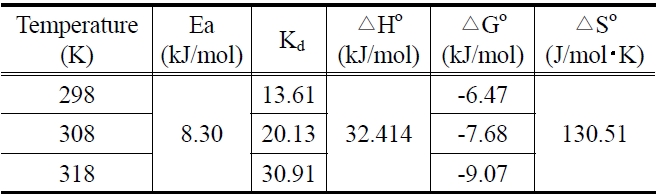
폐수로 부터 유독한 말라카이트 그린 성분을 제거하는데 있어서 제올라이트의 활용가능성을 살펴보았다. 흡착실험은 298, 308 및 318 K에서 수행하였으며, 흡착에 대한 온도, 접촉시간과 초기농도의 영향을 조사하였다. 흡착자료를 기초로 Langmuir 와 Freundlich 흡착등온식에 대한 적합성을 평가하였다. 흡착공정은 Freundlich 흡착등온식이 잘 맞았으므로 제올라이트 표면의 불균일한 에너지에 의해 선택적인 흡착이 이루어짐을 알았다. 계산된 흡착등온선의 상수 값으로부터 제올라이트에 의해서 말라카이트 그린의 효과적인 처리가 가능하다는 것을 알 수 있었다. 동력학적 실험으로부터, 흡착공정은 유사이차반 응속도식에 잘 맞으며, 속도상수(k2) 값은 말라카이트 그린의 초기농도가 증가할수록 감소하였다. 활성화에너지, 엔탈피, 엔트로피 및 자유에너지변화와 같은 열역학 파라미터들은 흡착공정의 특성을 평가하기 위하여 조사하였다. 활성화에너지의 계산값은 제올라이트에 대한 말라카이트 그린의 흡착이 물리적 공정임을 나타냈다. 자유에너지변화값(ΔGo = -6.47~ -9.07 kJ/mol)과 엔탈피변화값(ΔHo = +32.414 kJ/mol)은 흡착공정이 298~318 K 범위에서 자발적이고 흡열과정이라는 것을 나타냈다.
환경문제는 인간의 건강에 미치는 커다란 영향 때문에 전세계적인 관심사가 되고 있다. 오늘날 인류가 직면한 질병의 약 25%는 공기, 토양, 수질오염 등과 같은 환경오염에 장기간 노출됨으로써 발생하고 있다[1]. 섬유산업현장에서 발생하는 염색폐수는 인간건강에 심각한 손상을 미치는 것 중의 하나이다. 말라카이트 그린은 주로 가죽, 모직, 면, 견, 황마, 종이, 기타 섬유 등의 염색에 산업적으로 사용될 뿐만 아니라 식품착색제, 식품첨가제, 살균제, 구충제 등으로도 사용되기 때문에 매우 다양한 성분으로 많은 양이 생산되고 있다. 염색용도로 쓰인 말라카이트그린의 약 10~15% 정도가 염색 폐수로 방출되고 있다[2]. 염료의 배출과 오염을 개선하기 위하여, 수중으로 부터 염료성분을 제거하기 위한 여러 가지 방안들이 연구되었는데, 고급산화[3], 광촉매[4], 흡착[5], 막여과[6]와 응집법[7] 등이 보고되어 있다. 이 중에서도 흡착기술은 단순한 설계와 간편한 조작으로 특별한 매력을 가지고 있다. 활성탄, 점토(clay), 토탄, 키틴(chitin), 실리카(silica) 등과 같은 많은 흡착제가 수용액 중에 존재하는 저농도의 염료를 제거할 수 있는 가능성에 대해 조사된 바가 있다[8,9].
본 연구에서는 제올라이트를 흡착제로 사용하여 말라카이트 그린을 흡착제거하는 과정을 대상으로 Langmuir와 Freundlich 식의 흡착평형인자를 평가하여 흡착제로서 제올라이트의 타당성과 흡착조작의 유효성을 판단해 보고자 하였다. 흡착속도 실험을 통하여 말라카이트 그린의 초기농도와 흡착온도 등이 흡착반응에 미치는 영향을 고찰하여 동력학적인 해석과 함께 열역학적 파라미터를 조사하였다.
[Figure 2.] Langmuir isotherms for malachite green adsorption onto zeolite at different temperature.
