질병의 발생과 진행은 인체의 항병력 및 정상적인 생리기능과 발병인자의 충돌로 인하며, 한의학에서는 正氣와 邪氣의 개념으로 이해할 수 있다. 염증 반응은 이러한 正邪抗爭의 결과로 체내에 나타나는 병리적 현상이다1). 염증은 활성화된 면역세포에 의해 일어나는 일련의 면역반응으로 세균, 바이러스 등을 포함한 미생물 및 생체의 이물질 등이 인식되면 면역세포가 활성화되며 염증반응의 원인이 되는 많은 인자들이 분비되어 염증반응을 유발시킨다2).
대식세포는 초기 염증 반응에 관여하는 대표적인 면역세포로서 동물체 내 모든 조직에 존재하고 외부 이물질을 탐지하고 포식하며 전염증성 사이토카인을 비롯하여 다양한 염증매개물질들을 분비한다3). 이러한 대식세포는 외부자극으로부터 활성화되어 염증매개물질을 분비하여 염증반응을 유발함으로써 여러 염증질환을 유발하고 이를 악화시킨다. 따라서 최근에는 염증반응이 진행되는 동안 유의적으로 증가되는 각종 염증 물질들을 효과적으로 감소시킬 수 있는 항염증 효과에 대한 연구들이 침구 및 약물 등의 한의학적 치료방법으로 많이 이루어지고 있다4-7).
당귀(Angelicae Gigantis Radix)는 미나리과에 속한 다년생 초목인 참당귀(Angelica gigas Nakai)의 뿌리로 性은 溫無毒, 味는 甘辛하며 歸經은 心, 肝, 脾經의 三經이다. 또한 당귀는 養血潤燥, 活血舒筋하는 기능을 가지며 一切 血證에 대한 주치도 가지고 있다8). 당귀약침에 관한 실험적 연구로 박9)은 진통효과, 황10)은 면역기능저하, 문11)은 고지혈증, 성12)은 혈전증에 미치는 영향을 보고하였다. 당귀의 항염증에 관한 연구13-15) 또한 보고되어 있으나 이는 주로 에탄올 추출물로 시행한 것으로 이에 본 실험에서는 대표적인 補血 및 活血의 효능이 있는 당귀8)를 에탄올 추출 방식과 열수 추출 방식의 2가지 추출법을 이용하여, 대식세포에서의 염증 관련 물질인 산화질소(Nitric oxide, 이하 NO)와 Prostaglandin E2(이하 PGE2)의 변화를 관찰하여 유의한 결과를 얻었기에 보고하는 바이다.
실험에 사용한 당귀(Angelicae Gigantis Radix)는 세명대학교 부속제천한방병원에서 구입한 것을 정선하여 사용하였다. 본 실험에서는 에탄올 추출과 열수 추출의 2가지 방법으로 당귀약침액을 추출하였다. 에탄올 추출 방식으로 당귀 300 g을 70% 에탄올 2 L와 혼합하여 70℃로 4시간 추출하고 상층액을 여과지로 여과한 후 rotary evaporator를 이용하여 100 ㎖ 까지 농축하고 80℃로 동결하였다. 이렇게 농축된 동결액은 freezing dryer system(Labconco, USA)을 이용하여 7일간 동결건조 하였다. 열수 추출 방식은 당귀 300 g을 증류수 2 L에 넣고 100℃로 4시간 동안 추출하고 여과지로 여과하였다. 여과 후 농축 및 동결건조과정은 에탄올 추출방법과 동일하게 진행되었다.
Murine macrophage cell line인 RAW 264.7 대식세포는 American Type Culture Collection(ATCC, USA)에서 구입하였으며, 10% Fetal bovine serum(FBS)과 1% 항생제가 포함된 Dulbecco's Modified Eagle's Medium (DMEM) 배지를 사용하여 37℃, 5% CO2 환경이 유지되는 배양기에서 배양하였다.
