Pyungwi-san (PWS) plays a role in a number of physiologic and pharmacologic functions in many organs. Interstitial cells of Cajal (ICCs) are pacemaker cells that generate slow waves in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. We aimed to investigate the beneficial effects of PWS in mouse small-intestinal ICCs.
Enzymatic digestion was used to dissociate ICCs from the small intestine of a mouse. The wholecell patch-clamp configuration was used to record membrane potentials from the cultured ICCs.
ICCs generated pacemaker potentials in the GI tract. PWS produced membrane depolarization in the current clamp mode. Pretreatment with a Ca2+-free solution and a thapsigargin, a Ca2+-ATPase, inhibitor in the endoplasmic reticulum, eliminated the generation of pacemaker potentials. However, only when the thapsigargin was applied in a bath solution, the membrane depolarization was not produced by PWS. Furthermore, the membrane depolarizations due to PWS were inhibited not by U-73122, an active phospholipase C inhibitor, but by chelerythrine and calphostin C, protein kinase C inhibitors.
These results suggest that PWS might affect GI motility by modulating the pacemaker activity in the ICCs.
Pyungwi-san (PWS), a traditional herbal medicine, has been widely used for the treatment of gastrointestinal (GI) disorders such as inappetance, abdominal distension, borborygmus and diarrhea induced by gastric atony, gastric dilatation and GI catarrh [1,2]. It is composed of Atractylodis Rhizoma (Atractylodes japonica), Citri Pericarpium (Citrus unshiu), Magnoliae Cortex (Machilus thunbergii), Zingiberis Rhizoma Recens (Zingiber officinale), Zizyphi Fructus (Zizyphus jujube), and Gycyrrhizae Radix (Glycyrrhiza uralensis) [3]. Previous studies have shown that PWS has antioxidant properties. PWS exhibited a concentration-dependent inhibition of 1,1- diphenyl-2-picryl-hydrazil (DPPH) radical adduct formation and it showed dose-dependent free radical scavenging activity onto superoxide anions [4]. Moreover, PWS has protective and pharmacological effects on the gastric mucosal membrane [5]. A previous study also demonstrated the safety of PWS and reported an acute toxicity by using a rat model [6]. However, little is known about the beneficial effects of PWS on gastrointestinal (GI) motility.
Interstitial cells of Cajal (ICCs) are the pacemaking cells in the GI muscles and generate the rhythmic oscillations in the membrane potential known as slow waves [7-9]. Slow waves propagate within ICC networks, are conducted into smooth muscle cells via gap junctions, and initiate phasic contractions by activating Ca2+ entry through L-type Ca2+ channels. The pacemaker activity in the murine small intestine is due mainly to periodic activation of nonselective cation channels (NSCC) [10,11] or Clchannels [12,13]. ICCs also mediate or transduce inputs from the enteric nervous system. However, the effects of PWS in mouse small intestinal ICCs have not yet been investigated. Therefore, we undertook an investigating of the characteristics of PWS in mouse small intestinal ICCs.
2.1. Preparation of cells and cell cultures
Balb/c mice (3-7 days old) of either sex were anesthetized with ether and sacrificed by cervical dislocation. The small intestines from 1 cm below the pyloric ring to the cecum were removed and opened along the mesenteric border. Luminal contents were removed by washing with Krebs- Ringer bicarbonate solution. The tissues were pinned to the base of a Sylgard dish, and the mucosa was removed by sharp dissection. Small tissue strips of the intestine muscle (consisting of both circular and longitudinal muscles) were equilibrated in Ca2+-free Hanks solution (containing in mmol/L: KCl 5.36, NaCl 125, NaOH 0.34, Na2HCO3 0.44, glucose 10, sucrose 2.9, and HEPES 11) for 30 min. Then, the cells were dispersed using an enzyme solution containing collagenase (Worthington Biochemical Co., Lakewood, NJ, USA) at 1.3 mg/mL, bovine serum albumin (Sigma Chemical Co., St. Louis, MO, USA) at 2 mg/mL, trypsin inhibitor (Sigma) at 2 mg/mL and adenosine triphosphate (ATP) at 0.27 mg/mL. Cells were plated onto sterile glass coverslips coated with murine collagen (2.5 ㎍/mL, Falcon/BD, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA) in a 35-mm culture dish and were then cultured at 37°C in a 95% O2, 50-mL/L CO2 incubator in a smooth muscle growth medium (Clonetics Corp., San Diego, CA, USA) supplemented with 2% antibiotics/antimycotics (Gibco, Grand Island, NY, USA) and murine stem cell factor (SCF, 5 ng/mL, Sigma). ICCs were identified immunologically by using an anti-c-kit antibody (phycoerythrin-conjugated rat anti-mouse c-kit monoclonal antibody; eBioscience, San Diego, CA, USA) at a dilution of 1:50 for 20 min [14]. ICCs were morphologically distinct from other cell types in the culture, thus, identifying the cells by using phase contrast microscopy once they had been verified with the anti c-kit antibody was possible.
