Angiotensin-I-converting enzyme (ACE; EC 3.4.15.1) is a circulating enzyme that participates in the body’s rennin-angiotensin system and plays an important physiological role in regulating blood pressure. ACE is known as peptidyl dipeptidase A and primarily cleaves a C-terminal dipeptide from substrates. It converts an inactive form of a decapeptide (angiotensin-I) to a potent vasoconstrictor, an octapeptide (angiotensin-II), and also inactivates the catalytic function of bradykinin, which has a depressor action (Ondetii et al., 1977; FitzGerald et al., 2004).
To date, many peptides with high ACE-inhibitory activity have been isolated and characterized from both natural products and processed foods. These include various protein hydrolysates, such as those of cheese (Smacchi and Gobbetti, 1998), milk proteins (Gobbetti et al., 2000), egg white (Miguel et al., 2007), white and red wines (Pozo-Bayon et al., 2007), plant proteins (Dziuba et al., 1999; Wu et al., 2008), meat (Jang and Lee, 2005), and marine sources (Fujita and Yoshikawa, 1999; Je et al., 2005; Lo and Li-Chan, 2005; He et al., 2006). Some types of ACE-inhibitory peptide have also been isolated from fish proteins, such as sardines (Matsui et al., 1993), tuna (Kohama et al., 1988), cod (Kim et al., 2000), and bonito (Matsumura et al., 1993). These protein hydrolysates were usually produced using treatment with gastrointestinal (e.g., pepsin and pancreatin) or microbial (e.g., secreted by various microorganisms or supplied as commercial preparations, such as Protamex) enzymes under optimal conditions.
Salted jellyfish is a popular foodstuff because it contains about 97% moisture. Jellyfish have traditionally been used to treat asthma and hypertension in East Asian countries. Although jellyfish have been used for hypertensive therapy, information on the active compound(s) is lacking.
Thus, the purpose of this study was to determine the functional properties of the active compound of
The giant jellyfish,
>
Preparation of jellyfish hydrolysates
The influence of proteolytic enzymes on jellyfish hydrolysis was studied under the following conditions. First, jellyfish samples were lyophilized to remove excess water and then subjected to hydrolysis. Enzyme reactions were carried out for 1-4 h using 10% (w/v) lyophilized jellyfish and the following temperature and pH conditions: Alcalase, pH 7.0, 60℃; Flavozyme, pH 7.0, 50℃; Neutrase, pH 6.0, 50℃; papain, pH 6.0, 60℃; Protamex, pH 6.0, 40℃; and trypsin, pH 7.0, 40℃. To determine the optimal enzyme concentration, the ratio of reaction volume to enzyme quantity was varied from 1-4% (w/v). Reactions were stopped by heat treatment at 90℃ for 15 min. The resultant slurries were centrifuged at 3,000 g for 10 min and the supernatants used as hydrolysates for further analysis.
In all experiments, the degree of hydrolysis was evaluated as the proportion (%) of α-amino nitrogen (N) with respect to the total N in the samples (Taylor, 1957).
>
Determination of ACE-inhibitory activity
The ACE-inhibitory activity assay was performed using a modified version of the method of Cushman and Cheung (1971). The standard reaction mixture contained 5 mM His-His-Leu as a substrate, 0.3 M NaCl, and 5 mU ACE in 50 mM sodium borate buffer (pH 8.3). A sample (50 μL) was added to the enzyme solution (50 μL) and then mixed with 8.3 mM Hip-His-Leu (150 μL) containing 0.5 M NaCl to the same concentration as the standard reaction mixture. After incubation at 37℃ for 30 min, the reaction was stopped by the addition of 1.0 N HCl (250 μL). The resulting hippuric acid was extracted by the addition of 1.5 mL ethyl acetate. After centrifugation (800 g, 15 min), 1 mL of the upper layer was transferred into a new glass tube and evaporated at room temperature for 2 h in a vacuum. The extracted hippuric acid was dissolved in 3.0 mL distilled water, and absorbance was measured at 228 nm using a spectrophotometer (Model U-3210; Hitachi Co., Tokyo, Japan). The IC50 value of the purified active fraction was determined by the standard method and defined as the concentration of inhibitor required to inhibit 50% of ACE activity.