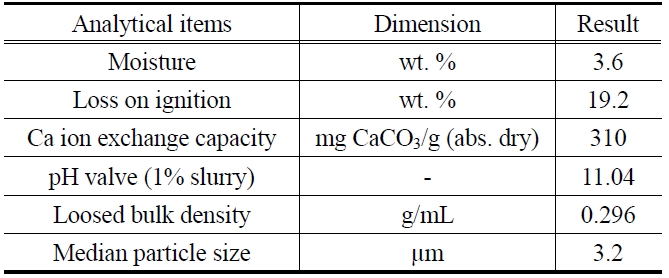
[Table 1.] Physical properties of zeolite
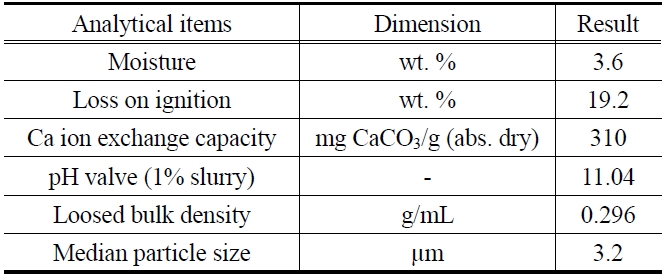
Physical properties of zeolite
본 연구에서는 회분식 흡착실험을 통하여 등온흡착평형관계를 밝히고, 흡착동력학 실험을 통해 흡착반응을 속도론 및 열역학적으로 평가하기 위하여 Figure 2에 나타낸 것과 같은 절차에 따라서 흡착실험을 수행하였다.
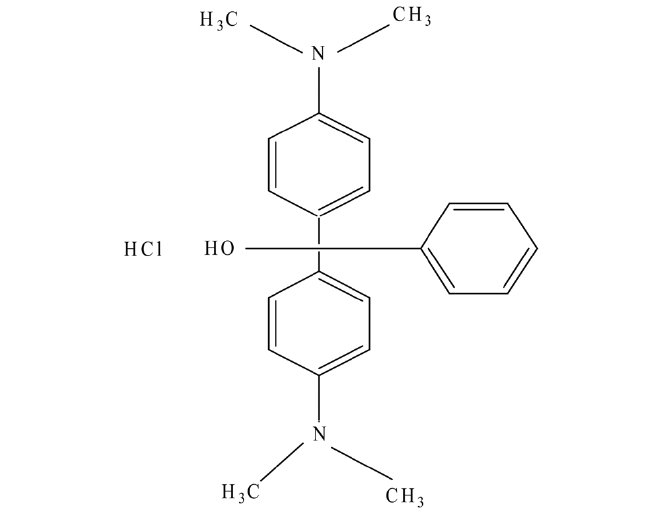
본 실험에서는 제오빌더(주)에서 제조한 4A 제올라이트를 80 ℃의 증류수로 수차례 수세한 후 오븐에서 무게변화가 더이상 발생하지 않을 때까지 건조시켜 무게를 측정하여 흡착제로 사용하였으며, 그 물성을 Table 1에 나타내었다. 실험에 사용한 말라카이트 그린(C23H26N2O?HCl, MW : 382.94)은 Figure 1과 같은 구조를 가진 Sigma사의 제품으로 증류수를 이용하여 1000 mg/L의 저장용액(stock solution)을 조제하였으며, 빛에 의한 분해를 막기 위하여 어두운 곳에 보관한 후 필요에 따라 적절한 농도로 희석하여 사용하였다. 말라카이트 그린의 농도 분석은 UV spectrophotometer (UV-1800, Shimadzu)를 이용하여 최대흡수파장 615 nm에서 흡광도를 측정하여 결정하였다.
흡착온도를 298, 308 및 318 K로 다르게 조절한 상태에서 초기농도 100 mg/L인 말라카이트 그린 용액 100 mL에 대하여 전 처리한 제올라이트를 20~150 mg의 범위에서 각각 유리병에 넣고 왕복식 항온진탕기(Jeio Tek, BS-21)에서 100 rpm의 속도로 흡착반응이 평형에 도달할 때 까지 흡착시켰다. 또한 초기농도 100, 150, 200 mg/L의 말라카이트 그린 용액 100 mL에 제올라이트 100 mg을 넣고, 위와 같은 방법으로 흡착시켰다. 흡착량의 변화는 1 시간마다 용액 중에 남아있는 말라카이트 그린의 농도를 측정하여 구하였다. 그 결과로 부터 Langmuir식과 Freundlich 식의 흡착평형인자와 흡착동력학 및 열역학적 파라미터들을 평가하였다.
흡착평형에 있어서 평형흡착량, qe (mg/g)는 다음 식에 의해 구해진다.
여기서 Co와 Ce (mg/L)는 각각 흡착질의 초기농도와 평형농도를 나타낸다. V는 용액의 부피(L)이고, W는 흡착제의 건조질량 (g)이다.
