The diatom genus
Ehrenberg (1843) established
Shim (1994) reported finding the genus
The present study examined planktonic diatoms of the genus
aPresent address: Laboratory of Plankton Ecology, Korea Institute of Coastal Ecology, Inc., Bucheon 421-808, Korea
From August 2008 to February 2009, we collected phytoplankton samples from Korean coastal waters (Table 1), by vertically towing a 20 ㎛ mesh net and immediately fixed the samples with neutralized formalin (final concentration 5%), glutaraldehyde (final concentration 2%) and Lugol’s solution. To remove organic matter in the diatom cells, we used the method described by Hasle and Fryxell (1970) and Simonsen (1974). The resultant materials were examined under an Axioskop 40 light microscope(Carl Zeiss, Jena, Germany) and photographed with an MRc 5 camera (Carl Zeiss) and a scanning electron microscope (JSM-5600LV; Jeol, Tokyo, Japan). To analyze diatoms’ sizes, we employed image calculation software (AxioVision AC version 4.5; Carl Zeiss). To identify previous reports of each taxon, we considered catalogues by Cupp (1943), Hendey (1964), Sundstrom (1986), Hasle and Syvertsen (1996). Terminology followed general proposals by Ross et al. (1979), Sundstrom (1986), Round et al. (1990) and Hasle and Syvertsen (1996).
[Table 1.] Collection site information for the Rhizosolenia specimens examined in the present study
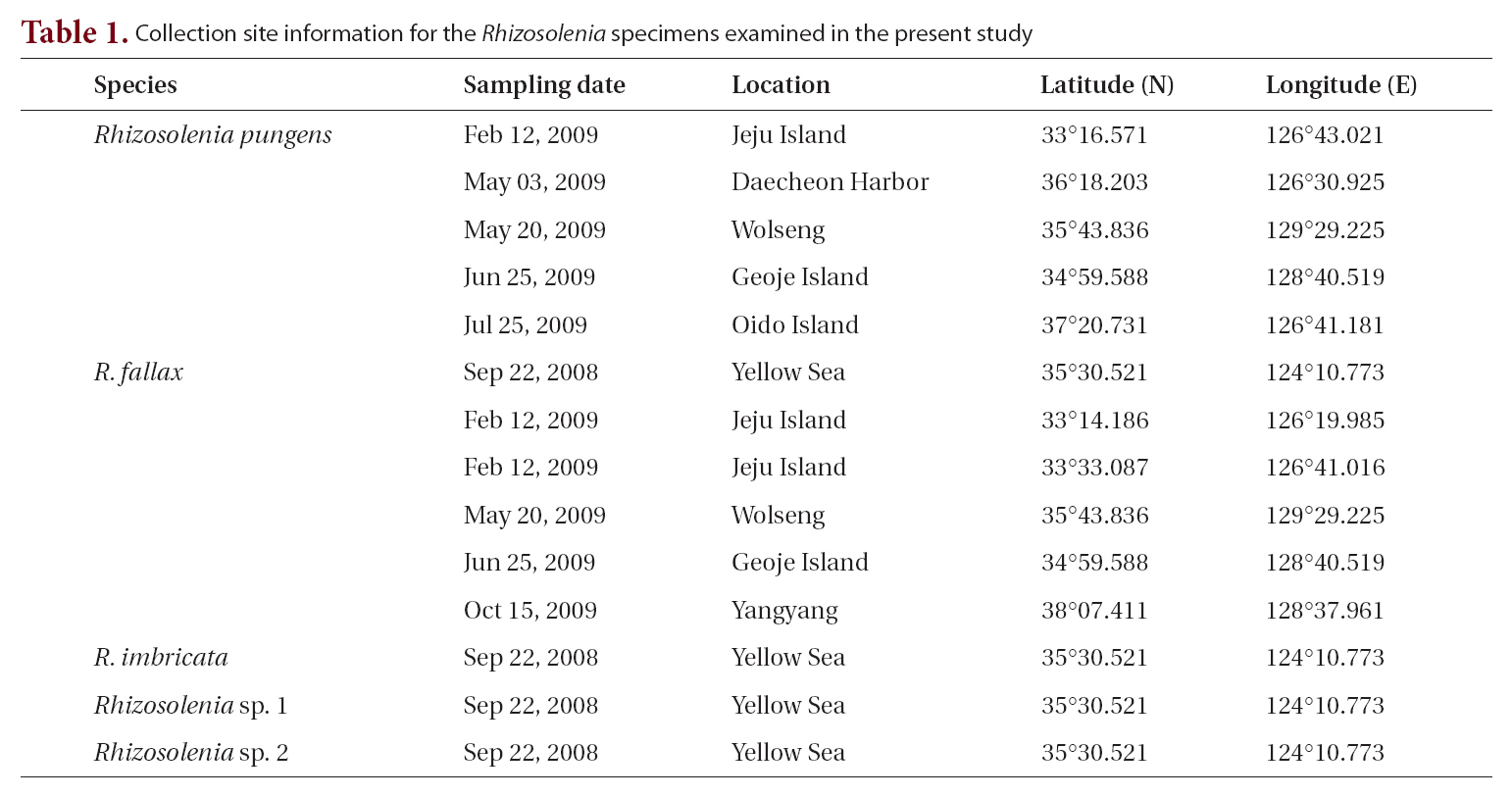
