The purpose of 29 case series is to report the possibility that a hand acupuncture is effective in relieving headache.
After approval from the Institutional Review Board (IRB), I analyzed 29 cases medical records of outpatients with headache, who visited OO oriental medical hospital from December 2008 to December 2010, who have taken a hand acupuncture's treatment without other intervention, and who were diagnosed with one disease of international classification of headache disease second version (ICHD-2)
The data was analyzed with Wilcoxon signed rank test to determine whether a hand acupuncture's treatment differed between before and after treatment's Visual Analogue Scale(VAS) according to types of headache and syndrome differentiation. Statistics program was used SPSS 18.0. Differences were considered significant at P<0.05.
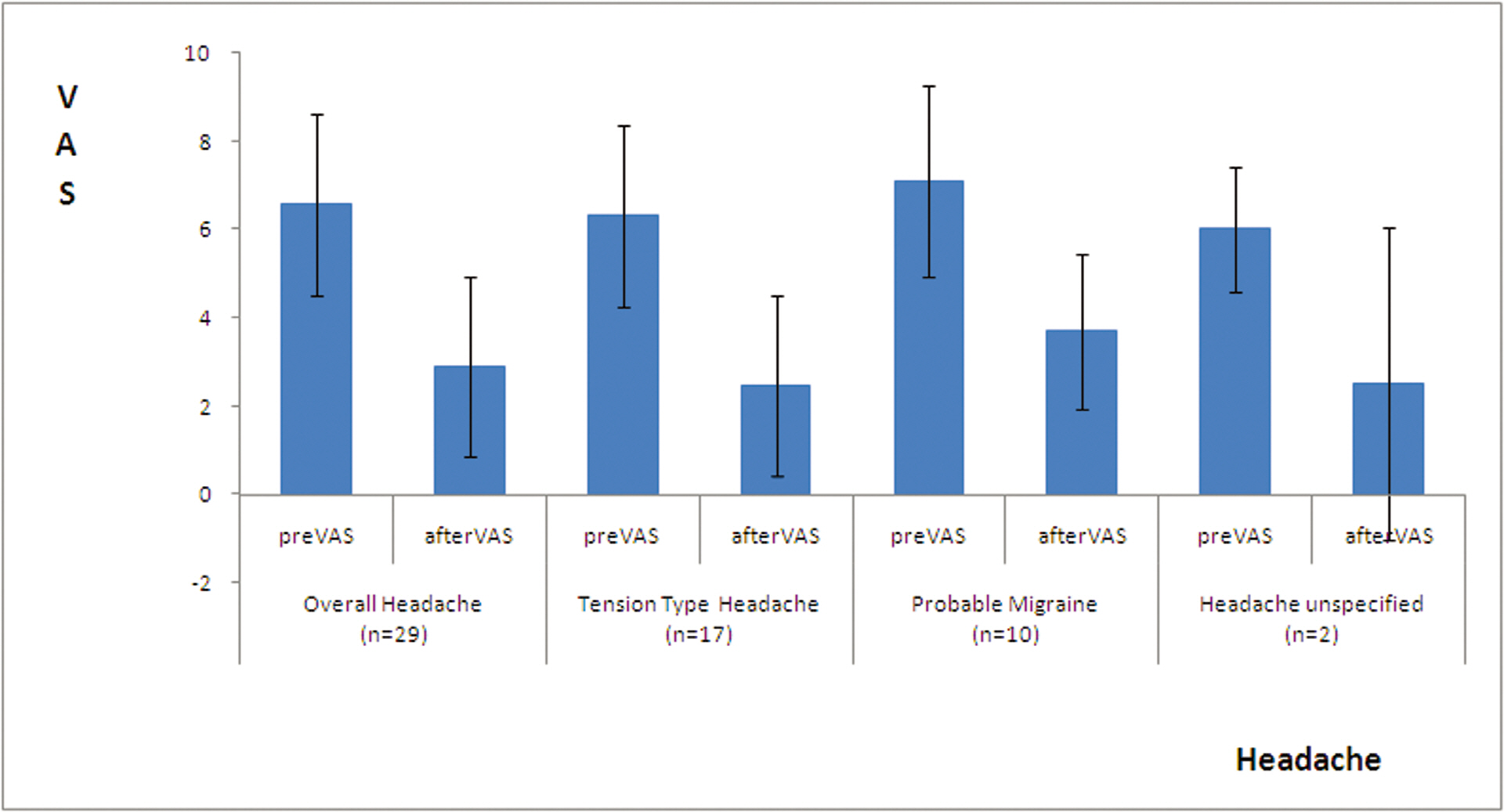
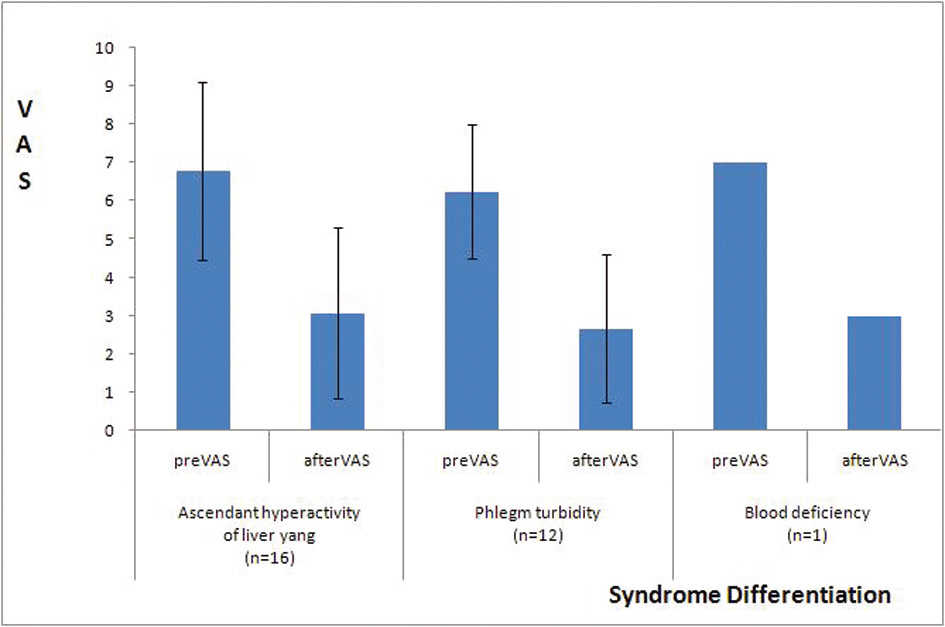
The VAS of patients with headache was reduced after treatment of hand acupuncture from 6.57±2.04 to 2.90±2.04 for overall headache, from 6.32±2.05 to 2.47±2.03 for tension-type headache(P<0.001), from 7.10±2.18 to 3.70±1.77 for migraine(P<0.001), and from 6.00±1.41 to 2.50±3.54 for headache unspecified. A hand acupuncture produced a decrease in VAS of both ascendant hyperactivity of liver yang(P<0.001) and phlegm turbidity according to syndrome differentiation(P=0.002). No adverse event were encountered in any of the patients.
It is suggested that a hand acupuncture may be effective in relieving headache, and could be applicable to first choice of acupuncture treatment for headache.
Headache is a unspecific and subjective symptom and one of most common symptom being able to experience. Many reports at home and abroad said the prevalence rate was 47% to 92.6%1-3).
Headache has been classified by many causes, such as migraine, tension-type headache, cluster headache, other primary headache, headache attributed to head and/or neck truma, headache attributed to psychiatric disorder and others4-5). Western medicine treatment of headache also was various depending on the cause5).
Headache was one of the important disease in oriental traditional medicine and has been categorized into external contraction such as wind-cold, wind-heat, and wind-dampness and internal damage such as hyperactivity of liver yang, phlegm turbidity, qi deficiency, blood deficiency, blood stasis, yin deficiency, and so on according to cause of oriental traditional medicine, which have diverse methods of treating that based on this cause and symptom differentiation6-7).
Acupuncture is representative treatment of oriental traditional medicine. Acupuncture treatment on headache havs been reported not only nationwide, but also worldwide8-19).
