Obesity is a worldwide problem that contributes to serious diseases, including diabetes, hypertension, and atherosclerosis. Recently, much research has examined functional natural materials and their anti-obesity activity. This study investigated the effect of enzyme-treated
대사증후군의 원인인 비만은 세계적으로 가장 문제가 되고 있는 질병 중 하나로써, 급격한 경제 발전과 식생활의 변화로 인하여 최근 들어 우리나라에서도 비만이 증가하는 추세이다(Jang and Choi, 2003). 세계보건기구에서는 비만을 만성질병으로 분류하고 있으며(Pi-Sunyer, 1991), 당뇨병, 고혈압, 동맥경화증 등 다양한 성인병의 원인이 되는 것으로 알려져 있다(Shin and Han, 2006). 꾸준한 비만치료제의 개발에도 불구하고 현재 시판되고 있는 치료제는 부작용을 동반하고 있기 때문에 항비만 효능을 가진 천연물질의 개발 및 연구가 필요하다(Ko, 2004). 항비만 효능을 가진 육상식물에 대한 연구는 많이 이루어지고 있으며, 최근 들어 해조류의 다양한 생리활성 기능들이 알려지면서 새로운 자원으로 주목을 받고 있다(Lee et al, 2012).
본 연구에 사용된 감태(
본 연구에 사용된 감태(
감태 칩(Taekyugnongsan, Jeju-do, Korea) 30 kg을 추출 탱크에 넣고 정제수 750 L와 2종의 효소 rapidase press L 0.3 kg, rohament CL 0.3 kg을 투입한 후 50℃에서 24시간 추출하였다. 추출 후 여과한 여액에 주정을 투입하여 18시간 침지하였다. 이 후 3,000 rpm에서 분당 21 rpm의 속도로 여과과정을 거친 후 농축기를 이용하여 최종 분말 제품 3.56 kg을 회수하였으며, 이를 감태분획물(EEc; JY202-MM130126R)로 명명하였다.
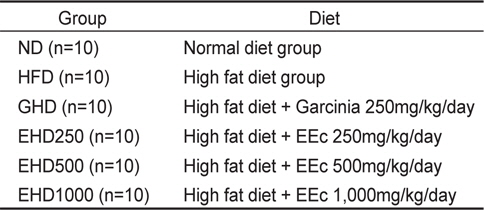
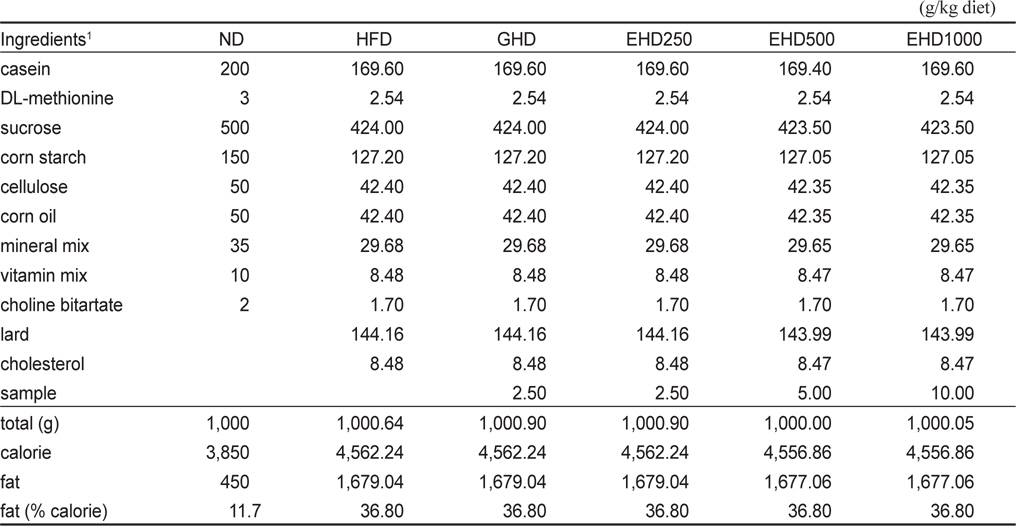
