Genus Skeletonema are the most important contributors to phytoplankton blooms in many coastal zones, worldwide (Karentz and Smayda 1984; Cloren et al. 1985; Estrada et al. 1985). In particular, S. costatum (Grev.) Cleve is the most conspicuous and widespread member of marine phytoplankton. Hasle (1973) reported that S. costatum was a cosmopolitan species, showing a wide range of tolerance for temperature and salinity, and that it exhibited extremely morphological variations in both size and shape. Moreover, this species is difficult to identify and easy to confuse with other Skeletonema species; in fact, Hasle wrote "To most marine phycologists, the name Skeletonema is synonymous with the specific name S. costatum." Other researchers also pointed out that Skeletonema costatum have high morphological variations (Gallagher 1980, 1982; Gallagher et al. 1984). It seems that many Skeletonema species might be hidden within the taxon.
The genus Skeletonema was established by Greville (1865) for a single species, S. barbadensel, recovered from the Barbados deposit. Characteristics given for the genus are cells joined by long marginal processes to form a filment. Plastids are disc-like or cup-shaped (Round et al. 1990). In the recent times, the 18 species of Skeletonema were recognized by various morphological characteristics and aquatic habits: S. subsalsum (Cleve) Bethge and S. potamos (Weber) Hasle in brackish and/or fresh-water regions (Hasle and Evensen 1975, 1976), S. tropicum Cleve in tropical regions (Hulburt and