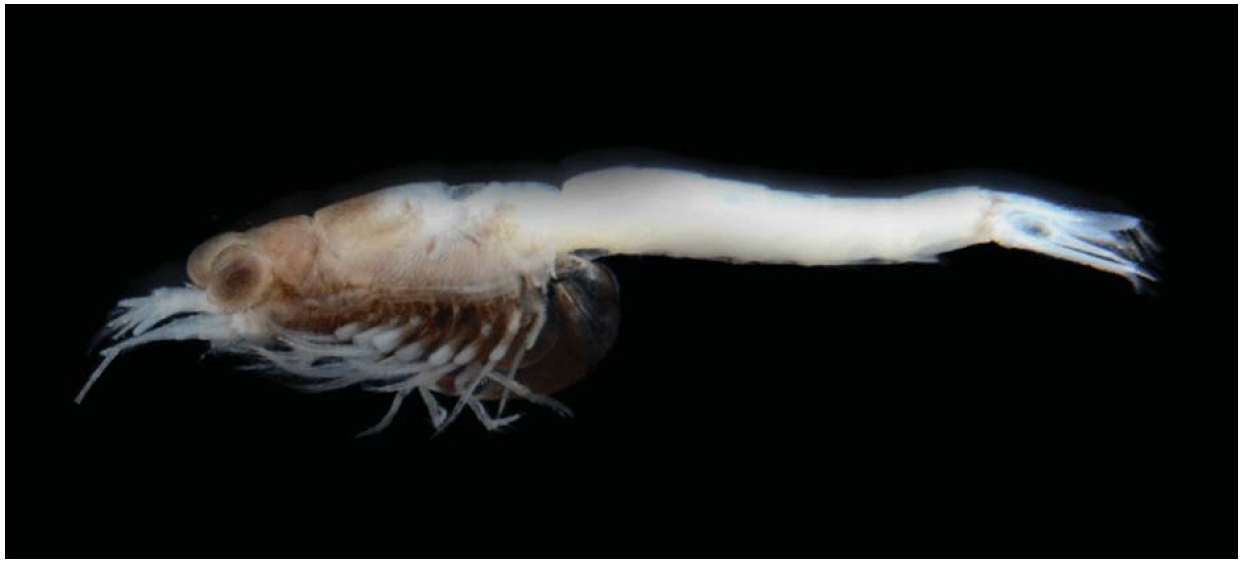
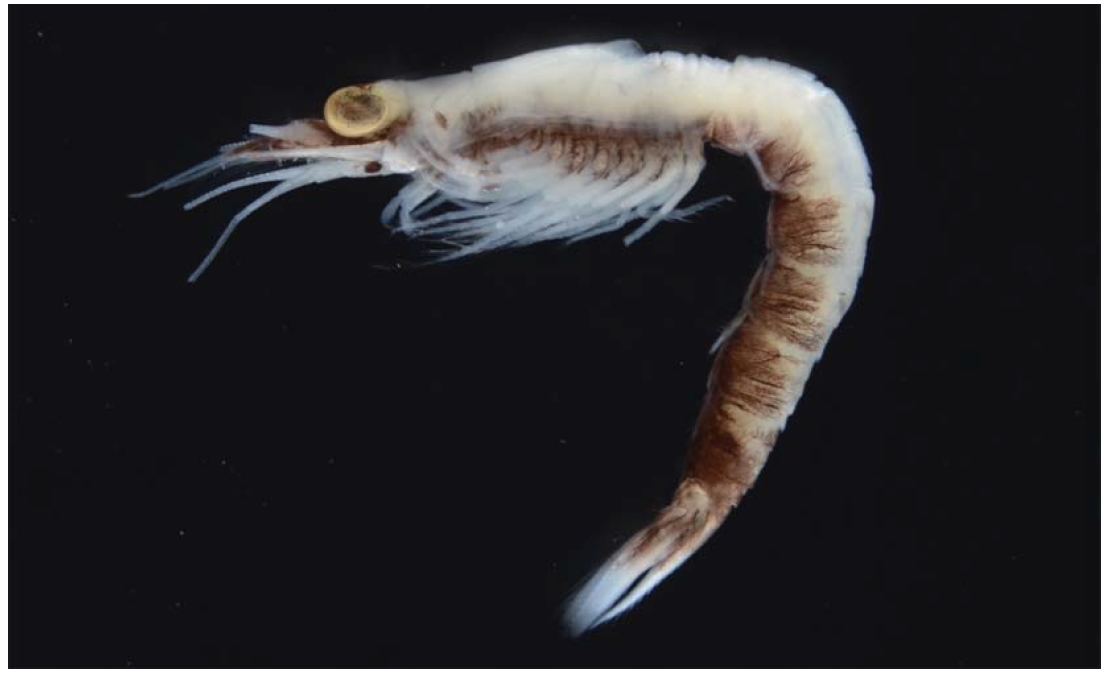
Mysids are one of the zooplanktons found in marine and freshwater ecosystems (Jo et al., 1998). They are served as an important food source for higher trophic levels (Mees et al., 1994). They are often called opossum shrimp because pregnant female carries their young in a brood pouch.