본 연구에 사용된 실험동물은 부경대학교 동물실험윤리위원회의 승인을 받아 진행하였다(승인번호 2013-01). 생후 4주령 C57BL/6NTac 수컷 mouse (15-18 g)를 샘타코(Samtako Bio Korea, Gyeonggi-do, Korea)에서 구입하여 시판되는 고형사료로 1주일간 예비사육 한 후, 10마리씩 6군으로 나누어 9주간 사육하였다. 실험동물의 분류는 정상식이군(ND), 고지방식이군(HFD), garcinia 고지방혼합식이군(GHD), 감태분획물(EEc) 고지방혼합식이군(EHD250, EHD500, EHD1000)으로 나누었으며, AIN-76 semipurified diet (MP0290545220, MP biomedicals, LLC, OH, USA)를 기본 사료로 사용하였다. 실험식이는 비만을 유도하기 위하여 지방함량을 총 열량의 37% 수준으로 증가시키고, 지질 급원으로 lard와 corn oil을 사용하였다. 실험식이에 첨가된 garcinia 추출물 및 효소를 이용한 EEc은 (주)주영엔에스(Ju Yeong NS Co., Ltd, Gangwon-do, Korea)로 부터 제공받았으며 garcinia 250 mg/kg/day, EEc 250, 500, 1,000 mg/kg/day로 조성하여 급이하였고, 사육실의 온도는 23±2℃, 습도 50±5%, 12 h light-dark cycle로 조절하였다. 실험군의 분류 및 식이조성은 Table 1 및 2와 같다.
[Table 1.] Manufacture of experimental diets
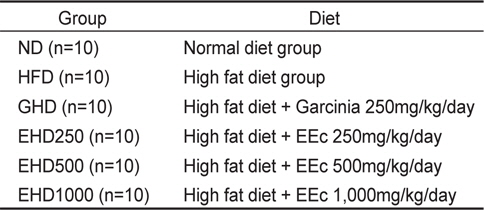
Manufacture of experimental diets
[Table 2.] The composition of experimental diets
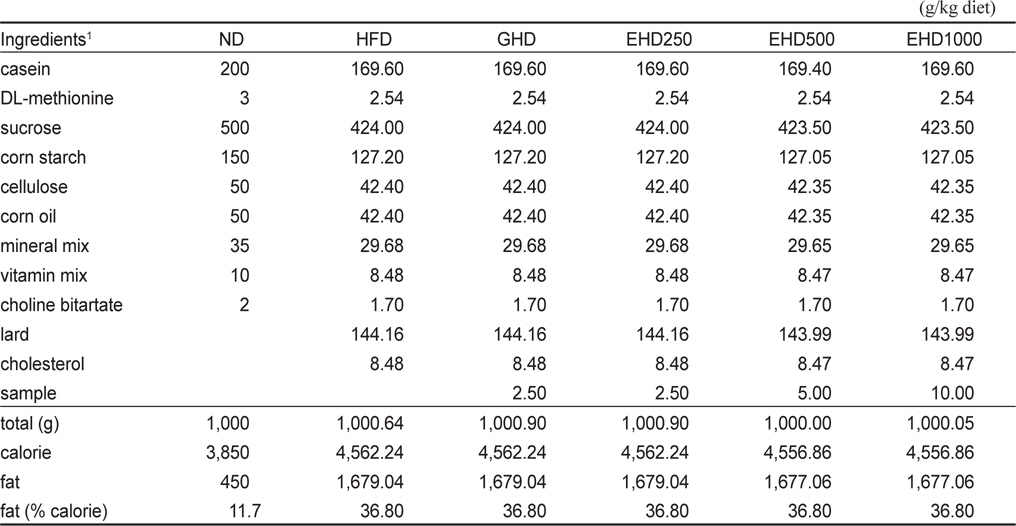
The composition of experimental diets
실험동물의 혈액은 실험종료 전 24시간 절식시킨 다음 복강 대정맥에서 회수하였다. 혈액은 2,500×g에서 20분간 원심분리(Supra-22K, Hanil, Korea)하여 혈청을 분리한 뒤, -70℃에서 냉동보관 하여 실험에 사용하였다.