Guillard 1968), and S. ardens Sarno & Zingon (Sarno et al. 2007), S. dohrnii Sarno & Kooistra (Sarno et al. 2005), S. grethae Zingone & Sarno (Sarno et al. 2005), S. grevillei Sarno & Zingone (Zingone et al. 2005), S. marinoi Sarno & Zingone (Sarno et al. 2005), S. menzelii Guillard, Carpenter & Reimann (Guillard et al. 1974), and S. pseudocostatum Medline emend. Zingone et Sarno (Medlin et al. 1991) in oceanic area, respectively.
Skeletonema blooms are frequently seen in Korean coastal waters throughout the year (e.g., Lee et al. 1997). Until now, these species have been usually reported as the name of S. costatum. Therefore, it is now needed to inform for species diversity in genus Skeletonema. The purpose of this study was to discriminate taxonomic features of four species in genus Skeletonema using light and scanning electron microscopy.
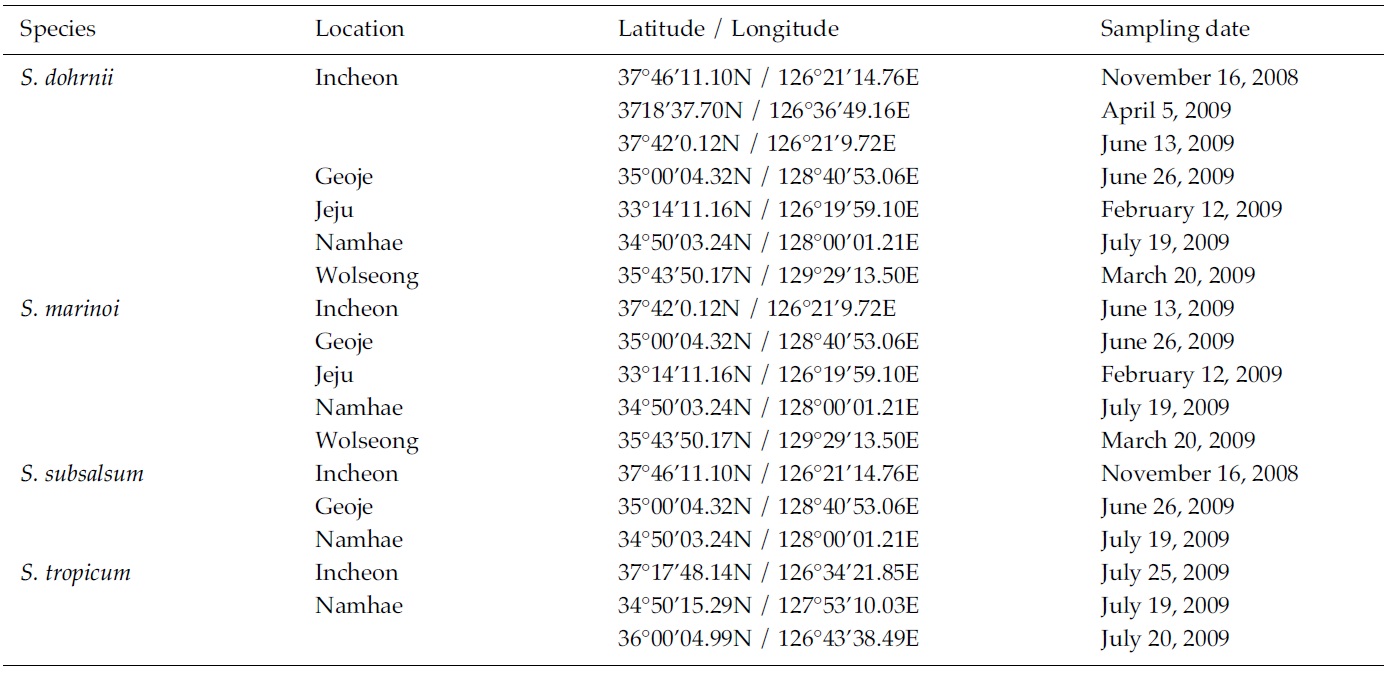
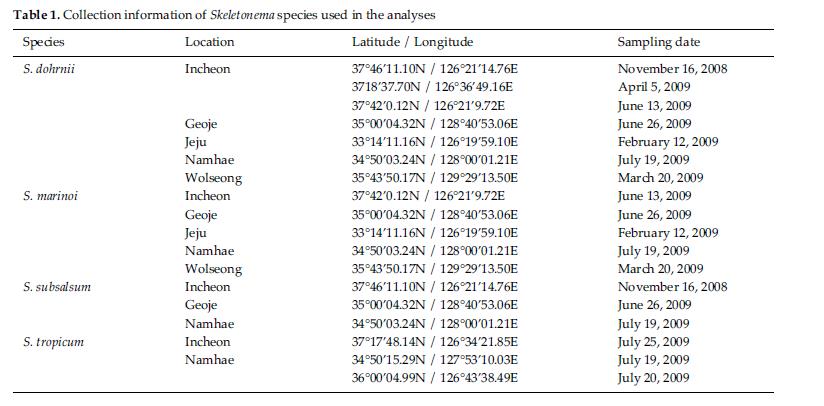
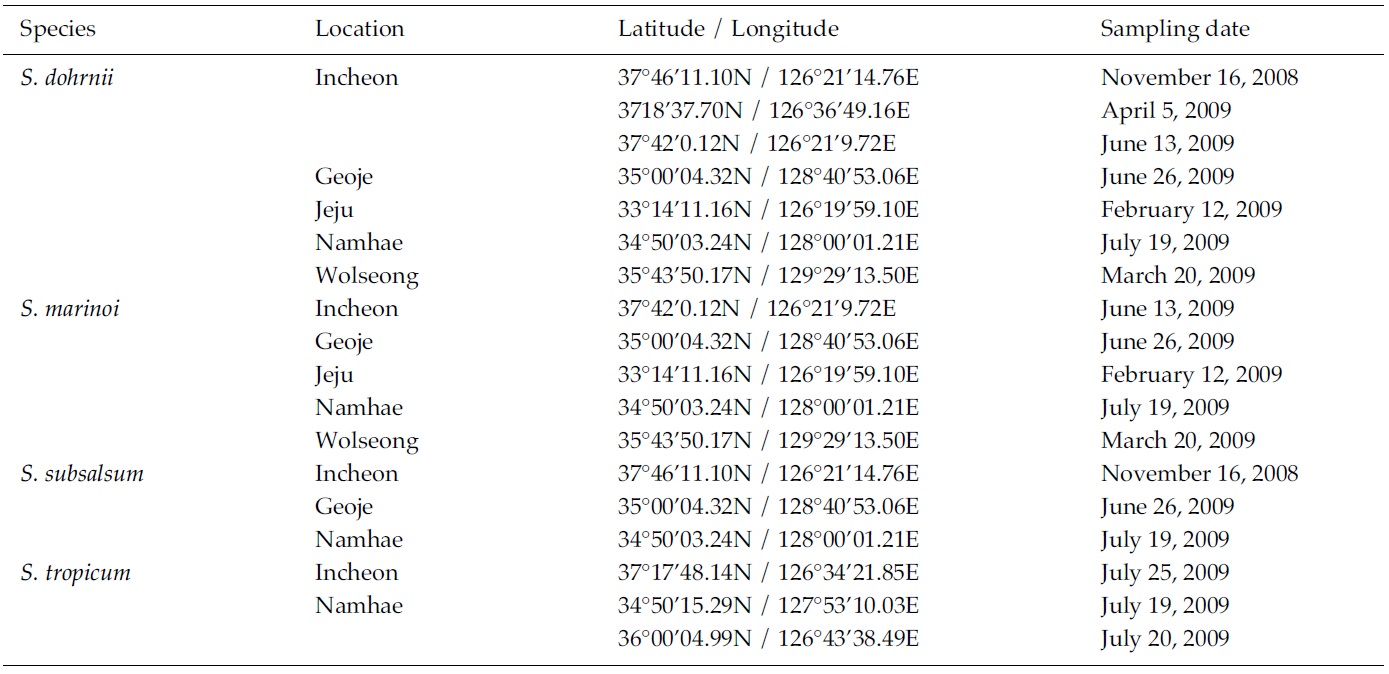
Skeletonema diatoms were collected with a 20 μm meshsizeplankton net from November 2008 to July 2009 in thecoastal waters of South Korea (Table 1). Morphologicaldifferences of Skeletonema species were assessed by lightmicroscopy (LM) (Axioskop; Zeiss, Jena, Germany)equipped with an MRc5 digital camera (Zeiss) and scanningelectron microscopy (SEM) (JSM-5600LV; Jeol,Tokyo, Japan). For removal of cell organelles, organicmatters in samples were removed according to Hasleand Fryxell’s method (1970). Samples were washed withdistilled water to remove NaCl. The rinsed