In the family Mysidae Dana, 1850, 45 species belonging to 19 genera have been reported in Korea. Continuous syste-matic study on the mysids in Korea revealed that two spe-cies,
The present two species were collected from a tidal pool by light trap and hand-net. Specimens were preserved in 70% ethyl alcohol, and illustrations were drawn with the aid of compound microscope (Model BX-60; Olympus, Tokyo, Japan) fitted with a drawing tube. Images were recorded using a digital camera ( Model D7000; Nikon, Tokyo, Japan), and produced with Helicon Focus software (Model Helicon Focus; Helicon Soft Ltd., Kharkov, Ukraine). Body length was mea-sured from the tip of the rostrum to distal apex of the telson excluding the spine. The simple setae and plumage of the plumose setae on the margin of antennae, antennules, mouth-parts, and uropods are omitted from the figures. Terminology for the dissection and measurement is after Tattersall and Tattersall (1951). All specimens have been deposited in the Marine Arthropod Depository Bank of Korea (MADBK), Seoul National University.
Order Mysida Haworth, 1825
Family Mysidae Dana, 1850
Subfamily Mysinae Haworth, 1825
Tribe Mysini Hansen, 1910
Genus Nipponomysis Takahashi and Murano, 1986
1*Nipponomysis calcarata Takahashi and Murano, 1986 (Figs. 1- 3)
Material examined. 1♀, Korea: Isl. Jejudo, Jeju-si, Jeju Port, 2 Nov 2010, in light trap; 1♀, Gyeongsangnam-do: Tongyeong-si, Isl. Yokjido, 8 Dec 2010, by hand-net; 1 juv.,
Gyeongsangbuk-do: Uljin-gun, Gol-jang Port, 37 ? 1?54?N,129 ? 24?32?E, 14 Jul 2011, in light trap; 1♀, Uljin-gun, 36 ? 59? 51?N, 129 ? 24?18?E, 24 Aug 2011, in light trap.