The whole-cell patch-clamp configuration was used to record membrane potentials (current clamp) for the cultured ICCs. An axopatch ID (Axon Instruments, Foster, CA, USA) was used to amplify the membrane currents and potentials. The command pulse was applied using an IBM-compatible personal computer and pClamp software (version 6.1, Axon Instruments). Data obtained were filtered at 5 kHz and displayed on an oscilloscope, a computer monitor, and a pen recorder (Gould 2200, Gould, Valley View, OH, USA). Results were analyzed using pClamp and Origin (version 6.0) software. All experiments were performed at 30-32°C.
The physiological salt solution used to bathe the cells (Na+-Tyrode) contained (mmol/L): KCl 5, NaCl 135, CaCl2 2, glucose 10, MgCl2 1.2 and HEPES 10, adjusted to pH 7.4 with NaOH. The pipette solution contained (mmol/L): KCl 140, MgCl2 5, K2ATP 2.7, NaGTP 0.1,creatine phosphate disodium2.5,4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1- piperazineethanesulfonic acid (HEPES) 5 and ethylene glycol tetraacetic acid (EGTA) 0.1, adjusted to pH 7.2 with KOH.
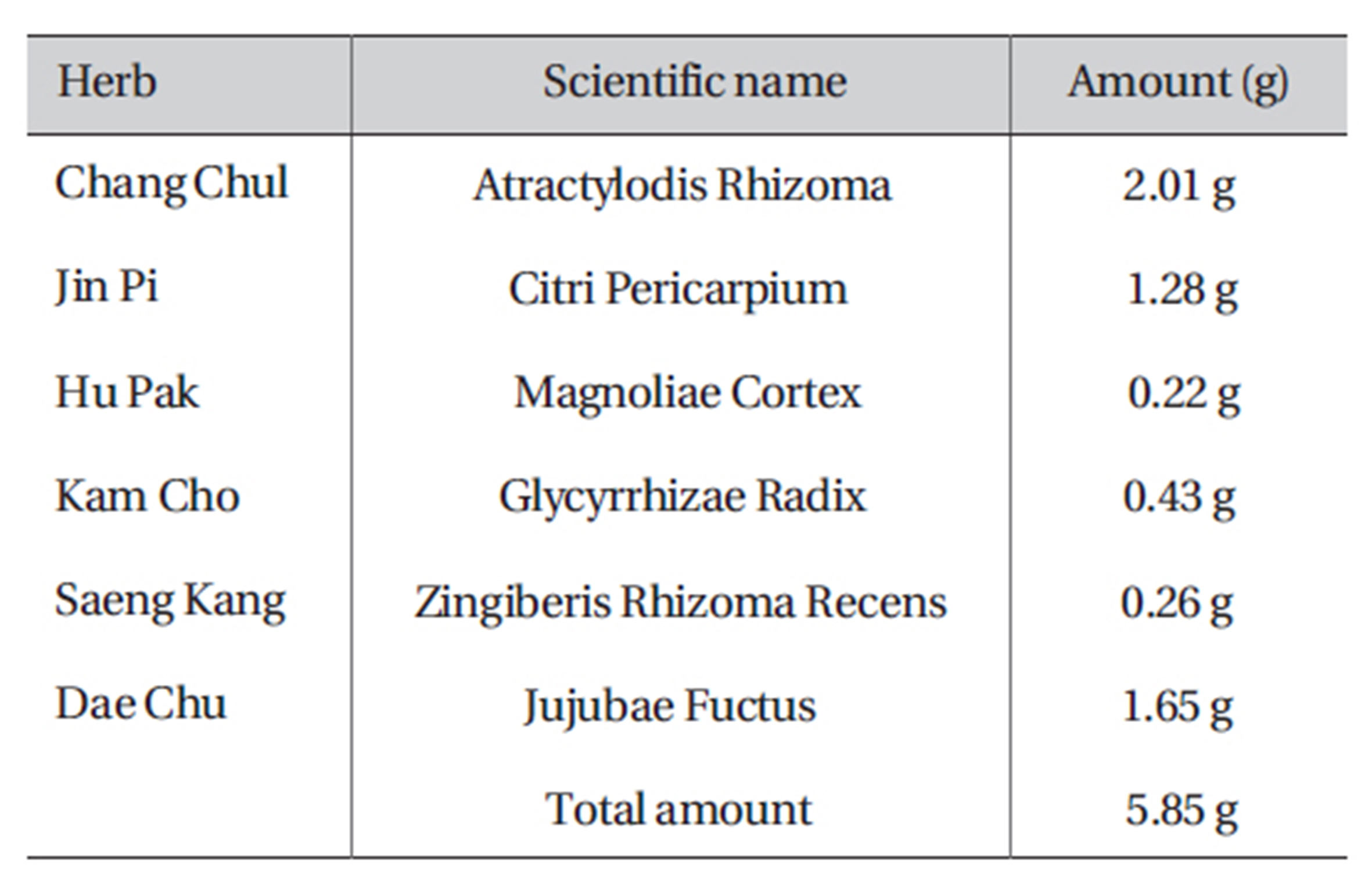
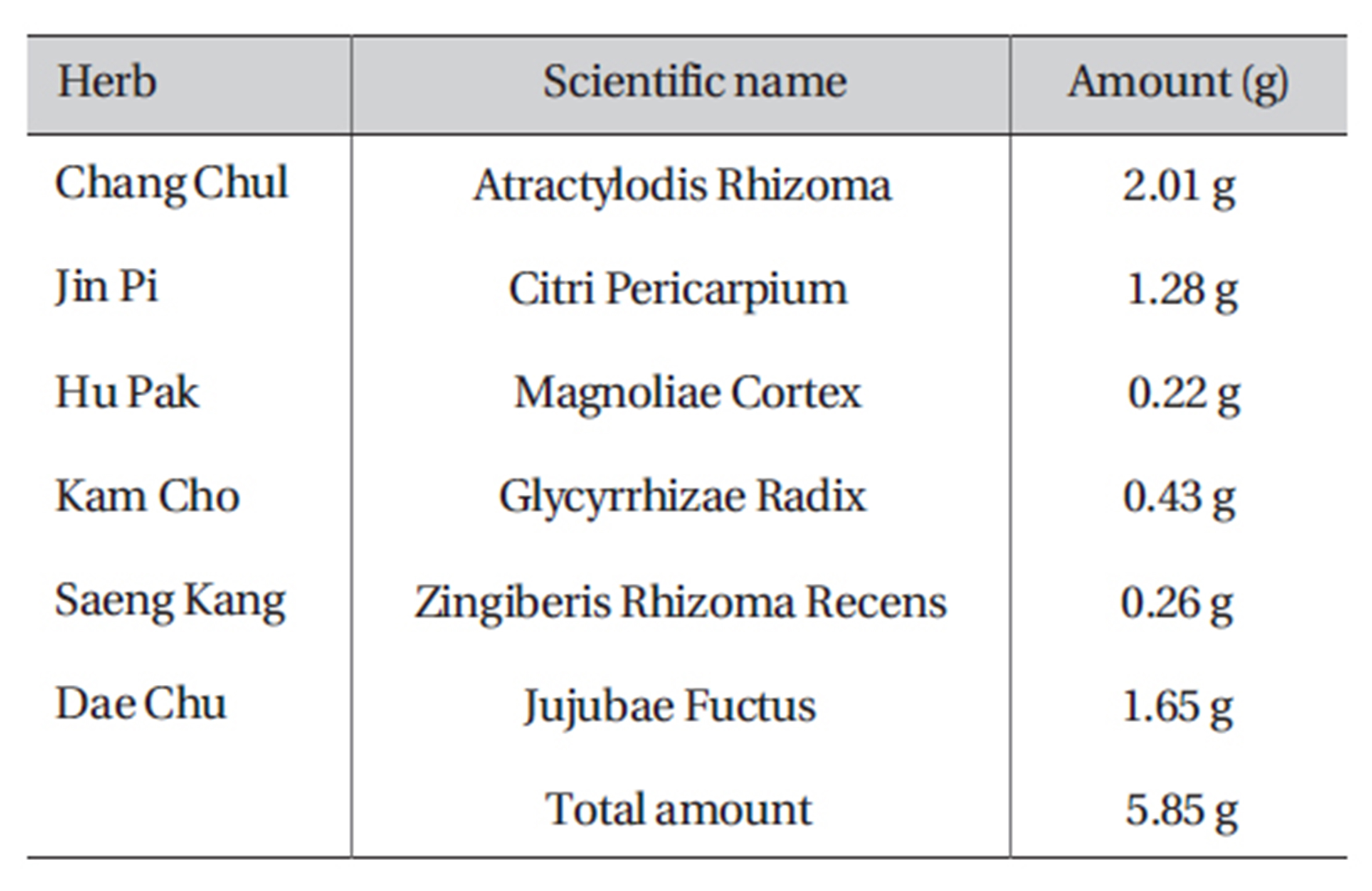