samples werecleaned by adding an equal amount of KMnO4 and HClin boiling water bath until the sample becomes clear oronly slightly colored. Then, samples were again washedwith distilled water. Another preparation procedure wasaccording to Jung et al.’s method (2009). Live cells werefixed with modified Parducz’s fixative (Parducz 1967) at1:1 v/v for 10 min at room temperature: the fixative comprised2% solution of osmium tetroxide (75632; Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) in filtered seawater and asaturated solution of mercuric chloride (M1136; Sigma)in distilled water mixed in the ratio of 5:1 v/v, respectively.Fixed cells were harvested by gravity filtration(XX10 025 00; Millipore, Bedford, MA, USA) onto a 2.0μm polycarbonate membrane (TTTP; Millipore). To preventthe formation of NaCl crystals, any seawaterremaining associated with the specimen was removed bywashing for 2 min at room temperature with drops ofdistilled water followed by drops of 0.05 M sodiumcacodylate trihydrate buffer (pH 8.0; 20838, Sigma). Fordehydration, drops of tert-butanol (308250; Sigma) werecontinuously dripped on the specimen for 10 min at 30°C. Following this procedure, several drops of hexamethyldisilazane(HMDS, H4875; Sigma) were immediatelydispensed onto the membrane to complete the dryingprocess. Finally, the specimens were coated with goldpalladiumfor 3 min, and examined using a SEM (JSM-5600 LV; Jeol).
Diatom terminology followed the literatures of Anonymous (1975), von Stosch (1975) and Ross et al. (1979).