간, 신장, 부고환과 주변지방을 적출하여 생리식염수에 세척한 후 여과지로 여분의 물기를 제거하여 무게를 측정하고 액체 질소로 급속냉동 시킨 후 -70℃에서 냉동보관 하였다.
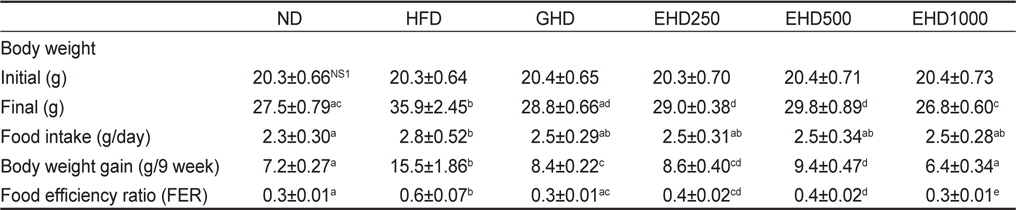
체중은 1주일에 1회, 일정한 시간에 측정하였으며 예비사육 직후의 체중을 초기(initial) 체중으로 하였고, 9주 후의 체중을 마지막(final) 체중으로 하여 체중 증가량을 계산하였다. 식이는 1일 1회 매일 일정한 시간에 규칙적으로 급이하고 다음 날 같은 시간에 잔량을 조사하여 1일 섭취량을 기록하였다. 식이효율은 체중 증가량을 9주간의 총 식이섭취량으로 나누어 계산하였다.
혈청 중 glutamic oxaloacetic tansaminase (GOT), glutamic pyruvic tansaminase (GPT), total cholesterol (T-CHO), high density lipoprotein-cholesterol (HDL-C), low density lipoprotein-cholesterol (LDL-C) 함량은 혈액생화학측정기(Thermo fisher Scientific, USA)를 이용하여 측정하였다. 혈청 중 triglyceride 함량은 TG 측정 kit (AM 157S-K, Asan Pharm, Seoul, Korea)를 사용하였고, 혈당 함량 및 혈청 leptin 농도는 glucose 측정 kit (AM 201-K, Asan Pharm)와 Leptin ELISA kit (ADI-900-019A, Enzo Life Sciences, Switzerland)를 사용하여 각각 측정하였다.
간 조직 내 triglyceride를 측정하기 위하여 간 조직을 세절한 후 PBS buffer에 넣고 균질화하였다. 그런 다음 원심분리(2,500×g, 4℃, 10 min)하여 상층액을 회수한 후, TG 측정 kit를 이용하여 측정하였다.
조직 내의 단백질 발현 변화를 관찰하기 위하여 간 조직을 RIPA buffer (1% NP-40, 0.25% sodium deoxycholate, 1 mM EGTA, 150 mM NaCl, 50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5)에 넣어 마쇄한 후 원심분리(2,500×g, 4℃, 10 min) 하여 상층액을 회수하였다. BCA protein assay kit (Pierce Biotechnology, IL, USA)를 사용하여 단백질 농도를 측정한 후 동일한 농도의 단백질을 취하여 sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) 한 다음 Polyvinylidene fluroide (PVDF) membrane (Millipore, USA)에 transfer하였다. Membrane은 실온에서 1% BSA/TBS-T로 blocking 시킨 후, 1차 항체를 TBS-T에 1:1,000 비율로 희석하여 반응시켰다. 1차 항체 반응이 끝난 membrane을 TBS-T 용액으로 세척한 다음 2차 항체를 TBS-T에 1:10,000 비율로 희석하여 실온에서 반응 시켰다. Super signal west pico luminal/enhancer solution (Pierce Biotechnology, USA)을 사용하여 KODAK X-ray film에 감광시켜 나타나는 밴드로 단백질 발현 정도를 확인하였다.
