The white stain symptom of grape clusters and canes by dust-like particles occurred in many vineyards recently. This study was conducted to investigate the ecological characteristics of white stain symptom in grapevines and vineyards.
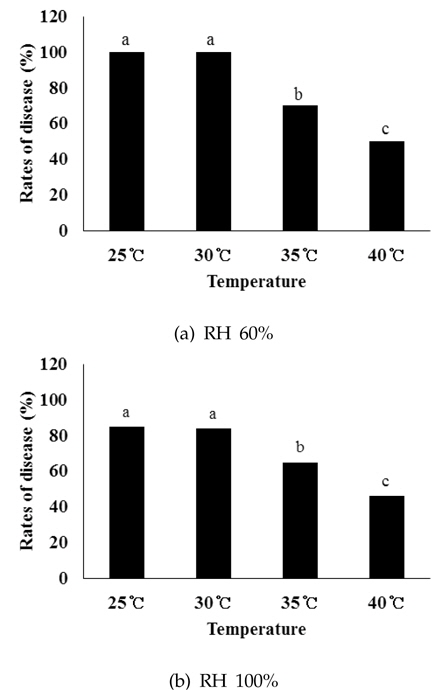
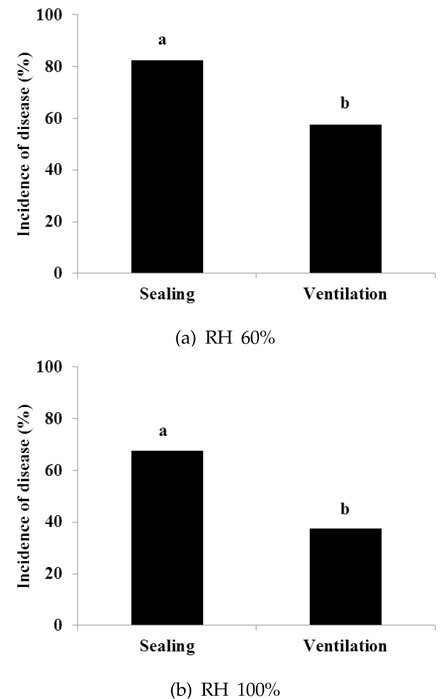
Optimal climate condition for white stain symptom was 25℃∼30℃ with 60% of humidity. Moreover, closed condition with same humidity showed higher incidence rate of white stain symptom than ventilation condition. Grape varieties with black berry skin such as Campbell-Early and Kyoho were more sensitive to white stain symptom compare to varieties with green and red berry skin. Although the pathogens were not detected until March, they increased from April, and increased sharply from mid of July. The pathogens may overwinter in the infected stems and/or on the bark as a mycelium. According to the increase of sugar content of grape from August to September, the mycelium which was parasitic on the bark grew to move to the fruits through the stems, and finally reached the fruit stalk to detach berries from the clusters.
Well ventilation is recommended inside the vineyard since mid-July with roll up an insect net. In addition, infected stems and fruits should be removed out from grapevines infected with pathogens in the vineyards.
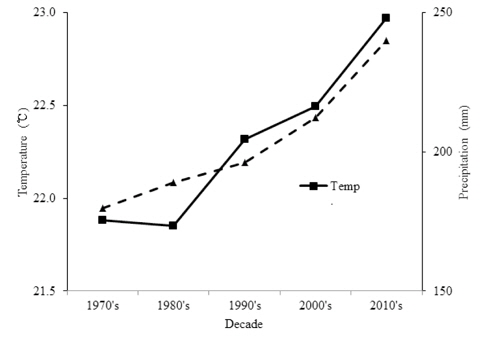
포도는 비가 적고 온난한 지역에 적합한 과수로 우리나라처럼 여름철 강수량이 많으면 병해충의 발생도 많다. 포도 생육기인 5월부터 9월까지의 우리나라 평균기온 및 강수량은 1970년에 비하여 2010년대에 각각 1.2℃와 60.4 mm가 높아졌다(기상청 기상자료)(Fig. 1). 이에 따라 포도생육기간의 기상조건이 고온다습해지면서 포도의 병해충 밀도가 증가하고 있으며, 그 중 병해에 의한 피해가 더 심각하다. Cha 등 (2000)은 농가 조사결과 병해에 의한 수량 감소는 시설재배에서 응답자의 30% 이상, 노지비가림재배에서 응답자의 50% 이상이 10% 이상 수량이 감소하였다고 하였다.