PWS was purchased from I-WORLD Pharmaceuticals (South Korea). PWS is composed of Atractylodis Rhizoma (Atractylodes japonica), Citri Pericarpium (Citrus unshiu), Magnoliae Cortex (Machilus thunbergii), Zingiberis Rhizoma Recens (Zingiber officinale), Zizyphi Fructus (Zizyphus jujube), and Gycyrrhizae Radix (Glycyrrhiza uralensis) (Table 1). The dosage for adult is 10-15 g (crude material) per day. More information about PWS can be found at I-WORLD Pharmaceuticals homepage (http://ipharm. koreasme.com). The PWS was dissolved in distilled water at a concentration of 0.5 g (crude drug)/ml and stored in a refrigerator. All other drugs were obtained from Sigma (Sigma Chemical Co., USA). Drugs were dissolved in distilled water and added to the bath solution just prior to use to make the desired concentrations. Addition of these chemicals to the bath solution did not alter the pH of the solution. Thapsigargin, U-73122, and U-73343 were dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) to obtain a 50-or 100-mmol/L stock solution that was the added (1000 times dilution) to the bath solution on the day of the experiment. The final concentration of DMSO in the bath solution was always < 0.1%, and we confirmed that this concentration of DMSO did not affect the results that were recorded.
[Table 1] Amount and composition of PWS
Amount and composition of PWS
All data are expressed as means ± standard error (SE). The Student’s
3.1. Effect of PWS on pacemaker potentials in cultured ICCs
