Pollination in terrestrial ecosystems is an important service supported by various pollinators. Their economic value is estimated at about 120 billion dollars a year (Costanza et al. 1997). The major insect pollinators are honeybees; their economic benefit is 11.7 billion dollars (77% of the total pollination value) in the United States (Calderone 2012) and 5.8 billion dollars in South Korea (Jung 2008). Honeybees have been cultivated since prehistoric times. They are one of the top three livestock resources in Europe (Tautz 2008).
However, Colony Collapse Disorder (CCD) has seriously affected honeybees all over the world since 2006 and caused enormous economic damage to agricultural crops (Johnson 2010). The number of apiaries and hives had constantly increased in Korea since 1970s, but a downward trend has continued after a peak in 2005 (Lee et al. 2010). This phenomenon seems to be caused by a decline in honey productivity because of sacbrood virus disease and an increase in the abundance of natural honeybee enemies (Kim et al. 2006, Kim et al. 2008, Jung et al. 2008). The best-known natural enemies of honeybees are hornets (Vespa species), which are common worldwide and cause constant damage to apiculture. A group of 10 to 20 workers of the giant hornet, Vespa mandarinia, is able to exterminate the population of a honeybee hive with 10,000 to 30,000 colony members (Matsuura and Yamane 1990).
Recently, the invasive yellow-legged hornet V. velutina has rapidly spread in South Korea as well as Europe, including France, where it has inflicted serious economic damage on beekeeping because V. velutina prefers honeybees rather than other Vespa species (Villemant et al. 2006, 2011a, 2011b, Tan et al. 2007, Rome et al. 2009, Beggs et al. 2011, Choi et al. 2012a, Jung 2012, Monceau et al. 2014).
Jirisan National Park (JNP) is the largest national park (total area: 483.022 km2) and one of the densest apicultural areas in South Korea (Lee et al. 2010). Various social wasps have damaged many apiaries within this region and a recent V. velutina invasion has aggravated the damage and led to the death of beehives (Choi et al. 2013).
In this study, to identify the vespid wasps in JNP, we collected them by trapping in the southwestern region of JNP. To investigate their foraging behaviors and to assess their impact on honeybees, we also determined the number of wasps and bees visiting an apiary in JNP. These data will be useful for protection of honeybee colonies.
To inspect the damage caused by wasps or bees, their foraging and predation behavior was recorded by observing the hive entrance. The apiary site (35°15′18.37″127°35′53.88″, 402 m above sea level) is a small farm with 6 Apis mellifera hives. Observations of the damage were conducted once in the middle of each month between May and December 2014 at 10 a.m. to 5 p.m.
One-way PERMANOVA (permutation multivariate analysis of variance) was used to test the independent effects of month and species. The non-parametric PERMANOVA test calculates a pseudo-F statistic (based on permutations), which is comparable to the F statistic from ANOVA and is not affected by non-normal distributions of the data. The Euclidean distance measure was used. Multivariate analyses were performed in PAST (Hammer et al. 2001) using 9999 permutations.
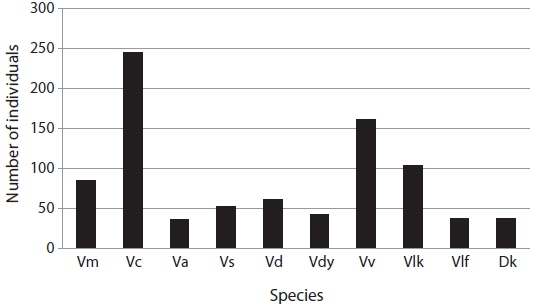
In total, 10 Vespidae species were identified (Fig. 2). Among them, V. crabro was the most abundant (245 individuals, 28.3%), followed by V. velutina (162 individuals, 18.7%). The Vespidae occurring in the forested areas of South Korea showed no significant differences in species composition according to the collection sites (Choi et al. 2012a, 2012b, 2014). However, V. velutina in South Korea in 2003, its abundance has been rapidly increasing (Kim et al. 2006, Choi et al. 2012a, Jung 2012). According to Choi et al. (2013), its range expanded to JNP in 2011.
[Fig. 2.] The numbers of Vespidae species collected from 61 traps in the southwestern part of JNP from July to September 2014. Vm, Vespa mandarinia; Vc, V. crabro; Va, V. analis; Vs, V. simillima; Vd, V. ducalis; Vdy, V. dybowskii; Vv, V. velutina; Vlk, Vespula koreensis; Vlf, Vl. flaviceps; Dk, Dolichovespula kuami.