RAW 264.7 대식세포를 96 well plate에 1 x 105 cell /well로 분주한 다음 16시간동안 37℃, 5% CO2 환경이 유지되는 배양기에서 세포를 안정화시켰다. 안정화 시킨 세포에 당귀약침액을 1, 5, 25, 125, 625 그리고 3125 ㎍/mL 농도별로 처리하고 16시간 동안 배양 후 생존세포에 MTT 시약을 넣고 2시간 배양한 후 배지를 제거하고 생성된 formazan crystals을 DMSO에 녹여 Enzyme-Linked Immuno-Sorbant Assay(이하 ELISA) reader(Bio-Tek, USA)를 사용하여 570 nm에서 흡광도를 측정하였다. 세포 생존율은 control cell에 대한 ratio로 나타내었다. [i.e. viability(% control) = 100 × (absorbance of treated sample)/(absorbance of control)]
안정화된 세포에 lipopolysacharide(이하 LPS)와 당귀약침액을 1, 5, 25, 125, 625 그리고 3125 ㎍/mL의 농도별로 처리하여 16시간 배양한 후 상층액 100 ℃와 Griess 시약(0.1% naphthylethylendeiamine dihydrochloride 50 ℃와 1% sulfanilamide in 5% phosphoric acid 50 ℃) 100 ℃를 혼합하여 ELISA reader(Bio-Tek, USA)로 흡광도를 측정하였다.
활성화된 대식세포로부터 분비되는 염증물질인 Prostaglandin E2(PGE2)의 양을 세포배양액으로부터 효소면역반응법(Enzyme Immuno-Assay; EIA)을 이용하여 측정하였다. RAW 264.7 대식세포에 당귀 약침액을 전 처리하고 10 ㎍/㎖의 LPS를 처리하여 18 시간 배양한 후 세포 배양액을 수거하여 배양액 내에 존재하는 PGE2의 양을 측정하였다. 배양액을 goat anti-mouse로 coating된 96 well plate에 각각의 배양액을 100 ℃씩 loading한다. 여기에 primary antibody solution 50 ℃와 PGE2 conjugate 50 ℃씩 첨가하여 4℃에서 overnight시켰다. 기질용액을 200 ℃씩 처리하여 5-20 분간 반응시킨 후, 50 ℃의 stop solution을 처리하고 450 nm에서 흡광도를 측정하였다.
실험결과는 SPSS Window program(Ver. 10.0)을 이용하였으며, 모든 측정값은 평균값±표준편차로 나타내었고, 효과를 판정하기 위한 통계학적 분석은 Student's
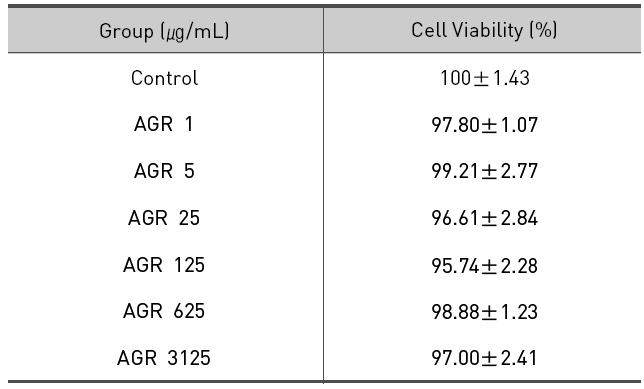
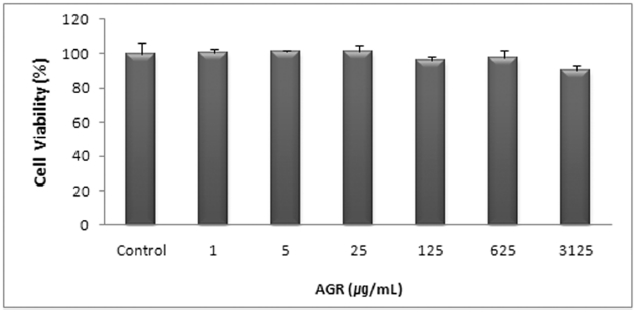
당귀약침액의 세포 생존율을 MTT assay 방법으로 조사하였다.
