The use of woven fabric reinforced polymer composites has increased in various indus-tries due to their excellent mechanical properties in both the longitudinal and transverse directions. Among the various reinforced polymer composites, carbon/polymer woven com-posites are prominent wear-resistant materials because oftheir highstrength, stiffness, and thermal conductivity. However, carbon/polymer woven composites generally suffer from weak adhesion at the carbon/matrix interface due to the hydrophobic properties of carbon fabric. Adhesion between carbon fabric and thepolymer matrix is crucial to the wear proper-ties of carbon/polymer woven composites. As such, a number of studies have been conducted to improve the adhesion strength of carbon fibersin the polymer matrix by modifying the sur-face properties of carbon fiber [1-6]. Epoxy polymer has outstanding stiffness, dimensional stability, and chemical resistance. However, only a few studies have been performedto inves-tigate the wear properties of carbon/epoxywoven composites [7,8]. In particular, research on the wear behaviors of oil-absorbed carbon/epoxy woven composites has yet to be reported.
In the present study, the effects of oilabsorption on the wearbehaviors of carbon/epoxy woven compositeswereinvestigated. Ball-on-disk wear tests were performed using dry and fully oil-absorbed carbon/epoxy woven composites. After the wear tests, the worn surfaces of the dry and fully oil-absorbed carbon/epoxy woven compositeswereanalyzedvia scanning electron microscopy(SEM).
The materials used in this work were carbon plain-woven fabric (CF332NON, Repub-
lic of Korea Carbon, Korea), bisphenol-A type epoxy (YD-115, Kukdo Chemical, Korea), and D-230 hardener (Dianiline, Kukdo Chemical). The epoxy resin and hardener were mixed in a 6:4 ratio by weight percent. Four-plied carbon/epoxy woven com-posites with fiber content of less than 67% by weight were used to fabricate the wear specimens. The carbon/epoxy woven com-posites were cured in an autoclave under a pressure of 2 kgf/cm2 at 130OC for 6 h. A diamond wheel cutter was used to cut the cured composites into 30 mm × 30 mm pieces. The wear speci-mens were immersed in automobile oil (SK Chemical, Korea) until they were fully saturated. Ball-on-disk wear tests, where one zirconia (ZrO2) ball was employed, were conducted at room temperature using a Neotribo Friction andWear test machine (Neo-Plus, Korea). The applied vertical load and rotational speed were 19.6 N and 10.6 m/min, respectively. The sectional shape of the wear track was measured with a surface profiler (Dektak 150, Veeco Ltd., USA) so as to determine the wear volume loss.
The oil contentsinthe carbon/epoxy woven composites (C)werecal-culated from the specimen weights before and after oil absorption:
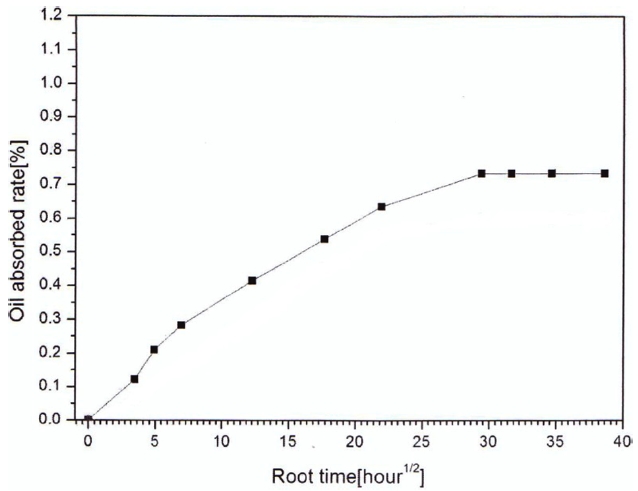
where Ww and Wd represent the weights of oil-absorbed and dry specimens, respectively. Theoil contentsofthe carbon/epoxy wo-ven composites are shown in Fig. 1 as a function of the immer-sion time. The oil absorptionvalues were in good agreementwith the dual-stage Fickian model, which states that oil absorption follows a linear curve before the saturation point and then gradu-ally reaches a fully saturated stage. Carbon/epoxy woven com-positeswere fully saturated after 36 days, at which point the oil absorption rate was 0.14%.