>
Fractionation of jellyfish hydrolysates
To identify the ACE-inhibitory compound, the papain hydrolysate showing the highest inhibitory activity was selected and the resultant hydrolysate was fractionated through millipore membranes (Amicon Co., Beverly, MA, USA) with 5,000, 3,000, and 1,000 Da molecular weight cut-offs. Each fraction was lyophilized and then stored at -70℃ until required.
>
Purification and peptide sequencing
Of the fractionated samples, fraction II showed the greatest inhibitory activity and was further purified by reverse-phase HPLC (5 μM, 10×250 mm; C18 ODS 3100A; Phenomenex, Torrance, CA, USA) elution with a linear gradient of MeOH-H2O (2 mL/min flow rate, ultraviolet detection at 214 nm). This procedure was repeated to increase purity. To determine the N-terminal sequence, the purified peptide showing the greatest ACE-inhibitory activity was subjected to automated Edman degradation on a protein sequencer (Perkin Elmer Model 470; Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The amino acid sequence identity was aligned by searching database non-redundant protein sequences using the positron-specific iterative basic local alignment search tool (PSI-BLAST) of the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI).
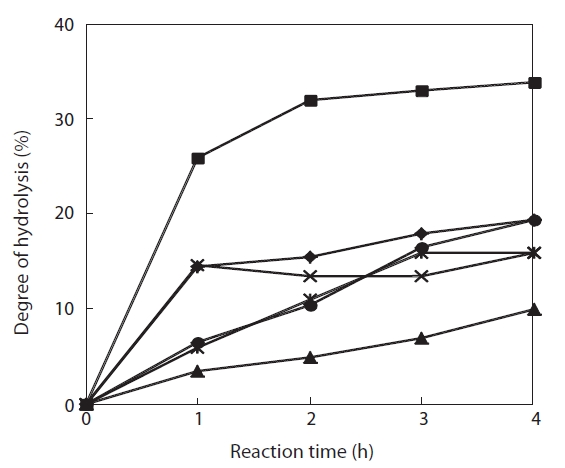
The degree of hydrolysis of the jellyfish hydrolysates obtained using 1-4% enzyme and a 4-h reaction varied from 13.1-36.8%, and leveled off even when enzyme concentration was increased to 4% (Fig.1 ). The degree of hydrolysis increased with reaction time; Flavozyme resulted in the greatest hydrolysis and Neutrase the lowest. Moreover, Alcalase and papain showed identical hydrolysis patterns and trypsin showed a pattern similar to that of Protamex (Fig.2 ). These results indicate that a 4-h reaction time allowed for complete hydrolysis under the conditions mentioned above. Lee et al. (2001) determined the degree of hydrolysis and ACE-inhibitory activity of laver (
>
ACE-inhibitory activities of enzymatic hydrolysates
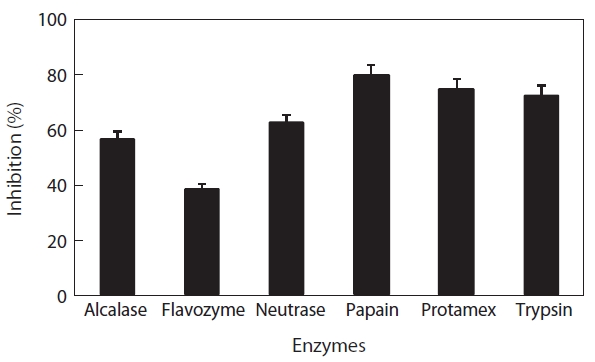
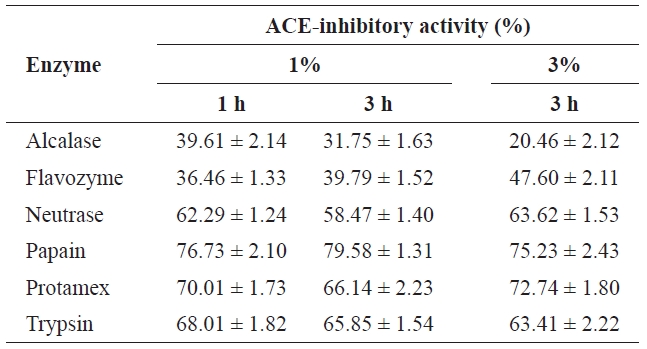