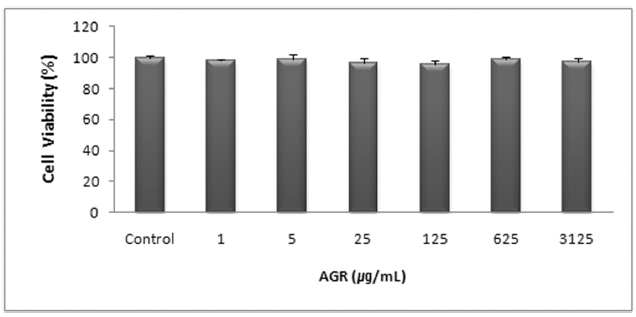
에탄올 추출 방식의 당귀약침액군에서는 1, 5, 25, 125, 625 그리고 3125 ㎍/mL 농도에서 세포 생존율은 각각 97.80±1.07, 99.21±2.77, 96.61±2.84%, 95.74±2.28, 98.88±1.23 및 97.00±2.41 %로 모든 농도에서 독성이 없는 것으로 나타났다(Table 1, Fig. 1).
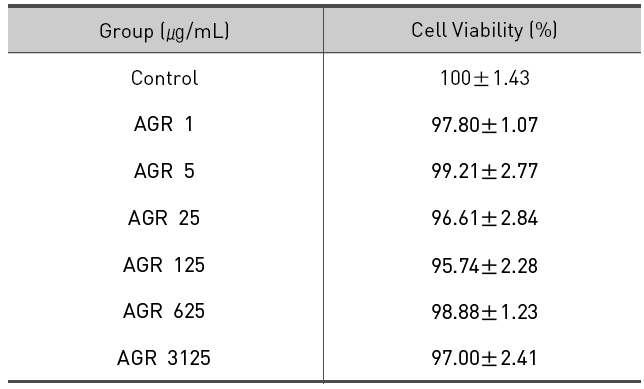
The effect of Angelicae Gigantis Radix pharmacopunctureby ethanol extract on cell viability ofRAW 264.7 macrophage cells by MTT assay.
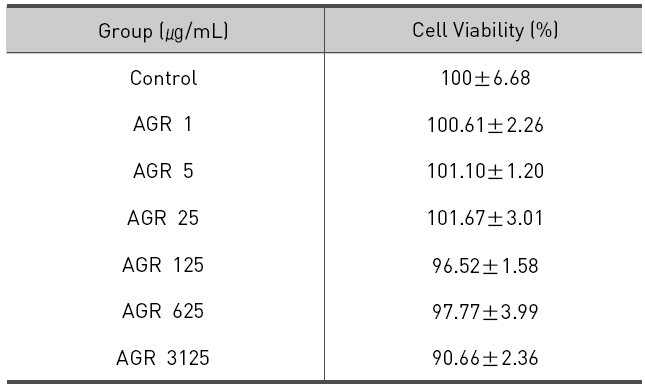
열수 추출 방식의 당귀약침액군에서는 1, 5, 25, 125, 625 그리고 3125 ㎍/mL 농도에서 세포 생존율은 각각 100.61±2.26, 101.10±1.20, 101.67±3.01, 96.52±1.58, 97.77±3.99 및 90.66±2.36 %로 모든 농도에서 독성이 없는 것으로 나타났다(Table 2, Fig. 2).
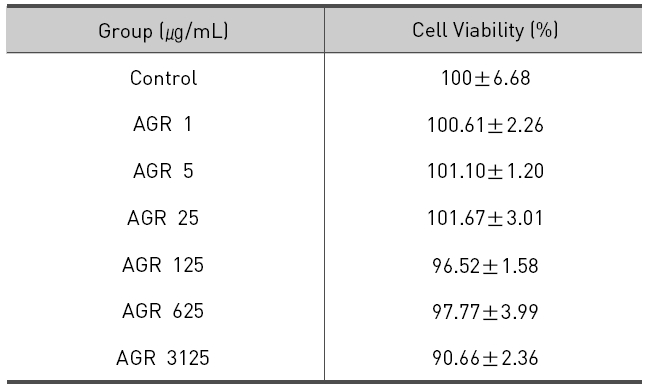
The effect of Angelicae Gigantis Radix pharmacopuncture by hot water extract on cell viability of RAW 264.7 macrophage cells by MTT assay.