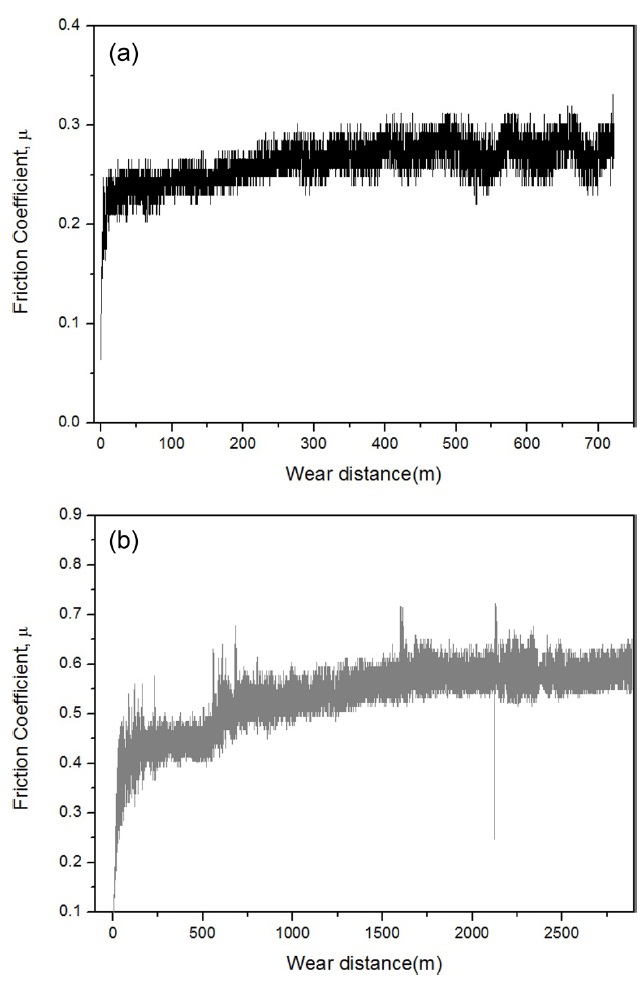
The effects of oil absorption on the wear behaviors of car-bon/epoxy woven composites wereinvestigated by determining changes in the friction coefficient as a function of the wear dis-tance.The changes in the friction coefficient as a function of the wear distance for dry and oil-absorbed carbon/epoxy woven compositesare shown in Fig. 2. The oil-absorbed carbon/epoxy woven composites had a higher friction coefficient when com-pared to thedry carbon/epoxy woven composites. Specifically,
the friction coefficients of dry and oil-absorbed carbon/epoxy woven composites were 0.25-0.30 and 0.55-0.6, respectively.
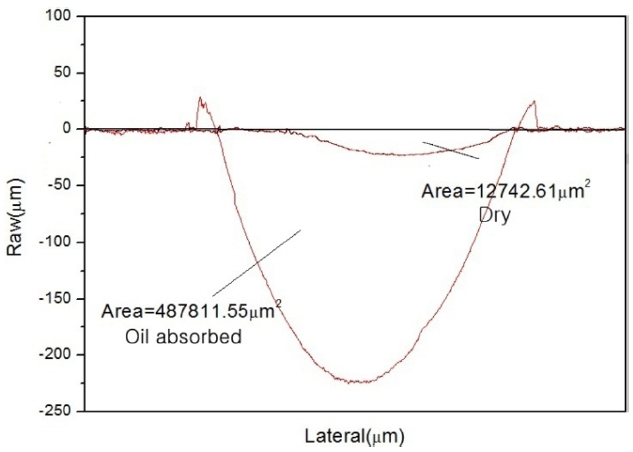
A comparison of the wear-depth profiles for dry and oil-ab-sorbed carbon/epoxy woven composites is shown in Fig. 3 As
expected from the change in the friction coefficient, the oil-ab-sorbed carbon/epoxy woven composites exhibited worse wear-resistant behavior than the dry carbon/epoxy woven composites. The maximum depth profiles of dry and oil-absorbed carbon/epoxy composites were 23 ㎛ and 223 ㎛, respectively. The wear volume loss of both composites was calculated based on the wear-depth profile. The wear volume losses of dry and oilabsorbed carbon/epoxy woven composites were 9.20 × 10-4 cm3 and 3.52 × 10-2 cm3, respectively.
