The root of Lithospermum erythrorhizon Sieb. et Zucc. (Lithospermi Radix, LR) is a kind of heat clearing and blood cooling medicinal herbs. It can clear away heat and cool the blood, reduce toxins and disperse maculae. LR has long been used as efficacious therapy for inflammation, burns, frostbite and skin diseases such as eczema and psoriasis.
In the present study, we investigate anti-allergic and anti-inflammatory effects of LR by using the 1-fluoro-2, 4- dinitrofluorobenzene (DNFB)-induced contact dermatitis mouse model.
Topical application of 10 mg/mL of LR effectively inhibited skin lesions induced by repeated paintings with DNFB. Topical application of LR also inhibited hyperplasia, edema, spongiosis and infiltrations of mononuclear cells. In addition, production levels of total immunoglobulin and IgG1 in serum were decreased by using LR in vivo.
These data suggest that LR acts as an antiinflammatory agent, improving skin lesions in CD mice.
In the theory of traditional medicine, dried root of
Allergic contact dermatitis, one of the most common occupational diseases in industrialized countries, is caused by delayed-type hypersensitivity (DTH) responses to environmental allergens [8]. A widely used animal model of human contact dermatitis, also known as contact hypersensitivity (CHS), is the DTH response to haptens such as dinitrofluorobenzene (DNFB) and dinitrochlorobenzene (DNCB) in mice [8,9]. Repeated applications of an antigen such as DNFB or DNCB is well known to induce typical features of contact dermatitis, including swelling, spongiosis and hyperplasia of tissues [10].
Based on this background, we evaluated the anti-allergic effects of LR by using the mouse model of contact dermatitis (CD). In the present study, we investigated the effects of LR on the skin’s condition, histopathological changes of tissues, and the levels of antibodies in serum.
LR was purchased from Kwangmyungdang Medicinal Herbs (Ulsan, Korea). Fifty (50) g of LR were immersed in 1,000 ml of methanol, sonicated for 30 mins, and then extracted for 24 hrs. The extract was filtered with Whatman filter paper (No. 20) and evaporated under reduced pressure by using a vacuum evaporator (Eyela, Japan). The condensed extract was then lyophilized using a freeze dryer (Labconco, USA). Finally, 15.0 g of lyophilized powder was obtained (yield: 30.0%).
Male balb/c mice (6 weeks old) were purchased from Samtaco (Incheon, Korea). Mice were housed under specific pathogenfree conditions with a 12 h light/dark cycle and had free access to standard rodent food and water. All animal experiments were approved by our Animal Care and Use Committee and were performed according to institutional guidelines.
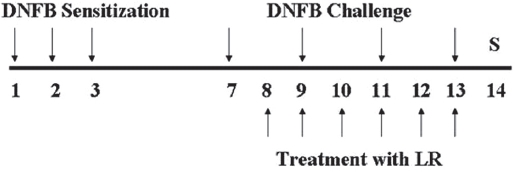
2.3. Induction of CD and experimental design
Mice were sensitized by painting 30 μL of DNFB (0.1%, v/v) in acetone:olive oil (AOO, 4:1) on the dorsum of each ear for three consecutive days. Three days later, dorsa of the mice were shaved, four days after sensitization, mice were challenged by painting 50 μL of DNFB (0.2%, v/v) in AOO on the shaved dorsa every 2 days. LR was dissolved in ethanol, then filtered using a syringe filter (0.45 μm), and finally diluted in AOO (ethanol:AOO, 4:1). LR solution, 10 mg/mL, was painted on the shaved dorsa for 6 days.
All animals, except naive mice were sensitized and challenged with DNFB. Naive animals (Naive) were treated with a vehicle (AOO) and painted with a vehicle (n = 6). Control animals (CTL) were sensitized and challenged with DNFB and then painted with a vehicle (n = 8). LR-treated animals were sensitized and challenged with DNFB and then painted with 10 mg/mL of LR solution (n = 8). The experimental design is shown in Fig. 1.
2.4. Macroscopic observation of the skin surfaces
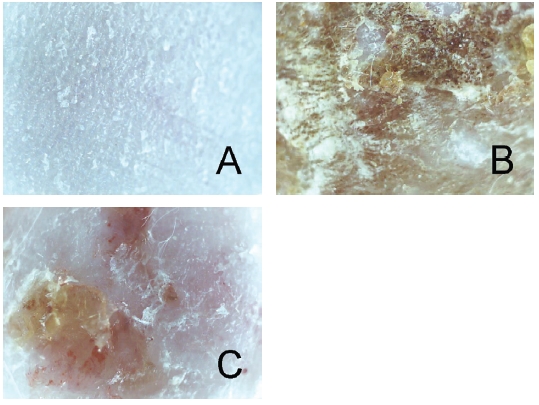
At the end of experiment, in order to observe the overall degree of CD, mice were sacrificed and the skins of the dorsa were observed using a skin image analysis system (Skin NBT, Korea) (x30).
2.5. Histopathological examination
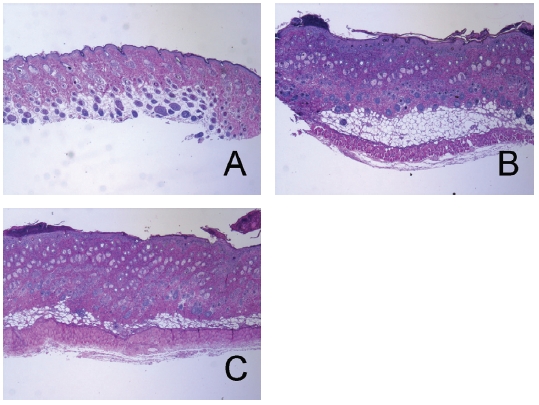
After observation of the skins of the dorsa, tissues were resected and paraffin-embedded. Sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) for histopathological observations such as immune cell infiltration and spongiosis. Stained tissues were observed using a light microscope (x100).