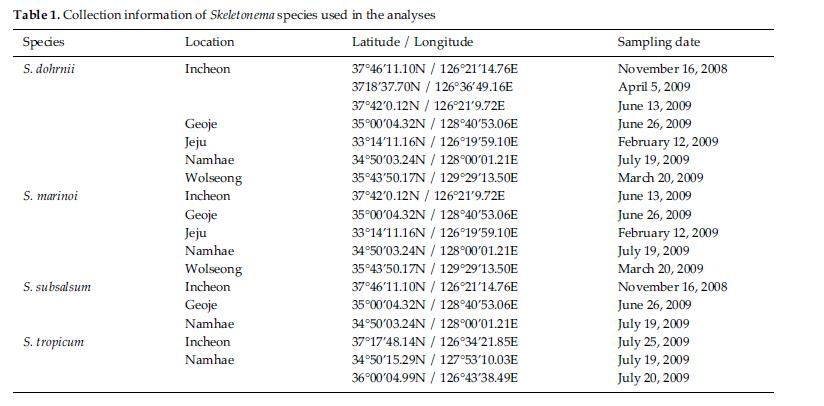
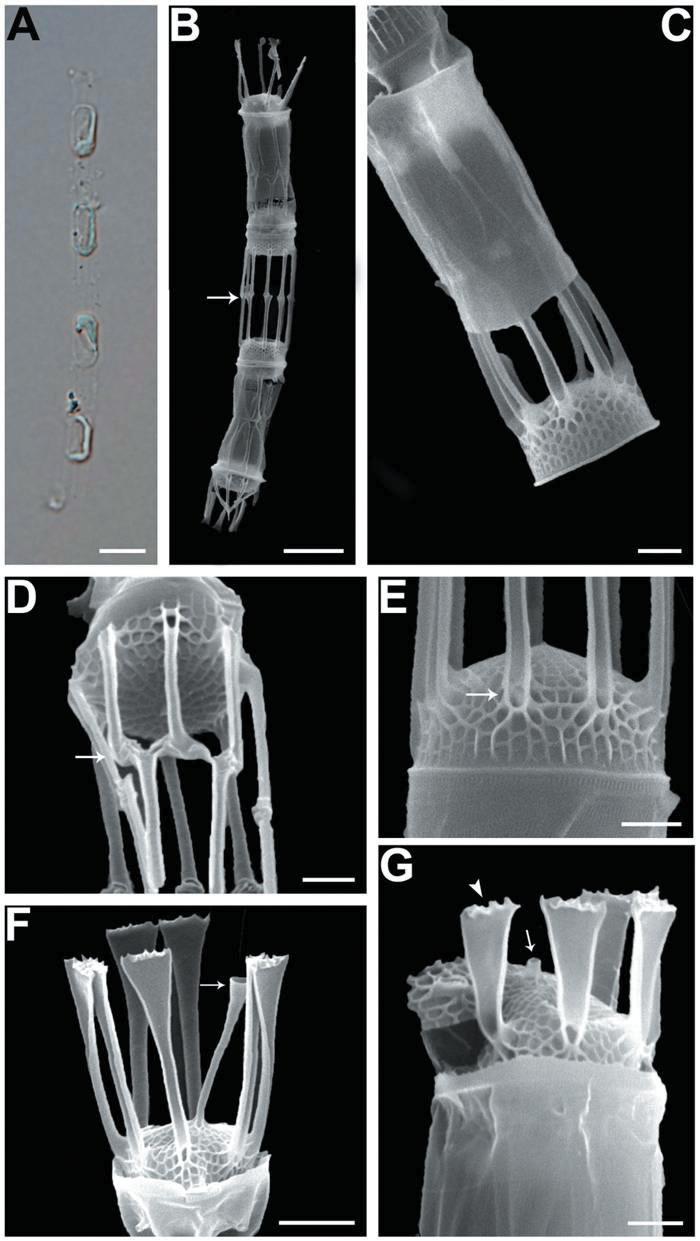
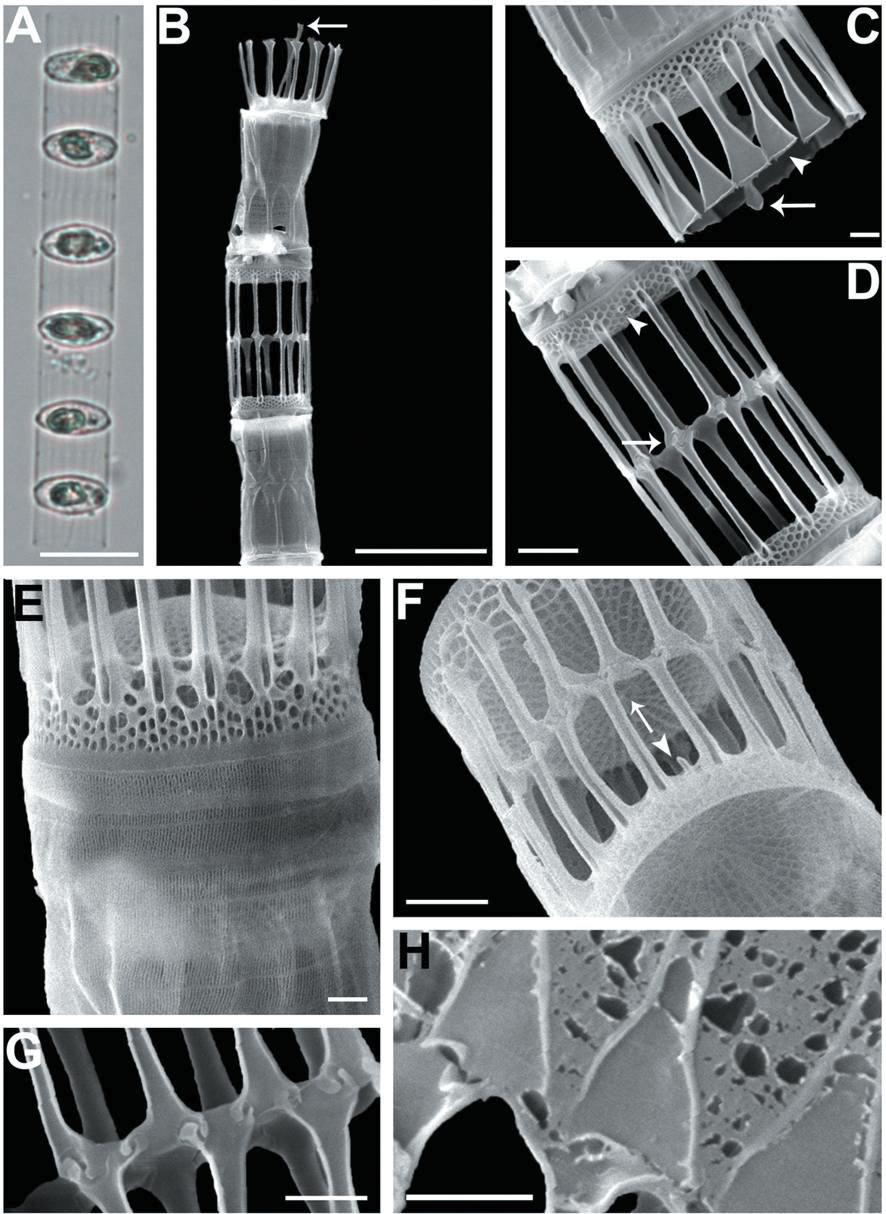
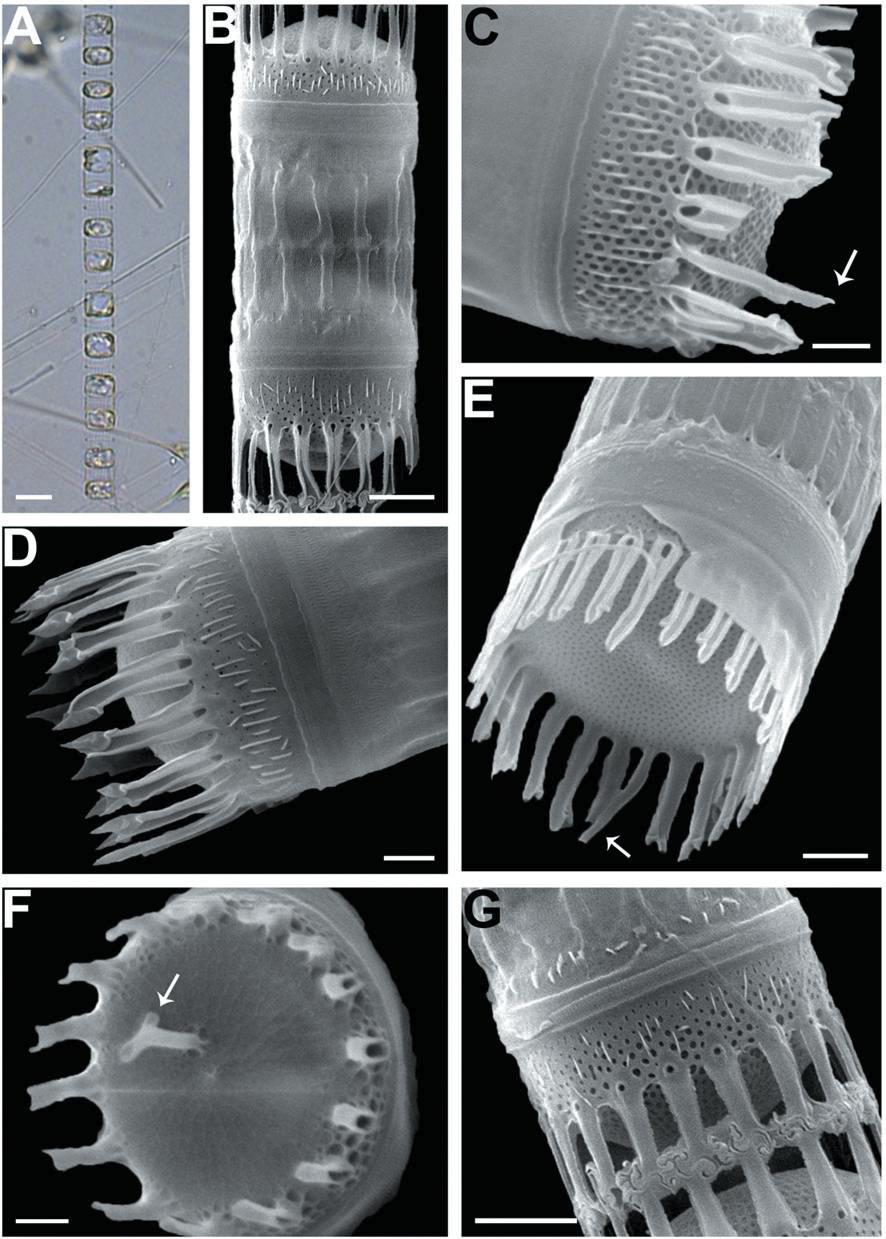
We recognized four Skeletonema species, whose characteristics are shown in Table 2 and Figs 1-4: S. dohrnii (Fig. 1), S. marinoi (Fig. 2), S. subsalsum (Fig. 3), and S. tropicum (Fig. 4).
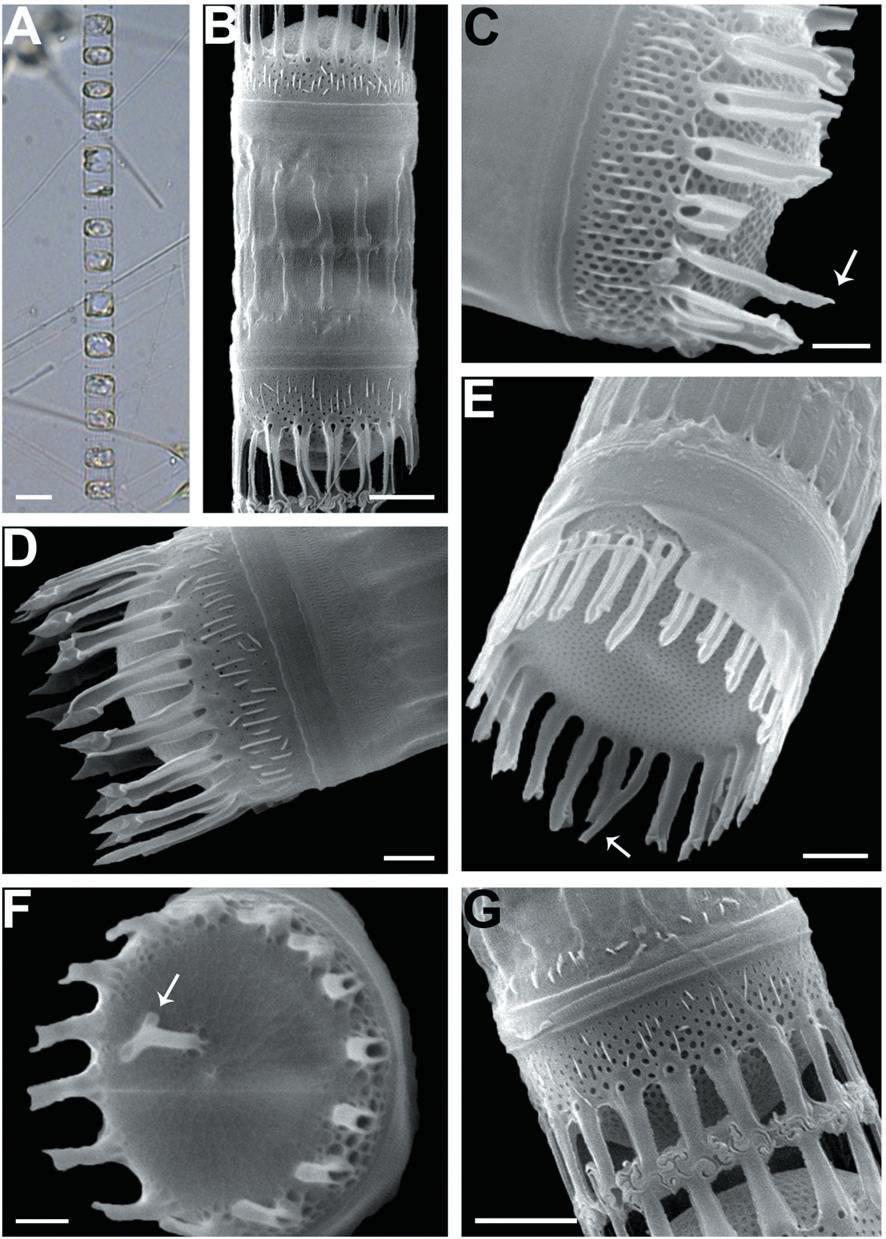
Skeletonema dohrnii Sarno & Kooistra. Cells 3-6 μm and the pervalvar axes 13-19 μm (16 μm in length). Short chains composed of 7-28 cylindrical cells, forming slightly curved (Figs 1A, B); longer chains at over 20 cells were very rare. One or two partial chloroplasts were visible in each cell (Fig. 1A). In SEM observation, the distances between sibling cells were 6-12 μm (9 μm). Numbers of the fultoportula processes (FPs) and distances between FPs were 8-10 and 0.6-0.9 μm, respectively. The bases of the terminal FPs (TFPs) were