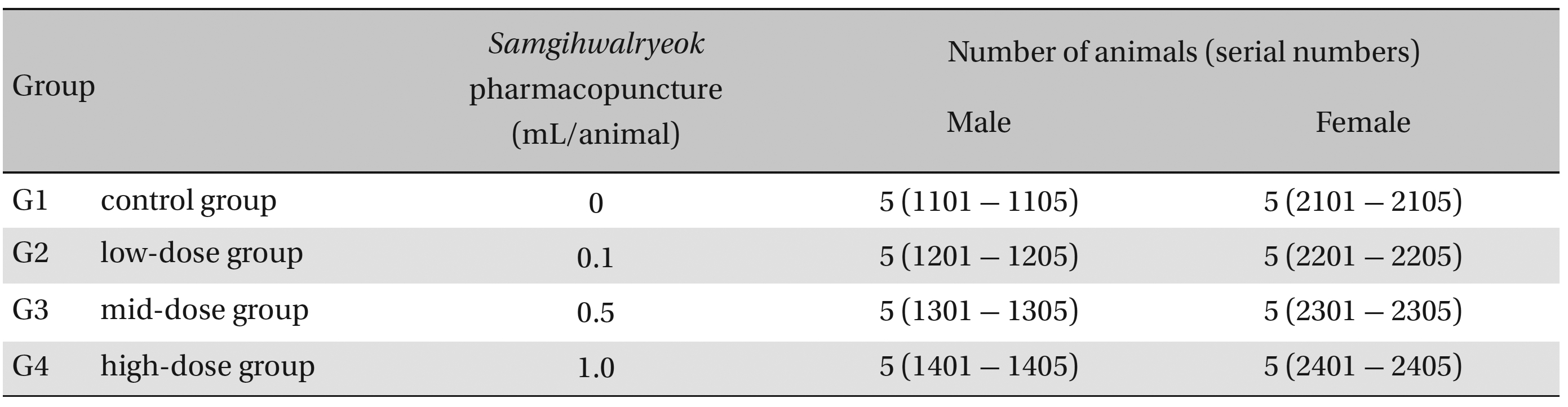
Groups of animals
In a pilot test (Biotoxtech Study No.: B12876P), 1.0 mL/animal, referring to a 1.0 mL dose for each clinical application, was administered by intramuscular (i.m.) injection (left thigh) to one male and one female rat and resulted in no deaths. From this result, the doses for
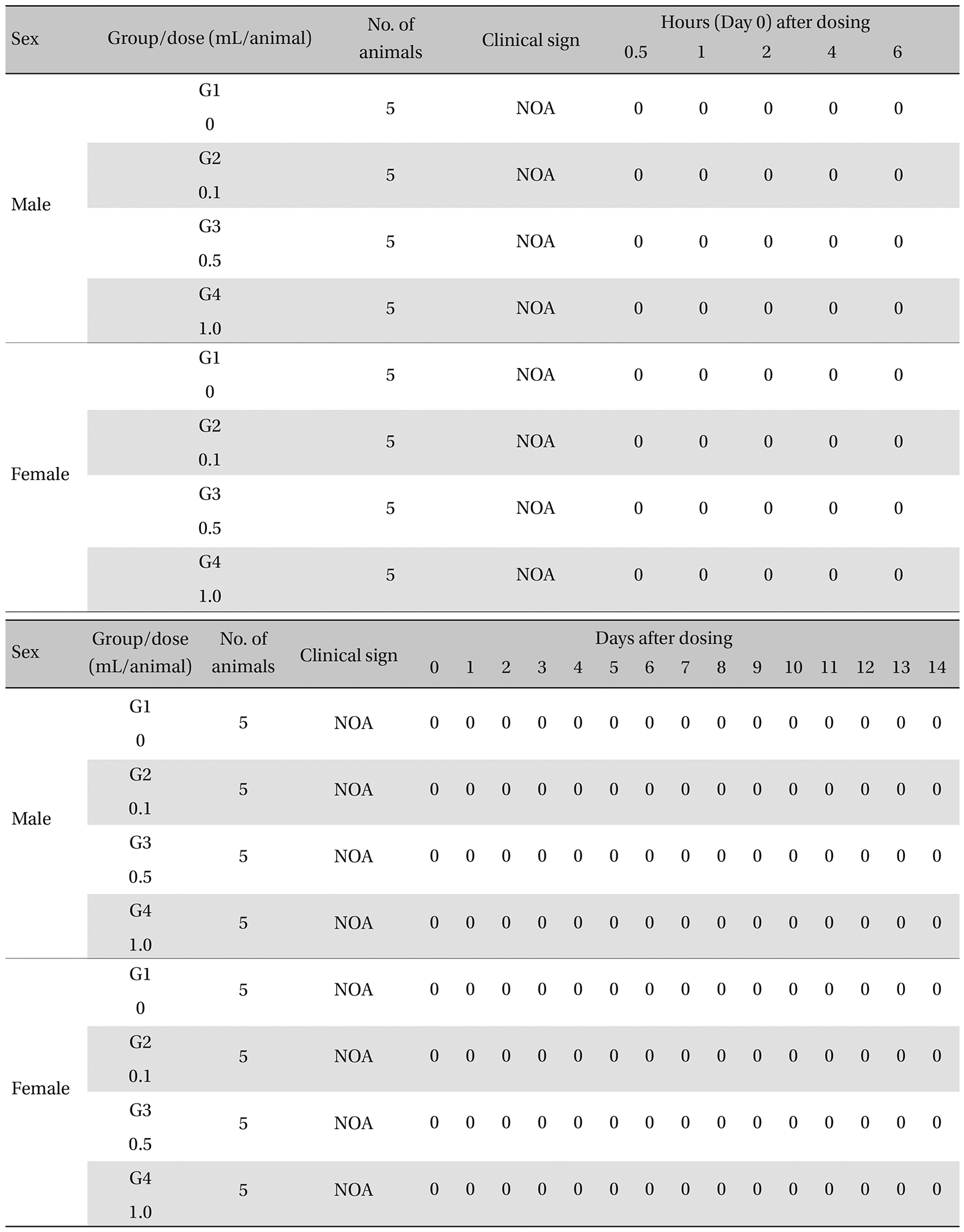
The general symptoms (side effects, revealing times recovery time etc.), as well as the mortalities, were examined for 10 seconds at 30 minutes and at 1, 2, 3, and 4 hours after injection on the day of dosing (day 0).
