The
Only one individual was collected by scuba diving in a depth of 24 m from the Jeju Island in Korea on the 17th of March, 2013. The morphology of the specimen was observed under a stereomicroscope (Leica MZ12.5; Leica, Germany) and identified as C. sponsalis Hwass in Bruguière, 1792, the first record of the Korean fauna. The voucher specimen was deposited in the Marine Mollusk Resources Bank of Korea (MMRBK; MMRBK no. G00000210) at Chungbuk National University, Cheongju, Republic of Korea.
Class Gastropoda Cuvier, 1797Order Caenogastropoda Cox, 1960Order Hypsogastropoda Ponder & Lindberg, 1997Order Neogastropoda Thiele, 1925 Superfamily Conoidea Fleming, 1822Family Conidae Fleming, 1822Genus Conus Linnaeus, 1758
>
Conus sponsalis Hwass in Bruguière, 1792: 635, Pl. 322, fig. 1 (cited from Kohn, 1959); Lamarck, 1810: 38; Adams and Adams, 1858: 248; Okutani, 2000: 588, 589, 591, Pl. 293, fig. 19; Poppe, 2008: 520, 521, Pl. 555, figs. 3-5; Zhongyan, 2004: 125, Pl. 075, fig. B.Conus nanus Broderip, 1833: 53.Coronaxis sponsalis Adams and Adams, 1858: 248.Conus nana Paetel, 1887: 302 (cited from Kohn, 1959).
Type locality. Indo-West Pacific; Rowley Shoals, New South wales.
Material examined. 1 individual, Korea: Jeju-do, Seogwiposi, Bomok-dong, Supseom, 17 Mar 2013.
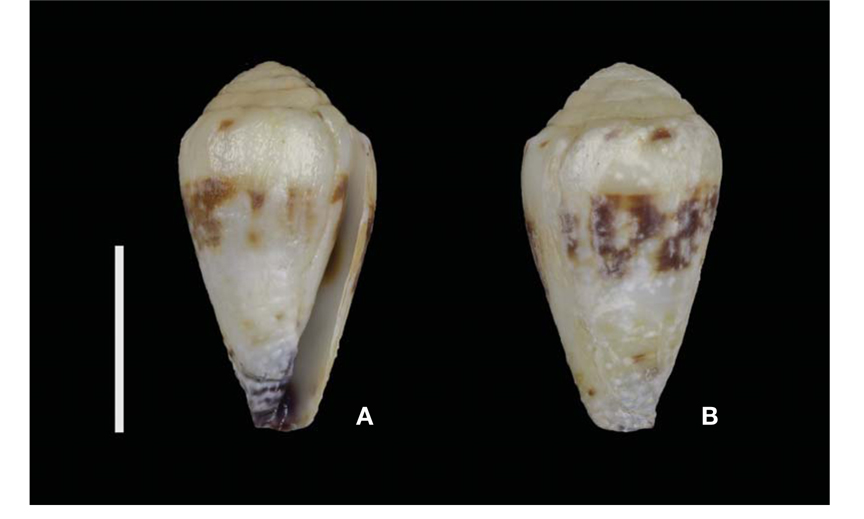
Measurement. Shell height 20 mm; shell width 11 mm.
Description. Shell is small, solid, obconic-cylindrical in shape, height up to 30 mm. Spire coronate, blunt, composed nearly of 1/5th of whole body. Shoulder broad, roundly tubercle on the edge; a fine beaded spiral on body whorl. One spiral band of pale-reddish brown spots on ivory background, anterior tip dark-purple. Aperture narrow, ivory in color; inner lip red-brown spot on white, outer lip yellowish-white in color. Spiral canal short and opened.
Remarks. This species resembles a
Habitat. On rocks and pebbles in intertidal region, and sand floors and coral reefs in subtidal zones.
Distribution. Australian, Papua New Guinea, Philippine, China, Japan, Korea (Jeju-do).