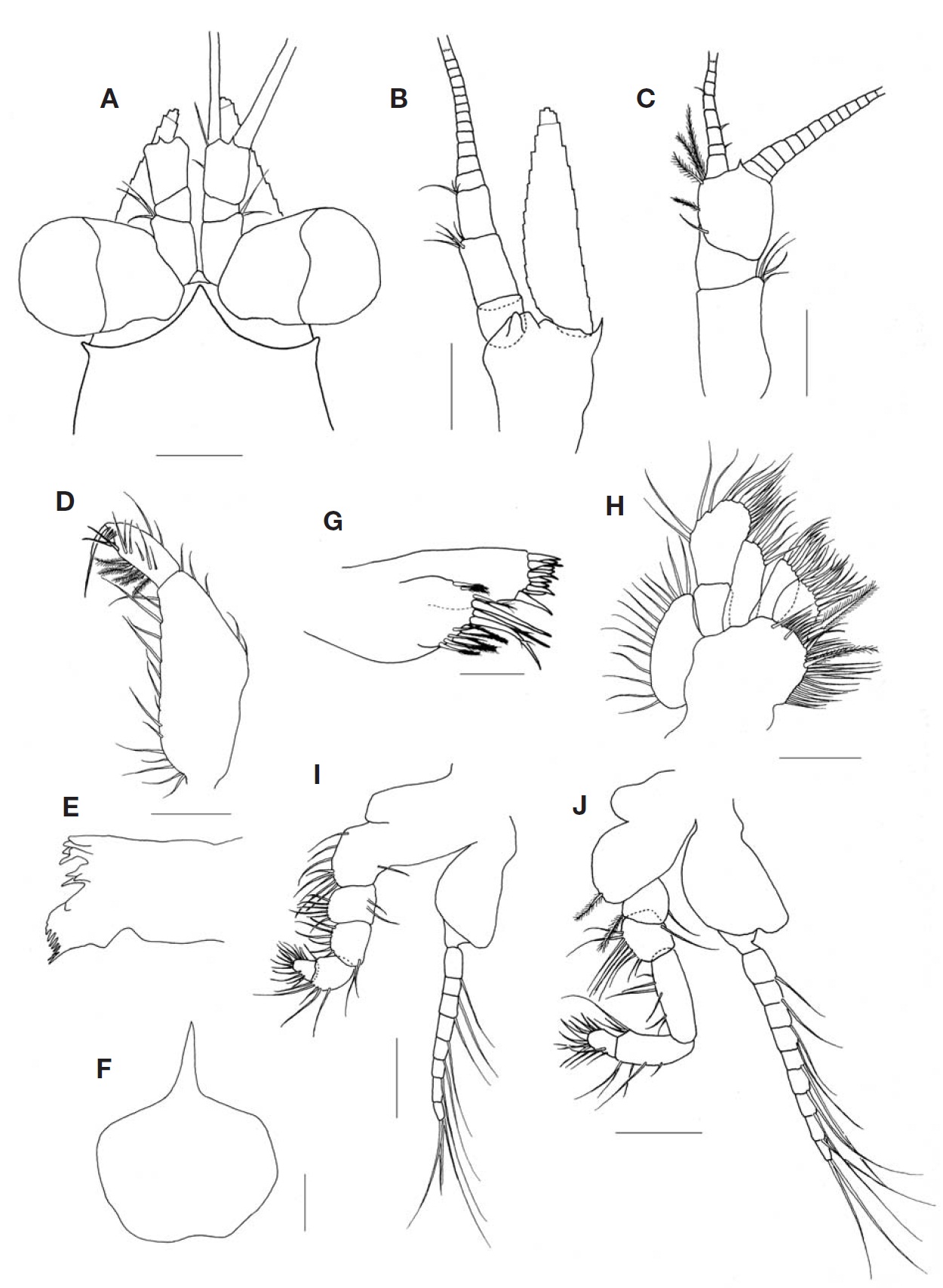
Description. Carapace (Fig. 2A) with anterior margin pro-duced into triangular rostral plate with bluntly pointed tip, reaching near base of first segment of antennular peduncle; posterior margin emarginated and covering abdominal somit-es dorsally except for last two.
Eye (Figs. 1, 2A) large, slightly flattened; cornea reniform in dorsal view and occupying 2/5 of whole eye; eyestalk without denticles.