Collection site information for the Rhizosolenia specimens examined in the present study
Table 2 summarizes the characteristics we observed in the
Class Bacillariophyceae Haeckel 1878
Order Centrales Hustedt 1930
Suborder Rhizosoleniineae Simonsen 1979
Family Rhizosoleniaceae De Toni 1890
Genus Rhizosolenia Brightwell 1858
R. pungens (Cleve-Euler) Brunel 1962
R. fallax Sundstrom 1986
R. imbricata Brightwell 1858
Rhizosolenia sp. 1
Rhizosolenia sp. 2
>
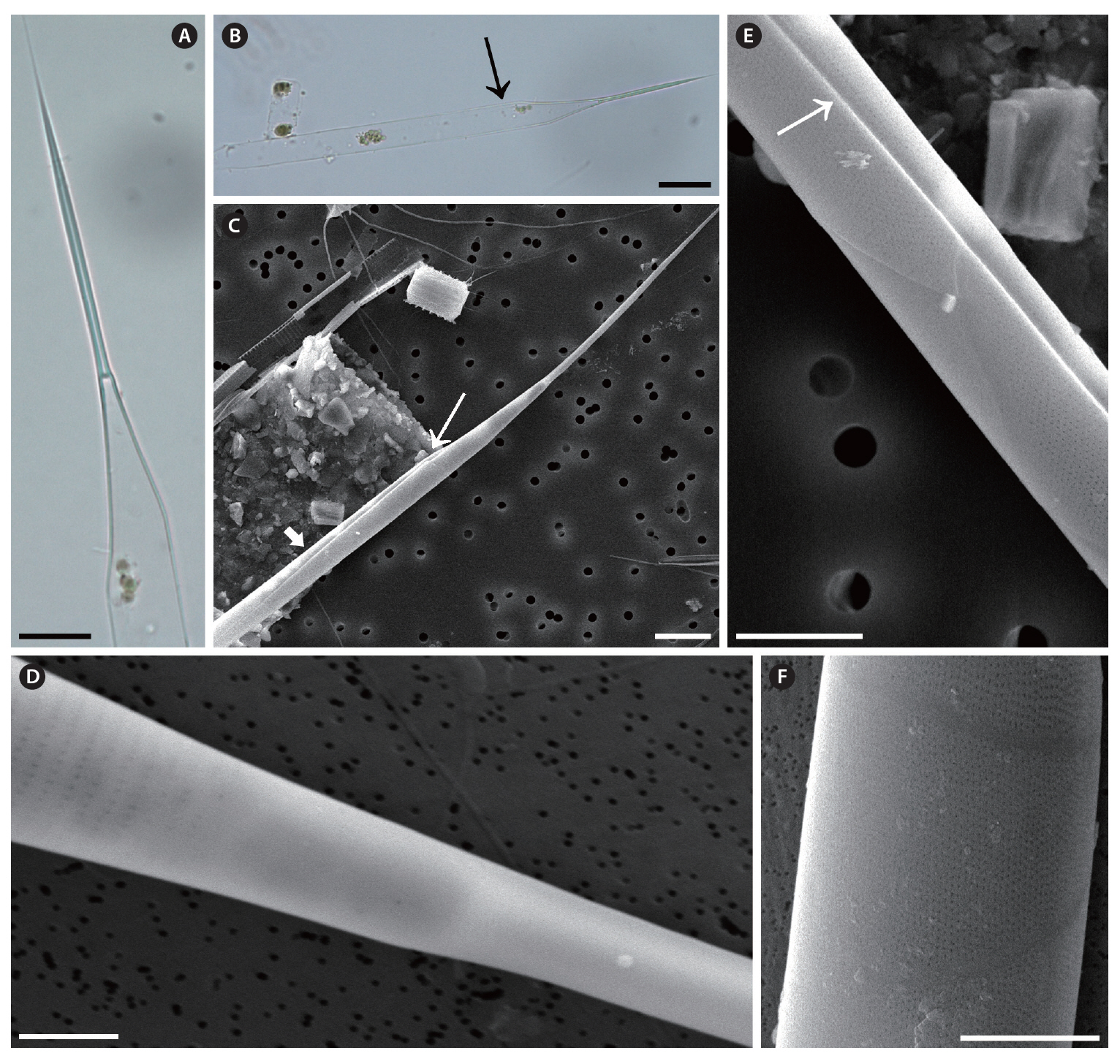
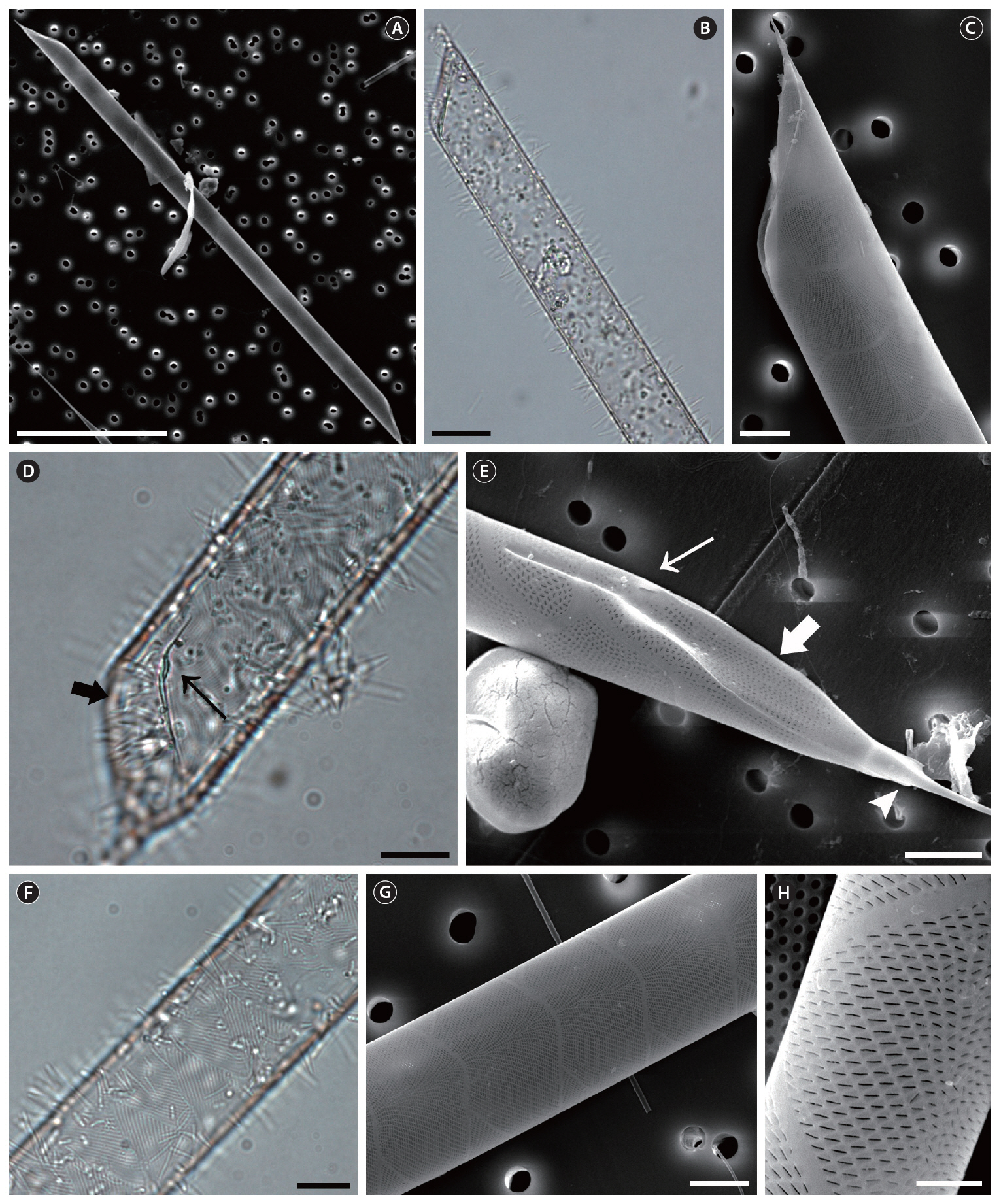
Rhizosolenia pungens (Cleve-Euler) Brunel, 1962 (
Brunel 1962, p. 66, Pl. 4, Fig. 5 & 6; Hernandez-Becerril 1995, p. 264, Fig. 36-40; Hasle and Syvertsen 1996, p. 157, Pl. 30; Sar 1996, p. 381; Sunesen and Sar 2007, p. 634, Fig. 35-47.