From the 1 st day to the 14 th day of treatment, the general symptoms were examined once a day. The body weights were measured immediately before treatment and at 3, 7 and 14 days after injections.
All animals were fasted for more than 18 hours before autopsy. The rats were anesthetized by using isoflurane, and blood samples were collected from the abdominal aorta on the day of autopsy (15 days after injection). An automatic hematology analyzer (ADVIA120, SIEMEMS, Germany) was used to analyze blood for the hematological examinations. For the blood coagulation test (3,000 rpm, 10 minutes), 2-mL samples of blood were placed in a tube with 3.23% sodium citrate to collect blood plasma. The RBC, HGB, HCT, MCV, MCH, MCHC, PLT, etc. were measured for the hematological examinations and the prothrombin time (PT) and the activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT) were determined for the coagulation tests. The results were obtained using an Automated Coagulation Analyzer (Coapresta 2000, SEKISUI, Japan). For the biochemical tests, the blood remaining after carrying out the hematological tests was centrifuged at 3,000 rpm for 10 minutes, and the serum was collected. Measurements were done using a biochemistry analyzer (7180, HITACHI, Japan) and an electrolyte analyzer (AVL9181, Roche, Germany).
After the observations, organs and tissues from the entire bodies of all animals were visually inspected and examined under an optical microscope. Tissue samples of all the animals were fixed in 10% neutral buffered formalin. Routine histological methods, such as trimming, dehydration, and paraffin embedding, were conducted on the fixed organs and tissues. Fixed samples were then sliced using a microtome and stained with hematoxylin & eosin (H&E).
All the results from the experiments were analyzed by using SAS (version 9.2, 9.3, statistical analysis system [SAS] Institute Inc., USA). The Bartlett test was conducted to evaluate the homogeneity of the variance and the significance. If the sample variances were equal, the significant result was obtained using a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) test. If the sample variances were not equal, a Kruskal-Wallis test was conducted post-hoc. Statistical significance was associated with
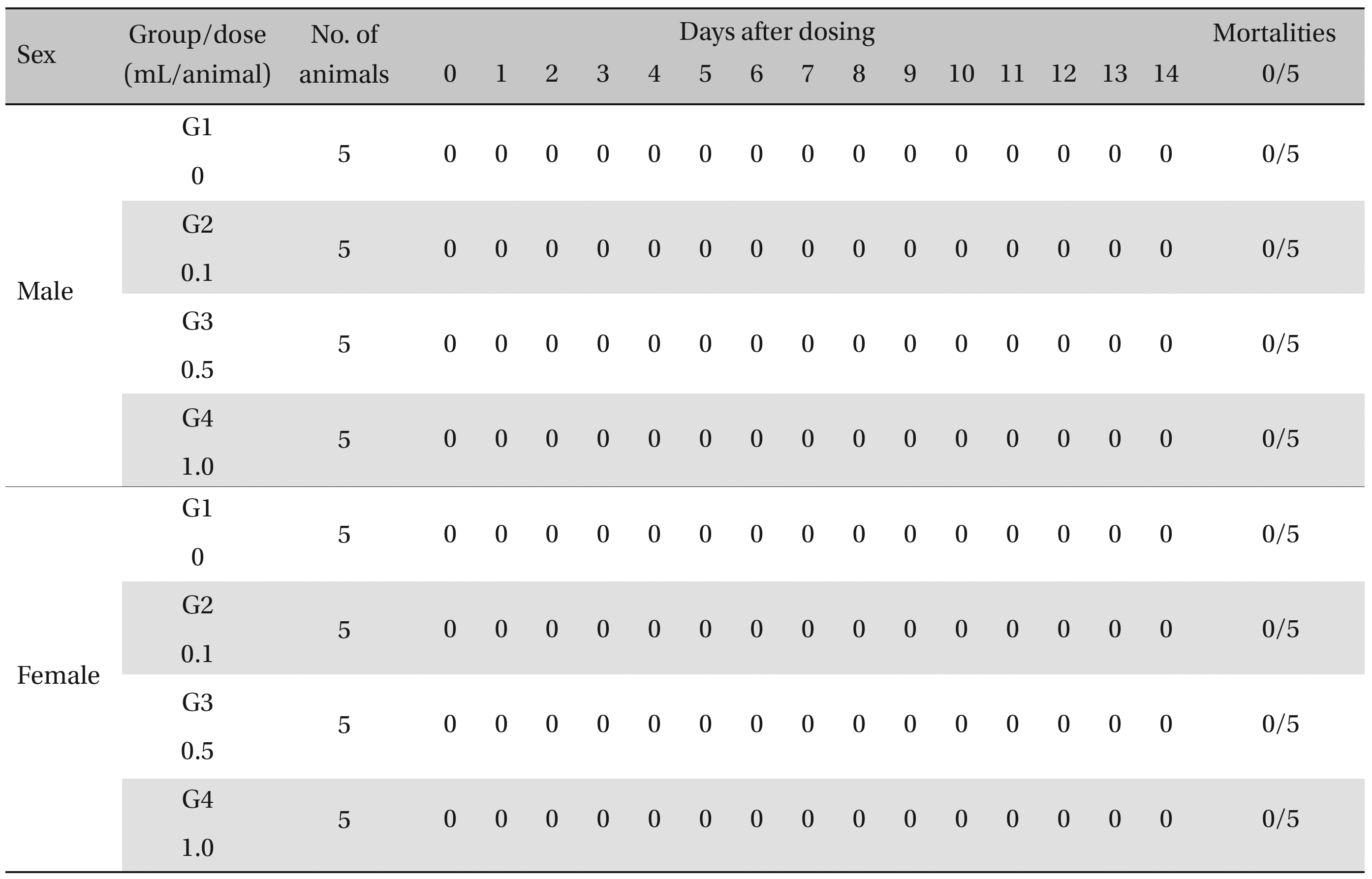
During the observation, no mortality or clinical signs were observed in the all of experimental (0.1, 0.5, and 1.0 mL/animal) or control groups (Table 2 and 3 ).