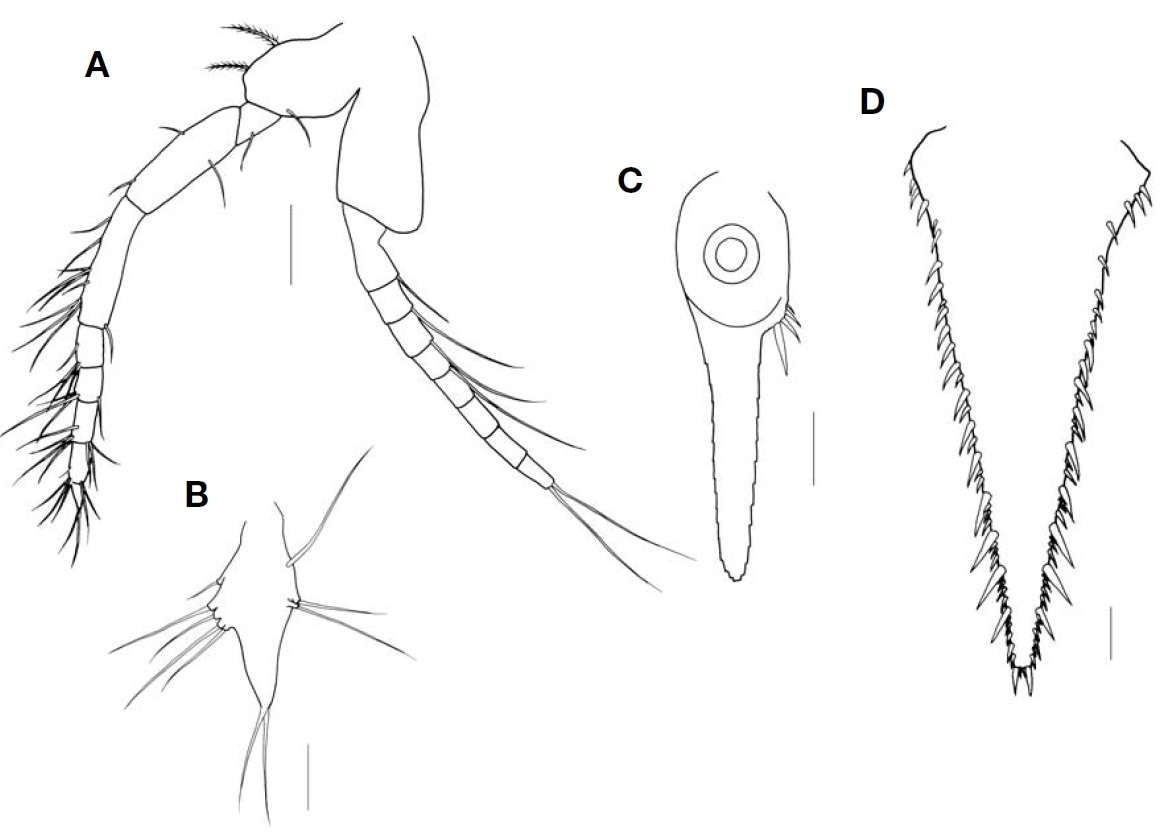
Antennal scale (Fig. 2B) lanceolate with round apex, about 4 times as long as broad, extending anteriorly beyond first segment of antennal peduncle; obscure suture occupying 1/13 of whole length of antennal scale; outer margin straig-ht, inner margin concave and entire margin with setose. Antennal peduncle 3-segmented; second segment with 4 simple setae on distal margin, twice as long as first; third segment with 3 simple setae on distal margin.
Antennular peduncle (Fig. 2C) 3-segmented; first segment longest and second shortest.
Mandibular palp (Fig. 2D, E) 3-segmented; first segment inconspicuous, second 3 times as long as third; third seg-ment with 5 plumose setae on inner margin and 6 simple setae on medial margin.
Labrum (Fig. 2F) with pointed apex on anterior margin.
Maxillule (Fig. 2G) with outer lobe bearing 11 robust setae on distal margin; inner lobe with 12 plumose setae.
Maxilla (Fig. 2H) armed with plumose setae along margin; endopod 2-segmented, second segment 1.7 times as long as broad; exopod with 15 plumose setae.
Endopod of first and second thoracopods (Fig. 2I, J) ro-bust with long and tough claw terminally.