Acupuncture treatment on headache has been studied about migraine8), tension-type headache9), and chronic headache10) mainly at overseas, but the effect of that has been a controversial issue because both positive9-10) and negative8) effect of that has been reported. Besides, various acupuncture treatments such as auricular acupuncture11-12), electroacupuncture13), laser acupuncture14-15) have been studied and the effect of them was good.
In addition to traditional acupuncture11-12), the domestic studies of new acupuncture treatment such as pharmacoacupuncture13) and aromatic acupuncture14-15) have been carried out and the effect of them was positive.
Hand acupuncture has been more widely used to treat acute and chronic pain and functional disorders, but it don't have now not only systemic researches but also case report and series and pilot studies based on them.
I request systemic clinical trial to evaluate the effect of headache and need case series that can offer a preliminary data and clue of them.
The purpose of 29 case series is to report that a hand acupuncture is effective in relieving headache.
Target subjects were outpatients with headache who visited OO oriental medical hospital from December 2008 to December 2010 and who have taken a hand acupuncture treatment without other intervention. These medical records were reviewed by inclusion and exclusion criteria, so twenty-nine cases were selected finally.
2.1 Patients were diagnosed with one disease of international classification of headache disease second version (ICHD-2)4), such as tension-type headache, migraine, cluster headache, headache attributed to head and/or neck truma, headache attributed to psychiatric disorder and others.
2.2 Patients have only to take a hand acupuncture without other intervention.
2.3 The evaluation records of before and after treatment, for example visual analog scale (VAS) or questionnaire, must be included in medical records.
2.4 Medical records must have western diagnosis, chief complain, symptom differentiation, past history, family history, onset, pain region, pain duration, pain frequency, drinking, and smoking.
The cases were dropped out if medical records meet at least one of the following conditions.
3.1 If herbal medication or moxibustions, or other physical treatment were recorded in medical records with hand acupuncutre.
3.2 If medical records of hand acupuncture and all western treatment except hypertension, Diabetes Mellitus, and hyperlipidemia have been documented.
1) Visual Analog Scale (VAS)
Visual Analog Scale was used to evaluate the subjective intensity of headache. Severest intensity of headache was consider 100 points of VAS and no pain was consider 0 point of that. The subjective intensity of headache was measured before and after treatment whenever outpatients visited a hospital to treat headache.
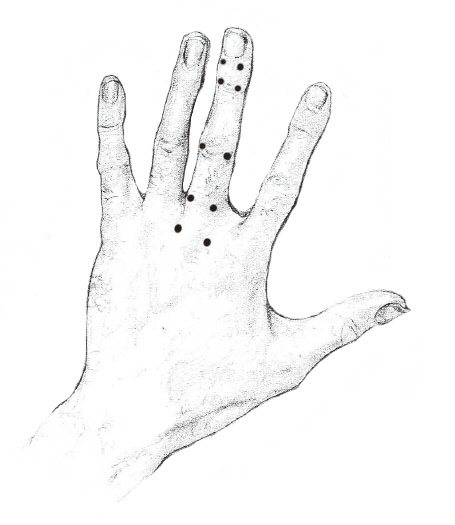
After a finger skin was disinfected with alcohol, sterile needles (gauge 0.20mm, length 15mm, stainless steel and manufactured by Hanglimseowon, Seoul) were inserted perpendicularly at ten acupoints (Fig. 1) on left middle finger of right-hander or on right middle finger of left-hander by practitioner of ten-years experience. Depth of insertion was 2 to 3mm and needle retention time was 20 minutes without finger's stimulation and obtaining qi. No intervention was used except acupuncture.
With approval from the Institutional Review Board of the Oriental medical hospital of Sangji University, data on patients with headache from December 2008 through December 2010 was collected retrospectively and was selected according to inclusion and exclusion criteria.
Data including VAS of before and after treatment, western diagnosis, chief complain, symptom differenciation, past history, family history, onset, pain region, duration, frequency, drinking, and smoking were retrieved from those of cases selected finally.
