This study was carried out to investigate the residual characteristics of insecticides used for Oriental Tobacco Budworm control and to establish the recommended pre-harvest residue limit leading to contribution in safety of paprika production.
The recommended Pre- Harvest Residue Limits (PHRLs) of insecticides during cultivation of paprika were calculated from residue analyses of insecticides in fruits 1, 3, 5, 7, 10, 12, 15, 18 and 21 days after treatment. Paprika samples were extracted with QuEChERS method and cleaned-up with amino propyl SPE cartridge and PSA, and insecticide residues were analyzed either by HPLC/DAD or GLC/ECD. The limits of detection were 0.01 mg/kg for 5 insecticides. Average recoveries were 81.3±1.62%-98.3±1.58% of 5 insecticides at fortification levels of 0.1 and 0.5 mg/kg. The biological half-lives of the insecticides were 8.5 days for bifenthrin, 11.8 days for chlorantraniliprole, 16.8 days for chlorfenapyr, 7.1 days for lamda-cyhalothrin and 31.3 days for methoxyfenozide at recommended dosage, respectively.
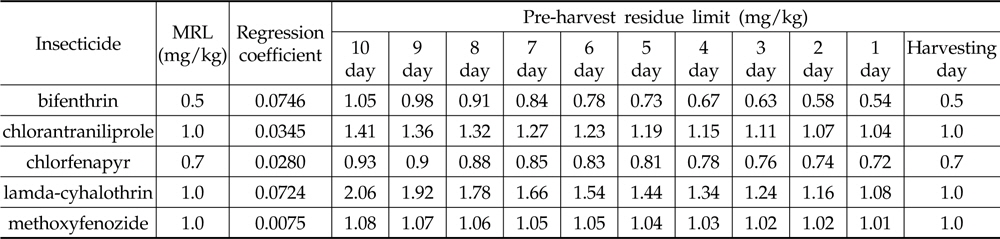
The pre-harvest residue limits for 10 days before harvest were recommended 1.05 mg/kg, 1.41 mg/kg, 0.93 mg/kg, 2.06 mg/kg and 1.08 mg/kg as bifenthrin, chlorantraniliprole, chlorfenapyr, lamda-cyhalothrin and methoxyfenozide, respectively. This study can provide good practical measures to produce safe paprika fruit by prevention of products from exceeding of MRLs at pre-harvest stage.
농약은 병해충 및 잡초로부터 농산물을 보호하고 생산량 증대와 품질 향상 및 수확한 농산물의 저장기간 중 손실을 방지하는 등 다양한 용도로 광범위하게 사용되고 있으며 현대 농업에 필요한 중요한 농업 자재로서 이러한 농약의 사용은 필수적이라 할 수 있다(Jeong
하지만 이러한 농약은 병해충 및 잡초를 효과적으로 방제하기 위하여 여러 형태의 화학구조를 가지고 있고, 본래의 목적으로 사용이 끝난 후에도 환경조건 등에 따라 농작물 및 환경 중에 잔류되는 경우가 발생하기도 한다(Kim
이렇게 농약이 지나치게 잔류된 농산물을 섭취하게 될 경우 인체 건강상의 문제를 유발할 수 있기 때문에 농작물 중 농약잔류허용기준(Maximum Residue Limit; MRL, 단위mg/kg)을 설정하여 국제적, 국가적으로도 관리 감독하고 있다(Lim
농약 잔류허용기준을 초과한 농산물에 대해서는 출하연기, 용도전환, 현장계도 및 폐기처분 등의 조치가 취해지지만, 잔류허용기준을 초과한 부적합 농산물들은 수확 후 신선도 유지의 어려움이 있어 실질적으로 출하연기가 불가능하고, 용도의 전환 및 재활용의 기회도 거의 없기 때문에 대부분의 부적합 농산물들은 폐기처분되고 있으며 이로 인한 생산자의 금전적 손실이 발생하고 있다. 이러한 문제점을 해결하기 위해서는 농산물들의 잔류농약에 대한 안전성 평가가 출하 전에 이루어지는 것이 바람직할 것이고, 이를 효율적으로 운영하기 위해서는 출하시점의 MRL과 농산물 재배 시 살포되는 농약의 생물학적 반감기에 근거한 생산단계에서의 잔류농약허용기준이 별도로 설정되어야 할 것이다(Lee
파프리카는 1994년 국내에서 처음으로 재배 된 이후 지속적으로 재배면적과 생산량이 증가하고 있으며(Cho
파프리카의 과실은 비대가 끝나고 난후 착색 기간에만 15일 전후가 소요되고, 이 시기에는 무게 증가에 의한 농약의 상대적 희석효과가 크지 않아 수확 전 살포 초기의 잔류농도가 출하 일까지 크게 감소되지 않을 수 있는 위험이 큰 작물로서, 수확 전 생산단계에서 농약사용에 각별한 주의가 필요하다고 할 수 있다.