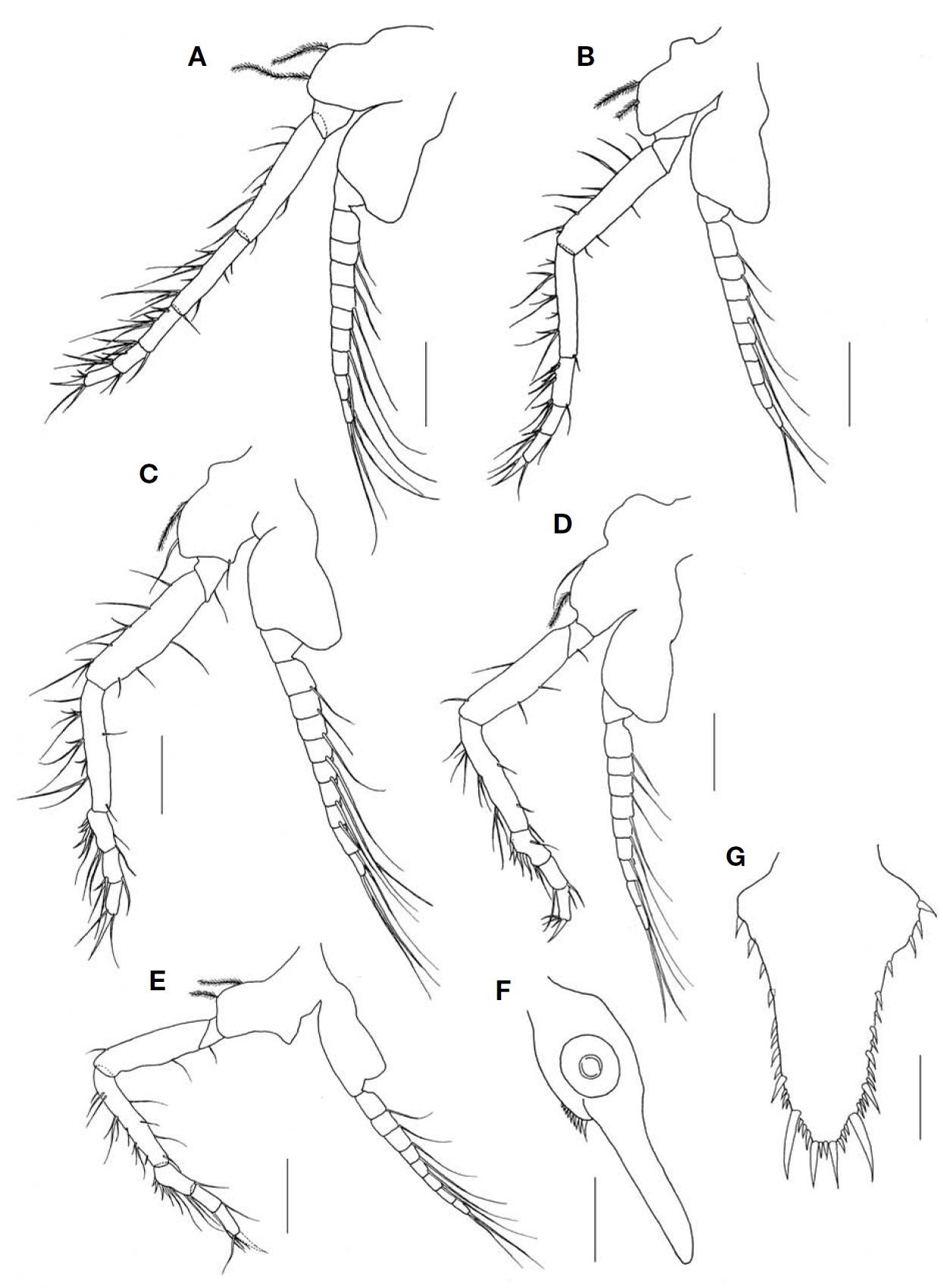
Endopod of third to eighth thoracopods (Fig. 3A-E) with 3-subsegmented carpopropodus, proximal segment of car-popropodus armed with two long and two short strong spines on inner margin of basal half region.
Marsupium composed of 2 pairs of oostegites.
Pleopod of female uniramous, rudimentary with well-developed endite.
