C/SiC composites were prepared by boron nitride (BN)-assisted liquid silicon infiltration (LSI), and their anti-oxidation and mechanical properties were investigated. The microstructures, bulk densities, and porosities of the C/SiC composites demonstrated that the infiltration of liquid silicon into the composites improved them, because the layered-structure BN worked as a lubricant. Increasing the amount of BN improved the anti-oxidation of the prepared C/SiC composites. This synergistic effect was induced by the assistance of BN in the LSI. More thermally stable SiC was formed in the composite,and fewer pores were formed in the composite, which reduced inward oxygen diffusion. The mechanical strength of the composite increased up to the addition of 3% BN and decreased thereafter due to increased brittleness from the presence of more SiC in the composite. Based on the anti-oxidation and mechanical properties of the prepared composites, we concluded that improved anti-oxidation of C/SiC composites can be achieved through BN-assisted LSI, although there may be some degradation of the mechanical properties. The desired anti-oxidation and mechanical properties of the composite can be achieved by optimizing the BN-assisted LSI conditions.
Carbon-fiber-reinforced carbon composites (C/C composites) have attracted much attention due to their excellent properties, such as high thermal conductivity, excellent thermal stability, low coefficient of thermal expansion, low density, high strength-to-weight ratio, excellent friction properties, and resistance to fatigue. These excellent properties are maintained even in extreme environments. Therefore, C/C composites have been considered as potential materials for applications in extreme environments, such as nozzles for solid rocket motors, heat shields for re-entry vehicles, and brake discs for advanced aircrafts [1,2]. However, their low oxidation temperature above 600 ℃ limits their use in these applications [3-5].
Recently, the formation of C/SiC composites from C/C composites has spurred efforts to enhance the anti-oxidation of C/C composites [6,7]. Two methods are commonly used to prepare C/SiC composites. One is chemical vapor deposition (CVD), and the other is liquid silicon infiltration (LSI). CVD requires a long procedural time and expensive equipment and produces high porosity in the composites, whereas LSI is a simple and inexpensive method [8,9]. The key to LSI is to infiltrate liquid silicon slurry into the carbon fibers. If the infiltration is not good, the composite properties will not be enhanced as desired. The addition of lubricating fillers to C/C composites is a cheap and efficient way to enhance the impregnation of liquid silicon [8,10]. Cu, Mo, and graphite fillers can be used, but their thermal properties limit the enhancement of the anti-oxidation properties of the filler-added composites [11-13]. However, boron nitride (BN) has high anti-oxidation properties up to 3000℃ and layered structures that can assist LSI by reducing abrasion between the liquid silicon and C/C composites.
In this study, C/SiC composites were prepared from C/C composites by BN-assisted LSI, and their anti-oxidation and mechanical properties were investigated.
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
PAN based needle-punched carbon preform was provided by DACC Co. (Jeonju, Korea), and resol-type phenol resin (HM2) was provided by Kolon Chemical (Gimcheon, Korea). The BN (ESK Ceramics, Boronid SCP1) had a diameter of 0.5-1.0 ㎛.
2.2 C/SiC composite preparation
Phenol resin and BN in various weight ratios (0, 1, 3, 5, and 10 wt%) were mixed and stirred vigorously for 30 min. Carbon preform was impregnated with the BN/phenol resin mixture at 0.2 bars for 10 min. The impregnated preform was dried in a thermo-reactor at 70℃ for 3 h. It was then heated to 130℃, and the temperature was maintained for 5 h to cure the phenol resin. Then, the product was carbonized at 1,000℃ for 2 h in N2 gas. Finally, liquid silicon was infiltrated at 3 × 10-3 Torr and 1,600℃ to prepare the C/SiC composites. They were named according to the amount of BN added: BN00, BN01, BN03, BN05, and BN10.
2.3 Characterization of the prepared C/SiC composites
The microstructures of the C/SiC composites were investigated by scanning electron microscopy (SEM, JEOL, JSM-7000F, Japan). The densities and porosities of the composites were measured using ASTM C20. Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA, Mettler-Toledo, TGA/SDTA851, Switzerland) was performed to evaluate the anti-oxidation properties of the prepared samples at a heating rate of 5℃/min. The flexural strengths of the prepared C/SiC composites were measured using a three-point flexural test based on ASTM D790.