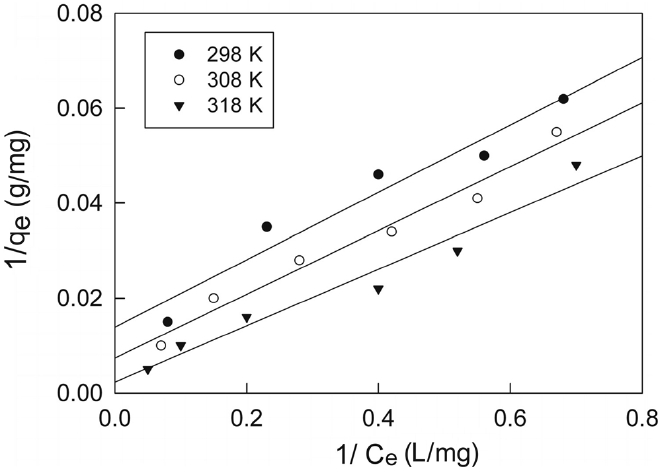
본 연구에서는 제올라이트에 대한 말라카이트 그린의 흡착 평형값을 Langmuir 식과 Freundlich 식에 각각 적용하여 보았다. 먼저 Langmuir는 흡착질이 흡착제의 표면에 있는 한정된 수의 흡착부위에 단분자층을 형성하는 것에 의해 일어난다고 가정하여 다음과 같은 식을 제안하였다.
한편 Freundlich의 흡착등온식은 흡착제의 표면이 불균일한 표면에너지를 갖는다고 가정한 식으로 다음과 같은 직선식이 잘 알려져 있다.
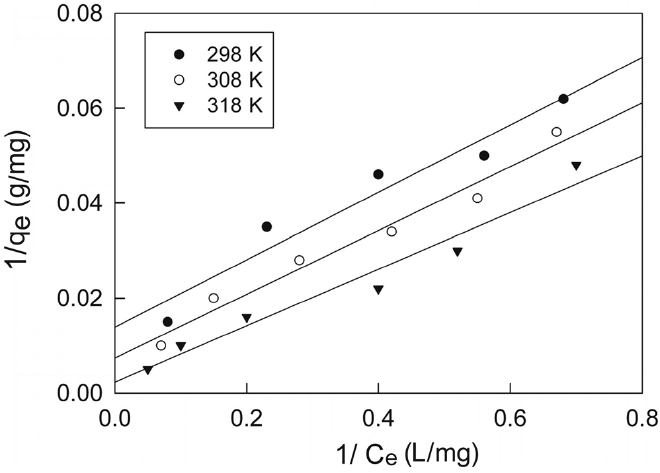
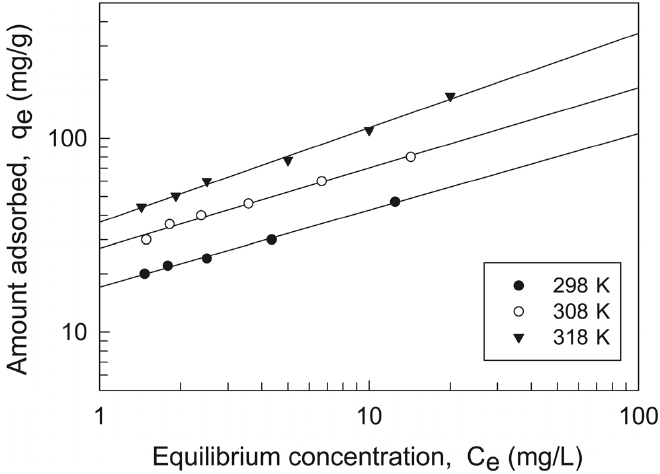
두 식에서 Ce는 흡착질의 평형농도(mg/L), qe는 흡착제 단위질량당 흡착된 흡착질의 양(mg/g), Qo와 b는 흡착용량과 흡착속도와 관련된 Langmuir 상수이고, KF와 1/n은 흡착공정이 얼마나 알맞은가를 나타내는 지표로 사용되는 Freundlich 상수이다. Figure 2와 3은 각각 Langmuir 흡착등온선과 Freundlich 흡착등온선을 나타낸 것이며, 회귀계산에 의해 구한 두 식의 상수 값들을 Table 2에 나타냈다.
