There are approximately 185 species of the snapper (family Lutjanidae) in 17 genera worldwide (Nelson, 2006); 11 species in five genera have been reported in Korea to date (Kim et al., 2005, 2007, 2011). Snappers are commercially important food fishes and generally occur in tropical and subtropical seas. These fishes are described as having enlarged canine teeth on jaws, small teeth, and scales on the cheek, preopercle and gill cover, but no scales on the snout or the preorbital area (Nelson, 2006). Within the family Lutjanidae, the genus
The specimens were preserved in 10% formalin for a week and then transferred to 70% ethanol. Counts and measurements followed the methods of Hubbs and Lagler (1964). The examined specimens were deposited at the Fish Genetics and Breeding Laboratory, Jeju National University (JNU), Korea.
>
Lutjanus malabaricus (Schneider, 1801) (
JNU-91, 296.0 mm in standard length (SL), Hallim-eup, Jeju-si, Jeju Island, Korea, gill net, caught at a depth of approximately 25 m, December 2, 2010.
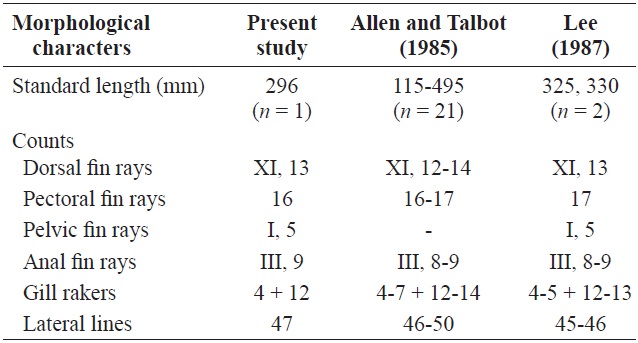
Counts for the present specimen are shown in Table 1. Measurements are presented as percentages against SL: body width 14.4; body depth 36.2; head length 39.7; predorsal fin length 39.1; prepectoral fin length 35.8; preventral fin length 39.5; preanal fin length 70.3; dorsal fin base length 