시설 내 파프리카 재배 시 발생하는 주요 해충 중 담배나방으로 인한 피해가 발생하고 있으며, 이 해충은 유충이 잎, 꽃봉오리 등을 가해하기도 하지만 주로 과실 속에 들어가 종실을 가해하여 피해과실은 대부분 부패하여 낙과하게 되며 계속 다른 과실로 옮겨가서 가해하여 큰 피해를 일으키며 (Song
본 연구에서는 담배나방 방제를 위해 등록되어 사용되는 주요 살충제인 bifenthrin, chlornatraniliprole, chlorfenapyr, lamda-cyhalothrin 그리고 methoxyfenozide를 농가조사를 통하여 선발한 후 5개 살충제의 수확 전 잔류농도를 예측하기 위하여 시험농약을 시설 내 파프리카 포장에 살포하여 경시적 농약잔류 특성을 파악하고 생물학적 반감기를 산출한 후 시험농약의 잔류허용기준과 비교하여 그 결과를 생산단계 에서 농약 잔류특성을 알아보고자 하였다.
시험에 사용된 살충제의 표준품들은 Dr. Ehrenstorfer사(독일)로부터 구입한 bifenthrin (순도 99.5%), chlorantraniliprole (순도 94.5%), chlorfenapyr (순도 99%), lamda-cyhalothrin (순도 98%)과 methoxyfenozide (순도 98%)를 사용하였고, 추출 및 정제를 위해 사용한 acetonitrile과 acetone은 Merck사(독일)에서 구입하여 사용하였으며, SPE 정제를 위해 사용한 