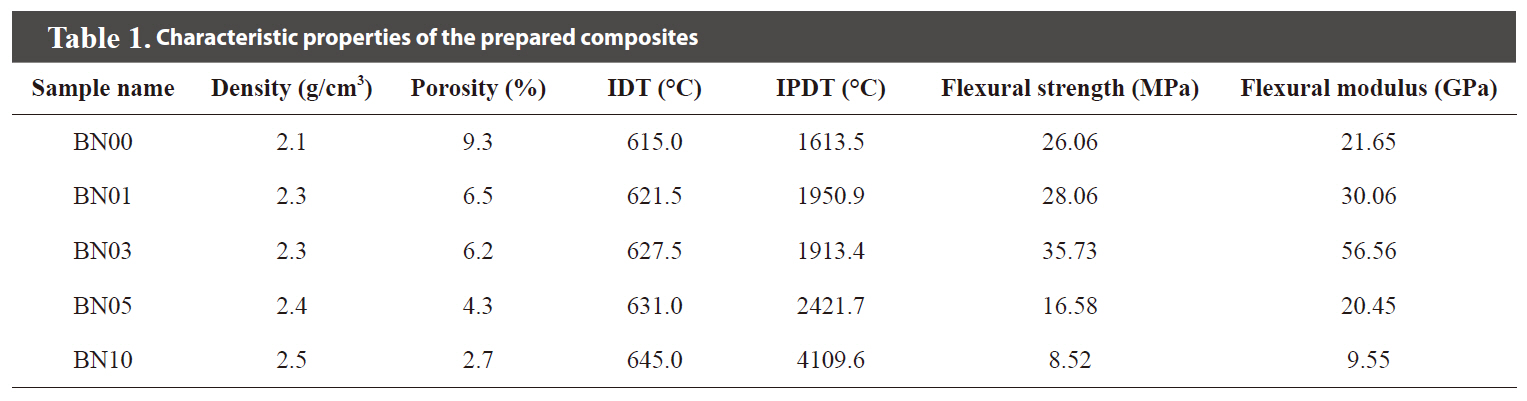
[Table 1.] Characteristic properties of the prepared composites
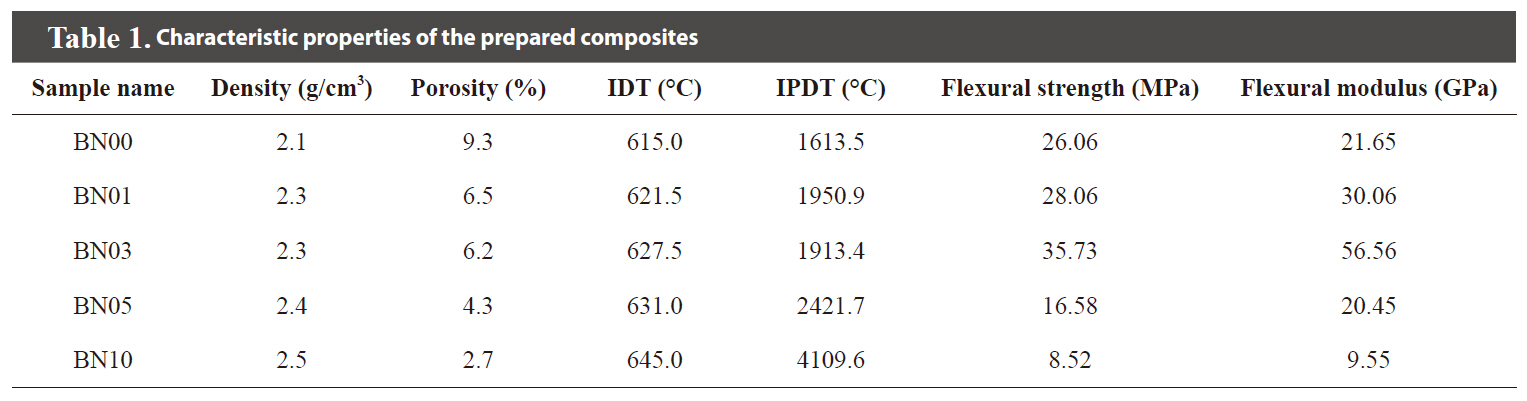
Characteristic properties of the prepared composites
3.1 Microstructures of C/SiC composites prepared by BN-assisted LSI
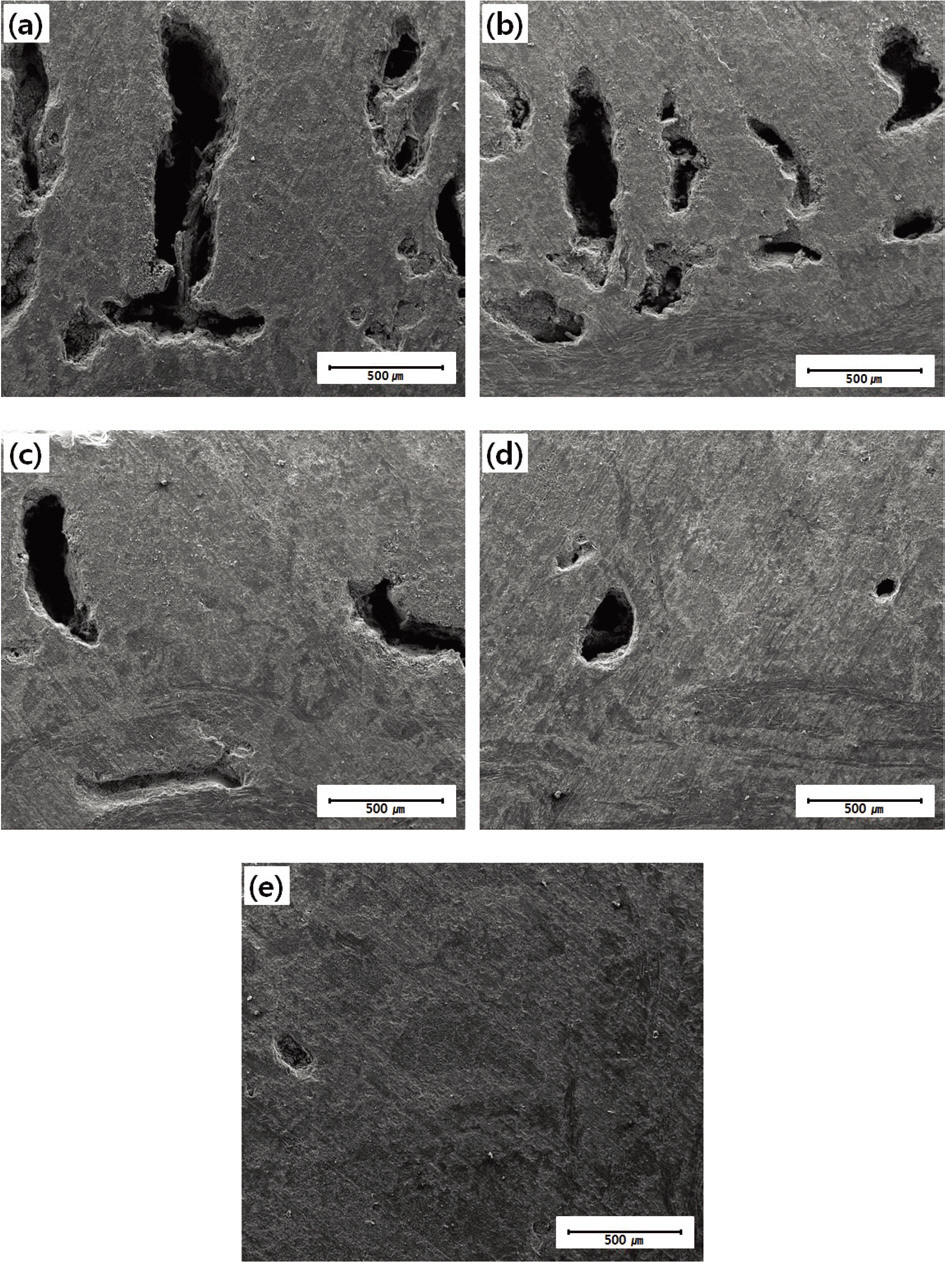
The microstructures of the prepared C/SiC composites are shown in Fig. 1. Fewer pores were observed in the composites as the amount of added BN increased. Because the microscopy investigation may show only part of the whole sample, the bulk densities and porosities of the prepared C/SiC composites were also measured by ASTM C20 and are shown in Table 1. As is shown in Fig.1, the bulk densities of the composites increased and the porosities of the composites decreased as the amount of BN added to the
[Fig. 1.] Microstructures of the prepared samples: (a) BN00 (b) BN01 (c) BN03 (d) BN05 and (e) BN10.