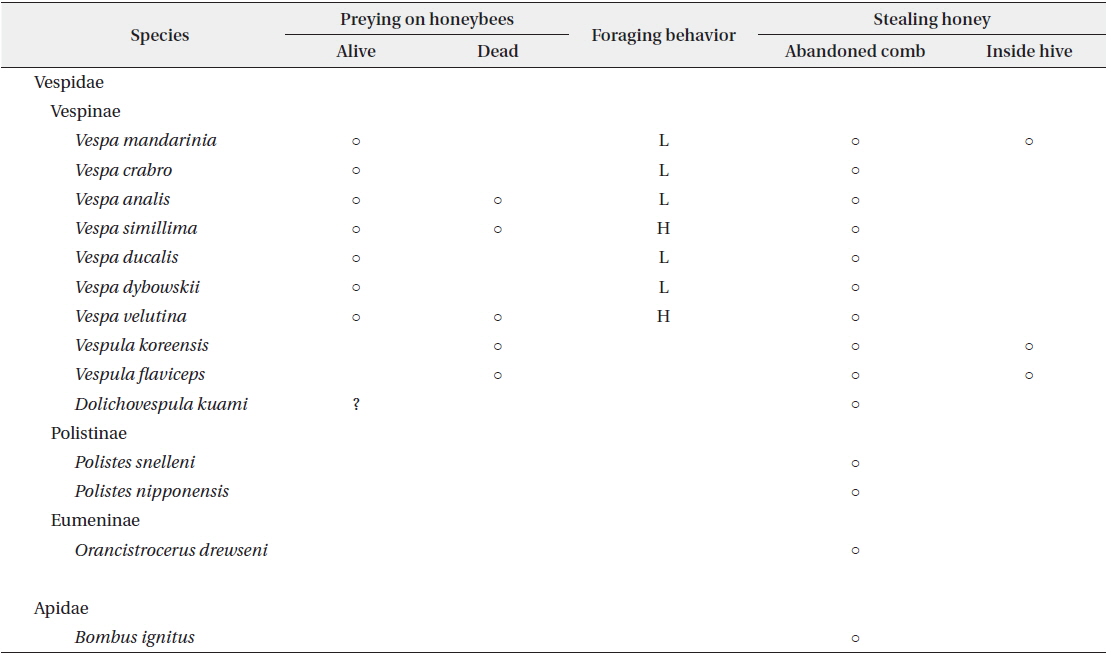
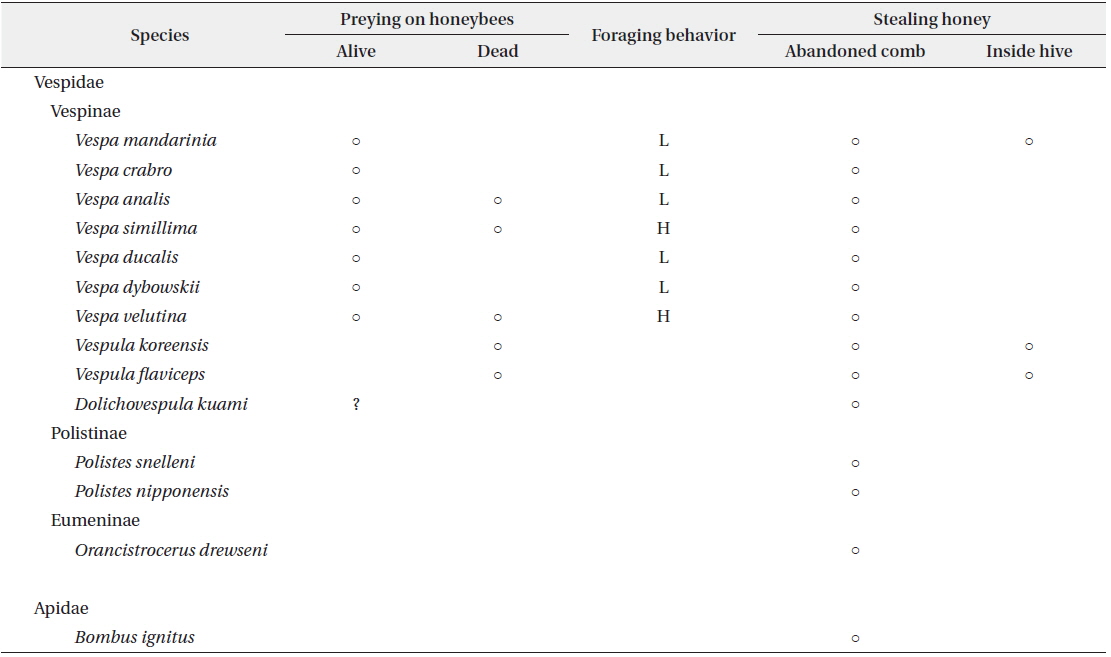
At the apiary site, 14 wasp and bee species were collected, including 13 species of Vespidae and one species of Apidae (Table 1). These included all species of Vespinae that we collected at other JNP sites. The species of wasps and bees in the JNP apiary were very similar to those reported in other domestic apiaries (Chang et al. 1993, Jung et al. 2007).