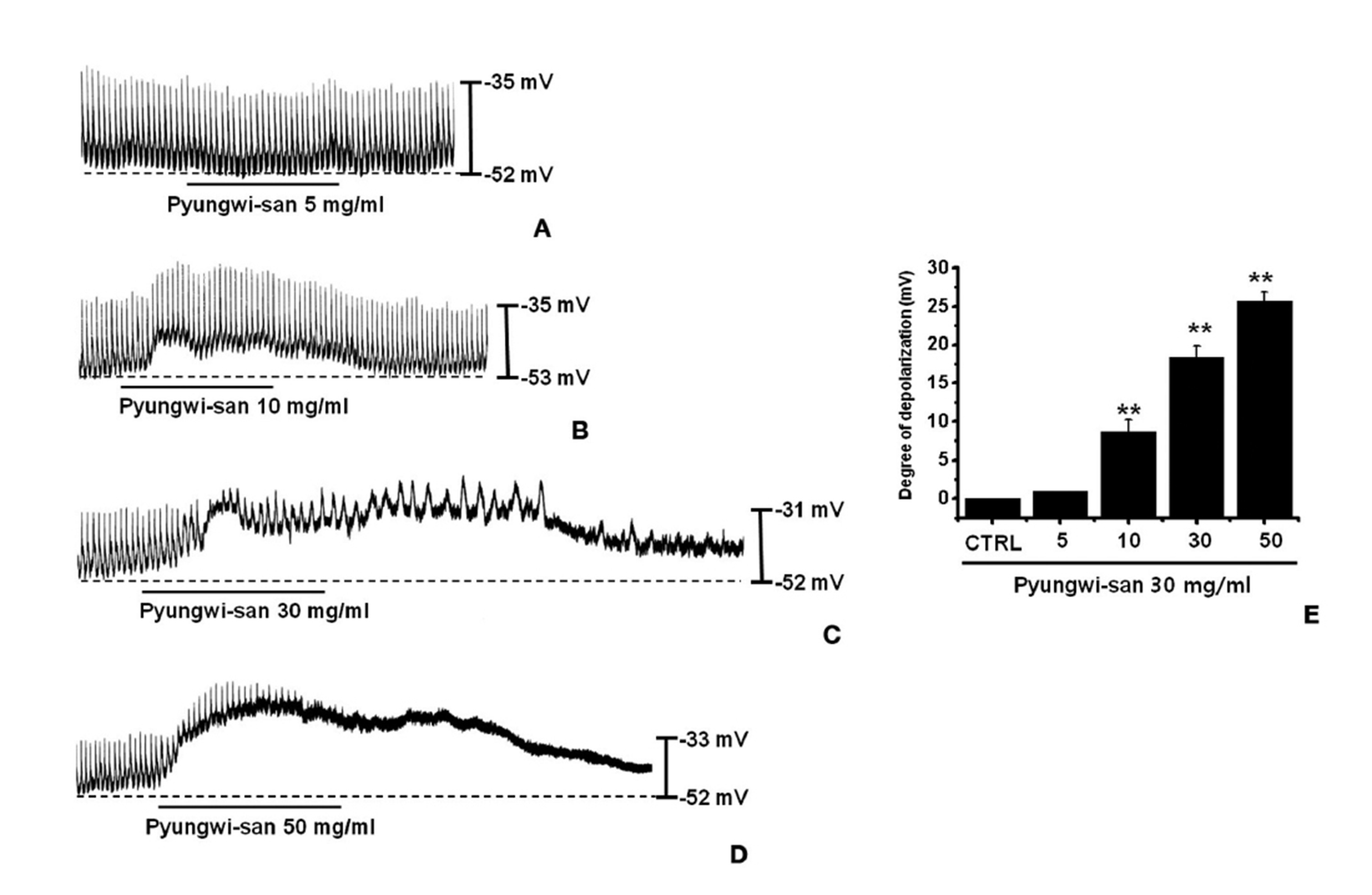
The patch-clamp technique was tested on ICCs that formed network-like structures in the culture (2-4 days). Spontaneous rhythms were routinely recorded from cultured ICCs under current- and voltage-clamp conditions, and the ICCs within networks displayed more robust electrical rhythms. Tissuelike spontaneous slow waves have been recorded from these cells [15]. To understand the relationship between PWS and the modulation of pacemaker activity in ICCs, we examined the effects of PWS on the pacemaker potentials. Recording from cultured ICCs under the current-clamp mode (I = 0) showed spontaneous pacemaker potentials. The resting membrane potential was -51.4 ± 1.2 mV, and the amplitude was 21 ± 3 mV. In the presence of PWS (5 - 50 mg/ml), the membrane potentials were depolarized to 1.0 ± 0.1 mV at 5 mg/ml, 8.4 ± 1.3 mV at 10 mg/ml, 18.3 ± 1.4 mV at 30 mg/ml, and 25.4 ± 1.1 mV at 50 mg/ml (Figs. 1A-D). A summary of the values and a bar graph for the effects of PWS on the pacemaker potentials are presented in Fig. 1E (n = 4).
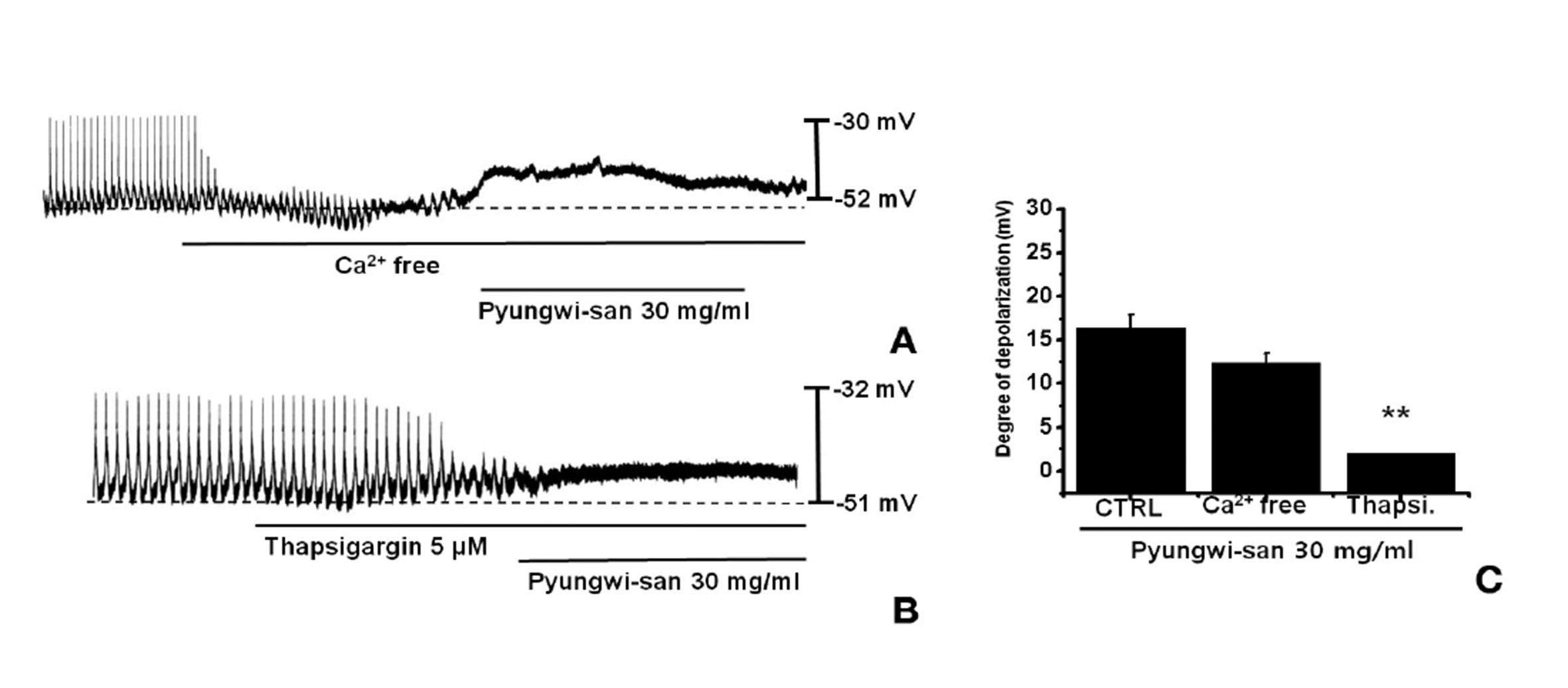
An external Ca2+ influx is necessary for GI smooth muscle contractions and is essential for generating pacemaker potentials in the ICCs. The generation of pacemaker currents depended upon intracellular Ca2+ oscillation [16]. To investigate the role of external Ca2+ vs internal Ca2+, we tested PWS under external Ca2+-free conditions and in the presence of thapsigargin, a Ca2+-ATPase inhibitor of the endoplasmic reticulum [10,17]. The pacemaker potentials were completely eliminated with an external Ca2+-free solution was used. In this condition, PWS induced membrane depolarizations (n = 4; Fig. 2A). Under external Ca2+-free conditions, the membrane depolarizations with PWS (30 mg/ml) were not significantly different when compared to those with PWS (30 mg/ml) in normal Ca2+ solution (n = 4, Fig. 2C). In addition, PWS-induced membrane depolarizations were inhibited by pretreatment with thapsigargin (Fig. 3B). In the presence of thapsigargin (5 ㎛), the membrane depolarizations with PWS were significantly different from those with PWS in the absence of thapsigargin (n = 4, Fig. 3C).
3.3. Effects of phospholipase C inhibitor on PWS-induced pacemaker potenials in cultured ICCs
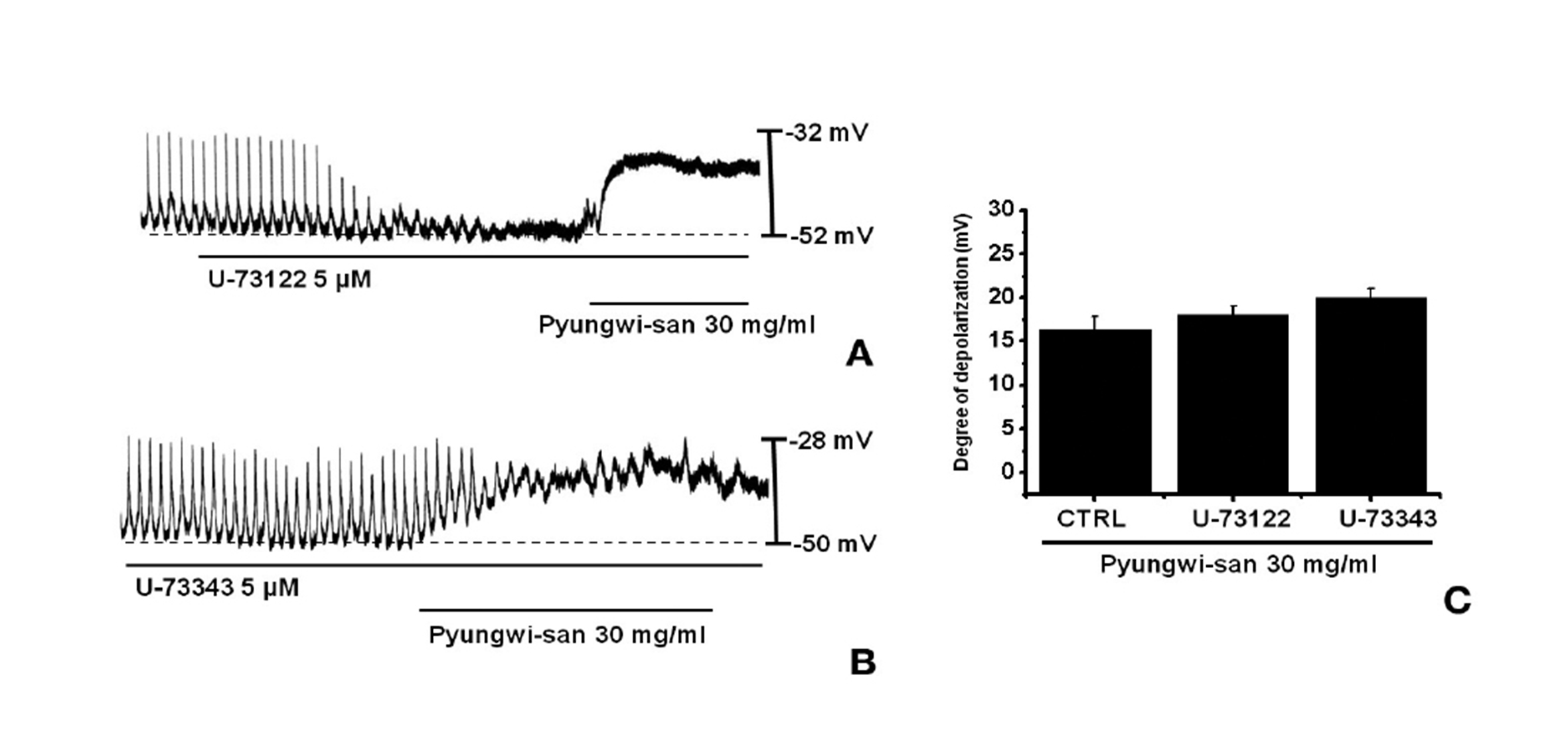
Since the membrane depolarizations caused by PWS were related to intracellular Ca2+ mobilization, we examined whether the effects on the pacemaker potentials required phospholipase C (PLC) activation. To test this possibility, we measured the PWS-induced membrane depolarizations in the absence and the presence of