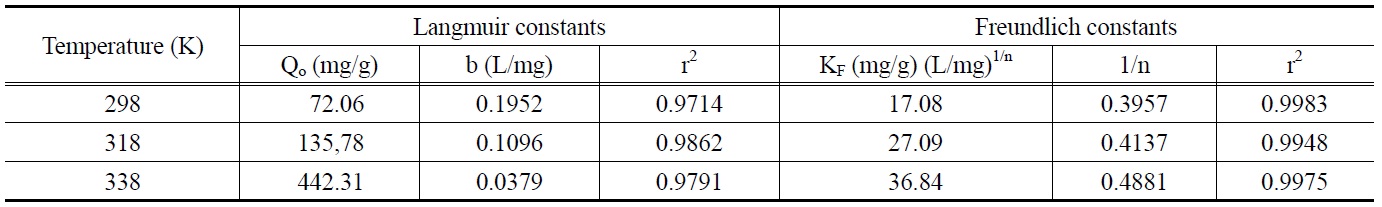
[Table 2.] Isotherm constants for adsorption of malachite green on zeolite
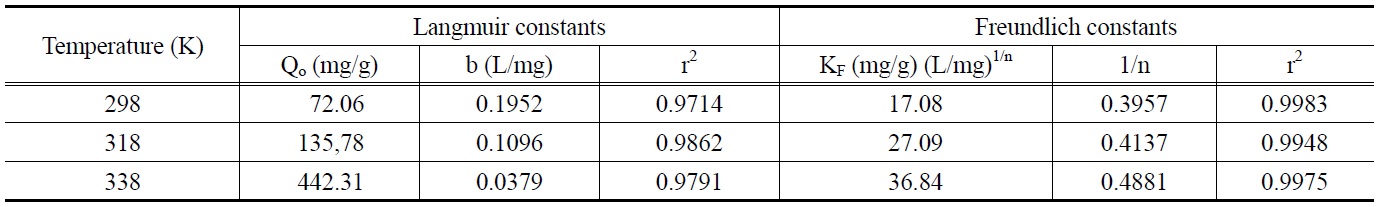
Isotherm constants for adsorption of malachite green on zeolite
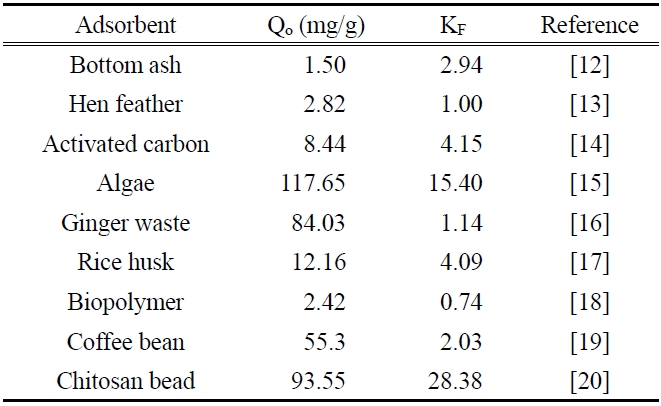
[Table 3.] Langmuir and freundlich isotherm constants of pesticide in previous studies
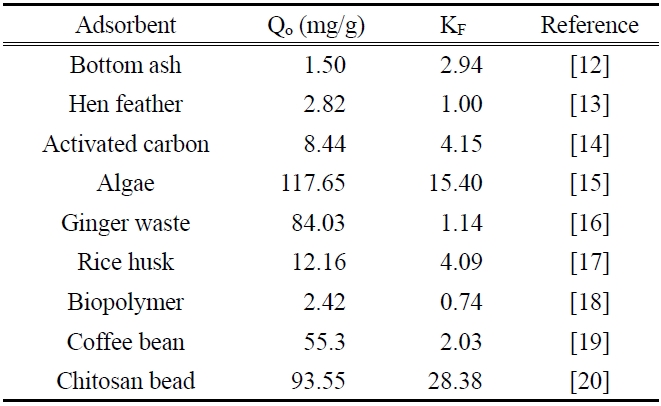
Langmuir and freundlich isotherm constants of pesticide in previous studies
두 식에 대한 적합성을 상관계수(r2)로부터 비교해 본 결과, Langmuir 식은 0.9714~9862이고 Freundlich 식은 0.9948~0.9983으로 나타나서 제올라이트에 대한 말라카이트 그린의 흡착평형관계는 Freundlich 등온식이 더 적합함을 알 수 있었다. 따라서 제올라이트에 의한 말라카이트 그린의 흡착은 단일층으로 흡착되는 것이 아니라 제올라이트의 흡착표면의 불균일한 에너지에 의해 선택적으로 흡착되는 것으로 판단되었다[10]. 또한 Freundlich 상수, 1/n 값은 0.3957~0.4881로 평가되었는데, 이 값은 알맞은 흡착공정범위인 0.1~0.5에 들어가기 때문에 제올라이트에 의한 말라카이트 그린의 흡착처리가 효과적인 제거방법이 될 수도 있다는 사실을 알 수 있었다[11]. Table 3에 몇가지 흡착제에 대한 말라카이트 그린의 흡착용량을 나타내었다. 본 실험에서 평가된 298 K에서 Qo와 KF 값은 각각 72.06과 17.08로 상위권에 속한다. 따라서 제올라이트가 말라카이트 그린의 흡착제거에 아주 유용한 흡착제가 될 수 있다는 것을 알 수 있었다.