2.6. Measurement of immunoglobulin production
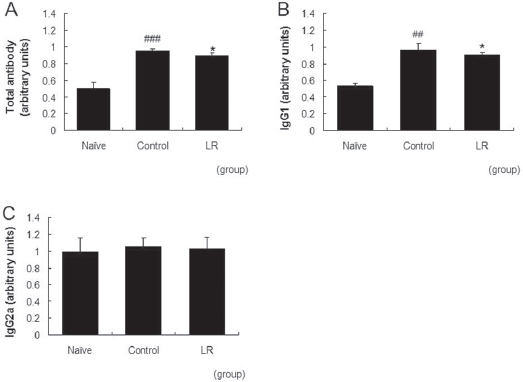
The levels of total antibodies, IgG1 and IgG2a in serum were measured by using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Blood samples were centrifuged at 220 g for 5 min to obtain sera. For ELISA, 96-well plates (Nunc, USA) were coated with goat anti-mouse polyvalent antibody (Sigma, 1:1000) dissolved in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) at RT for 3 hrs, and incubated at 4℃ overnight again. After the plates had been coated, blocking solution (1% skim milk and 0.05% Tween 20 in PBS) was added, and the plates were incubated at RT for 1 h. After washing, 100 μl of diluted serum (1:20 in PBS) was added to each well, and plates were incubated at RT for 2 hrs. After washing, alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-mouse immunoglobulin was added, and plates were incubated at RT for 1 h. After incubation, p-NPP was added. The optical density (OD) was measured at 405 nm by using a microplate spectrophotometer (ELx808Multichannel, BioTek, VT, USA). Secondary antibodies used were goat anti-mouse polyvalent antibody (1:1000), goat anti-mouse IgG1 antibody (1:1000) and goat antimouse IgG2a antibody (1:1000). The serum obtained from another experiment was used as a standard serum and all the titers were calculated as values relative to this serum.
All statistical comparisons were made with the Student’s ttest. The SigmaPlot version 11.0 (SYSTAT software, USA) software was used for statistical analysis. All data were presented as mean ± SD. Differences with a value of
3.1. Effects of LR on skin lesions in CD mice
There were no abnormal changes in the naive group (Fig. 2A). Repeated paintings of DNFB resulted in skin lesions of CD such as erythema, scaling and crust (Fig. 2B). The group treated with 10 mg/mL of LR showed diminished skin lesions compared to the vehicle-treated control group (Fig. 2C).
3.2. Effects of LR on histopathological changes of tissues in CD mice
There were no abnormal changes in tissues in the naive group (Fig. 3A). The epidermis in the control group showed hyperplasia, and significant edema and spongiosis were observed. In addition, marked infiltrations of mononuclear cells were also observed in the dermis (Fig. 3B). LR treatment slightly diminished hyperplasia, edema and spongiosis (Fig. 3C).
3.3. Effects of LR on production levels of immunoglobulin in CD mice
Repeated application of DNFB resulted in increased total antibody and IgG1 levels in the serum. The level of IgG2a was almost the same as that for the naive group in our model. Treatment with 10 mg/mL of LR suppressed the increases in
the total antibody and the IgG1 levels significantly (Fig. 4A,B). The level of IgG2a was not affected by topical applications of LR (Fig. 4C).
Physiological stress, air pollution, exposure to chemicals or exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light can induce allergic diseases including CD [11]. The main etiologic treatment of CD is avoidance of the contact allergen, but in certain circumstances, elimination of the offending agent is insurmountable. For this reason, the therapy is reduced to assuaging the inflammatory component [12,13]. An emerging class of agents, such as antiinflammatory agents or immunomodulators, have provided various options for treatment of CD [12,13]. In recent years, interest has arisen in the use of medicinal plants as complementary and alternative medicines, possibly because of low cost and favorable safety [14]. In Korea, many medicinal herbs have been used to treat dermatological disorders.
In the present study, we demonstrated the anti-allergic and the anti-inflammatory actions of LR by using a mouse model of CD. Topical application of LR was found to suppress allergic reactions in the DNFB-induced allergic contact dermatitis model for mice. Skin lesions such as erythema, scaling and crust were diminished by topical application of LR (Fig. 2). Inflammatory hyperplasia was slightly decreased in histopathological observation (Fig. 3). Spongiosis refers to intercellular epidermal edema and is recognized as the microscopic hallmark of inflammatory skin diseases such as allergic contact and nummular dermatitis [15]. In our results, topical application of LR reduced spongiosis and mononuclear cell infiltration effectively (Fig. 3). Taken together, epidermal spongiosis, edema and inflammatory cell infiltration resulted in skin lesions such as erythema, scaling and crust, and LR prevented these inflammatory reactions effectively in DNFB-induced CD.
Specific antibodies are well known to be involved in pathophysiology of CD. A guinea pig model was used to investigate the potential role of hapten-specific antibodies in allergic contact dermatitis. Hapten-specific antibodies of both the IgG1, IgG2 and IgM (sub) classes could be detected by using ELISA in sera [16]. In our results, repeated paintings with DNFB elevated serum levels of total immunoglobulin and IgG1. Topical application of LR effectively prevented elevations of total immunoglobulin and IgG1 in serum (Fig. 4). These results imply that LR acts as an anti-inflammatory agent, improving skin lesions in CD mice. In our model, the serum IgE levels of all experimental groups were shown as basal levels, which may have been due to the low concentration of IgE in the serum (data not shown). Taken together, we believe that LR can be used to treat patients with CD and may be useful as a complementary or alternative medicine to steroids.