amino propyl cartridge (MEGA BE-NH2 SPE cartridge 1.0 g, 6 mL)와 PSA (Primary Secondary Amine)은 Agilent사(미국)에서 구입하여 사용하였다.
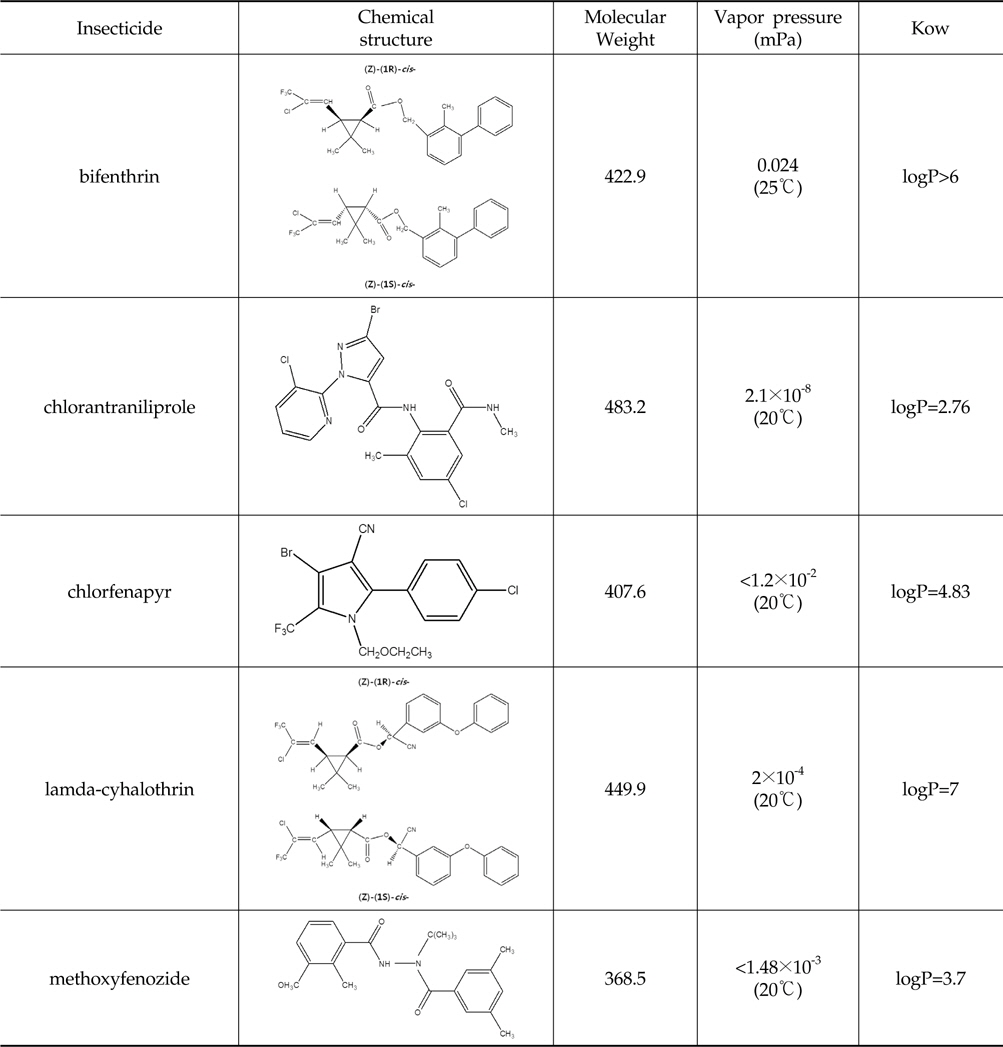
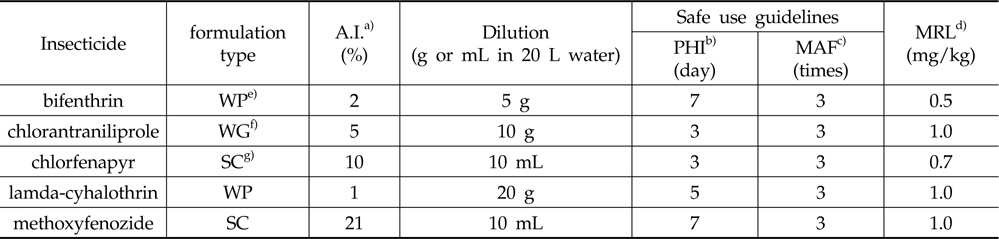
시험에 사용한 살충제의 물리화학적 특성 및 화학구조식은 Table 1과 같고, 안전사용기준 및 잔류허용기준은 Table 2와 같다.
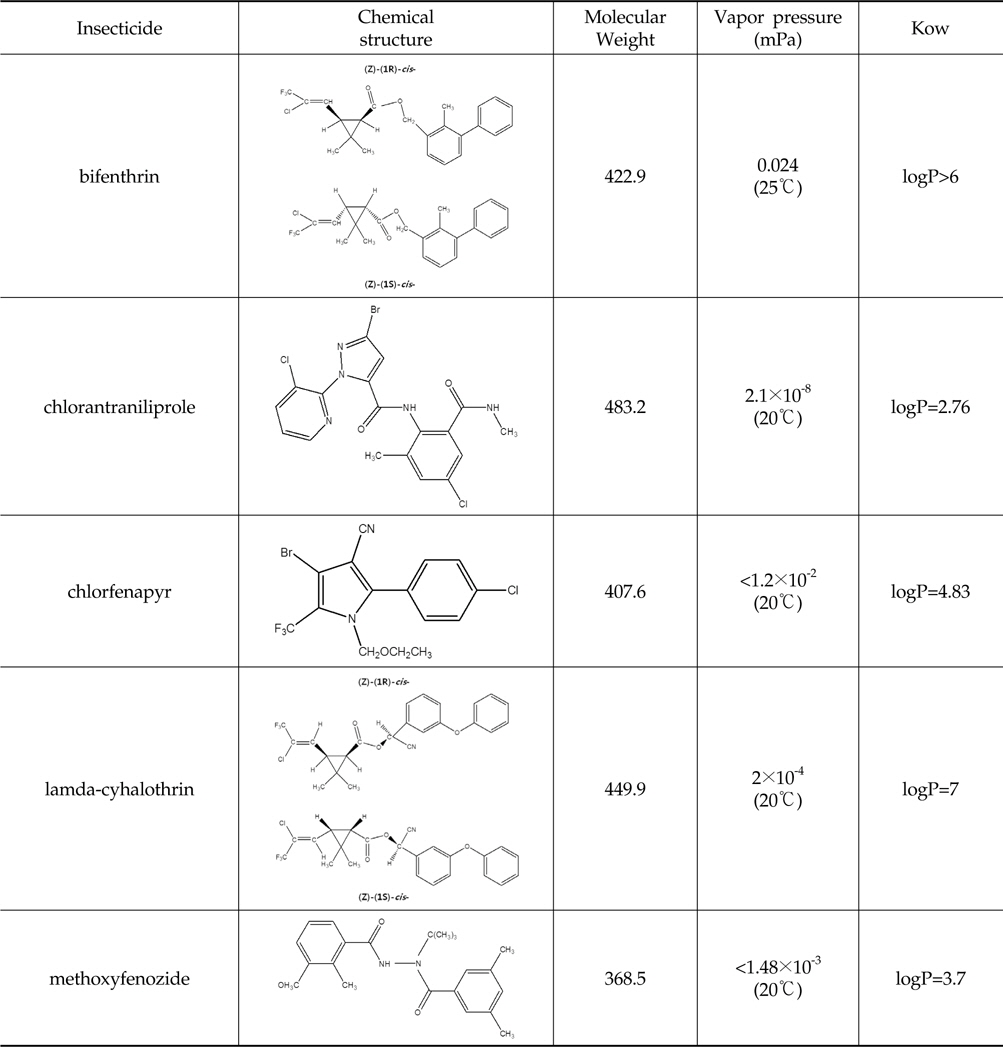
Physico-chemical properties and chemical structures of 5 insecticides used in this study (Tomlin, 2009)
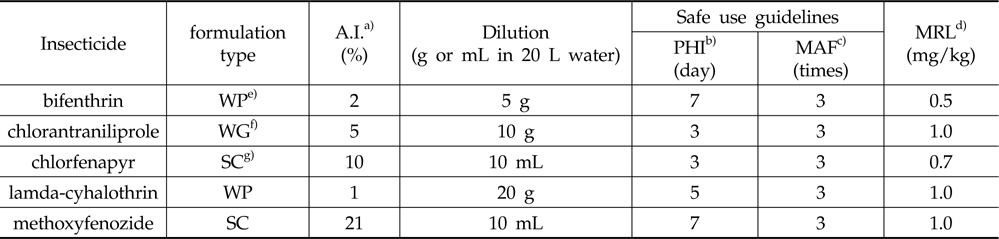
Pesticide formulations, safe use guidelines, and MRLs of 5 insecticides (Korea Crop Protection Association, 2011)
시험 작물인 파프리카(
농약의 처리구는 반복 구간별로 파프리카 9그루로 설정하여 작물의 수확예정 21일 전인 2011년 5월 30일, 4그룹 열매가 비대생장 후 아래쪽에서 2, 3번 열매가 착색이 시작되는 시점을 택해 배부식 분무기를 