48.9; pectoral fin base length 5.7; ventral fin base length 4.5; anal fin base length 12.4; upper jaw length 12.5; interorbital length 8.9; eye diameter 6.4; snout length 13.9; caudal fin peduncle depth 15.0; caudal fin peduncle length 10.7.
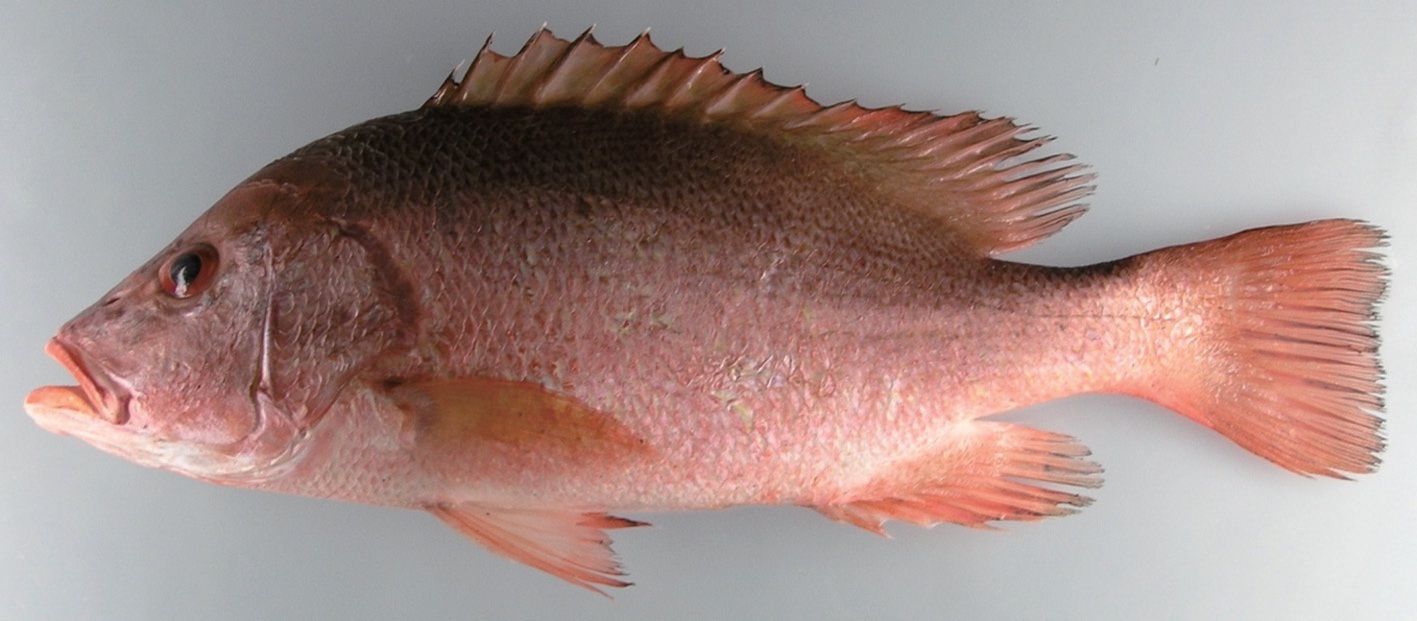
Body oblong, compressed, covered with ctenoid scales aligned in oblique rows above the lateral line and horizontal rows below the lateral line, except for a few oblique rows anteriorly. Scales present on the base of the soft dorsal and anal fins; three and five series of scales on the cheek and opercle, respectively. Eye somewhat oval; snout projecting and rounded; mouth large and oblique; posterior margin of the upper jaw does not reach below the eye; interorbital area well convex; vomerine teeth in a crescentic patch; posterior margin of preopercle serrate without preopercular notch; interopercle bony knob absent; dorsal fin continuous and posterior profile of its soft part rounded; pectoral fin pointed and its posterior tip reaching below the eighth dorsal spine; posterior profile of anal soft fin rounded; caudal fin truncate.
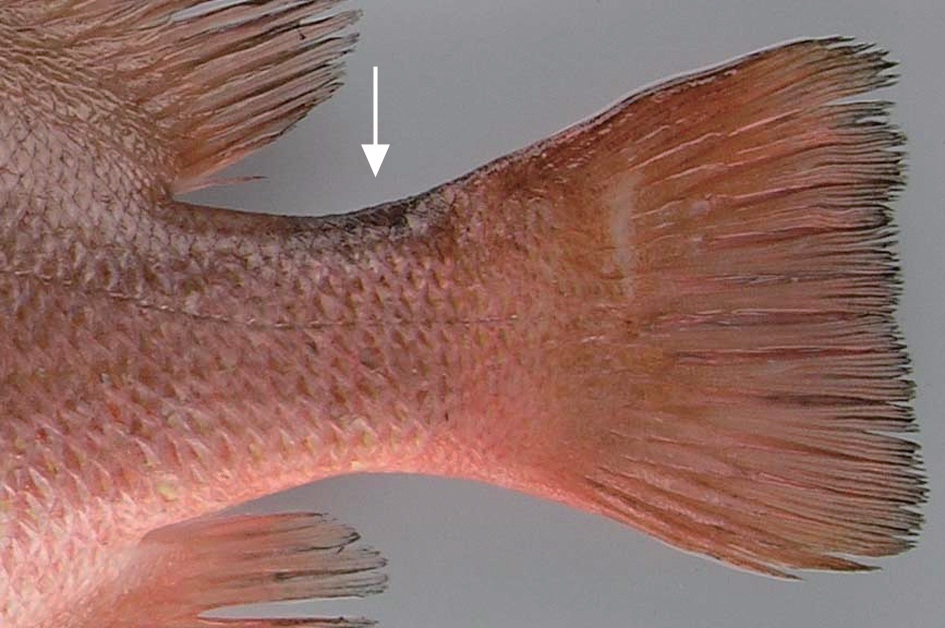
Head and body nearly uniformly reddish; all fins except pectoral fin reddish with black posterior margins; pectoral fin reddish-yellow; dorsal part of caudal peduncle with black marking (Fig. 2).