모든 실험결과는 각 군별의 평균과 표준편차(mean±S.D.)로 나타내었으며, 각 실험군 간의 유의성은 SPSS ver. 18.0 프로그램을 사용하여 통계처리 하였다. 각 군에 대한 유의성 검증은 ANOVA test와 Duncan's multiple range test를
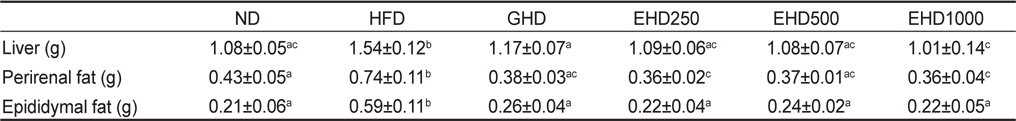
실험 종료 후 간, 신장과 부고환 장기 및 주변지방의 무게를 측정한 결과를 Table 3에 제시하였다. 간 무게 측정 결과 HFD군에 비하여 GHD군과 EHD군에서 유의적 감소를 나타내었으며, 특히 EHD1000군은 HFD군에 비하여 34.4% 감소하여 양성 대조군인 GHD군보다도 감소하는 경향을 나타내었다. 신장 및 부고환 주변지방의 무게는 HFD군에 비하여 GHD군, EHD군에서 유의적인 감소를 나타내었고, EEc 농도에 따른 유의적 차이는 나타나지 않았다.
[Table 3.] Effect of the enzyme-treated Ecklonia cava extracts on the lipid profiles
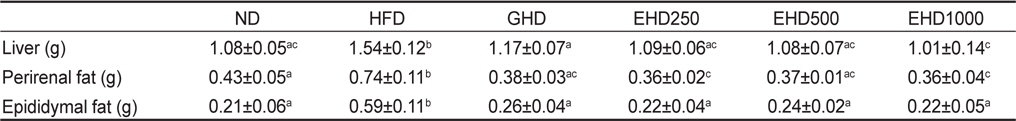
Effect of the enzyme-treated Ecklonia cava extracts on the lipid profiles
9주간의 실험기간 동안 변화된 체중과 식이섭취량, 식이효율을 측정한 결과를 Table 4에 나타내었다. 체중 증가량은 실험 종료 직후 체중(final)에서 예비사육 직후의 무게(initial)를 뺀 것으로 나타내었으며, HFD군에 비하여 GHD군 및 EHD군에서 유의적인 감소를 나타내었다. 특히, EHD1000군은 6.4±0.34 g/9 weeks로 ND군 7.2±0.27 g/9 weeks보다도 더 낮은 체중 증가량을 보여 EEc에 의한 체중감소효과를 확인하였다. 각 군별 식이효율은 HFD군은 ND군에 비해 80.6% 증가하였으며, EHD군은 ND군과 GHD군 수준과 유사하였다.