[Table. 2] Summary of Mortalities
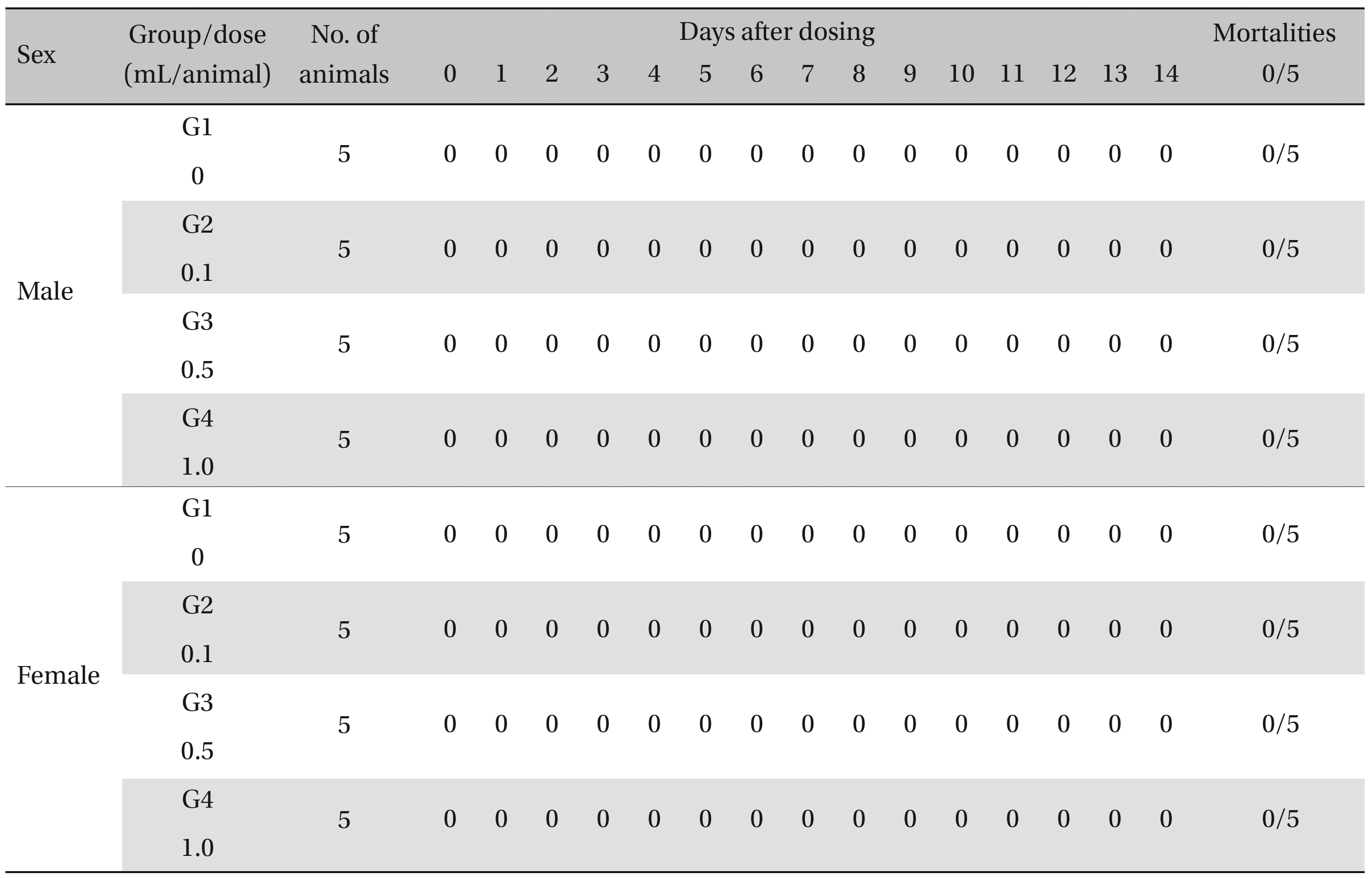
Summary of Mortalities
[Table. 3] Summary of clinical signs
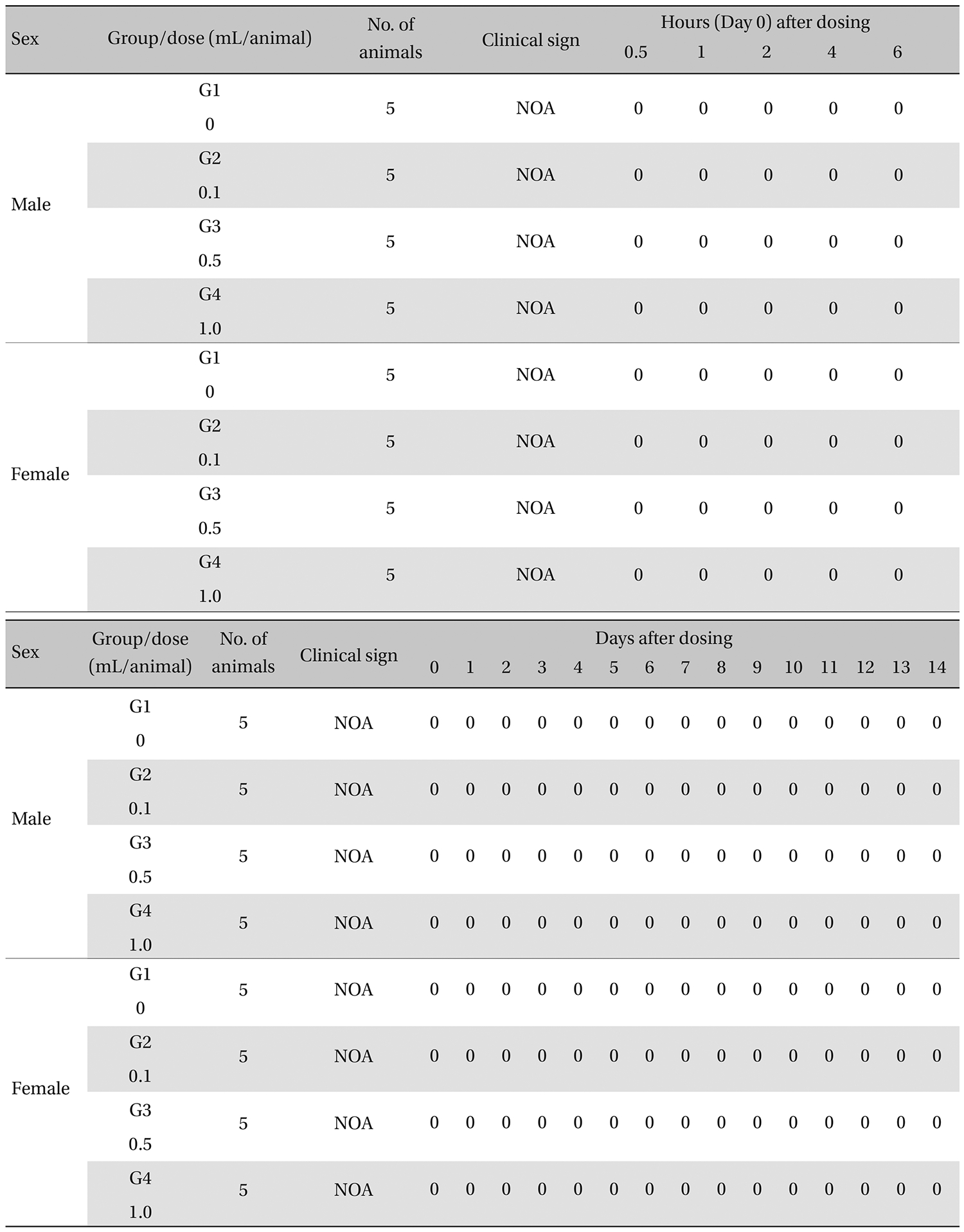
Summary of clinical signs