이용하여 시험농약별로 각각 해당 농약의 안전사용기준에 따라 표준희석 살포용액(기준량) 과 표준희석 살포용액의 2배 농도로 제조한 살포용액(배량)을 작물에 충분히 흐를 정도로 구간별 5 L씩 1회 살포하고, 처리 후 1, 3, 5, 7, 10, 12, 15, 18 그리고 21일째 시료 및 무처리 구 시료를 구간별로 6개의 시료를 총 1 kg 이상 채취하고 -20℃에 저장하였다.
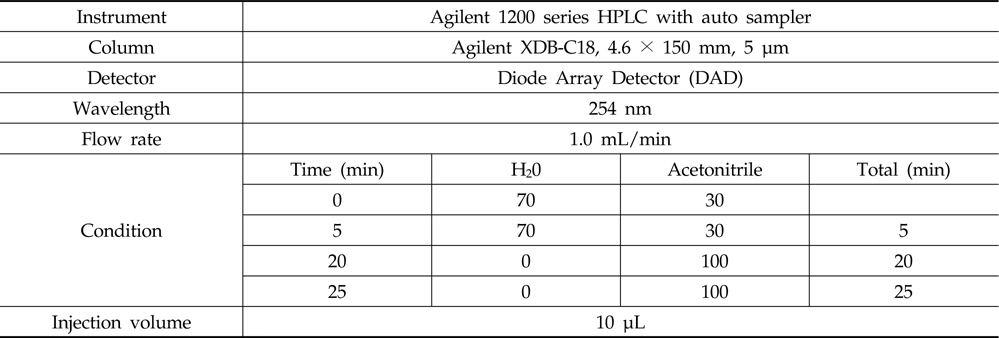
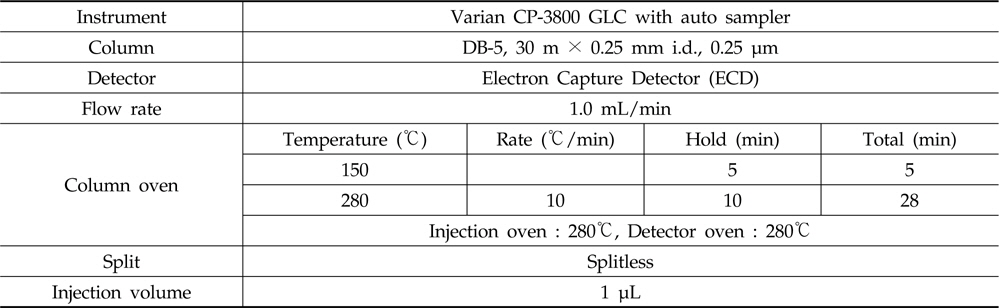
시험농약인 bifenthrin, chlorfenapyr와 lamda-cyhalothrin 표준품은 acetone으로 녹여 1,000 mg/L 농도로 조제한 stock solution을 0.01, 0.05, 0.1, 0.2, 0.5, 1, 2, 5 mg/L농도로 희석하여 1 μL 씩 GLC/ECD (Electron Capture Detector)에, chlorantraniliprole과 methoxyfenozide 표준품은 acetonitrile으로 녹여 1,000 mg/L 농도로 조제한 stock solution을 0.05, 0.1, 0.5, 1, 2, 5, 10 mg/L이 되게 희석하여 10 μL 씩 HPLC/DAD (Diode Array Detector)에 주입하여 나타난 크로마토그램상의 피크면적을 기준으로 표준 검량선을 작성하였다.