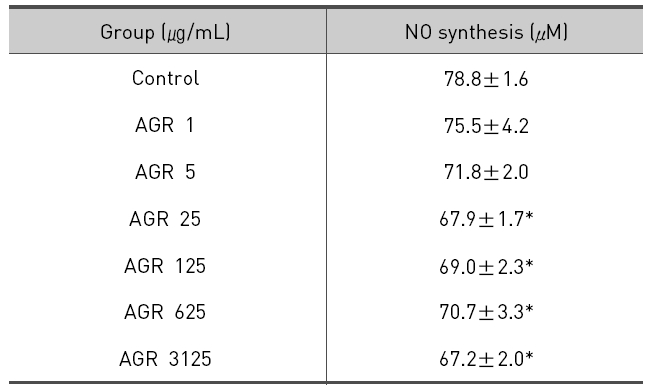
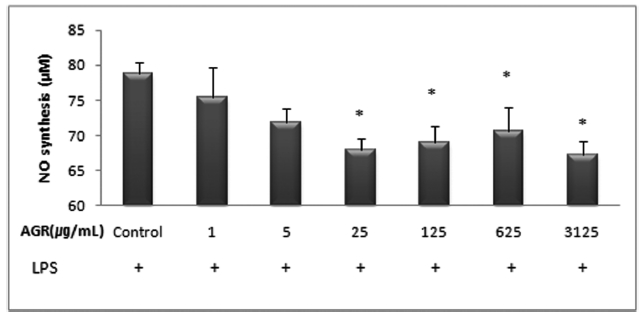
LPS에 의해 RAW 264.7 대식세포로부터 생성되는 NO에 대한 당귀약침액의 억제효과를 Griess assay 방법에 의해 측정하였다.
에탄올 추출 방식의 당귀약침액군에서 NO는 LPS 10 ㎍/mL만 단독 처리시 78.8±1.6 μM/mL의 농도로 측정되었고, 당귀약침액을 1, 5, 25, 125, 625 그리고 3125 ㎍/mL의 농도로 추가 처리한 경우 각각 75.5±4.2, 71.8±2.0, 67.9±1.7, 69.0±2.3, 70.7±3.3 및 67.2±2.0 μM/mL로 측정되었으며 25, 125, 625 그리고 3125 ㎍/mL의 처리 농도에서 NO의 생성이 유의적으로 감소되었다(Table 3, Fig. 3).
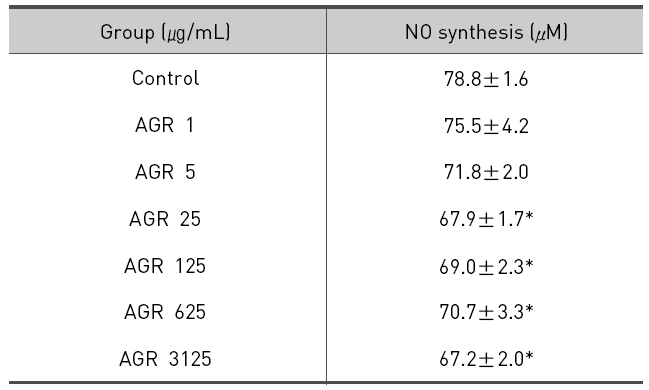
The effect of Angelicae Gigantis Radix pharmacopuncture by ethanol extract on the Nitric Oxide(NO) production of LPS induced RAW 264.7 macrophage cells by NO synthesis assay.