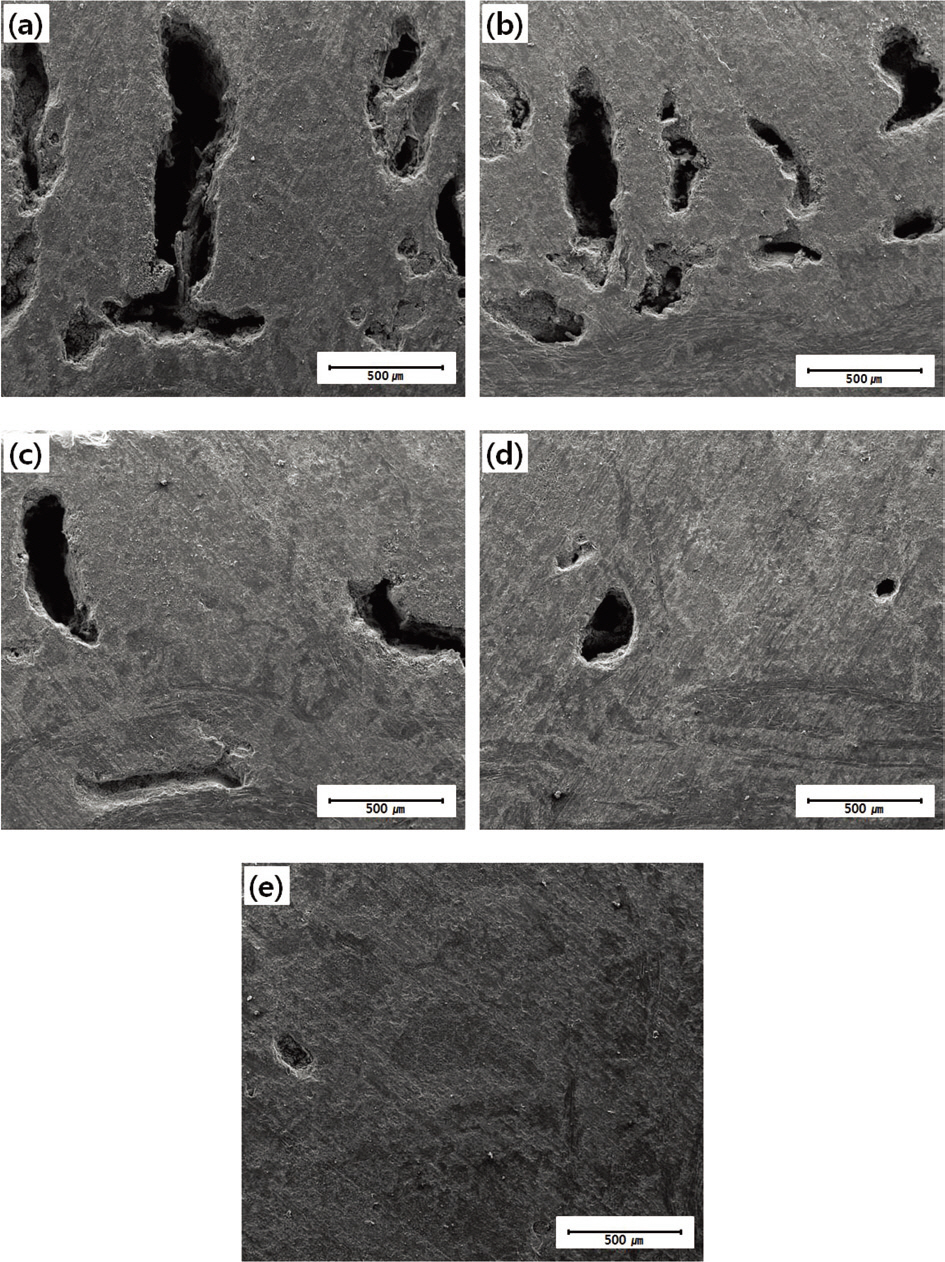
composite increased. This was attributed to the lubricating effect of BN caused by its layered structure. It has been reported that layered graphite can reduce abrasion and work as a lubricant [14]. Because BN has a layered structure, it worked as a lubricant, as expected, and when liquid silicon was infiltrated into the C/C composites, the BN assisted the silicon infiltration by reducing abrasion between the C/C composite and the liquid silicon. As a result, the amount of liquid silicon infiltrated increased.