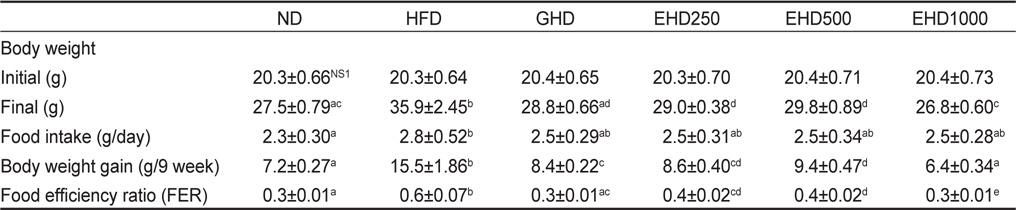
Effect of the enzyme-treated Ecklonia cava extracts on the weight gain, food intake and FER
Kwon은 감태의 polyphenol 추출물인 seanol을 비만 모델 마우스에 경구 투여한 결과 체중과 식이효율에서 감소효과를 나타내었는데, 이는 seanol이 영양소의 소화흡수에 영향을 미쳐 체중 및 식이효율이 감소된 것이라고 하였다(Kwon, 2013). 본 실험에서는 고지방식이에 인한 체중 증가가 EEc섭취에 의하여 정상식이군 수준으로 감소되는 것을 확인하였다. 즉, 비만을 유도한 그룹과 비교하여 EEc를 고지방식이와 혼합하여 급이한 그룹의 경우 농도의존적인 체중저하 효과를 확인할 수 있었다.
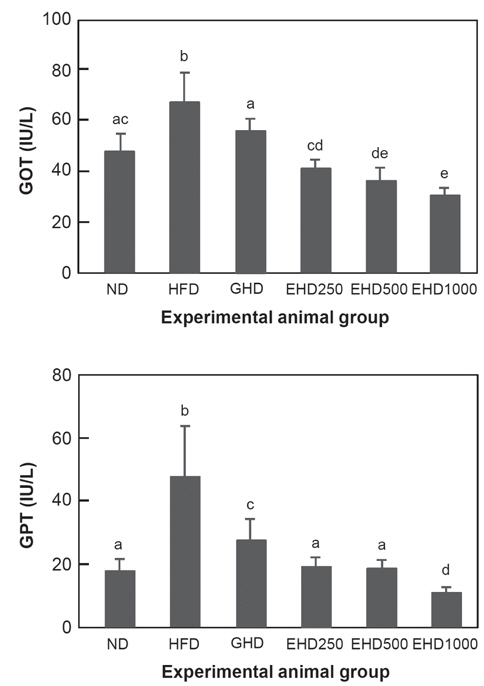
혈청 중의 GOT 및 GPT 농도 측정 결과를 Fig. 1에 나타내었다. GOT 및 GPT는 간세포에 다량 존재하는 효소이며, 간 손상시 혈액으로 유출되어 혈청 수치가 증가됨으로써 간 손상의 지표로 활용되고 있다(Friedman et al., 2003). GOT 및 GPT 활성변화를 측정한 결과 HFD군이 ND군에 비하여 유의적 증가를 보였고, EHD군에서 농도의존적으로 감소하였다. 이는 고지방 식이군에서는 간 조직 내에 지방 축적이 발생하여 GOT, GPT활성이 증가하였으나, 증가된 GOT 및 GPT의 활성이 EEc식이군에서는 저하된 것으로 보아 EEc가 간 독성 예방 효과와 간 기능 회복에 효과를 나타낸 것으로 사료된다.