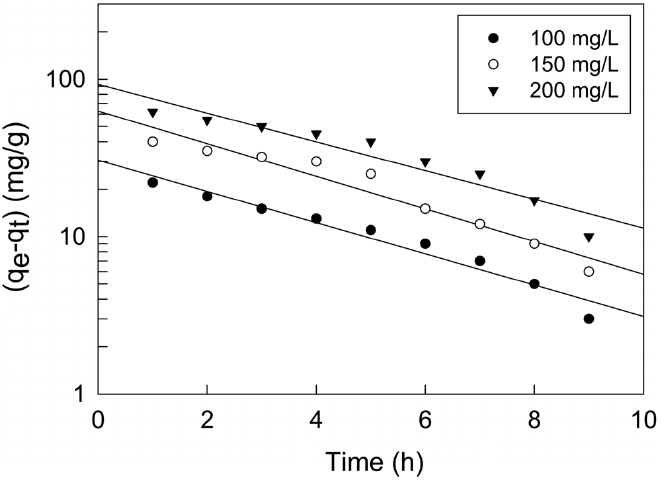
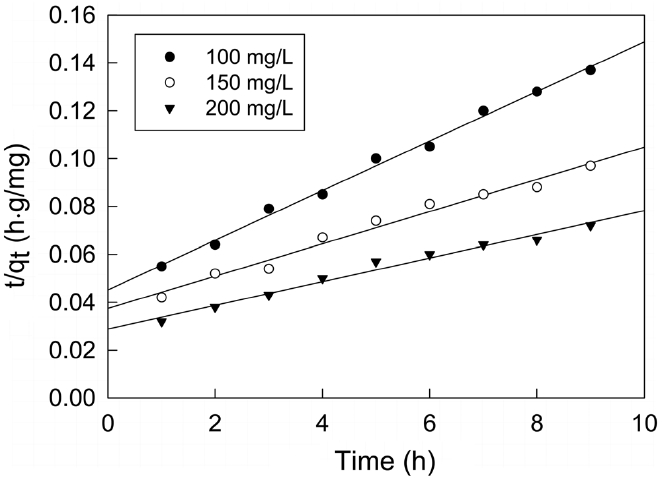
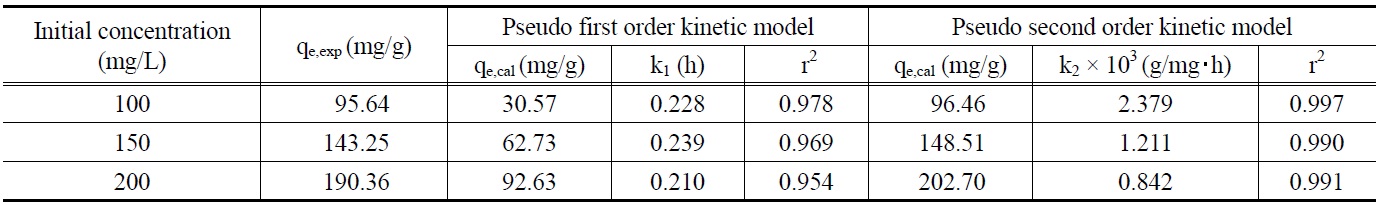
본 연구에서는 제올라이트에 대한 말라카이트 그린의 흡착반응을 식 (4)의 유사일차반응식(pseudo first order kinetics model) 과 식 (5)의 유사이차반응식(pseudo second order kinetics model)에 적용하여 속도론적으로 살펴보았다.
여기서 qe와 qt는 각각 평형상태와 t 시간에서 흡착된 말라카이트 그린의 양(mg/g)이며, k1은 유사일차반응속도상수(h-1), k2는 유사이차반응속도상수(g/mg?h)이다.