Inner uropod (Fig. 3F) with 9 spines in ventral statocyst region; outer uropod 1.3 times longer than inner uropod.
Telson (Fig. 3G) slightly short, linguiform, about 1.6 times as long as broad; lateral margin bearing 3-4 spines one-by-one on proximal half, remaining distal region armed with 3-4 groups of spines composed of large and small spines alter-natively, 1-3 smaller spines and 1 larger spine gradually increased in length to distal part; apex truncated, armed with 2 pairs of spines, outer spines especially robust and 3 times as long as inner ones, 1/3 shorter than lateral distalmost spines.
Distribution. Korea (present study) and Japan (Otsuchi Bay, Iwate Prefecture).
Remarks.
According to the original description of Takahashi and Murano (1986), the number of spines on ventral margin of the inner uropod varies from 7 to 9. In the present speci-mens, however, the number of spines varies 6 to 9 as for adult and 4 in case of immature specimens.
1* Genus Exacanthomysis Holmquist, 1981
2* Exacanthomysis japonica Murano, 1991 (Figs. 4-7)
Material examined. 10♀♀, Korea: Gangwon-do, Go-seong-gun, Geojin Port, 38 ? 26?53.14?N, 128 ? 27?46.37?E, 4 Apr 2011, in light trap.
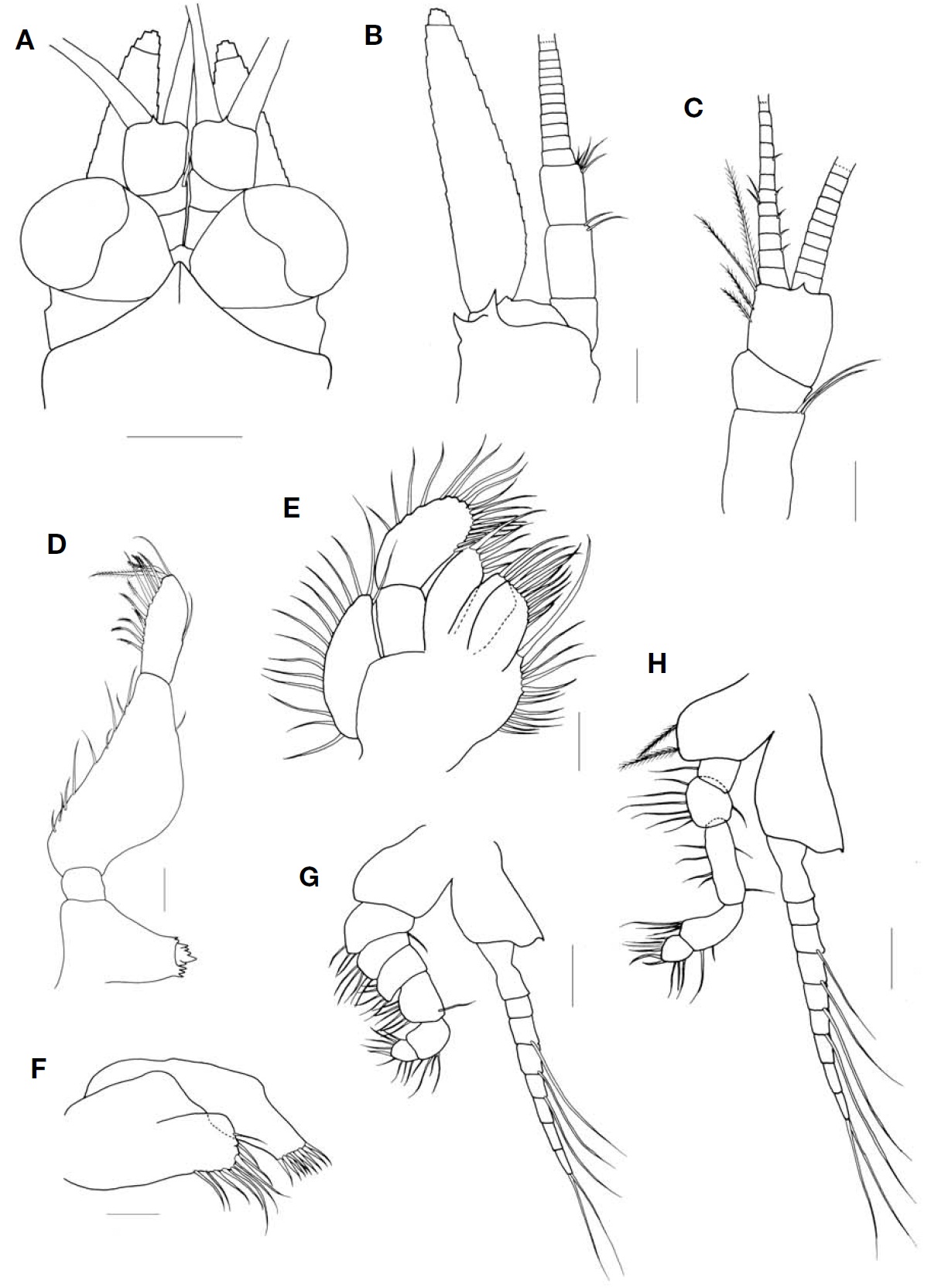
