Although
Four samples were collected as follows:
Specimens used in this study are deposited in the private herbarium of Yasuo Suto (herb. YSH).
Macroscopic features of lesions and algal thalli were observed under a hand-lens and a stereoscopic microscope. Several pieces were peeled from the leaf surface and sections were made by hand with a razor blade. Sections were placed in a drop of Shear’s fluid (1 g of potassium acetate, 30 mL ethanol, 20 mL of glycerin, and 50 mL of distilled water) on a glass slide with a cover glass sealed to observe under a light microscope. Microscopic features of thalli, filaments, and reproductive organs were observed. Dimensions of filamentous cells, gametangia, and zoosporangia were measured (n = 20 or 30) and the ranges of the value were noted.
>
Cephaleuros parasiticus Karsten
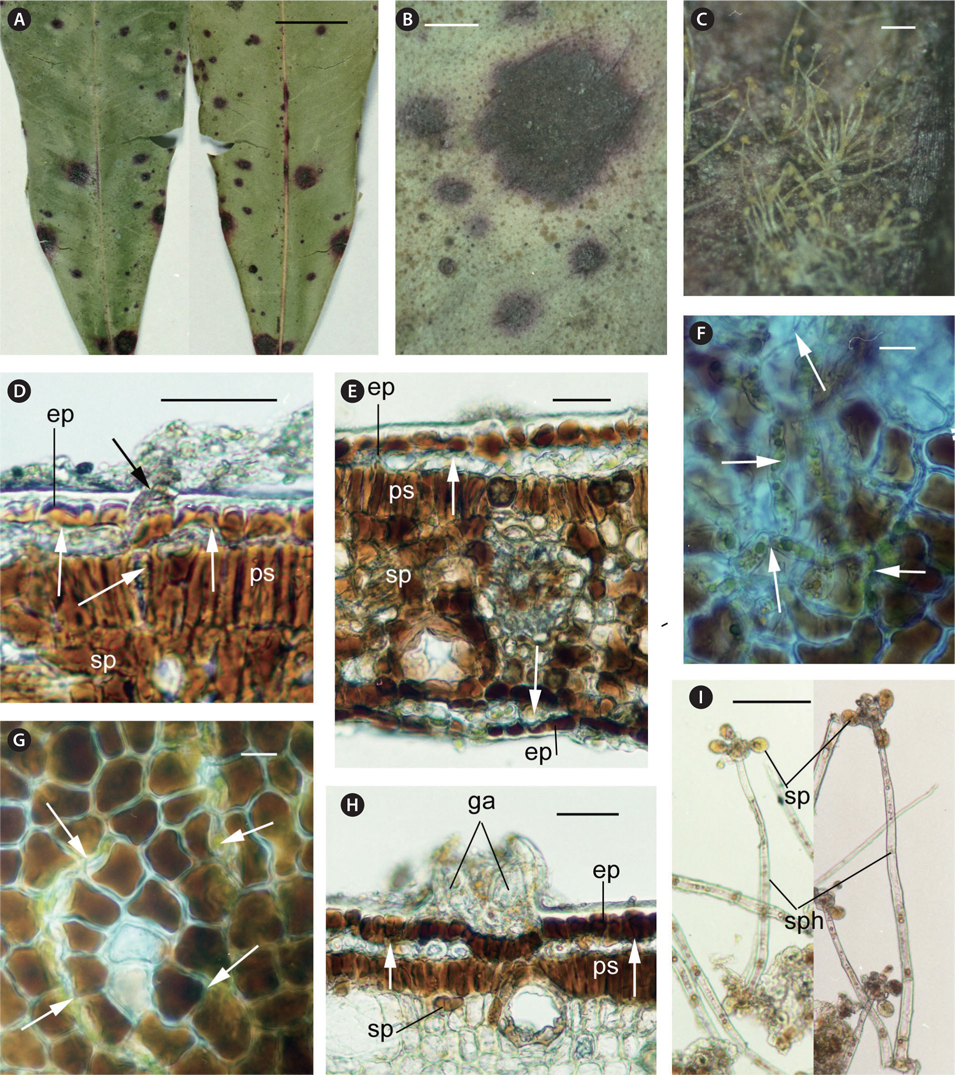
Lesions are more or less circular spots, 1-5 mm in diameter, dark red brown with a purple stained margin. Lesions develop into the leaf tissue from the upper surface to the lower surface and each spot is visible on both the surfaces (Fig. 1A & B). Tufts of sporangiophores with zoosporangia are produced on the lower surface of the lesion (Fig. 1C).
Thalli grow subepidermally on the upper and lower leaf surfaces and intramatrically. The filamentous cells invade the cuticle and occasionally make a small mass, but do not expand subcuticularly. They develop vertically beneath epidermal cells and invade into intercellular space of cells of the palisade and spongy tissues (Fig. 1D-G). No setae project on the lesions. A few immature gametangia are formed subcuticularly (Fig. 1H). Sporangiophores project mainly from the lower leaf surface and rarely from the upper leaf surface, being cylindrical, erect, 300-640 μm long and 13-19 μm wide, 4 to 8 cells, in tufts of 2 to 5. Head cells are borne terminally on the sporangiophores and produced mostly 4 or 6 sporangiate-laterals, zoosporangia and their suffultory cells. Zoosporangia are elliptical, 21.5-29 μm long and 17-21.5 μm wide, yellow to orange (Fig. 1I).
The cells of the whole leaf tissues, including the epidermis, palisade tissue, spongy tissue, and vascular bundles become necrotic, turning brown to dark brown (Fig. 1D-H).