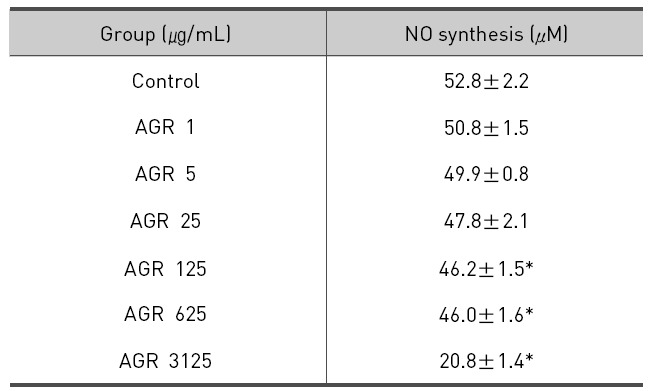
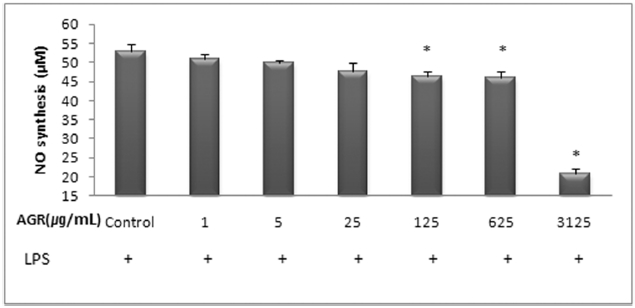
열수 추출 방식의 당귀약침액군에서 NO는 LPS 10 ㎍/mL만 단독 처리시 52.8±2.2 μM/mL 의 농도로 측정되었고, 당귀약침액을 1, 5, 25, 125, 625 그리고 3125 ㎍/mL 의 농도로 추가 처리한 경우 각각 50.8±1.5, 49.9±0.8, 47.8±2.1, 46.2±1.5, 46.0±1.6 및 20.8±1.4 μM/mL로 측정되었으며, 125, 625 그리고 3125 ㎍/mL 의 처리 농도에서 NO의 생성이 유의적으로 감소되었다(Table 4, Fig. 4).
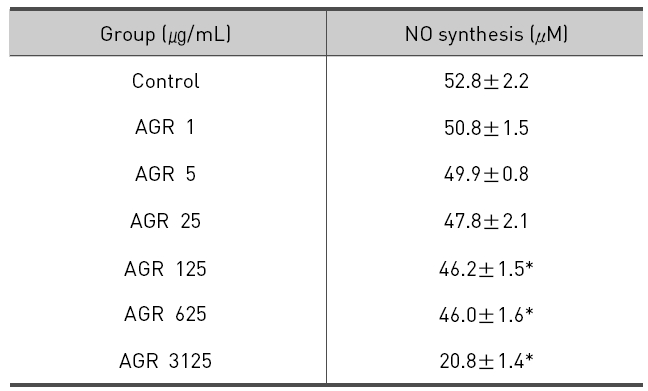
The effect of Angelicae Gigantis Radix pharmacopuncture by hot water extract on the Nitric Oxide(NO) production of LPS induced RAW 264.7 macrophage cells by NO synthesis assay.
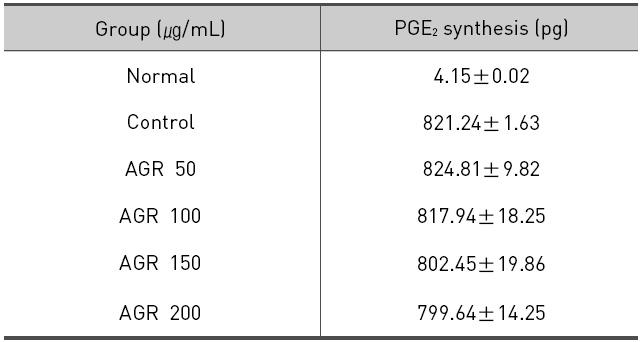
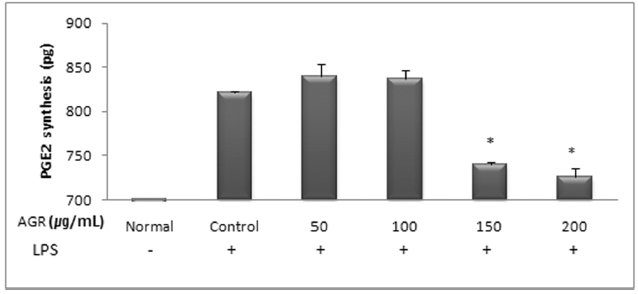
LPS에 의해 RAW 264.7 대식세포로부터 생성되는 PGE2에 대한 열수 추출 방식의 당귀약침액과 에탄올 추출 방식의 당귀약침액의 억제효과를 세포배양액으로부터 효소면역반응법에 의해 측정하였다. 먼저 세포만 배양했을 때 세포배양액 내 PGE2의 농도는 4.15±0.02 pg/mL로 매우 낮게 측정되었으며, LPS에 의해 821.24±1.63 pg/mL 농도로 현저히 증가되었다.