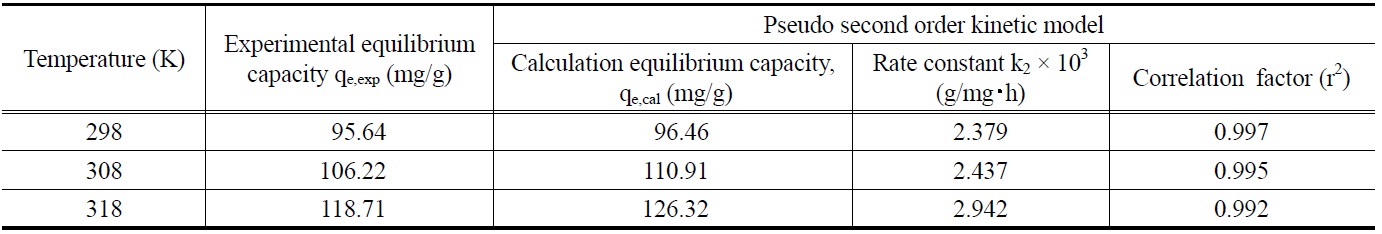
먼저, 말라카이트 그린의 초기농도가 각각 100, 150, 200 mg/L 일 때 흡착평형에 도달할 때까지 1시간 간격으로 흡착량 변화를 측정한 결과로부터 얻은 흡착속도실험데이터를 식 (4)와 (5)에 적용하여 본 결과는 Figure 4 및 5와 같다. 이들 그래프로부터 속도식의 파라미터 값들을 계산한 결과를 Table 4에 나타 냈다. 속도식에 대한 일치도를 나타내는 상관계수 값(r2)을 보
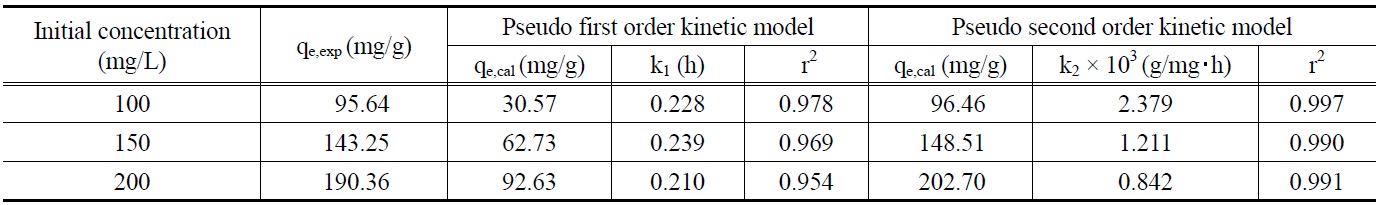
Pseudo first order and pseudo second order kinetic model parameters for different initial malachite green concentration at 298 K
면 유사이차반응속도식은 0.990~0.997로 유사일차반응식의 0.954~0.978 보다 크다. 따라서 제올라이트에 대한 말라카이트그린의 흡착반응은 유사이차반응속도식을 더 잘 따르는 것으로 볼 수 있다. 유사이차반응속도식의 속도상수(k2)값은 초기농도가 증가할수록 감소하는 것으로 나타났다. 유사이차반응속도식에 의해 구한 평형흡착량(qe,cal) 값들을 실험값(qe,exp)들과 비교해 보기 위해 식 (6)을 사용하여 오차율을 구하였다. 말라카이트 그린의 초기농도가 100, 150, 200 mg/L일 때 오차율은 각각 0.86%, 3.67%, 6.48%로 나타나 본 실험조건에서는 오차율 10% 이내에서 잘 맞는 것으로 나타났다.
흡착공정에 있어서 열역학적 파라미터의 값들은 그 공정이 자발적으로 일어나는지를 평가할 수 있으며 실제적인 공정운전에 있어 중요한 지표로 사용될 수 있다.
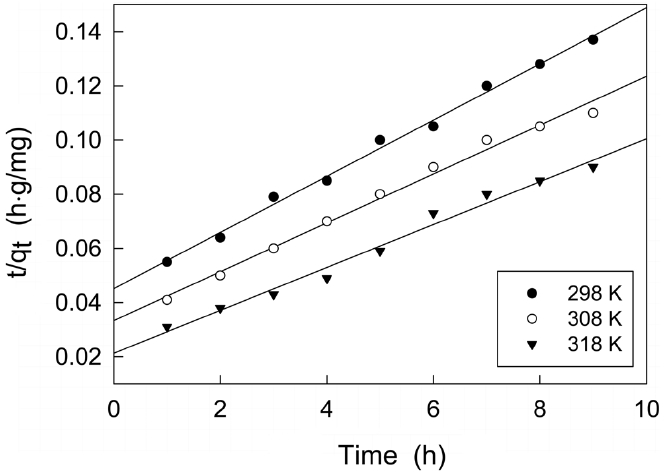
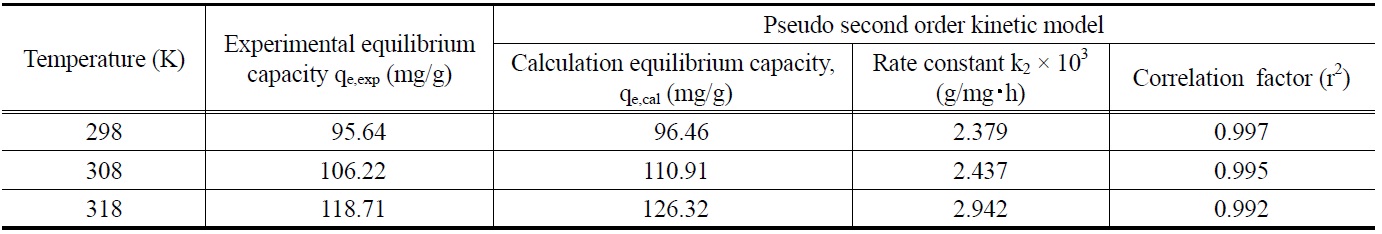
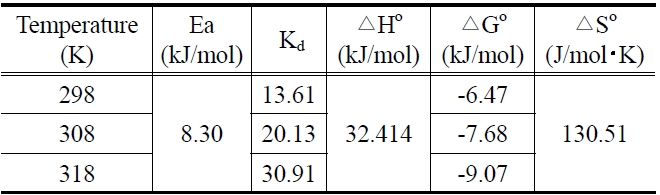
제올라이트에 대한 말라카이트 그린의 흡착에 있어서 반응온도가 미치는 영향을 조사하고자 말라카이트 그린의 초기농도를 100 mg/L로 고정한 상태에서 반응온도를 298, 308, 318K로 변화시키면서 시간대별 흡착량을 조사한 결과를 식 (5)의 유사이차반응속도식에 적용하여 Figure 6을 얻었으며, 각 반응온도에서의 평형흡착량과 속도상수를 계산한 결과는 Table 5와 같다. 흡착공정의 반응온도가 증가할수록 평형흡착량과 속도상수가 증가하는 것으로 나타났다.