Genus Vespa
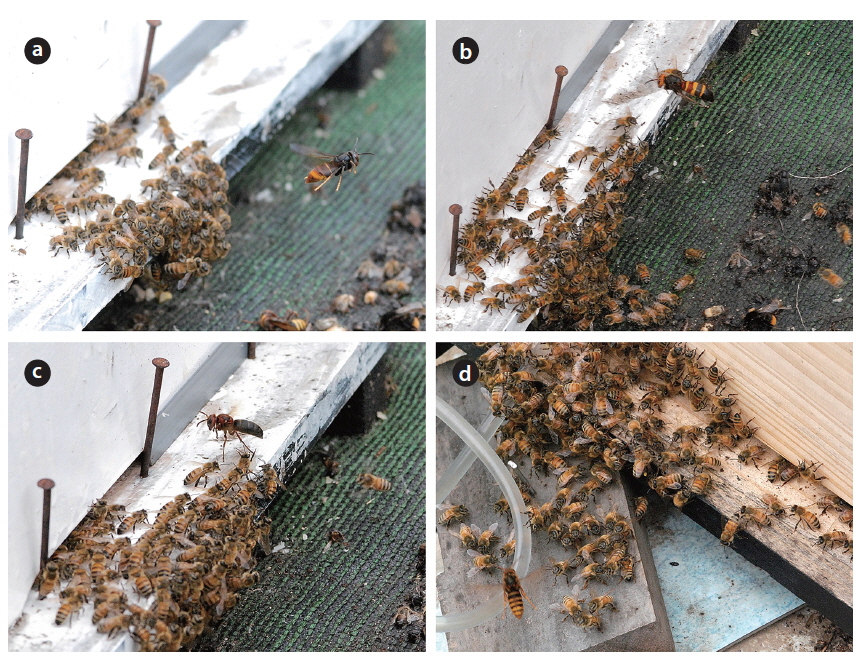
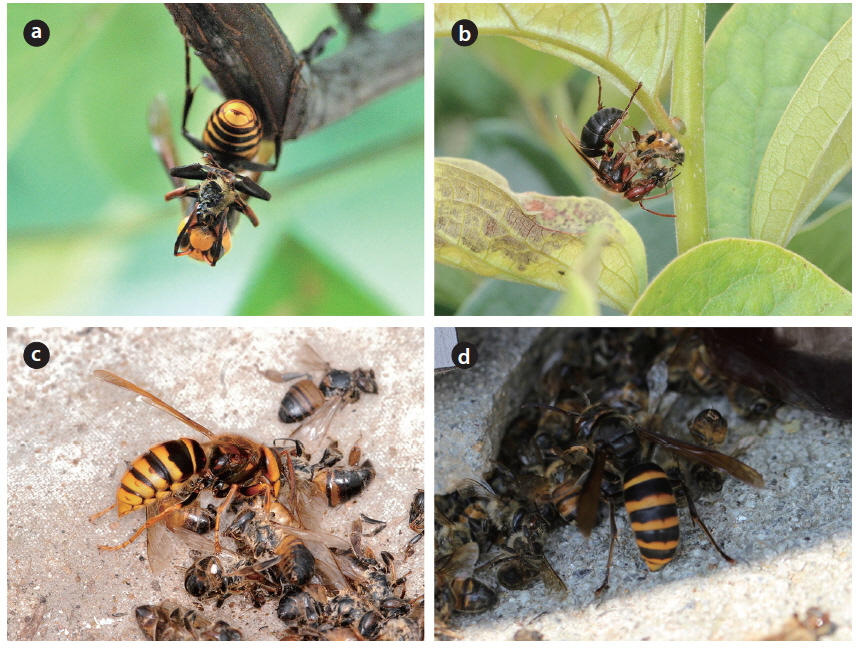
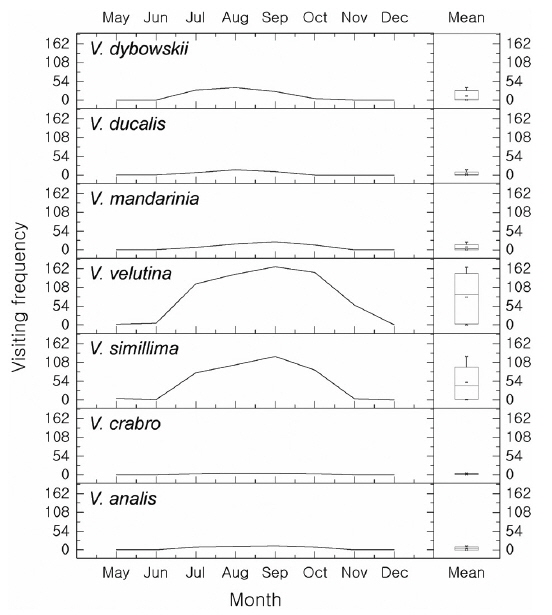
The hornets have the largest and most continuous impact on apiaries (Matsuura and Yamane 1990). In total, 7 species were found in the apiary and all of them attacked beehives and predated on honeybees (Figs. 3 and 4). The visiting frequency of Vespa significantly differed among months (PERMANOVA, F = 2.144, P = 0.05) and species (F = 6.108, P = 0.0005). We found hundreds of thousands of dead honey bees piled up; they must have been attacked by a group of V. mandarinia. While observing, each individual foraged for honeybees one at a time (Fig. 5a). According to Chang et al. (1994), a group of V. mandarinia slaughters honeybees once in 3-4 days, but otherwise V. mandarinia forages individually. In line with these observations, we found that, unlike continued visits by other Vespa species, visits by V. mandarinia fluctuated. Even though the frequency of V. mandarinia in the apiary was low, they caused serious damage or even loss of entire beehives. A queen of V. mandarinia appeared occasionally around the apiary in May and June and the frequency of her visits increased from July and reached its peak in September (Fig. 3). It has been reported that V. mandarinia visits apiaries seasonally: these wasps are not seen until mid-August and then the number of their visits increases gradually (Matsuura and Sakagami 1973, Matsuura 1984, Chang et al. 1994). In our study, however, many workers attacked the apiary since July. Further observations are needed to explain this difference.
V. analis was observed going back to their nest with live or fresh honeybees but not rotten ones when they selected the carcasses of honeybees killed by V. mandarinia (Table 1, Fig. 5c and 5d). However, they barely attacked live honeybees in the apiary (Fig. 3).