Data are reported as frequency(n) and percent(%) for ordinary variable and as mean±SD for continuous variable. The data was analyzed with Wilcoxon signed rank test to determine whether a hand acupuncture's treatment differed between before and after treatment's VAS according to types of headache and syndrome differentiation. Statistics program was used SPSS 18.0. Differences were considered significant at P<0.05.
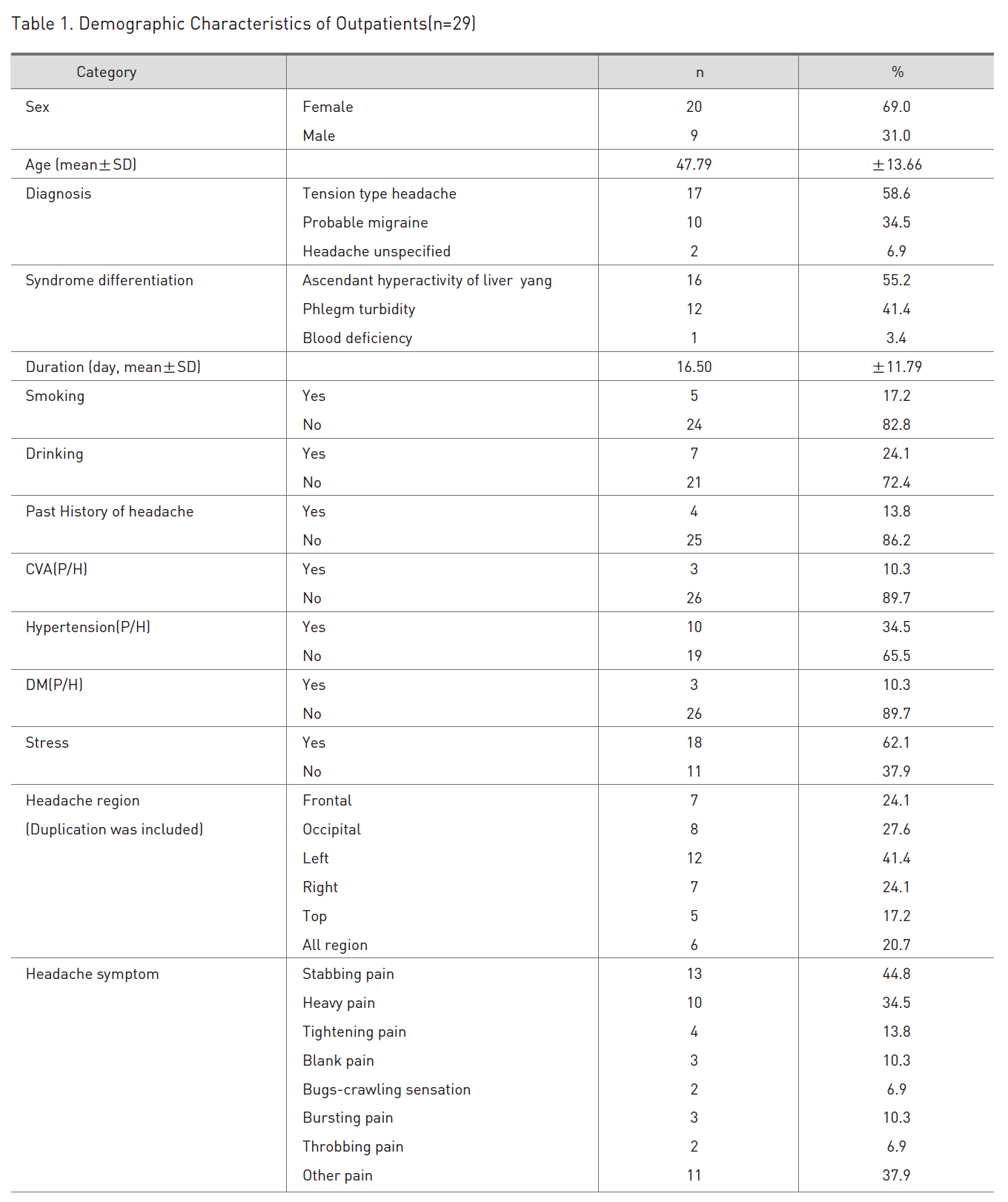
The number of women was 2.2 times more than that of men, and mean age was 47.79±13.66 years. The types of headache were 17(58.6%), 10(34.5%), and 2(6.9%) persons for tension-type headache, probable migraine, and headache unspecified, respectively.