Pseudo second order kinetic model parameters of malachite green onto activated carbon at different temperature
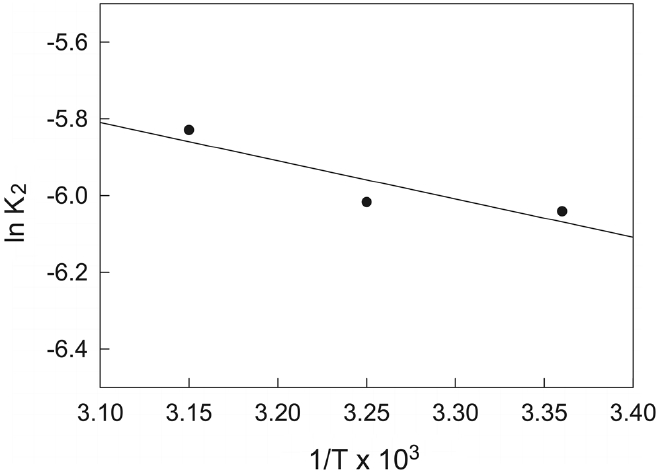
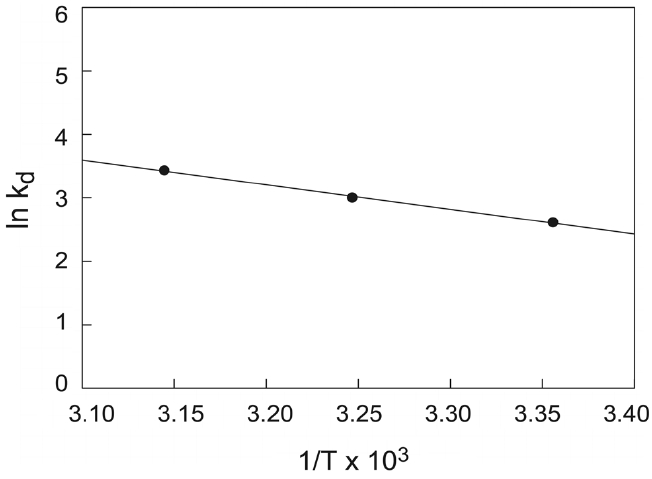
유사이차반응속도상수(k2)는 다음과 같은 Arrhenius형 관계식에 의해 온도의 함수로 나타낼 수 있는데, 이 식으로부터 흡착반응의 활성화에너지를 구하는 것이 가능하다.
여기서 Ea는 흡착반응의 Arrhenius 활성화에너지(kJ/mol), A는 Arrhenius 인자, R은 기체상수(8.314 J/mol?K), T는 흡착조작 온도(K)이다. Figure 7과 같이 ln k2와 1/T의 관계를 나타내고, 직선의 기울기(Ea/R)로부터 활성화에너지를 계산하였다. 본 연구에서 제올라이트에 대한 말라카이트 그린의 흡착반응 활성화에너지는 8.30 kJ/mol인 것으로 조사되었는데, 이것은 낮은 활성화에너지(5~40 kJ/mol)영역에 속하므로 물리흡착의 특성을 갖는 것임을 알 수 있다[21].
엔탈피와 엔트로피는 공정설계와 관련된 중요한 핵심인자이다. 흡착공정의 흡열성과 타당성을 평가하기 위해 주로 표준 자유에너지변화(△Go), 엔탈피변화(△Ho) 및 엔트로피 변화 (△So)와 같은 열역학 인자의 변화를 밝히는 것은 필수적이다 [22]. 본 연구에서는 열역학적 파라미터들에 대해서는 다음 식들을 이용하여 구하였으며, 그 결과는 Figure 8과 Table 6에 나타냈다.