파프리카 중 잔류농약의 추출은 QuEChERS법으로 수행하였다(Anastassiades
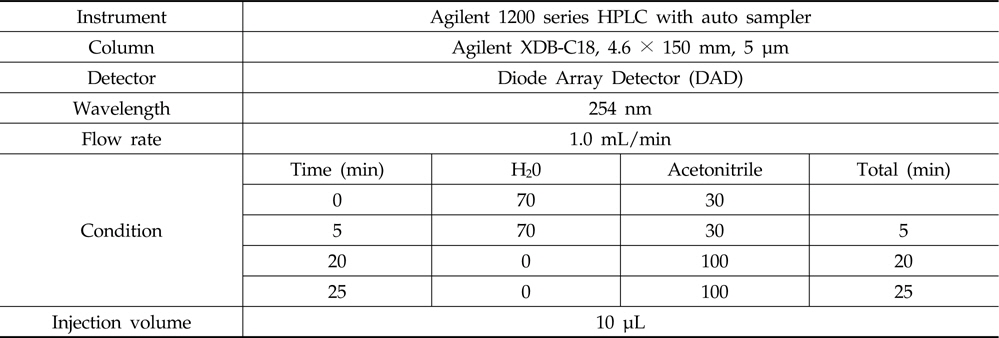
HPLC/DAD conditions for the analyses of insecticides chlorantraniliprole and methoxyfenozide
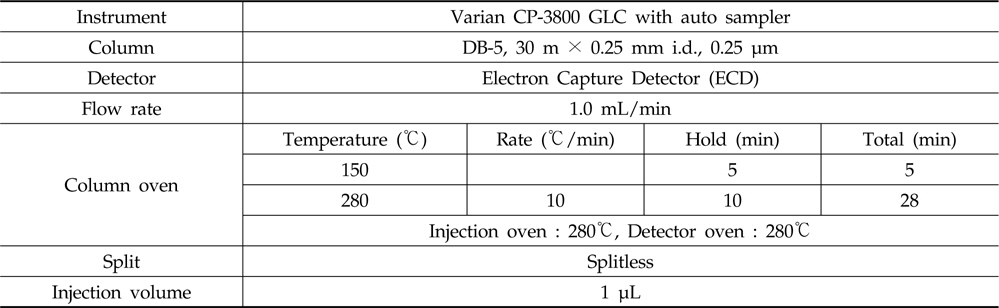
GLC/ECD conditions for the analyses of insecticides bifenthrin, chlorfenapyr and lamda-cyhalothrin
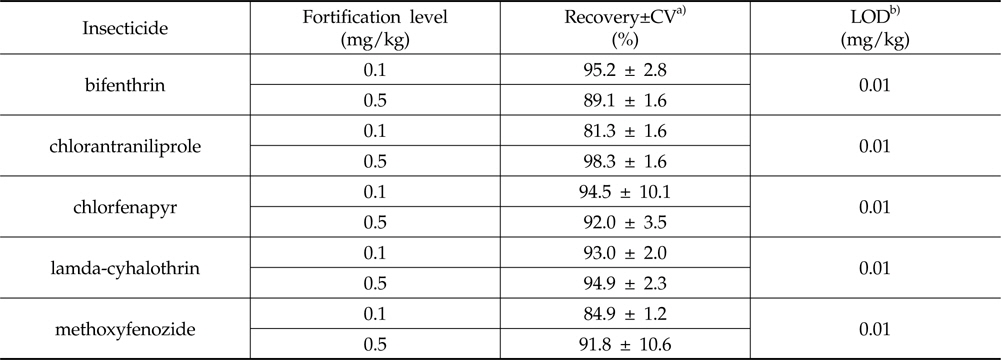
회수율 시험은 재배기간 중에 시험약제를 처리하지 않은 시료에 각 농약의 표준용액을 검출한계의 10배, 50배 농도인 0.1와 0.5 mg/kg이 되도록 처리하고 균일하게 혼화하여 상기 잔류분석과정을 수행하여 회수율을 산출하였다.