open (Fig. 1E), and the tips of the TFPs were flat and flared, with slightly jagged margins (Fig. 1F). The shape of the intercalary FPs (IFPs) was similar to that of the TFPs (Figs 1F, G). Each IFP was connected with one or two processes of the adjoining cell, forming a slightly interdigitated linkage (Figs 1B, D). The terminal rimoportula process (TRP) was located at the sub-central zone of a valve face and consisted of a long tubular process, which widened along its length and truncated at its apex like a trumpet (Fig. 1F). The intercalary RP (IRP) was shorter than the IFPs and was located near the center of the valve, with a tube-shaped distal end (Fig. 1G). The valves were convex (Fig. 1E), and the areolae were clear, widely spaced and irregularly arranged (Figs 1F, G).
Skeletonema marinoi Sarno & Zingone. Cells 4-10 μm and the pervalvar axes 8-18 μm. A colony was straightly connected with 16-33 cells, and each cell contained one chloroplast (Figs 2A, B). In SEM, distances between sibling cells 3-9 μm. The numbers of FPs and distances between FPs were 9-13 and 0.6-1.1 μm, respectively. In TFPs, the base was open and the end of split tube was flat and flared or sometimes jagged (Fig. 2C). The shape of the IFPs was similar to that of the TFPs (Figs 2B, F, H). IFPs between sibling cells formed 1 : 1 or 1 : 2 linkages, and the intercellular junctions were either interdigitated or simply connected (Figs 2D, F, G, H). The TRP located in the valve center was long with a trumpet-shaped end (Figs 2B, C). The IRP was a short tube located at the margin of the valve face (Fig. 2F). The valves were flat or slightly convex (Figs 2C, D). The areolae distributed from the valve center had clear tetragonal forms (Fig. 2F).
Skeletonema subsalsum (Cleve) Bethge. Cells 8-13 μm and the pervalvar axes 11-20 μm. A colony was straightly connected with 12-46 cells, and each cell contained 1-2 chloroplasts (Figs 3A, B). In SEM, the numbers of FPs and distances between FPs were 15-24 and 0.4-0.9 μm, respectively. An external larger pore on the base of the tube of TFPs was open and the tips of them were pointed at the end (Fig. 3D). Sibling cells were joined by IFPs, which were generally short at a mean of 5 μm (Figs 3B, G). Each IFP was connected to one or two processes (1 : 1 or 1 : 2 linkages) of the adjoining cell, forming an interdigitated linkage (Figs 3B, G). The TRP on the center was long and had a hook-like end (Fig. 3F). The marginal IRP was a curved tube with a trumpet-shaped end and was longer than the IFP (Figs 3C, E). The valves were convex (Fig. 3D) or flat (Fig. 3E). The areolae of the valve face were rectangular to triangular and ran radially from the center (Figs 3C, E). In the mantle, the areolae were paral-lel to the pervalvar axis (Fig. 3C).