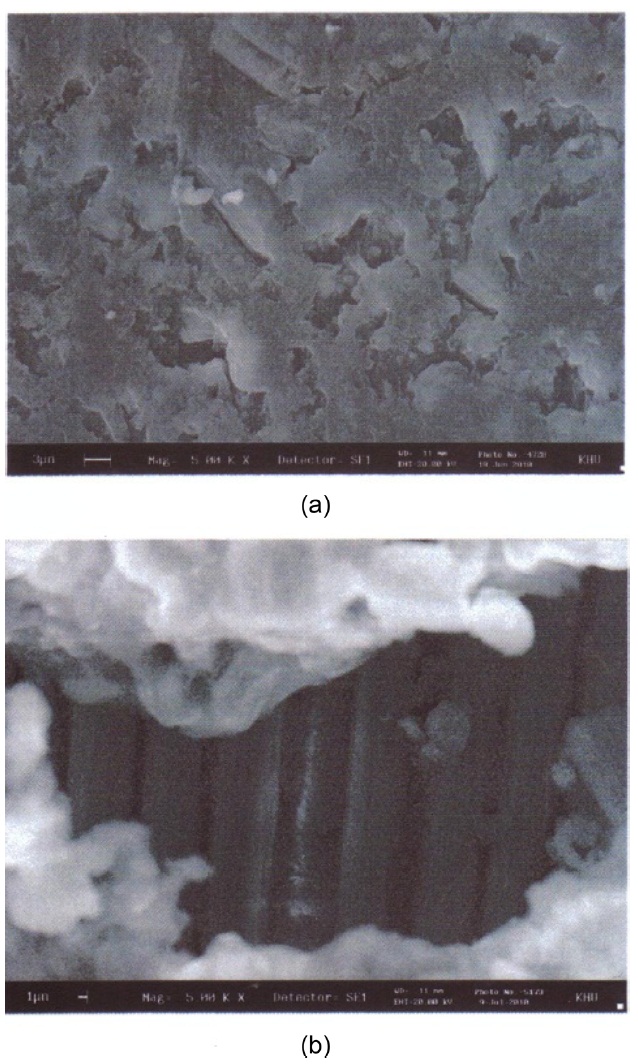
The worn surfaces of thedry and oil-absorbed carbon/epoxy woven composites were examined via SEM. A comparison of the worn surfaces of both carbon/epoxy woven composites is shown in Fig. 4. As evident in the figure, abrasive wear occurred for both composites. Fibers were broken and randomly dispersed in the epoxy matrix for the dry carbon/epoxy woven composites.
These fibers were peeled off from the epoxy, and their surfaces were found to be relatively clean. The existence of peeled fibers was due to the weak adhesion forces between the carbon fibers and the epoxy matrix. Such weak adhesion forcesoriginate from the swallowing effect of the epoxy matrix.
In conclusion, the wear properties of carbon/epoxy woven composites were adversely affected by oilabsorption. The fric-tion coefficients and wear losses of oil-absorbed carbon/epoxy woven composites were higher than those of dry carbon/epoxy woven composites. The higher friction coefficients and wear losses of the oil-absorbed carbon/epoxy woven composites are attributed to the weak adhesion forces between the carbon fibers and the epoxy matrix.