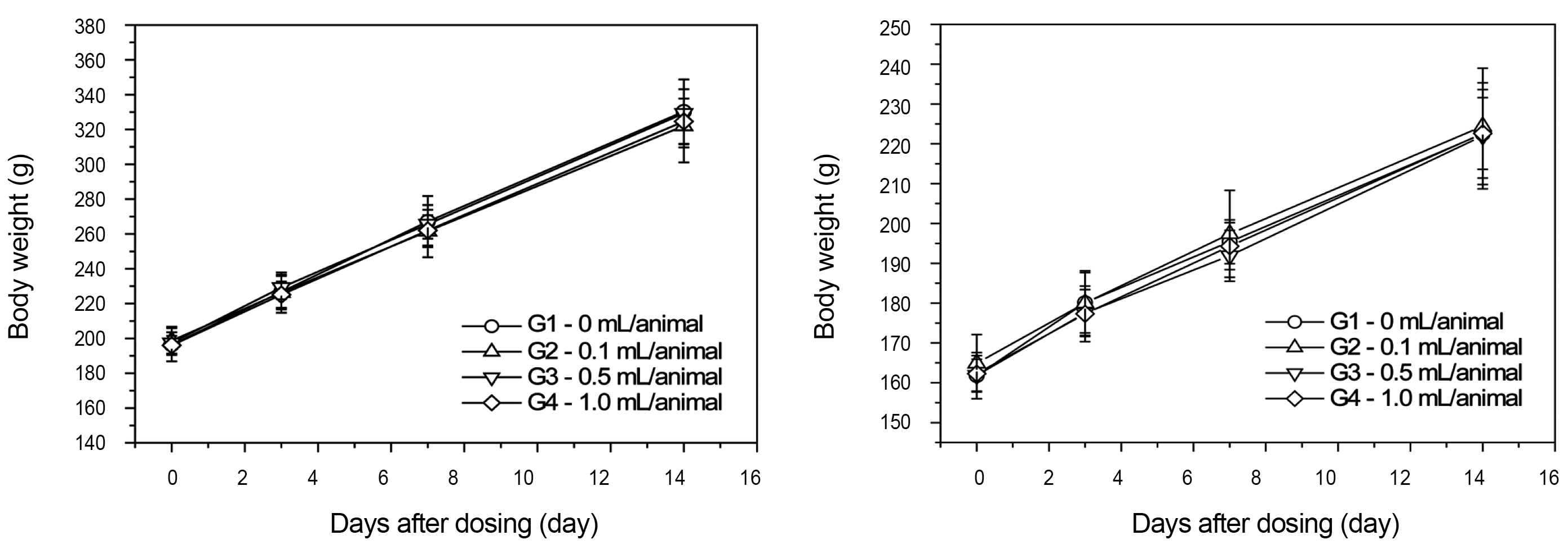
There was no significant change in body weight shown by comparison of the experimental (0.1, 0.5, and 1.0 mL/animal) and the control group (Fig 1 ).