Known from Indo-West Pacific: Persian Gulf to Fiji, north to Taiwan, south to New South Wales (Myers, 1991) and Korea (Jeju Island, present study).
[Table 1.] Comparison of morphological characters of Lutjanus malabaricus
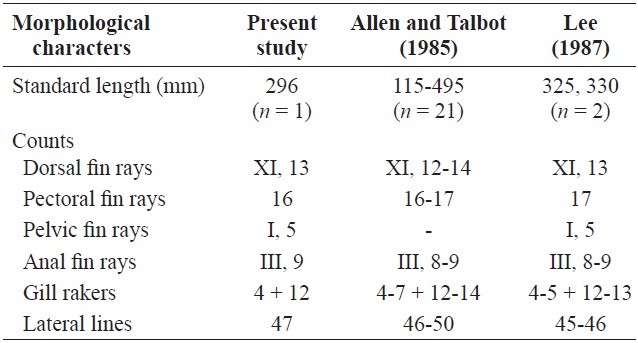
Comparison of morphological characters of Lutjanus malabaricus
The present specimen was collected from Jeju Island, Korea, and was characterized by having a black marking on the upper half of the caudal peduncle and rows of scales running obliquely above the lateral line, a band of vomerine teeth that does not protrude posteriorly at the middle, and nine anal soft rays. Thus, the morphological characteristics agreed well with previous reports of
>
Lutjanus stellatus Akazaki, 1983 (
JNU-119, 350.0 mm in SL, Daejeong-eup, Jeju Island, Korea, gill net, December 18, 2010.
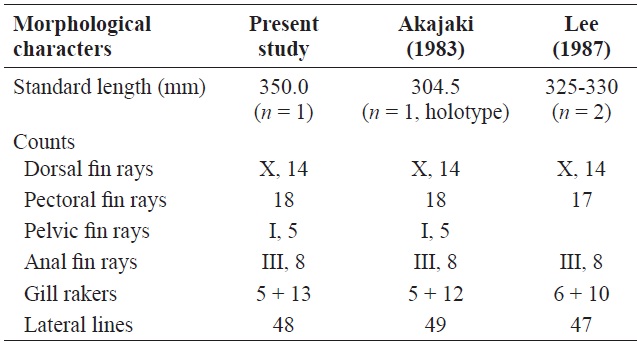
Counts for the present specimen are shown in Table 2. Measurements are presented as percentages against SL: body width 15.9; body depth 41.4; head length 36.7; predorsal fin length 35.1; prepectoral fin length 35.1; preventral fin length
[Table 2.] Comparison of morphological characters of Lutjanus stellatus
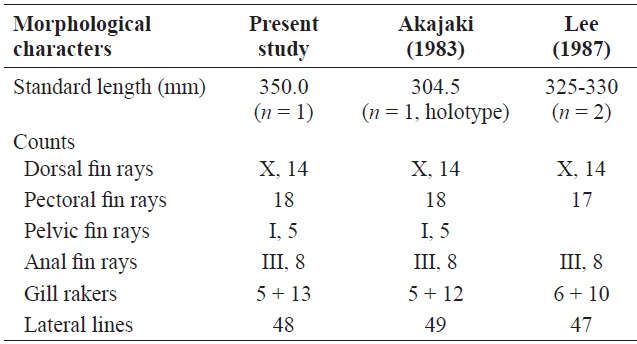
Comparison of morphological characters of Lutjanus stellatus
38.3; preanal fin length 69.7; dorsal fin base length 51.7; pectoral fin base length 7.1; ventral fin base length 3.7; anal fin base length 15.6; upper jaw length 15.4; interorbital length 10.9; eye diameter 6.0; snout length 13.1; caudal fin peduncle depth 12.1; caudal fin peduncle length 12.9.