우리나라에서 포도는 주로 생식을 목적으로 소비되기 때문에 품질과 외관이 모두 중요하다(Park
포도흰얼룩증상을 일으키는 병원균은
따라서 본 연구에서는 포도흰얼룩증상을 일으키는 원인균인
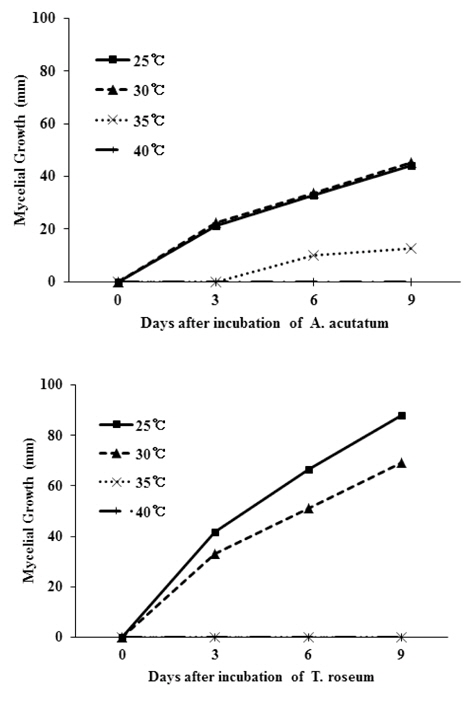
포도흰얼룩증상을 일으키는 병원균에 대하여 온도 조건에 따른 생장 특성을 조사하기 위해 분리균을 PDA(potato dextrose agar)에 치상한 후, 배양기의 온도를 25℃ 부터 40℃ 까지 5℃ 간격으로 달리하여 균사의 생장을 조사하였다. 또한 포도흰얼룩증상의 발병과 온도 및 습도와의 관계를 알아보기 위하여 과실에 포자현탁액(104 spores/mL)을 인공적으로 접종한 후, 온도는 25℃, 30℃, 35℃, 그리고 40℃로 달리하고, 상대습도는 60%와 100%로 달리하여 병발생 양상을 조사하였다. 통풍 조건과 병발생과의 관계를 조사하기 위하여 공기 흐름이 없는 밀폐조건과 공기가 순환되는 통풍조건을 조성한 Growth Chamber(VS-8111H-350, Vision Scientific, Korea)에 접종한 과실을 보관하면서 병발생율을 조사하였다.
포도흰얼룩증상의 병발생 특성을 조사하기 위하여 안성의 2농가, 화성의 3농가를 대상으로 3월부터 수확기까지 일주일 간격으로 발생 생태를 조사하였다. 우선 포도나무의 가지, 잎 그리고 과실에서 발생하는 포도흰얼룩증상을 육안으로 관찰하 였으며, 포도나무의 수피, 가지, 잎 그리고 과실을 채집하였다. 채집한 시료는 멸균된 인산완충용액으로 세척한 후 세척액을 tetracyclin이 포함된 water agar에 희석평판법을 이용하여 25℃ 배양기에 48시간 배양한 후 colony 수를 측정하였으며, 전체 colony 중 포도흰얼룩증상 원인균인
경기도 화성과 안성의 포도 과수원에서 포도흰얼룩증상의 발생양상을 조사한 결과, 전년도에 포도흰얼룩증상이 발생했 던 이병가지에서 균사가 육안으로 관찰 되었으며, 이 균사를 배양, 동정한 결과
포도흰얼룩증상의 원인균인