에탄올 추출 방식의 당귀약침액군에서는 당귀약침액을 50, 100, 150 그리고 200 ㎍/mL의 농도로 추가 처리한 경우 각각 824.81±9.82, 817.94±18.25, 802.45±19.86 및 799.64±14.25 pg/mL로 측정되어 PGE2의 생성이 감소되는 경향을 보였지만 통계적인 유의성은 없었다(Table 5, Fig. 5).
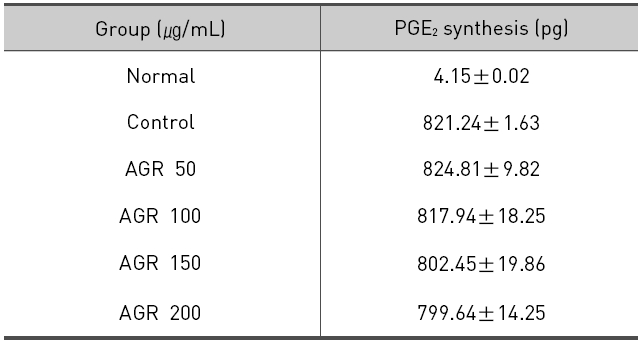
The effect of Angelicae Gigantis Radix pharmacopuncture by ethanol extract on the Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) production of RAW 264.7 macrophage cells by PGE2 synthesis assay.
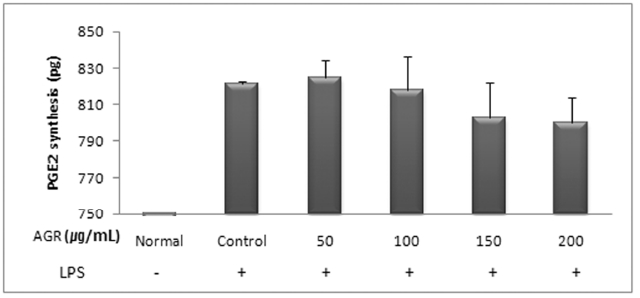
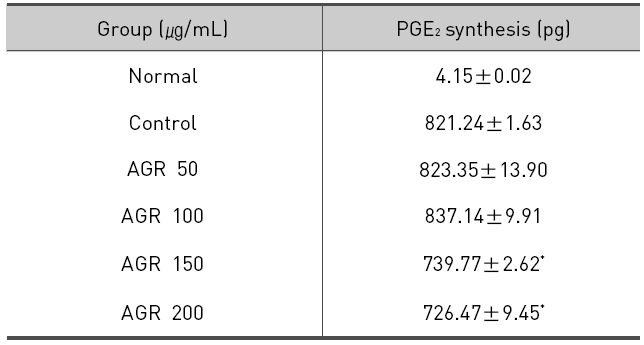
열수 추출 방식의 당귀약침액군에서는 당귀약침액을 50, 100, 150 그리고 200 ㎍/mL의 농도로 추가 처리한 경우 각각 839.35±13.90, 837.14±9.91, 739.77±2.62 및 726.47±9.45 pg/mL로 측정되었으며, 특히 150 과 200 ㎍/mL의 처리농도에서 PGE2의 생성이 유의하게 감소되는 것으로 나타났다(Table 6, Fig. 6).
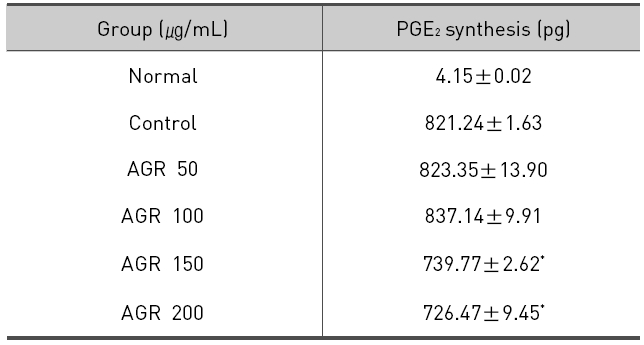
The effect of Angelicae Gigantis Radix pharmacopuncture by hot water extract on the Prostaglandin E2(PGE2) production of RAW 264.7 macrophage cells by PGE2 synthesis assay.