Ascendant hyperactivity of liver yang(n=16) and phlegm turbidity(n=12) occupied most of types of syndrome differentiation(Table 1).
[Table 1.] Demographic Characteristics of Outpatients(n=29)
Demographic Characteristics of Outpatients(n=29)
The duration of onset was 16.50±11.79 days. Non-smoking and non-drinking was more than smoking and drinking. The patients with past history associated with headache were four people. The patients with past history such as stroke, hypertension, and Diabetes Mellitus were less than those without past history.
The patients with headache related to stress were 18(62.1%) and were more than those without stress. Left-side region placed first in headache region, occipital region came second, followed by frontal, right-side, all region and top region. Stabbing pain came first in headache symptoms, followed by heavy pain and tightening pain.
Twenty-nine cases, selected finally, had the results to evaluate VAS before and after single treatment without repeated treatments.
The VAS of 29 patients with Overall headache decreased significantly from 6.57±2.04 before treatment to 2.90±2.04 after treatment. (P<0.001)
The VAS of 3 types of headache was reduced after treatment of hand acupuncture from 6.32±2.05 to 2.47±2.03 for tension-type headache(P<0.001), from 7.10±2.18 to 3.70±1.77 for migraine(P<0.001), and from 6.00±1.41 to 2.50±3.54 for headache unspecified (Fig. 2).
A hand acupuncture produced a decrease in VAS of both ascendant hyperactivity of liver yang(P<0.001) and phlegm turbidity according to syndrome differentiation(P=0.002).
No adverse event were encountered in any of the patients.
A hand acupuncture used at 29 cases is different from that of textbook and is depending on the principle of Park's human body matched structure's theory and Koryo hand treatment20).
This hand acupuncture's principle is that the region of distal phalax at middle finger is commensurate with headache of human body and that of middle and proximal phalanx is equal to neck of that. Based on this principle, the acupuncture points of middle finger is stimulated to relieve headache.
The acupuncture points of these cases was selected for myself to reduce headache beacause stimulation of the acupoints at middle finger, which are corresponded to head and neck region, accelerate the circulation of qi and blood between head and truck. It is presumed that it is more convenient to use intradermal needle instead of 20 mm × 0.15 mm needle used at these cases.
Most of patients were non-smokers, non-drinkers, and middle-age and stressful women without past history such as hypertension, stroke and Diabetes Mellitus and so on. The region of headache was all alike except left region.
The international classification of headache disorders 2nd edition (ICHD-2)4) used at these cases, made by Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society, have been used to diagnose headache globally.
Patients was diagnosed with tension-type headache and probable migraine mainly. It was presumed that a hand acupuncture may have a significant effect about both tension-type headache and probable migraine according to our results. Nevertheless, I speculated that a hand acupuncture may have different effect depending on the intensity of migraine and mild one could be more effective than severe one.
The types of syndrome differentiation among patients with headache were ascendant hyperactivity of liver yang and phlegm turbidity. A hand acupuncture had a good effect on both of them. Based on the fact that patients with ascendant hyperactivity of liver yang were more than those with phlegm turbidity among 29 cases, I postulated that a hand acupuncture may be more effective in treating headache caused by stress or ascendant hyperactivity of liver yang but further study will be required about that.
As a result, a hand acupuncture treatment appears to have the possibility to relieve headache. I think this treatment is a convenient acupuncture's technique to apply to headache first regardless of syndrome differentiation and types of headache in situation not to be able to find cause or syndrome differentiation.
Study limitation cannot generalize because of case series. This study has another problem not to prove the lasting effect for repeated treatment because the only VAS of before and after treatment was evaluated. Rigorous studies like randomized clinical trials will be needed about the effect of repeated treatment and the lasting effect of after-treatment for a hand acupuncture.
It is suggested that a hand acupuncture may be effective in relieving headache, and could be applicable to first choice of acupuncture treatment for headache.