U- 73122, an active PLC inhibitor [18]. The pacemaker membrane depolarizations were completely eliminated when U-73122 (5 ㎛) was applied; however, under these conditions, PWS-induced (30 mg/ml) membrane depolarizations were produced (n = 4; Fig. 3A). In the presence of U-73122, the membrane depolarization produced by using PWS were 18.1± 1.5 mV. The membrane depolarizations caused by PWS with U-73122 were not different from those caused by PWS in the absence of U-73122 (n = 4, Fig. 3C). The treatment of U- 73343 (5 ㎛), an inactive analog of U-73122, had no influence on the PWS-induced pacemaker potentials and under these conditions, PWS-induced (30 mg/ml) membrane depolarizations were not suppressed by using U-73343 (Fig. 3B).
3.4. Effect of protein kinase C inhibitor on PWS-induced pacemaker potentials in cultured ICCs
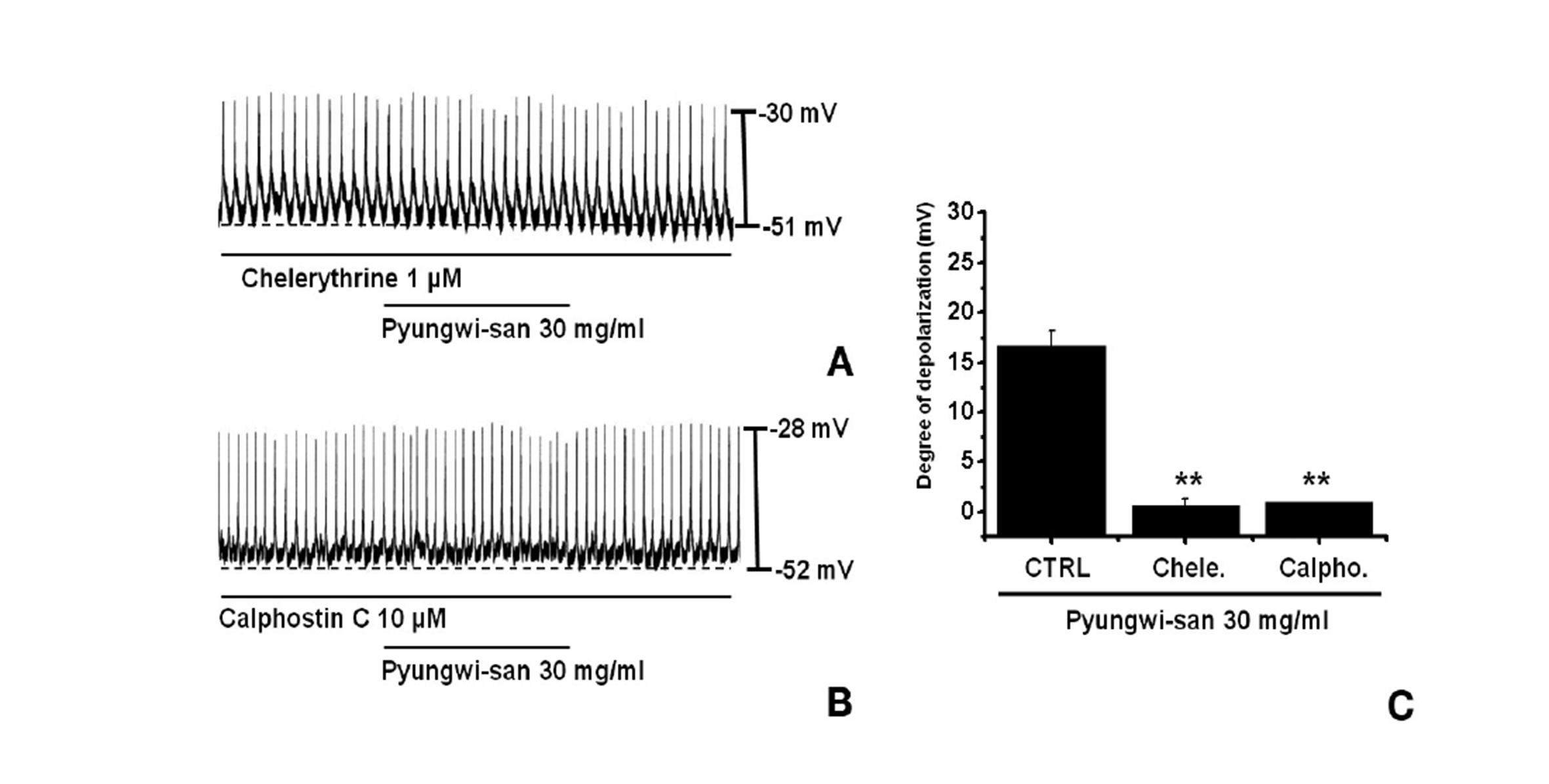
We tested the effects of chelerythrine or calphostin C, an inhibitor of protein kinase C [17,19], to investigate whether the PWS-induced responses to the pacemaker potentials were mediated by the activation of protein kinase C. Chelerythrine (1 ㎛) or calphostin C (10 ㎛), had no effect on the membrane depolarizations caused by PWS (30 mg/ml; Fig. 4) and the values of the membrane depolarizations were significantly different from those caused by PWS in the absence of chelerythrine or calphostin C (n = 5; Fig. 4C).