To select the protease hydrolysate with the maximum ACE-inhibitory activity, lyophilized jellyfish were hydrolyzed with papain, trypsin, Flavozyme, Alcalase, Protamex, and Neutrase. Of these hydrolysates, that of papain revealed a high ACE-inhibitory activity in a 1-h reaction (76.73±2.10%) (Table 1). Increasing the enzyme concentration up to 3% or prolonging the reaction time up to 3 h had no effect on ACE-inhibitory activity, although the degree of hydrolysis increased (Fig.2 ). Interestingly, Flavozyme-treated hydrolysate showed the highest degree of hydrolysis (Fig.1 ) but the lowest inhibitory activity (Table 1). In contrast, the papain and Alcalase hydrolysates, which showed similar hydrolysis patterns, had differing ACE inhibition ratios (papain 76.73%, Flavozyme 36.01%), indicating that the primary structure of the hydrolysates obtained by these two enzyme reactions affected ACE inhibition (Fig.3 ).
[Table 1.] ACE-inhibitory activities on incubation times and addition amounts of enzymes
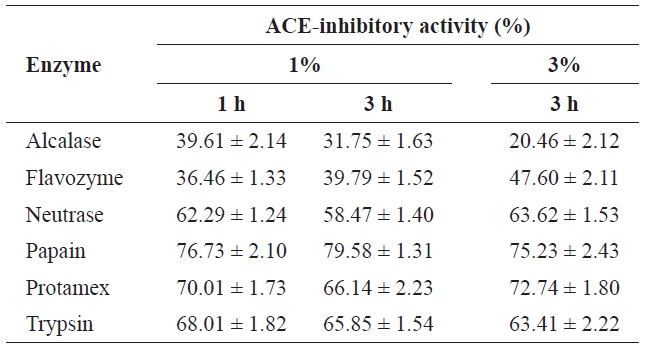
ACE-inhibitory activities on incubation times and addition amounts of enzymes
Fujita and Yoshikawa (1999) isolated the prodrug-type ACE-inhibitory peptide LKPNM from the thermolysin digest of katsuobushi (
>
Characterization of the papain hydrolysate
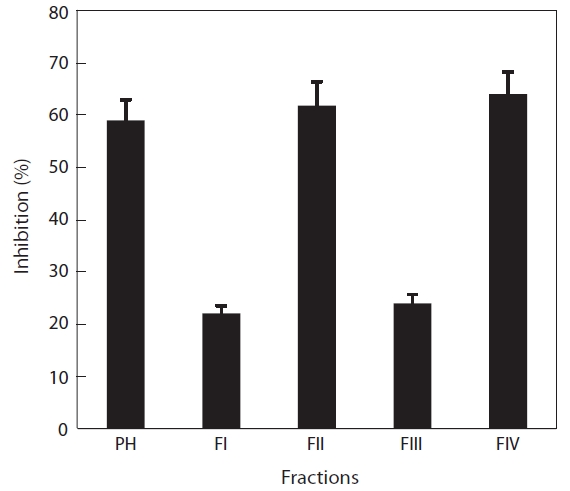
Digestion with papain resulted in the greatest ACE-inhibitory activity. The papain hydrolysate was fractionated by ultrafiltration (5, 3, and 1 kDa Mw cut-offs) and then subjected to ACE-inhibitory activity assays. The ACE-inhibitory activities of fractions II and IV were 63.2 and 61.1%, respectively, whereas fractions I and III showed lower activities (30.2 and 27.8%, respectively) (Fig.4 ). We assumed that most of the inhibitory compounds were within fractions II and IV, and that those activities were newly exposed by papain treatment, because no recognizable inhibitory activity was detected in a plain water extract (data not shown). The Mw of fractions II and IV were approximately 3,000-5,000 Da and less than 1,000 Da, respectively. The inhibitory activity of fraction II was similar to that of papain hydrolysate and fraction IV, suggesting that their specific activities were similar.