Description. Carapace (Fig. 5A) with anterior margin pro-duced into triangular rostral plate with pointed tip bearing ventral median keel, not reaching near base of first segment of antennular peduncle; posterior margin emarginated, antero-lateral corners rounded form.
Eye (Figs. 4, 5A) well developed; cornea reniform in dor-sal view and occupying half of whole eye; eyestalk without denticles, bearing hairs on surfaces.
Antennal scale (Fig. 5B) lanceolate with round apex, about 4.3 times as long as broad; distal suture occupying 1/17 of whole length of antennal scale; outer margin straight, inner margin concave and entire margin with setose. Antennal peduncle 3-segmented; second segment with 2 simple setae on distal margin, 1.3 times as long as first; third segment with several setae on distal margin, subequal to first.
Antennular peduncle (Fig. 5C) 3-segmented; first longest, second shortest and 1/2 as long as third.
Mandibular palp (Fig. 5D) 3-segmented; second segment almost 2 times as long as third, slightly swollen; third seg-ment bearing 12-13 plumose setae on inner margin.
Maxilla (Fig. 5E) armed with plumose setae along margin; endopod 2-segmented, second segment 1.7 times as long as first.
Maxillule (Fig. 5F) with hump-shaped process on medial margin of outer lobe.
Endopod of first and second thoracopods (Fig. 5G, H) with short claw terminally, basal plate of exopod bearing 1 or 2 spinules.
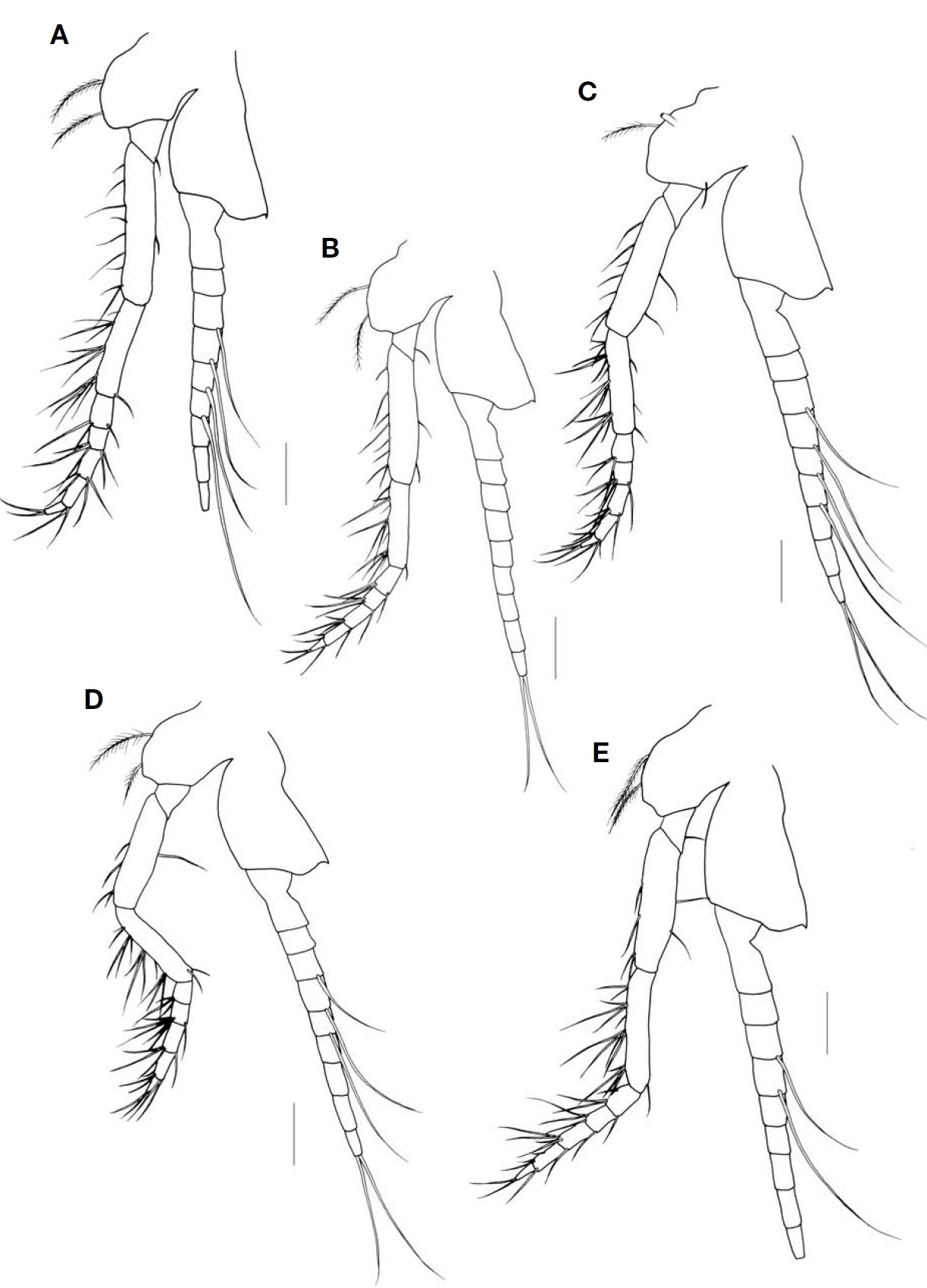