>
잔류농약의 생물학적 반감기 및 추천 생산단계 농약잔류 허용기준의 산출
파프리카 중 잔류농약의 생물학적 반감기는 Microsoft사의 Microsoft Office Excel 2007의 지수곡선식을 이용하여 산출하였다(Lee
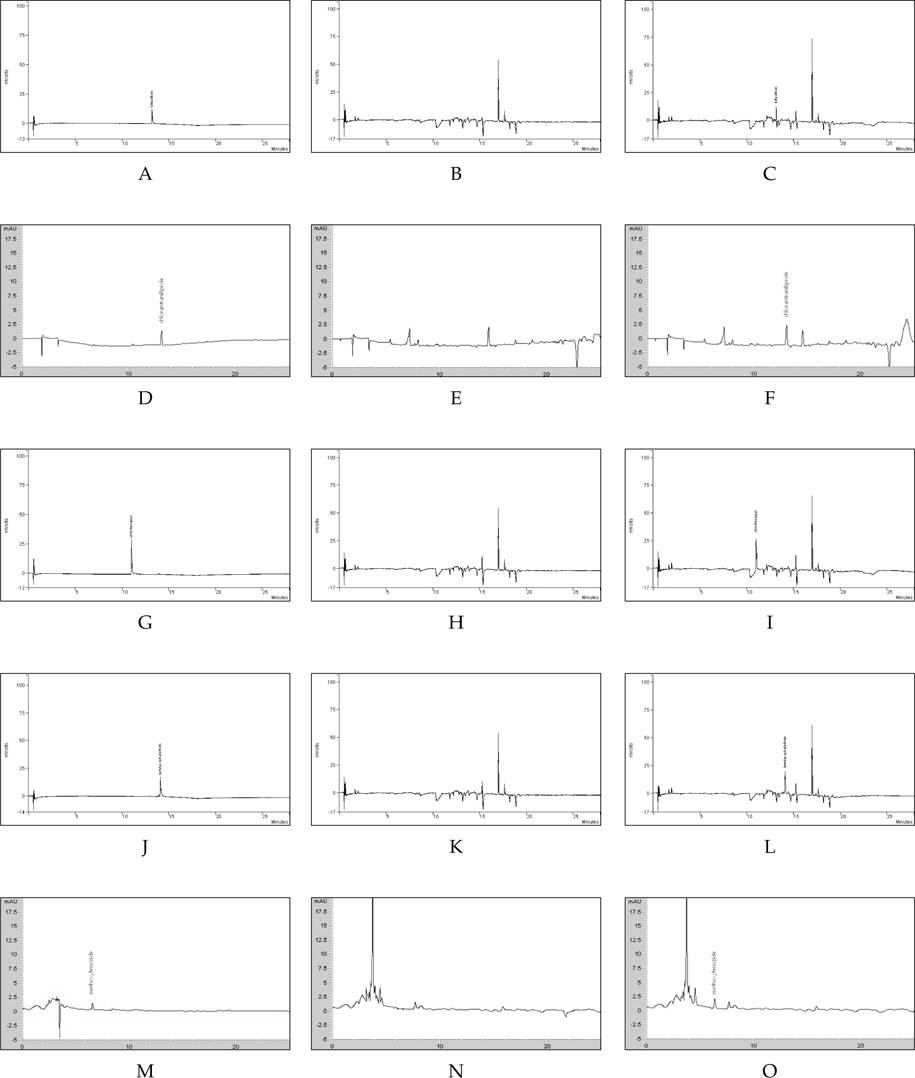
상기 시험분석법을 수행한 파프리카 시료에서 5개 살충제의 머무름 시간은 bifenthrin 13.1 min, chlorantraniliprole 13.0 min, chlorfenapyr 10.9 min, lamda-cyhalothrin 14.0 min 그리고 methoxyfenozide 6.3 min임을 확인하였으며, 크로마토그램상에서 peak를 방해하는 물질은 존재하지 않았다(Fig. 1). 시험분석법의 검출한계는 시험약제에서 모두 0.01 mg/kg이었고, 분석법에 의한 시험농약의 회수율 시험 결과는 0.1 및 0.5 mg/kg 수준에서 식품의약품안전청에서 권고하는 회수율 범위인 70-120%, 반복 회수율 수치 간 변이계수 20% 이하의 기준과 잘 부합하여 본 연구에서 사용한 시험농약의 잔류소장을 구명하기에 효율적인 분석방법이라고 판단된다(Table 5).