3.2 Anti-oxidation properties of C/SiC composites prepared by BN-assisted LSI
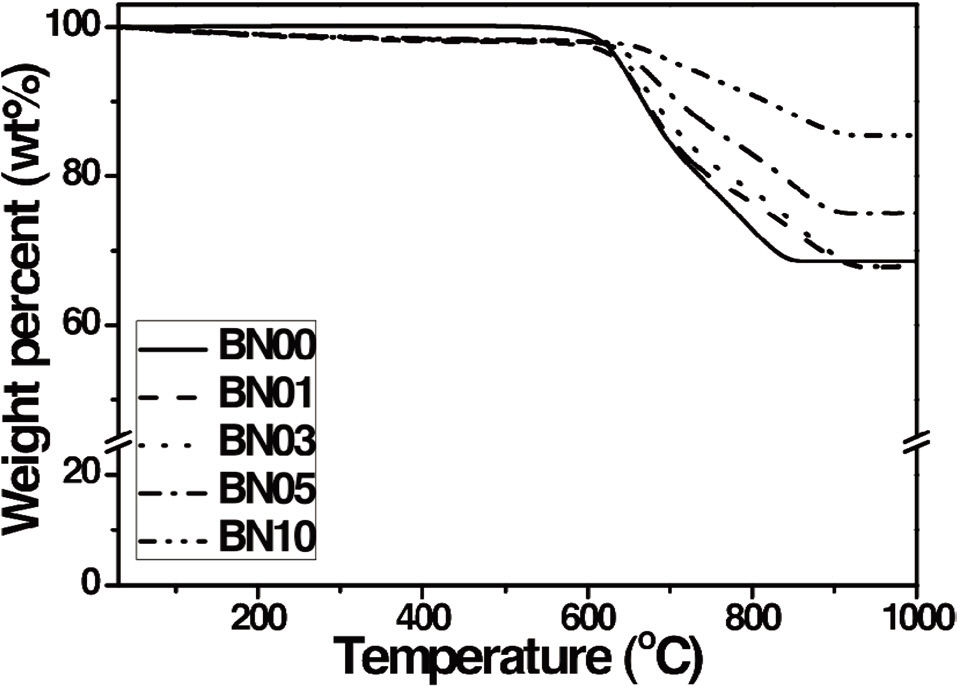
The anti-oxidation properties of the prepared C/SiC composites are shown in Fig. 2. The characteristic parameters of anti-oxidation in the composites are shown in Table 1. Fig. 2 and Table 1 confirm that the initial decomposition temperatures of the composites increased as the amount of added BN increased. The integral procedural decomposition temperatures of the composites also increased as the amount of added BN increased. These improved anti-oxidation properties of the C/SiC composites can be attributed to BN addition prior to LSI. As mentioned previously, BN assisted in the infiltration of liquid silicon and resulted in higher bulk densities and lower porosities in the C/SiC composites. Therefore, it was expected that more thermally stable SiC would be formed, due to the increased infiltration of the liquid silicon. The resulting composites were expected to have improved anti-oxidation properties as well. The formation of more SiC led to more residuals even after heating above 900℃, as the amount of added BN increased. On the other hand, it is generally believed that oxidation of the composite proceeds through contact of the composite and oxygen with heat, whereas the pores of the composite work as paths for oxygen to diffuse inward [15]. Because the C/SiC composites prepared with BN had lower porosities, it was more difficult for oxygen to penetrate into the composites and this resulted in improved antioxidation of the prepared composites.