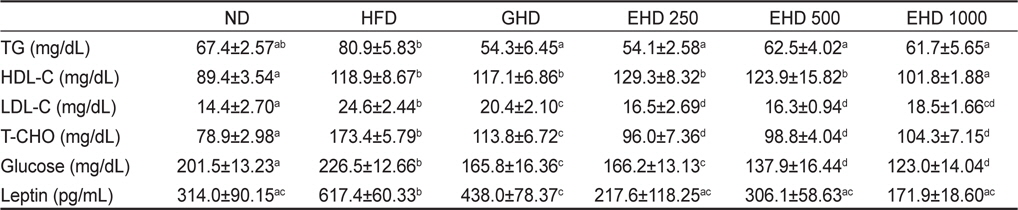
EEc식이에 따른 혈청 중 triglyceride, total cholesterol, HDLcholesterol, LDL-cholesterol의 함량을 측정하였다(Table 5). 혈청 중 total cholesterol 함량은 ND군에 비하여 HFD군에서 119.9%로 급격한 증가를 나타내었으며, HFD군에 비해 EHD군에서는 유의적인 감소를 보였다. 또한 LDL-cholesterol함량은 ND군에 비하여 HFD군에서 70.2% 증가하였고, HDL-cholesterol함량은 HFD군에 비하여 유의적인 증가는 보이지 않았으나 EHD250군, EHD500군에서 각각 129.3 mg/dL, 123.9 mg/dL로 8.8%, 8.35%의 증가를 보여주었다. HDL-cholesterol 및 LDL-cholesterol은 체내 cholesterol을 운반하는 역할을 하며, 특히 LDL-cholesterol의 경우 체내 다른 조직에 cholesterol을 축적하여 심혈관계 질환의 발병의 원인이 된다(Imano et al., 2011). 본 실험 결과, EEc는 고지방식이에 의하여 증가된 total cholesterol 및 LDL-cholesterol 함량의 수치를 감소시켜 비만에 의한 고지혈증, 심혈관계 질환의 위험성을 줄여줄 것으로 여겨진다.

Effect of the enzyme-treated Ecklonia cava extracts on triglyceride, HDL-cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol, total cholesterol, glucose and leptin contents in serum
Triglyceride 함량 측정 결과, ND군과 HFD군에서는 유의적 차이를 나타내지 않았지만, HFD군에 비하여 GHD과 EHD군에서는 유의적인 감소경향을 나타내었다. 복부비만일수록 혈중 triglyceride의 함량이 높은 것으로 알려져 있는데(Lee et al., 2011), 본 연구에서도 부고환 주변 지방의 무게가 가장 많았던 HFD군에서 혈중 triglyceride 함량이 증가되는 것을 확인할 수 있었다(Table 5).
혈청 glucose 함량 및 leptin 농도 측정 결과를 Table 5에 나타내었다. 혈청 glucose 함량 측정 결과 HFD군은 226.4±12.66 mg/dL로 ND군에 비하여 유의적인 증가를 나타내었고, EHD250, EHD500, EHD1000군은 각각 166.2±13.13 mg/dL, 137.9±16.44 mg/dL, 123.0±14.04 mg/dL으로 HFD군에 비하여 26.6%, 39.1%, 45.7%씩 감소하였다. 이러한 결과는 해조류에 다량 함유되어있는 알긴산이 포도당의 흡수를 저해하여 혈중 glucose 수치를 낮추어 주었다는 연구결과(Lee et al., 2004)와 동일하게 본 연구의 EEc 또한 비만에 의한 당뇨병 및 내당능 장애에 효과가 있을 것으로 사료된다.
Leptin은 지방조직에서 생산되는 Obese (Ob) 유전자의 산물로 비만일 경우 leptin의 혈중 농도가 높아지는 것으로 알려져 있다(Meier, 1995). Leptin은 뇌 시상하부에서 neuropeptide Y(NPY)와 α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH)의 분비를 자극함으로써 식욕을 조절하고 체내 지방 축적을 조절하는 기능을 하게 된다. 지방조직에서 분비되는 leptin의 양은 지방세포의 수, 크기와 관련이 있으며 지방조직의 양이 감소하면 혈중 leptin의 양이 줄어드는 것으로 알려져 있다(David and Michael, 2004). 본 연구에서 혈중 leptin의 농도는 ND군에 비하여 HFD군에서 유의적인 증가를 나타내었고, EHD군에서 농도에 따른 유의적인 감소는 나타나지 않았으나 HFD군에 비하여 유의적인 감소를 보였다. 특히 EHD1000군의 혈중 leptin 농도는 171.9 pg/mL로 HFD군(617.4 pg/mL)에 비해 73.0% 감소되었다. Hong et al. (2001)은 고지방식이가 체중증가 및 혈중 leptin의 농도를 증가시킨다고 하였는데, 본 실험에서 HFD군의 혈중 leptin 농도가 증가된 것과 같은 경향을 보여주었다. 또한 앞서 고찰한 바와 같이 체중 감소 및 장기 주변 지방량의 감소를 볼 때 EEc는 지방조직의 축적을 저해하고 그로 인해 leptin의 분비량이 줄어든 것으로 사료된다.