Byun and Kim (2001) revealed that activity increased markedly with decreasing Mw. A correlation was observed between hydrolysate Mw and the specificity of the ACE-inhibitory activity. Kinoshita et al. (1993) obtained two major fractions of high and low Mw from soy sauce, but reported that only the high-Mw fraction reduced blood pressure in hypertensive rats. In this study, we found no correlation between Mw and ACE-inhibitory activity.
>
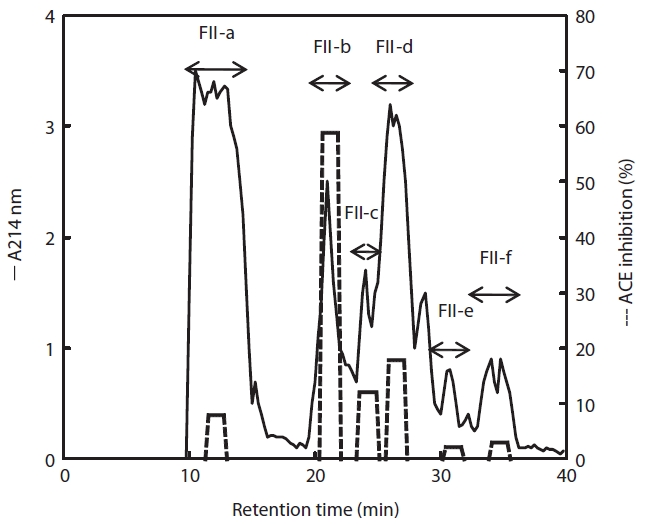
Purification and characteristics of the inhibitory peptide
To purify the active compound, fraction II was subjected to reverse-phase column (ODS C18) chromatography and the inhibitory activity of each eluate was determined. The FII-b fraction showed the highest inhibitory activity (59%), whereas the activities of FII-a, -b, and -c were less than 20% (Fig. 5). Therefore, the majority inhibitory activity was present in the FII-b fraction, although lower inhibitory activities were detected in the whole range (FII-a, -c, -d, -e, and -f). Treatment with papain thus produced a peptide of Mw 3,000-5,000 Da. To determine the primary structure, the FII-b fraction was again separated by chromatography to increase purity, and the N-terminal sequence was determined and the sequence identity compared. The N-terminal sequence of FII-b was Asp-Pro-Gly-Leu-Glu-Gly-Ala-His-Gly- and showed 87% identity to the collagen type IV alpha-2 fragment from
ing determined, we believe that FII-b may represent a novel antihypertensive food additive.
Several types of ACE-inhibitory peptide have been reported, especially those originating from animal sources (Kohama et al., 1988; Matsui et al., 1993; Smacchi and Gobbetti, 1998; Jang and Lee, 2005). Most of these peptides have low Mw. Here, we isolated and characterized ACE-inhibitory peptides with a Mw of 3,000-5,000 Da originating from jellyfish collagen. FII-b was predicted to originate from an alpha-2 fragment of the type IV collagen of the jellyfish,
![Degree of hydrolysis of Giant jellyfish hydrolysates obtained by the action of proteolytic enzymes. Each enzyme reaction was varied in enzyme amounts (1-4% [w/v]). After 4 h reaction all the treatments were followed by the same procedure. Alcalase (◆); Flavozyme (■); Neutrase (▲); papain (×); Protamex (*); and trypsin (●).](http://oak.go.kr/repository/journal/10828/E1HKAL_2011_v14n3_174_f001.jpg)