3.3. Hematological test findings
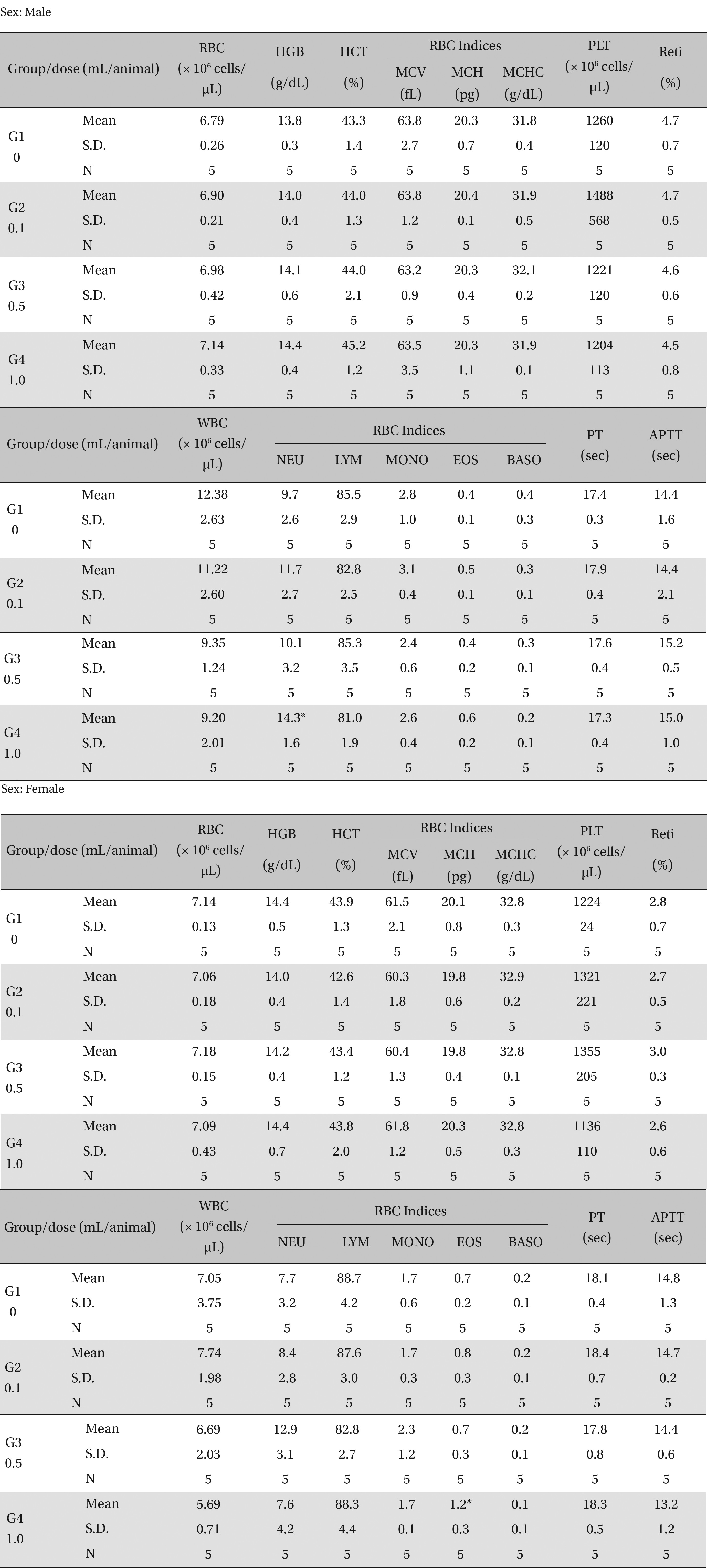
There was no significant change in the hematological test results observed from comparison of the experimental (0.1, 0.5, and 1.0 mL/animal) and the control group (Table 4 ).