[Table 5.] Recovery rates and Limits of Detection(LOD) of the analytical methods
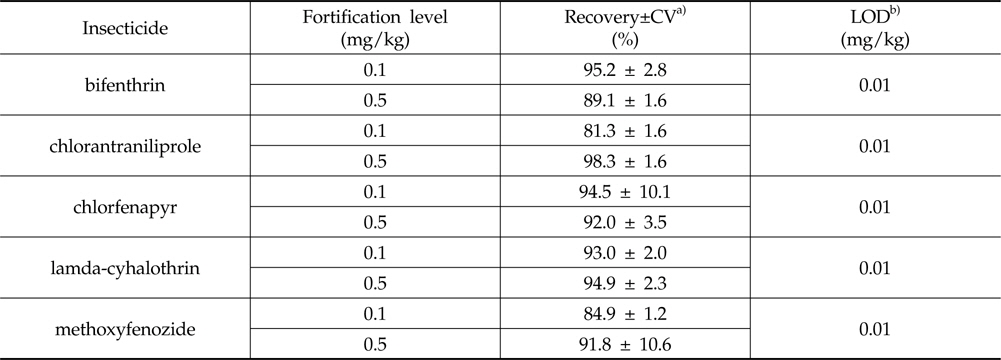
Recovery rates and Limits of Detection(LOD) of the analytical methods
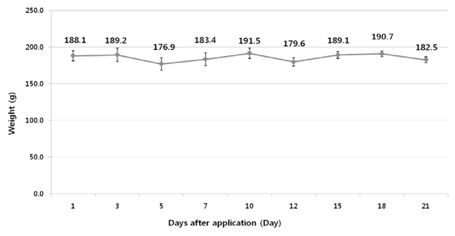
시험기간 중 시설 내 포장의 평균 온도의 범위는 24.6-27.8℃였고 평균 습도는 62.8-78.7%를 기록하였다. 또한, 약제 살포 후 경과일자별 파프리카의 증체율은 채취 시료의 무게를 측정한 후 평균무게를 산출하였고, 가장 적은 평균무게는 176.9 g이었고, 가장 높은 평균무게는 191.5 g으로 시험기간 중 비대생장은 거의 일어나지 않았으며 각 수확일자별 평균 무게는 Fig. 2와 같이 조사되었다.
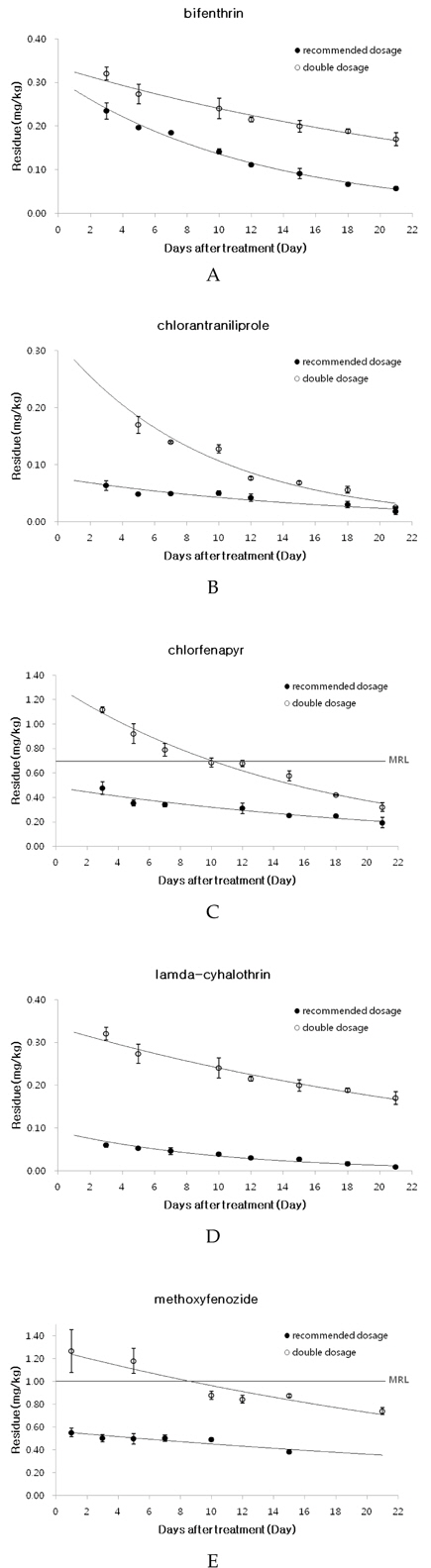
시험약제를 살포한 후 0(살포 2시간 후), 1, 3, 5, 7, 10, 12, 15, 18 그리고 21일에 시료를 채취하여 잔류농도를 계산한 결과 bifenthrin 기준량 살포와 배량 살포시 잔류농도는 각각 0.06-0.23 mg/kg, 0.17-0.32 mg/kg 수준이었고, chlorantraniliprole 기준량 살포와 배량 살포시 잔류농도는 각각 0.02-0.06 mg/kg, 0.03-0.17 mg/kg 수준으로 나타났 으며, chlorfenapyr 기준량 살포와 배량 살포시 잔류농도는 각각 0.19-0.47 mg/kg, 0.32-1.12 mg/kg 수준이었으며 배량살포 구간에서는 처리 후 4회 조사구간에 걸쳐 MRL인 0.7mg/kg을 초과하는 구간이 나타났다. lamda-cyhalothrin에서 잔류농도는 각각 0.01-0.06 mg/kg, 0.17-0.32 mg/kg 수준이었으며 두 약제는 시험기간동안 MRL을 초과하는 구간은 나타나지 않았다. 그리고 methoxyfenozide 기준량 살포와 배량 살포시 잔류농도는 각각 0.38-0.58 mg/kg, 0.12-1.27 mg/kg 수준이었으며 배량살포 구간에서는 처리 후 2회 조사구간에 걸쳐 MRL인 1.0 mg/kg을 초과하는 구간이 나타났다(Fig. 3).