3.3 Mechanical properties of C/SiC composites prepared by BN-assisted LSI
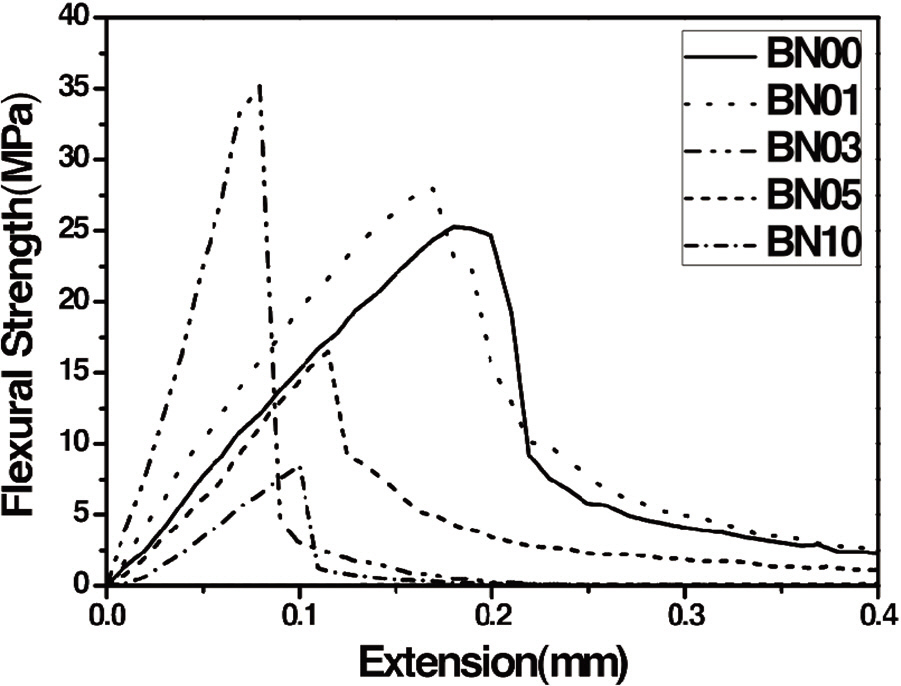
The results of three-point flexural test are shown in Fig. 3 and
Table 1. Until the amount of added BN reached 3%, both the flexural strength and modulus of the prepared C/SiC composites increased with more BN. However, when the amount of added BN was at 5 and 10%, both the flexural strength and modulus of the composites decreased with more BN. As discussed in Section 3.1, the amount of the infiltrated liquid silicon increased with more BN. Increased amounts of infiltrated liquid silicon were expected to increase hard SiC formation. Because there was more hard SiC present in the composite, the flexibility of the composite decreased as the amount of BN increased. In other words, the composites became more brittle as the amount of BN increased. Hence, when the amount of BN increased, the flexural strength of the composite increased up to a point and then began to decrease. The increased brittleness of the C/SiC composites was also apparent in the reduced plastic deformation of the composites. After reaching the yield point, the flexural strength of the composite dropped more quickly as the amount of added BN increased, suggesting less plastic deformation. Less plastic deformation could lead to increased brittleness in the composites.
To prepare C/SiC composites, LSI was carried out in C/C composites with the addition of BN. The microstructures, bulk densities, and porosities of the prepared C/SiC composites showed that the amount of the infiltrated liquid silicon into the C/C composites improved due to the assistance of BN, which has a layered structure and works as a lubricant. Anti-oxidation of the C/SiC composites improved with an increased amount of BN due to the synergistic effect induced by the assistance of BN in the infiltration of liquid silicon. One effect was the formation of more thermally stable SiC in the composite, and the other was the formation of fewer pores to reduce oxygen diffusion inward. The mechanical strength of the composite increased until 3% BN was reached and decreased thereafter due to increased brittleness caused by the presence of more SiC in the composite. Based on the anti-oxidation and mechanical properties of the prepared composites, those properties of the composite can be achieved by optimizing the BN-assisted LSI conditions.