[Table. 4] Mean hematology parameters
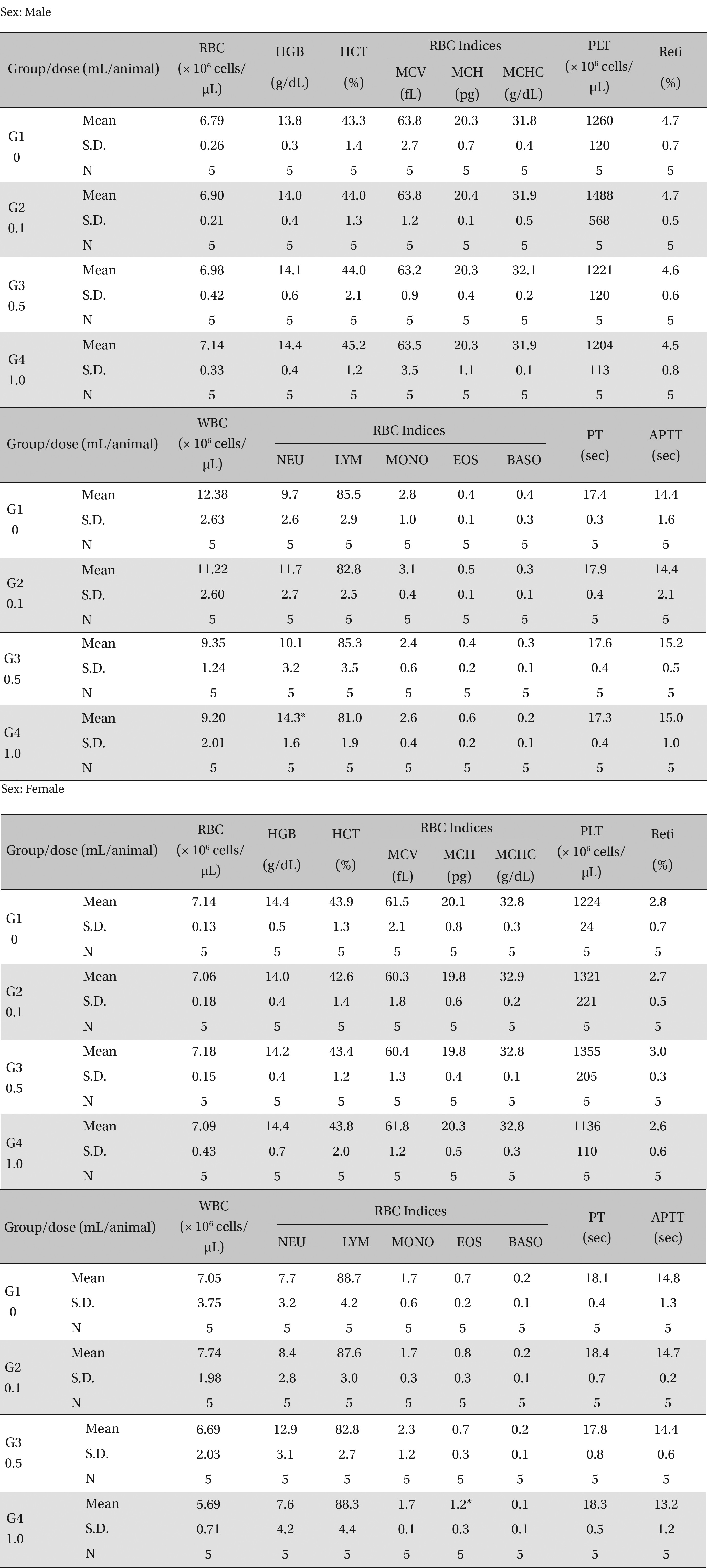
Mean hematology parameters
3.4. Biochemical test findings
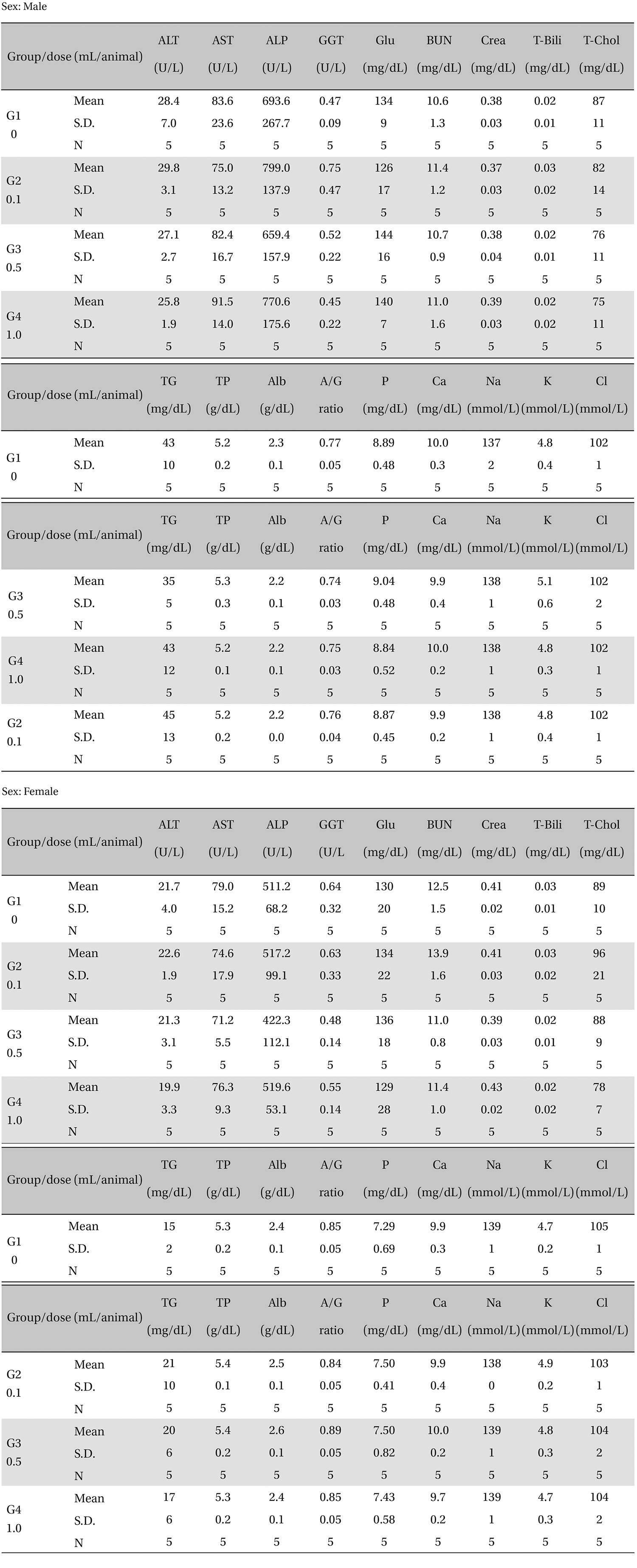
There was no significant change in the biochemical test results from experimental and control group (Table 5).