포도 과원의 통풍 정도가 포도흰얼룩증상의 발생에 미치는 영향을 알아보기 위하여 통풍과 밀폐 조건에 따라 내부의 온도는 25℃로 고정하고 상대습도를 60%와 100%로 다르게 설정한 후 포도흰얼룩증상의 발생 정도를 조사하였다. 습도 조건 및 밀폐 여부와 상관없이 모든 처리구에서 포도흰얼룩증상이 발생되었는데(Fig. 5), 특히, 동일한 습도 조건에서는 밀폐상태에서의 발생율이 더 높았다. 상대습도 60%인 통풍조건에서는 57.5%의 발병율을 보인 반면, 밀폐조건에서는 82.5%의 발병율을 보여 유의한 차이를 보였다(Fig. 6a). 또한 상대습도 100%인 조건에서도 비슷한 경향으로 발생되었으나 상대습도 60%보다는 다소 낮아 통풍시 37.5%, 밀폐시 67.5%의 발병율을 보여 이 역시 유의한 차이를 보였다(Fig. 6b). 포도흰얼룩증상은 착색기 이후 습한 날씨가 계속되는 해에 많이 발생하는데(Park
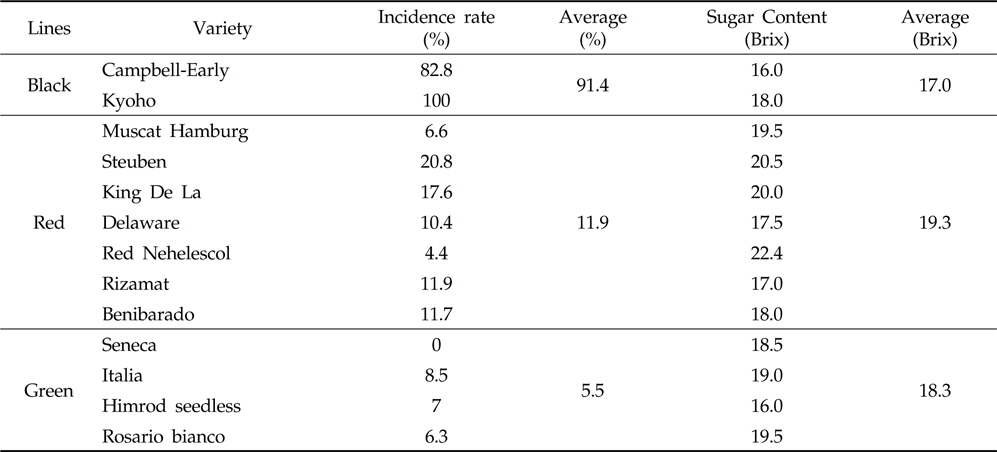
포자 현탁액을 인위적으로 접종하여 포도 품종별 포도흰얼룩증상의 발병 정도를 조사한 결과(Table 1), 흑색계통인 거봉(Kyoho)에서는 100%, 캠벨얼리(Campbell-Early)에서는 82.8%가 발병되어 평균 91.4%의 발병율을 보였다. 적색계통인 Muscat Hamburg 등 7개 품종에서는 평균 11.9%의 발병율을 보였는데 그 중 Steuben이 20.8%로 가장 높았고 Red Nehelescol은 4.4%로 가장 낮았다. 녹색계통의 4개 품종에서는 평균 5.5%의 발병율을 나타내었는데, Seneca 품종에서는 발병되지 않았다. 또한 품종별 당도와 발병율간의 관계를 보면, 흑색계통의 평균 당도는 17.0 Brix, 적색계통은 평균 19.3 Brix, 녹색계통은 평균 18.3 Brix로 조사되어 당도와 포도흰얼룩증상간의 상관관계(R2=0.1196)는 낮았다. 따라서 포도흰얼룩증상이 흑색계통의 품종에서 발병이 잘되는 원인은 품종별 당도의 차이는 아닌 것으로 생각된다. 우리나라는 거봉과 캠벨얼리의 재배면적이 85%에 이르고 있으며 거봉의 면적 비중이 점차 증가하고 있다(농업전망 2014). 우리나라의 기후변화 양상에 따라 포도 착색기 이후의 기상은 고온다습한 조건이 잦아질 것으로 추정되는 바, 포도흰얼룩증상의 발병에 따른 피해를 줄이기 위하여 흑색계통 보다는 적색 또는 녹색 계통의 포도 재배로 다양화해야 할 것으로 판단된다.