ICCs are the pacemaking cells in the GI muscles and generate the rhythmic oscillations in the membrane potential known as slow waves [8-10]. Slow waves propagate within ICC networks, conduct into smooth muscle cells via gap junctions, and initiate phasic contractions by activating Ca2+ entry through L-type Ca2+ channels. The pacemaker activity in the murine small intestine is due mainly to periodic activation of nonselective cation channels (NSCCs) [11] or Cl- channels [12,13]. ICCs also mediate or transduce inputs from the enteric nervous system. Because of the central role of ICCs in GI motility, loss of these cells would be extremely detrimental. Research on the biological function of ICCs provides exciting new opportunities for understanding the etiology of diseases that have long eluded comprehension [9,11].
PWS is a mixture of six herbs and is traditionally used in northeast Asia (especially Korea and Japan) for the treatment of gastrointestinal disorders, such as dyspepsia and inappetance induced by gastric dilatation and gastrointestinal catarrh. A composite traditional Korean medicine, PWS is a basic prescription consisting of six herbs and contains hesperidin, 6-gingerol, honokiol, glycyrrhizin and magnolol [20]. Although, the beneficial effects of PWS have been elucidated for antioxidant and clinical uses, the effects of PWS on GI motility and on the ICCs have not been investigated yet.
In this study, PWS produced membrane depolarization in the current-clamp mode. Pretreatment with a Ca2+-free solution and thapsigargin, a Ca2+-ATPase inhibitor in the endoplasmic reticulum, eliminated the generation of pacemaker potentials. Under Ca2+-free solution conditions, PWS was found to cause membrane depolarizations. Also, the pacemaker membrane depolarizations were not inhibited by the use of U-73122, an active phospholipase C inhibitor. Furthermore, the protein kinase C inhibitors, chelerythrine and calphostin C, did block the PWS-induced pacemaker potentials. These results suggest that PWS might affect GI motility through a modulation of the pacemaker activity in the ICCs, and that the activation is associated with protein kinase C activation, and with Ca2+ release from internal storage in an external-Ca2+-independent and phospholipase C-independent manner.
Taken together, our data suggest that the gastroprokinetic effects of PWS might be mediated by the induction of pacemaker potentials in the ICCs. Considering the effects of this drug on the ICCs, further research, including finding active compound(s) and examining their action mechanisms, is clearly needed.