[Table. 5] Mean clinical chemistry
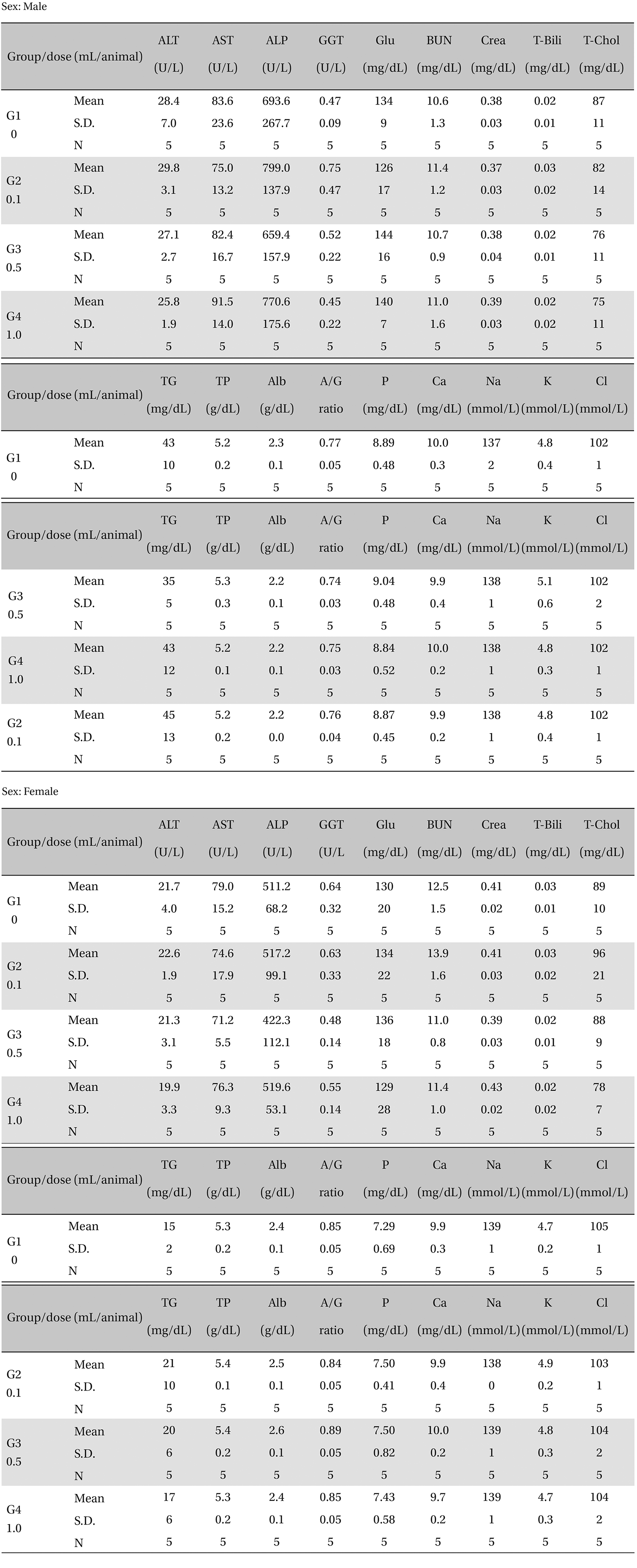
Mean clinical chemistry
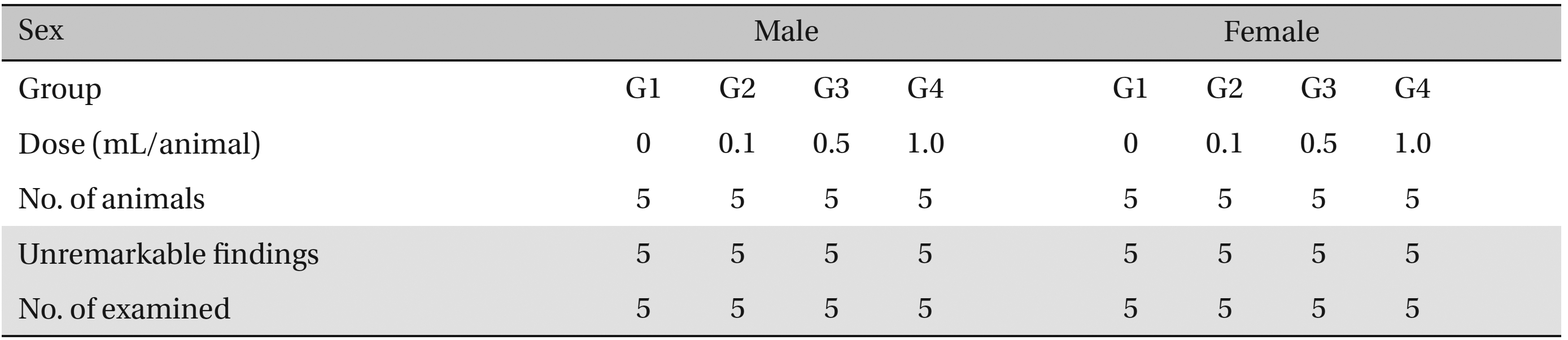
No abnormalities were observed when the visual inspection was conducted on all of the animals in experimental and control group (Table 6 ).