White stain symptom on the grape fruits artificially infected with isolates of Acremonium acutatum and Trichothecium roseum
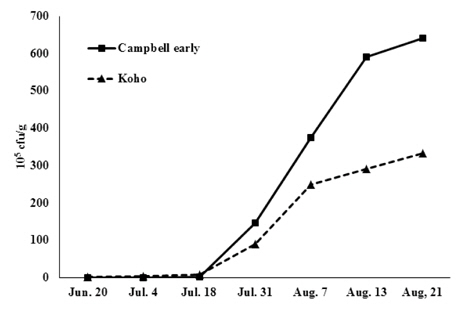
거봉과 캠벨얼리의 과원에서 포도흰얼룩증상을 유발하는 원인균의 밀도를 시기별로 조사한 결과, 3월까지의 동절기에 는 거의 검출되지 않았으나 4월초부터 점차 증가하기 시작하여 7월 중순 이후 급격히 증가하였다(Fig. 7). 거봉은 7월 중순부터 8월 초까지 2주간 병원균의 밀도가 크게 증가하였으나 그 이후 증가폭이 둔화된 반면, 캠벨얼리는 7월 중순부터 8월 중순까지 3주간 병원균의 밀도가 급격히 증가하였다. 8월 하순에 캠벨얼리에서의 병원균 밀도는 거봉보다 2배 정도 높게 나타났다.
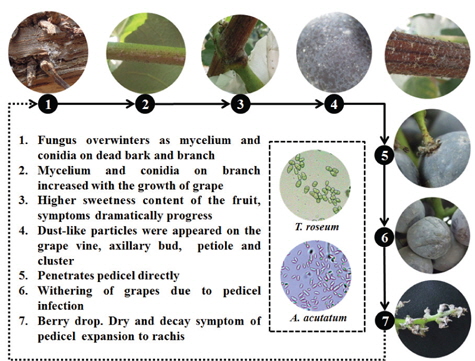
3월부터 수확기까지 포도흰얼룩증상의 발생 양상을 관찰하여 종합한 결과(Fig. 8), 포도흰얼룩증상의 원인균들은 이병가지 및 수피에서 균사로 월동하며, 8월부터 9월까지 과실의 당도가 증가함에 따라 수피에 기생하던 균사들이 과실쪽으로 생장하여 과경부까지 도달하는 것으로 조사되었다. 포도 가지의 표면에 만연된 균사로부터 포자가 과실로 비산되어 만연하게 되고, 과실의 당도가 높아지는 수확기에 급격하게 증가하며 심하면 과경부를 침입하여 탈립을 조장하기도 하였다.
본 연구는 포도흰얼룩증상의 발생생태적 특성을 구명하기 위하여 2010년부터 2012년까지 3년간 경기도 일원의 포도농장에서 수행하였다. 포도흰얼룩증상의 최적발병조건은 온도 25∼30℃, 상대습도 60%의 조건이었으며, 동일한 습도 조건에서는 밀폐상태에서의 발생율이 더 높았다. 포도흰얼룩증상은 적색 및 녹색계통의 품종보다는 캠벨얼리와 거봉과 같은 흑색계통의 품종에서 발병율이 월등히 높았다. 포도흰얼룩증상을 유발하는 원인균의 밀도를 시기별로 조사한 결과, 3월까지의 동절기에는 거의 검출되지 않았으나 4월초부터 점차 증가하기 시작하여 7월중순 이후 급격히 증가하였다. 포도흰얼룩증상의 원인균들은 이병가지 및 수피에서 균사로 월동하며, 8월부터 9월까지 과실의 당도가 증가함에 따라 수피에 기생하던 균사들이 과실쪽으로 생장하여 과경부까지 도달하는 것으로 조사되었다.