염증반응은 생체 조직의 손상에 대해 반응하는 능동적인 과정으로, 생체의 세포나 조직이 어떤 원인에 의하여 손상을 받으면 이에 대한 반응을 일으켜 손상을 극소화시키고, 손상된 부위를 수복시키려는 과정이 일어난다16). 이러한 염증 반응은 한의학적으로 正邪抗爭의 관점에서 관찰 할 수 있으며, 이 때 正은 正氣로 邪氣에 대응하는 인체의 항병력 및 정상적인 생리기능을 총칭하고 邪는 邪氣로 발병인자를 총칭한다1).
염증반응에 주요한 역할을 담당하는 산화질소는 arginine과 O2로부터 nitric oxide synthase를 경유하여 생성되는 radical로, 과도하게 생성된 NO는 septic shock, 뇌경색, 당뇨, 퇴행성 신경질환과 연관되어 있다17). 따라서 염증반응의 조절에 영향을 미치는 NO에 대한 연구가 활발하게 이루어지고 있다18,19).
PGE2는 NO와 마찬가지로 손상된 부위나 조직에서 통증과 발열의 전달에 주로 관여하는 중요한 염증매개물질로서 COX-2에 의해 합성되는데, 과량 생산되면 과도한 면역반응을 야기하여 다발성 경화증, 파킨슨병, 알츠하이머병, 대장암과 같은 각종 염증성 질환을 유발시키게 된다20). 따라서 PGE2 생성 억제는 염증과 통증을 완화시켜 염증질환의 치료에 효과적인 것으로 알려져 있다21,22).
최근에는 염증반응이 진행되는 동안 유의적으로 증가되는 각종 염증 물질들을 효과적으로 감소시킬 수 있는 항염증제제 및 치료보조제 개발에 대한 연구가 많이 이루어지고 있으며16), 한의학적으로는 주로 한약 복합처방4,23,24) 이나 단미 한약재 추출물5,25,26)을 이용하여 다양한 염증질환을 대상으로 대식세포에 의한 염증반응을 억제시켜주는 연구가 많이 진행되고 있다.
이러한 염증질환에 대한 한약재 추출물의 연구를 살펴보면 주로 淸熱藥6,7,27,28)에서 이루어지지만 이외에도 補益藥29-32), 溫裏藥33), 解表藥25,26) 등 다양한 약재로 연구를 진행한 것이 관찰된다. 補益藥 중 당귀는 대표적인 補血劑로 ?形科에 속하는 다년생 초본의 뿌리로 性은 溫하고 味는 甘辛하며 活血和血, 調經止痛, 潤燥滑腸하는 등의 효능을 가진다8). 이러한 당귀에 대한 연구로 류34)의 난소기능에 미치는 영향, 안35)의 항산화 효과, 한36)의 허혈성 뇌질환에 미치는 영향, 장37)의 소음 stress를 받은 상태에서 신경세포생성에 미치는 영향, 류38)의 관절염에 미치는 영향, 김39)의 肝이 손상된 상태의 혈액에 미치는 영향에 대한 실험적 연구 등이 보고되어있다.
당귀의 항염증 효과에 대한 연구로 신13)과 이14)는 당귀 에탄올 추출물이 대식세포에서의 여러 염증 인자를 효과적으로 억제한다고 하였고, 정15) 또한 대식세포에서 당귀 에탄올 추출물이 NO의 생성을 농도 의존적으로 억제한다고 하였다. 당귀의 항염증에 대한 연구는 이와 같이 보고되었으나 모두 에탄올 추출 방식을 사용한 당귀에 대한 연구이며 열수 추출 방식을 사용한 당귀약침액에 대한 연구는 미흡하여 본 연구에서는 기존의 에탄올 추출 방식과 열수 추출 방식의 2가지 추출법을 이용하여 당귀약침액을 얻어 실험을 진행하였다.