3.6. Histopathological findings
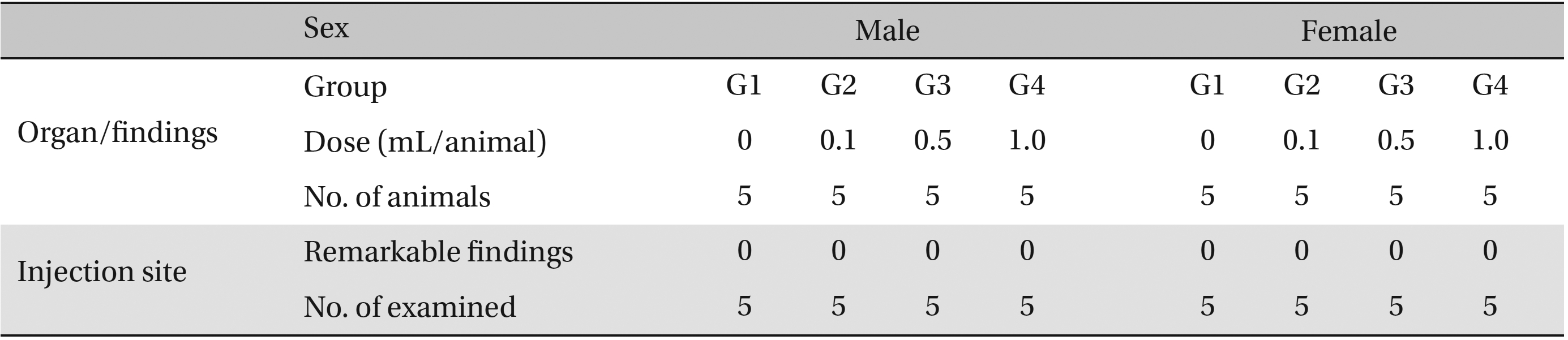
No abnormalities were observed in the local tolerance test on the injection sites (Table 7 ).
[Table. 6] Summary of necropsy findings
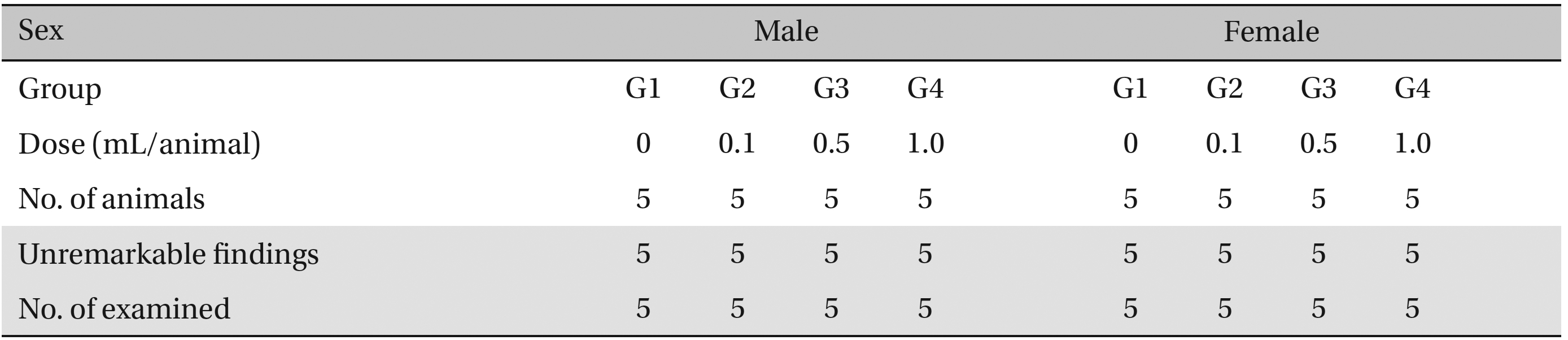
Summary of necropsy findings
[Table. 7] Summary of histopathological findings
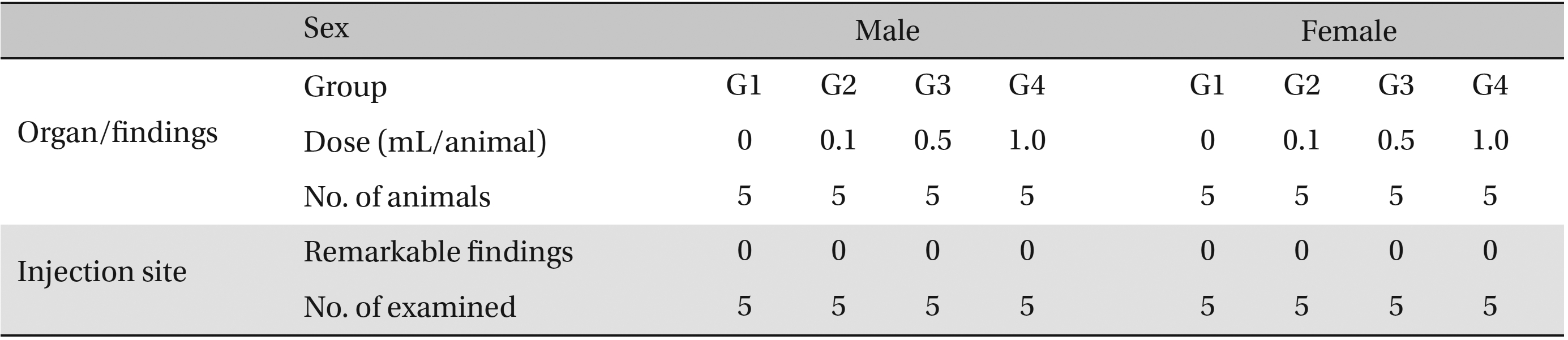
Summary of histopathological findings
Pharmacopuncture is a type of new acupuncture technique that combines acupuncture and drug therapies. It can be seen as a unique treatment technique of Korean Oriental medicine that provides the effects of meridian theory in acupuncture therapy and flavor theory in drug therapy [ 6 ]. The
Recent reports have suggested that
This study was performed to determine the safety of using
This study was designed to investigate the safety of