Thermodynamic parameters calculated with the pseudo second order rate constant for malachite green onto zeolite
298, 308, 318 K에서의 표준자유에너지변화는 온도가 증가할수록 -6.47 > -7.68 > -9.07 kJ/mol 순으로 감소하였다. 이것으로부터 제올라이트에 의한 말라카이트 그린의 흡착공정은 온도가 증가할수록 자발성이 더 높아진다는 것을 알 수 있었다. 또한 본 연구에서의 자유에너지 변화값은 일반적인 물리흡착의 자유에너지 변화범위인 -20~0 kJ/mol에 속하므로, 흡착공정이 물리흡착이라는 것을 다시 확인할 수 있다[23].
Van't Hoff가 제시한 식 (10)으로부터 구한 흡착반응의 표준엔탈피변화가 양의 값(32.414 kJ/mol)을 갖는 것은 제올라이트에 대한 말라카이트 그린의 흡착공정이 흡열반응임을 나타낸다. 엔트로피 변화값이 양의 값(130.51 J/mol?K)을 갖는 것은
Thermodynamic parameters for the adsorption of malachite green onto other adsorbents in previous studies
고액계면에서 무질서도가 증가하였다는 것으로 그만큼 제올라이트에 대한 말라카이트 그린의 친화력이 좋다는 것을 나타낸다[24].
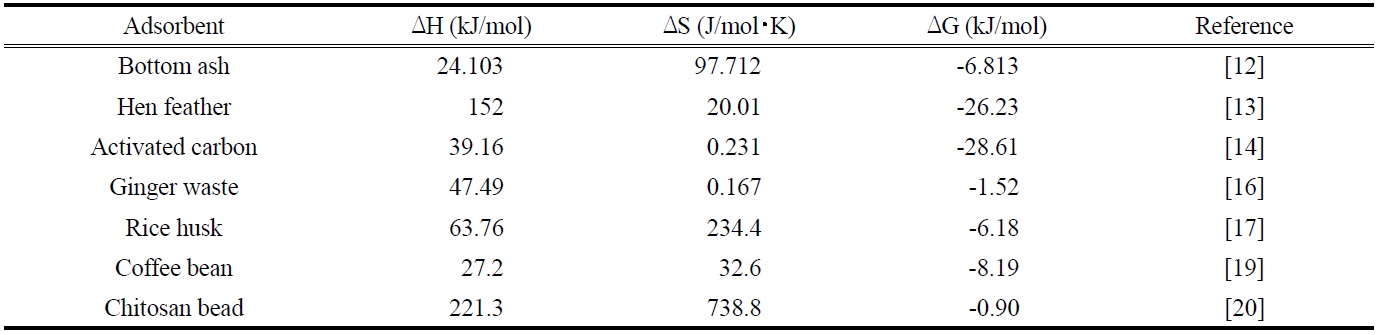
한편 본 연구의 결과를 여러 가지 흡착제를 사용하여 말라카이트 그린을 흡착한 결과를 나타낸 Table 7과 비교해 보면 엔탈피변화(32.414 kJ/mol)는 작고, 엔트로피 변화(130.51 J/mol?K)는 큰 편에 속함으로써, 제올라이트에 의한 말라카이트 그린의 흡착공정이 다른 흡착제를 사용했을 때 보다 반응의 수월성이나 자발성측면에서 적용가능성이 높다는 것을 확인할 수 있었다[25].
본 연구에서는 제올라이트에 대한 말라카이트 그린의 흡착평형과 흡착동역학에 대하여 조사하였다. 제올라이트에 대한 말라카이트 그린의 흡착평형관계는 흡착등온식에 적용하여 본 결과 Freundlich 식이 Langmuir식 보다 더 잘 맞는 것으로 나타났으며, 등온파라미터인 1/n 값에 의해 흡착조작이 효과적으로 이루어질 수 있음을 알았다.
제올라이트에 대한 말라카이트 그린의 흡착은 흡착온도변화와 말라카이트 그린의 초기농도에 대한 영향을 살펴 본 결과, 흡착온도가 높아질수록, 말라카이트 그린의 초기농도가 증가 할수록 제올라이트에 대한 평형흡착량이 증가하는 것으로 나타났다. 이 실험값들을 반응속도식에 적용하여 본 결과, 유사이차반응속도식이 유사일차반응속도식보다 일치도가 높았고, 유사이차반응속도식에 의해 계산한 평형흡착량은 실험값과 오차율 10% 이내에서 잘 맞는 것으로 나타났다. 평가된 활성화에너지값(32.414 kJ/mol)과 자유에너지값(-6.47~-9.07 kJ/mol)으로부터 흡착공정이 흡열반응 물리흡착임을 알았다. 또한 온도가 올라갈수록 자유에너지값이 감소하는 경향을 보여 제올라이트에 대한 말라카이트 그린의 흡착반응은 온도가 올라갈수록 더 자발적으로 일어나는 것으로 판단되었다.