Endopod of third to eighth thoracopods (Figs. 6A-E, 7A) with 4-subsegmented carpopropodus, all segments of car-popropodus subequal in length or proximal segment longest and with dactylus short; basal plate of exopod bearing 1-3 spinules except in eighth thoracopod.
Pleopod of female (Fig. 7B) uniramous, short and rudi-mentary; all pleopods almost same length.
Inner uropod (Fig. 7C) bearing 4-5 spines in ventral stato-cyst region; outer uropod 1.3 times longer than inner uro-pod.
Telson (Fig. 7D) elongated triangular in shape, about 2.3 times as long as broad; lateral margin bearing 10-12 spines on proximal half and remaining part armed with 7 or 8 groups of spines composed of large and small spines alternatively,1-5 smaller spines and 1 larger spine gradually increased in
length to distal part, except last group composed of 6-8 smaller spines; apex narrow and truncated, 13 times as long as broad, bearing 2 pairs of spines, outer spines twice as long as inner ones.
Distrubution. Korea (present study) and Japan (Ishikari Bay, Hokkaido).
Remarks. Three species of the genus Exacanthomysis Holm-quist, 1981 were reported from the coastal waters in the north-eastern Pacific (Murano, 1991):
According to the original description of Murano (1991),
Korean name: 1* 며느리발톱곤쟁이(신칭)
Korean name: 1* 네마디안다리곤쟁이속(신칭); 2* 네마디안다리곤쟁이