Skeletonema tropicum Cleve. Cells 10-18 μm and the pervalvar axes 4-9 μm, rarely exceeding twice the cell diameter. A colony was straightly connected with 12-52 cells, and 2-4 chloroplasts were seen in each cell (Figs 4A-C). In SEM, 18-22 FPs per valve were seen, and the distances between FPs were 0.6-0.9 μm. The TFPs were open along the full length of the tubes, the ends of which were slightly broadened and the tips of which were clawshaped (Figs 4D, F). The IFPs were open at both the ends and the bases, and centers were closed (Fig. 4D). The intercellular junctions between sibling cells were intricate, tight, and knuckle-like, and were usually joined with 1 : 1 linkage (Figs 4E, G). Sibling IFPs were not vertical to the valve face but were slightly deflective (Fig. 4E). The tubular TRP was long and was located between the sub-central valve face, with a slightly dilated trumpet- like end (Fig. 4F). The TRP diameter was longer than those of the TFPs. The short IRP, such as a spine, was located in the marginal valve (Fig. 4H). The valves were flat or sometimes slightly convex (Fig. 4E). Tetragonal areolae in straight or curved tangential rows were radially arranged and tended to fasciculate. The areolae of the mantle were round (Fig. 4H).
Identification of genus Skeletonema is according to the key characteristics: cylindrical cells with a ring of long processes emerging from the edge of the valve face. However, exact identification of species in the genus Skeletonema is very difficult due to varying expression (Castillo et al. 1995). S. dohrnii and S. marinoi are morphologically involved in a same group (Sarno et al. 2005) and differ from other species in that their FPs possess flat and flare tips with dentate margins. They commonly appear the 1 : 2 linkages with displaced IFPs. The only morphological distinction between two species is the ultrastructure of the cingular bands (Sarno et al. 2005). S. subsalsum has a thick frustule with a pseudoloculate structure and short IFPs, which are displaced in mainly 1 : 1 junction. Somewhat similar IFPs forms of S. subsalsum are found in those of S. costatum (Sarno et al. 2005): description of S. subsalsum in Hasle and Evensen (1975) is rather similar to the S. costatum in Fig. 3G in Zingone et al. (2005). However, the short and irregular TFPs of S. subsalsum look quite different from the straight and narrow clawshaped ones of S. costatum (Sarno et al. 2005). Cell shapes of S. tropicum are similar with those of S. costatum. Hasle (1973) demonstrated that S. costatum and S. tropicum were not distinguishable from the morphological patterns of the frustules in LM, even though S. tropicum has a range of cell diameter that includes some sizes larger than S. costatum. We could identify four species of the genus by taking into account as many characters as possible, but some forms showed a certain overlap in some characters, mainly the shape of the external part of the fultoportula and rimoportula, and the number of chloroplasts.
Distribution of Skeletonema dohrnii, S. japonicum and S. tropicum in Korean coastal areas was reported by Kooistra et al. (2008). S. marinoi and S. subsalsum were the first species demonstrated in this study. S. tropicum, a warm water species, was collected in summer in the South and Yellow Sea. S. dohrnii and S. marinoi were observed in all sampling sites. S. subsalsum was collected in the Kyung-gi and Gang-mok Bay, both of which have low salinity (< 25 psu). S. japonicum, a cold water species, was not collected in these investigations. S. costatum has a wide geographical distribution and presented in all seasons (Castillo et al. 1995). However, the species was not collected in this study.
More than four Skeletonema species (S. dohrnii, S. marinoi, S. subsalsum and S. tropicum) may occur in Korean coastal waters. The shape and size of the chains are useful taxonomic characters for species identification as described above. In LM, it is possible to use these characters to observe identification keys. Fine structures such as number and position of the processes (both rimo- and fultoportulae), and number of areolae between processes seen only by electron microscopy are important keys (Medlin et al. 1991). To overcome this identification confusion, many ultra-structural key characters can be estimated using SEM. For increase of species diversity, specimens are carefully observed. Furthermore, to estimate the increase of biodiversity, physiological factors such as life cycle based on laboratory, field, and molecular studies are needed.