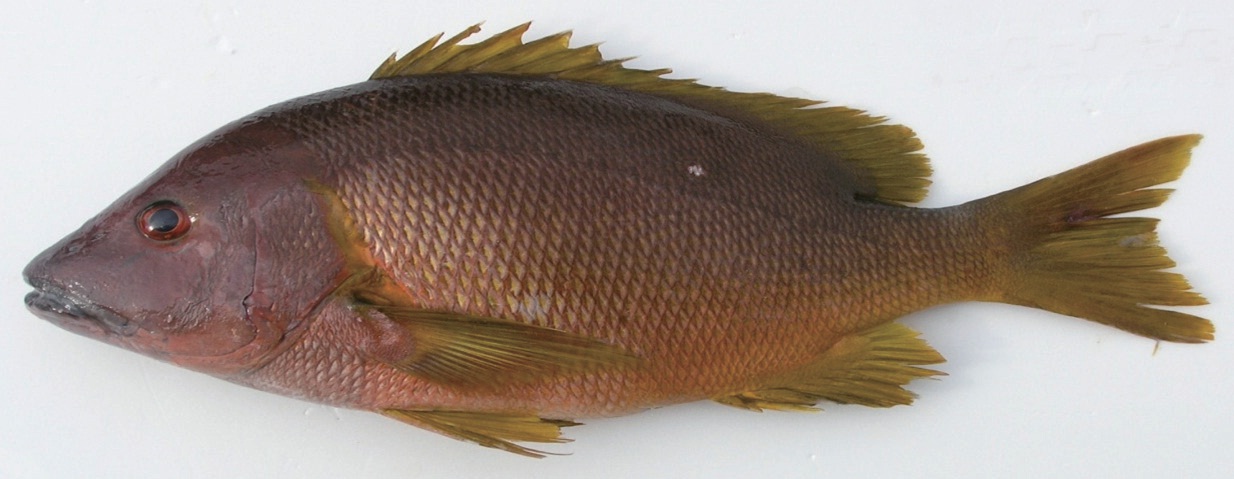
Body elongate, oval and compressed, covered with ctenoid scales aligned in oblique rows above the lateral line and horizontal rows below the lateral line. Scales present on the base of the dorsal and anal fins; three and five series of scales on the cheek and opercle, respectively. Eye moderate in size relative to the head; snout projecting; mouth large and oblique; posterior margin of the upper jaw nearly reaching below the middle of the eye; interorbital area well convex; one series of 13 weak conical teeth on the lateral outer side of the lower jaw and a short patch of villiform teeth on the lateral inner side on both jaws; four and three canines on the anterior part of the upper and lower jaw, respectively; a band of vomerine teeth without a posterior extension; posterior margin of preopercle finely serrate with a shallow preopecular notch; dorsal fin continuous and posterior profile of its soft part rounded; pectoral fin pointed and its posterior tip not reaching below the first spine of the anal fin; posterior profile of the anal soft fin rounded; caudal fin slightly forked.
Body brown and tinged yellowish-orange or pale orange; head uniformly brownish; all fins and posterior margin of opercle yellowish brown; a white spot on the side above the lateral line.
Japan (Shimada, 2002), Taiwan (Lee, 1987), South China sea (Randall and Lim, 2000) and Korea (Jeju Island, present).
The present specimen was characterized by having a white spot on the upper half of the body and a band of vomerine teeth that did not protrude posteriorly at the middle (Lee, 1987; Shimada, 2002). Those and the remaining morphological characters of the specimen agreed well with previous reports of