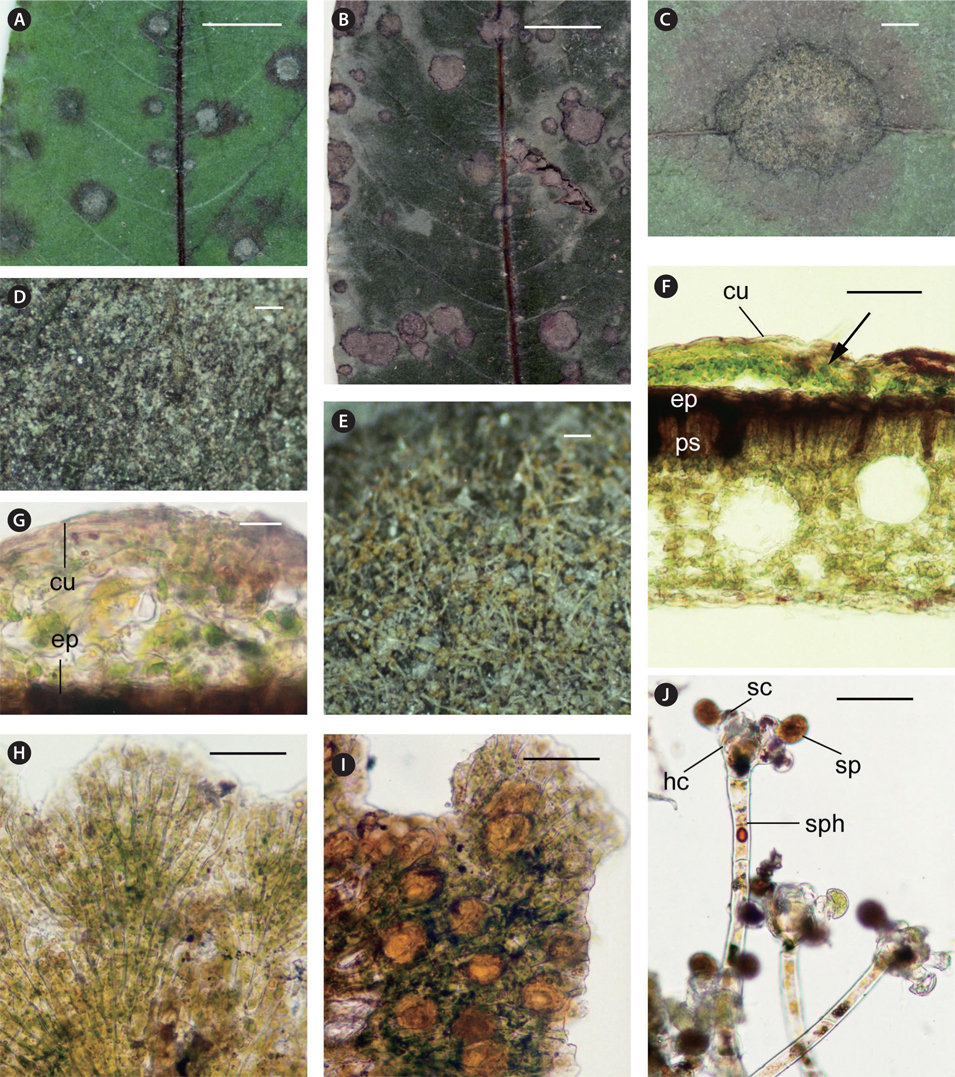
Thalli form more or less circular raised disks with crenate margins, 1-7 mm (mostly 3-4 mm) in diameter, 15-50 μm in height, olive in color (Fig. 2A-C). No thalli grow on the lower leaf surface. On young leaves, a circular purple stain occurs around the thallus on the upper surface and also the opposite lower surface (Fig. 2A). On old leaves, although no stain occurs around the thallus, a circular yellow stain occurs on the opposite lower leaf surface. Green black granules of gametangia aggregate at the marginal portion of thallus (Fig. 2D). Tufts of sporangiophores with zoosporangia are produced on the thallus (Fig. 2E).
Thalli grow subcuticularly on the upper leaf surface (Fig. 2F & G). Disks of thalli are composed of pseudoparenchymatous ramuli with no gaps. Filamentous cells are long-cylindrical, 29-48 μm long and 10-16 μm wide with a length / width ratio of 2.4-3.6, branching by equal dichotomy (Fig. 2H). Setae rarely develop as slender filaments of 3 to 6 cells, pale yellow solitary. Gametangia are produced beneath the cuticle, enlarging in an elliptical shape, 26-36 μm long and 17-22 μm wide, yellow to orange, solitary or in clusters (Fig. 2I). Sporangiophores project from the thallus of the upper leaf surface, being cylindrical, erect, 110-310 μm long and 14-19 μm wide, 3 to 5 cells, solitary or in tufts of 2 to 5. Head cells are borne terminally on the sporangiophores and produce 4 to 8 sporangiate-laterals, zoosporangia and their suffultory cells. Zoosporangia are elliptical, 22-25 μm long and 19-23 μm wide, yellow to orange (Fig. 2J).
Epidermal and palisade cells of the leaf become necrotic, turning brown and red-brown beneath the thallus (Fig. 2F).
The morphological characteristics of the samples largely agreed with the description by Thompson and Wujek (1997) and Suto and Ohtani (2009). In our collection, mature gametangia were not observed in
Macroscopic features of the spots on the leaves are clearly different between
[Table 1.] Comparative features of Cephaleuros parasiticus and C. virescens

Comparative features of Cephaleuros parasiticus and C. virescens
Thompson and Wujek (1997) reported fusion of biflagellate gametes forming zygotes that grew into dwarf plants (= sporophytes) in
Evidently