우선 당귀약침액의 RAW 264.7 대식세포에 대한 생존율을 평가하기 위해 MTT assay로 조사한 결과 에탄올 추출 방식, 열수 추출 방식의 당귀약침액 1, 5, 25, 125, 625 그리고 3125 ㎍/mL 농도 모두에서 독성이 없는 것을 확인할 수 있었다.
당귀약침액이 LPS로 활성화된 RAW 264.7 대식세포에서 NO의 생성 억제에 미치는 영향을 평가한 결과 에탄올 추출 방식의 당귀약침액군에서는 25, 125, 625 그리고 3125 ㎍/mL 농도로 처리하였을 때 LPS 단독처리한 군에 비해 통계학적으로 유의한 감소가 나타났으며, 열수 추출 방식의 당귀약침액군에서는 125, 625 그리고 3125 ㎍/mL 농도로 처리하였을 때 LPS 단독처리한 군에 비해 통계학적으로 유의한 감소가 나타났다. 이러한 결과는 당귀약침액이 NO의 생성을 억제함을 의미한다.
당귀약침액이 LPS로 활성화된 RAW 264.7 대식세포에서 PGE2에 미치는 영향을 평가한 결과 LPS는 PGE2의 생성을 증가시켰으며, 에탄올 추출 방식의 당귀약침액군에서는 모든 농도에서 PGE2의 생성을 감소시켰으나 유의성은 관찰되지 않았다. 열수 추출 방식의 당귀약침액군에서는 PGE2의 생성을 감소시켰으며 특히 150 과 200㎍/mL의 농도에서 유의성 있게 감소시켰다.
기존에 에탄올 추출 방식의 당귀약침액의 항염증 효과에 관한 연구38)에서는 NO와 PGE2 모두 농도 의존적인 생성 억제를 나타냈으나 이에 대한 유의성 있는 결과가 관찰되지 않은 반면, 본 실험에서는 NO 생성 억제에 관해서는 열수 추출 방식의 당귀약침액과 에탄올 추출 방식의 당귀약침액이 모두 유의성 있는 결과를 보였고, 열수 추출 방식의 당귀약침액의 경우 PGE2 생성에도 유의성 있는 억제를 나타내었다.
이에 당귀약침액은 에탄올 추출 방식과 열수 추출 방식 모두에서 항염증의 효과를 보인다고 할 수 있으며, 열수 추출 방식의 당귀약침액이 에탄올 추출 방식의 당귀약침액 보다 염증성 병리상태에 효과적으로 활용될 수 있을 것으로 사료된다.
LPS로 유도된 RAW 264.7 대식세포에서의 염증반응에 당귀약침액이 NO와 PGE2 생성에 미치는 영향을 관찰한 결과 다음과 같은 결론을 얻었다.
1. 세포 생존율을 확인하기 위해 MTT assay를 수행한 결과 에탄올과 열수 추출 방식의 당귀약침액 모든 농도에서 세포독성이 나타나지 않았다.
2. NO 생성의 억제에 대한 영향을 관찰 시 에탄올 추출 방식의 당귀약침액군에서는 25, 125, 625 그리고 3125 ㎍/mL 농도로 처리하였을 때 LPS 단독처리한 군에 비해 통계학적으로 유의한 감소가 나타났으며, 열수 추출 방식의 당귀약침액군에서는 125, 625 그리고 3125 ㎍/mL 농도로 처리하였을 때 LPS 단독처리한 군에 비해 통계학적으로 유의한 감소가 나타났다.
3. PGE2 생성의 억제에 대한 영향을 관찰 시 에탄올 추출 방식의 당귀약침액군에서는 PGE2의 생성이 감소되는 경향을 보였지만 통계적인 유의성은 없었고, 열수 추출 방식의 당귀약침액군에서는 150 과 200 ㎍/mL 농도로 처리하였을 때 LPS 단독처리한 군에 비해 유의한 감소가 나타났다.
이상으로 보아 당귀약침액이 LPS로 유발되는 RAW 264.7 대식세포의 염증 상태에서 NO와 PGE2 생산을 억제하는 항염증 효과를 보이고, 열수 추출 방식이 에탄올 추출 방식보다 효과적으로 염증을 제어하는 것으로 나타났다.