농약의 작물잔류에 영향을 미치는 주요 인자로 과실의 비대생장에 따른 희석효과를 들 수 있다(Lee
>
잔류 농약의 생물학적 반감기 및 생산단계 잔류허용 기준의 산출
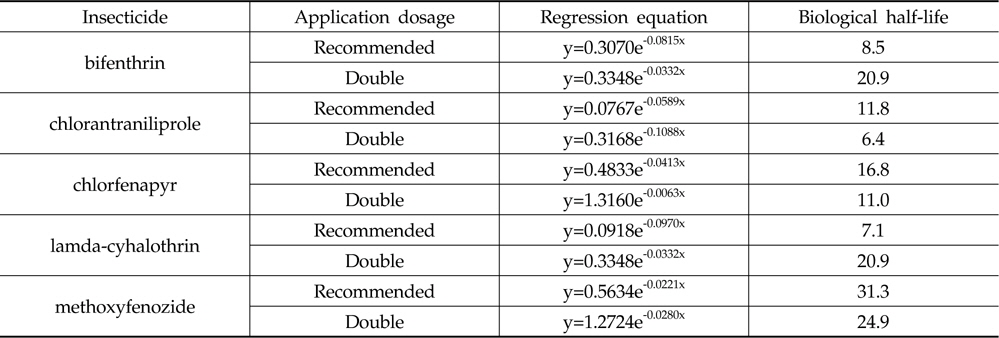
시험 살충제의 기준량처리와 배량처리 구간에서 잔류 감소 회귀식과 생물학적 반감기는 Table 6과 같은 결과를 나타내었다. bifenthrin의 경우 8.5일과 20.9일로 나타났으며 이는 Lee
[Table 6.] Regression equations and biological half-lives of insecticides
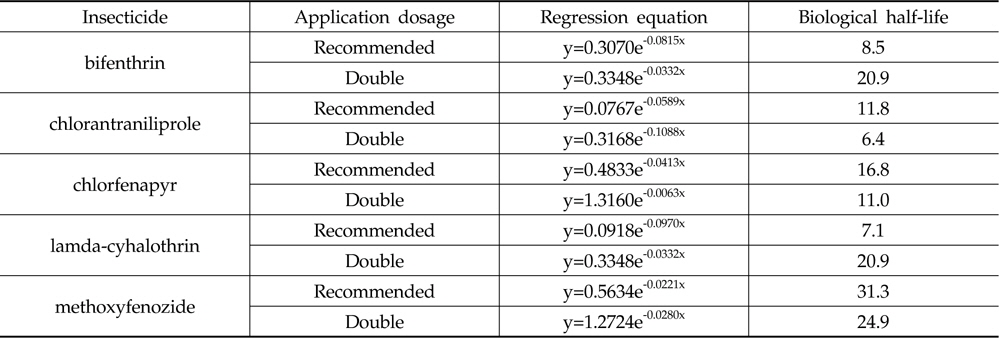
Regression equations and biological half-lives of insecticides
생산단계 잔류허용 기준의 설정은 수확 시에 잔류농도가 MRL을 초과하지 않도록 수확 전 일자별 잔류농도를 설정한 수치로서(Lee
[Table 7.] Recommended pre-harvest residue limit of 5 insecticides in paprika (mg/kg)
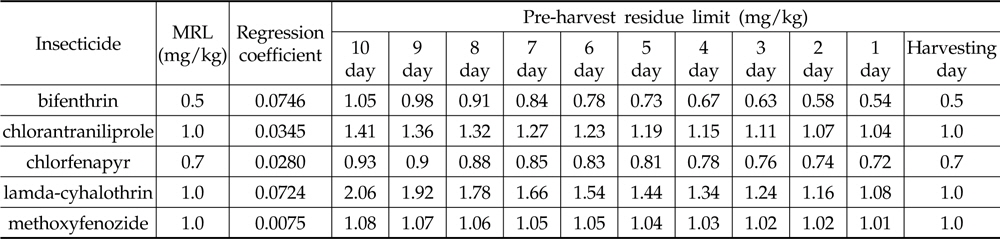
Recommended pre-harvest residue limit of 5 insecticides in paprika (mg/kg)