Although the number of trapped V. crabro was the highest (Fig. 2), the frequency of its occurrence in the apiary was quite low (Fig. 3). Whereas V. crabro often appears around most apiaries in South Korea, its impact on honeybees is negligible (Chang et al. 1993, Jung et al. 2007). Therefore, V. crabro seems not to prefer to prey on honeybees, unlike other Vespa species.
V. ducalis, a known natural enemy of Polistinae (Starr 1992), occurred occasionally in the apiary and foraged on honeybees from June to September in this study, but the damage was low (Figs. 3 and 4b). V. dybowskii is a known social parasite (Matsuura and Yamane 1990). There have been few reports of its foraging for honeybees. This study found, however, that V. dybowskii actively foraged for honeybees from July to October (Figs. 3, 4c and 5b). In July, there was a rapid increase in the number of V. dybowskii visiting the apiary; this number reached a peak in August, which lasted into September. Consequently, V. dybowskii became the third most frequent hornet in the apiary and its frequency exceeded that of V. mandarinia, the most serious natural enemy of honeybees. Therefore, we consider V. dybowskii to be a new pest of honeybees; the impact of this species on apiaries is considerable in South Korea.
V. simillima was the second most frequent Vespa species, which began to appear in the apiary from May (Fig. 3). In Japan, it is known as the most damaging species to apiaries, together with V. mandarinia (Matsuura and Sakagami 1973, Matsuura 1984). Notably, V. simillima hawked honeybees, which is similar to the foraging behavior of V. velutina (Fig. 4a and 4d), while the other Vespa species landed in front of a hive to hunt the honeybees (Fig. 4b and 4c). It is thought that similar foraging behavior of V. velutina and V. simillima is due to their close phylogenetic relationship (Perrard et al. 2013).