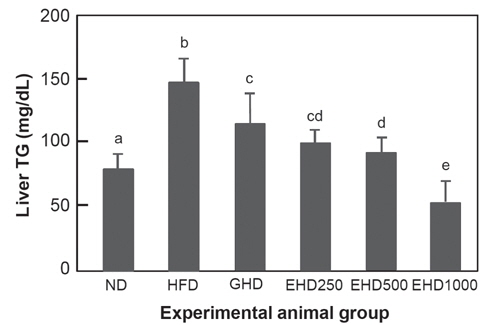
9주간 EEc를 고지방식이와 혼합하여 급이한 마우스의 간 조직에서의 triglyceride 함량에 미치는 영향을 측정한 결과를 Fig. 2에 제시하였다. HFD군이 144.5±16.25 mg/dL로 ND군 74.4±12.84 mg/dL에 비하여 94.4% 증가하였으며 특히 EHD1000군은 52.5±13.34 mg/dL로 HFD군에 비하여 63.7% 감소하여 EHD군 중에서도 triglyceride의 축적이 가장 저해되었음을 확인할 수 있었다. Triglyceride는 간 조직 내의 지방세포에 흡수, 저장되어 간 기능을 떨어뜨리고 비만의 원인이 된다. 간 조직 내의 지질 함량의 감소는 항비만 효과의 중요 지표가 되며, Kwon은 감태에서 추출한 seanol을 고지방식이와 함께 급이한 결과 간 조직 내 triglyceride 함량이 최대 47%까지 감소하였다고 보고하였다(Kwon, 2013). 또 연잎 추출물의 간 조직 지질함량에 미치는 영향에 대한 연구에서도 연잎 추출물 급이에 따른 혈청 지질의 감소와 함께 간 조직 내 지질함량에도 감소효과가 있었다고 하여(Lee and Lee, 2011), 본 연구와 유사한 결과를 보여주었다.
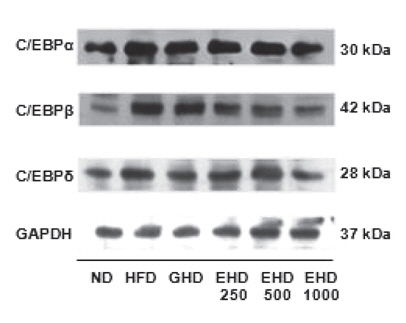
마우스의 간에서 회수한 단백질로 지방생성억제효과를 western blot을 통해 분석한 결과, HFD군에서는 CCAAT/enhancerbinding proteins (C/EBP) family의 발현이 유의적으로 증가하고, EHD군에서 농도의존적으로 감소하는 것을 관찰할 수 있다(Fig. 3). C/EBP family는 갈색지방세포와 백색지방세포에서 발현되는 전사인자로 C/EBPβ와 C/EBPδ는 지방세포 분화초기 단계에서 발현이 증가되고 C/EBPα는 분화과정의 후반기에 발현이 촉진되는 인자로 알려져 있다(Cowherd et al., 1999). C/EBP family는 adipogenic transcription factor들 중에서 PPARγ와 함께 지방세포 분화에 중요한 역할을 하는 인자들로써(Park et al., 2011) AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) 경로를 활성 시켜 에너지 대사 조절에 관여하고 항비만 활성을 나타내는 것으로 알려져 있다(Cho et al., 2010). 본 연구에서는 EHD군에서 C/EBP family 발현이 감소함을 확인하였는데, 이는 EEc가 지방세포 생성을 억제하고 triglyceride 생성을 감소시킴으로써 항비만효과를 나타내는 것으로 사료된다.