V. velutina occurred most often in the apiary and caused serious damage (Fig. 3). A V. velutina queen hovered around the apiary from May to June and workers were observed since in July. In September, workers visited a maximum of 167 times a day, which corresponded to one visit in 2.5 min. The reported occurrence of V. velutina in apiaries was once in 2.2 min in India (Abrol 1994) and once in 1.7 min in China (Tan et al. 2007). Although V. velutina was introduced into JNP only about 4 years ago, the damage it caused to the apiary was similar to that in India and China, where V. velutina is native. If this trend continues, the frequency of its visits will likely increase and this wasp will cause more damage. V. velutina continuously visited until October, and from November to early December it was the only Vespa species that occurred in the apiary (Fig. 3). This is in line with V. velutina having the most serious impact for the longest time on the apiaries in South Korea.
According to Jung et al. (2008), soon after its introduction, V. velutina attacked an apiary near Busan city and completely destroyed 10 colonies of honeybees in a week and 50 colonies in 3 weeks. If a colony reaches 20,000 to 50,000 individuals, however, it seems impossible for V. velutina to annihilate entire colonies by bee-hawking one at a time. We suspect that Jung et al. (2008) may have overestimated the colony damage caused by V. velutina, considering that the foraging success rate of this species is up to 40% (Tan et al. 2007). Jung et al. (2008) may have confused the damage caused by V. velutina with that caused by V. mandarinia. Despite these considerations, V. velutina is a serious pest of honeybees and has already spread inland over 2/3 of the country (Choi et al. 2013), which will have an impact on the apiary industry of South Korea.In addition to foraging for honeybees, all Vespa species visiting the apiary ate honey left in abandoned combs (Table 1).
Genera Vespula and Dolichovespula
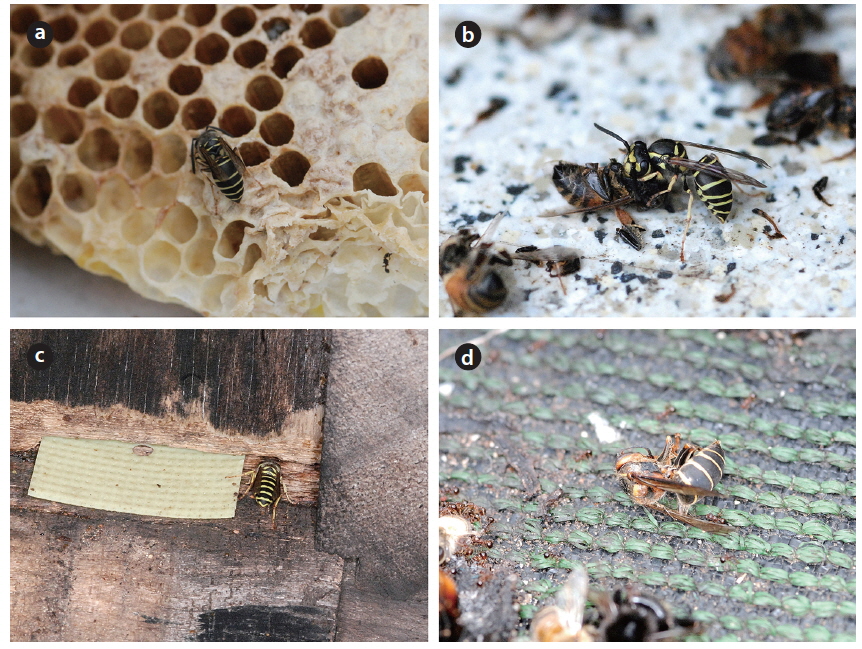
Vespula species did not forage directly for live honeybees but took over their nests, making meat-balls with honeybees killed by V. mandarinia (Table 1 and Fig. 6b). These species also crawled along the edges of weak hives to steal honey (their size is similar to that of honeybees) or ate honey left in abandoned honeybee combs (Table 1 and Fig. 6a and 6c). Although Vespula species are not more serious pests than Vespa species, many adults cause damage to honey production by stealing honey from beehives (Rawson 1963, Matsuura and Sakagami 1973). These losses are not negligible, taking into account that apiaries are built to harvest honey. Dolichovespula kuami was occasionally seen in front of beehives, but no direct attacks on honeybees were observed. Also, D. kuami was found dead in front of beehive entrance; it is not certain whether its death was due to heat-balling bees as a defensive behavior of honeybees (Fig. 6d). However, since Dolichovespula species are known to attack honeybees (Watson 1922), further observations are needed.
Others species
Polistes species and Orancistrocerus drewseni (potter wasp) did not directly damage the apiary and only ate honey left in abandoned honeybee combs (Fig. 7b). Although Bombus ignitus hovered in front of honeybee hives, they also only ate honey from abandoned honeybee combs (Fig. 7a). Therefore, they had no impact on honeybee colonies in the apiary.