The cells are solitary or in pairs, cylindrical, bilaterally symmetrical, circular in cross-section, and 4.1-16.7
[Table 2.] Morphological characteristics of Rhizosolenia species examined in this study
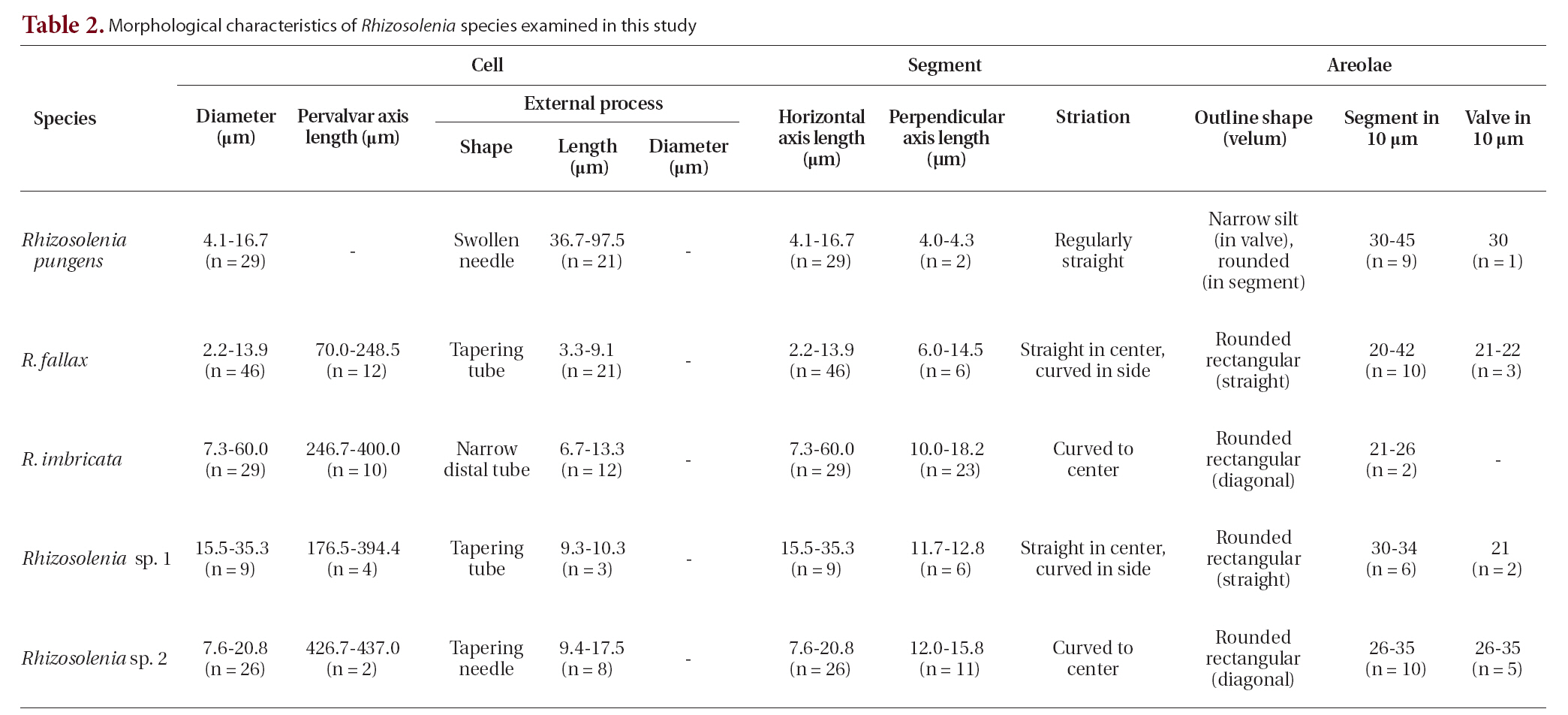
Morphological characteristics of Rhizosolenia species examined in this study
㎛ in diameter. The valve is sharply sub-conical, elongated,with a tapering needle-shaped process, almost straight, basally shallow up to the middle and 36.7-97.5 ㎛ in length. A contiguous area is present and otaria are absent. An impression of the adjacent valve process appears from the ventral valvar edge or the advalvar edge. It is groove-shaped and deeper in the basal than in the terminal region. Claspers are poorly noticeable. Valve areolae are poroid, external areolae with slit-like pores, 30 in 10 ㎛, and have a secondary quincuncial pattern. Scattered pores are circular, occurring in irregular distribution among the areolae or taking the place of some areolae distinguishable in external view. The segment horizontal and perpendicular axes are 4.1-16.7 ㎛ and 4.0-4.3 ㎛, respectively. Girdle segments are rhomboidal to trapezoidal and arranged in two dorsiventral columns. Segment areolae are rounded, 30 to 45 in 10 ㎛, arranged in striae oriented along the pervalvar axis, with a secondary quincuncial pattern.
Distribution. According to Hasle and Syvertsen (1996),
Remarks.
>
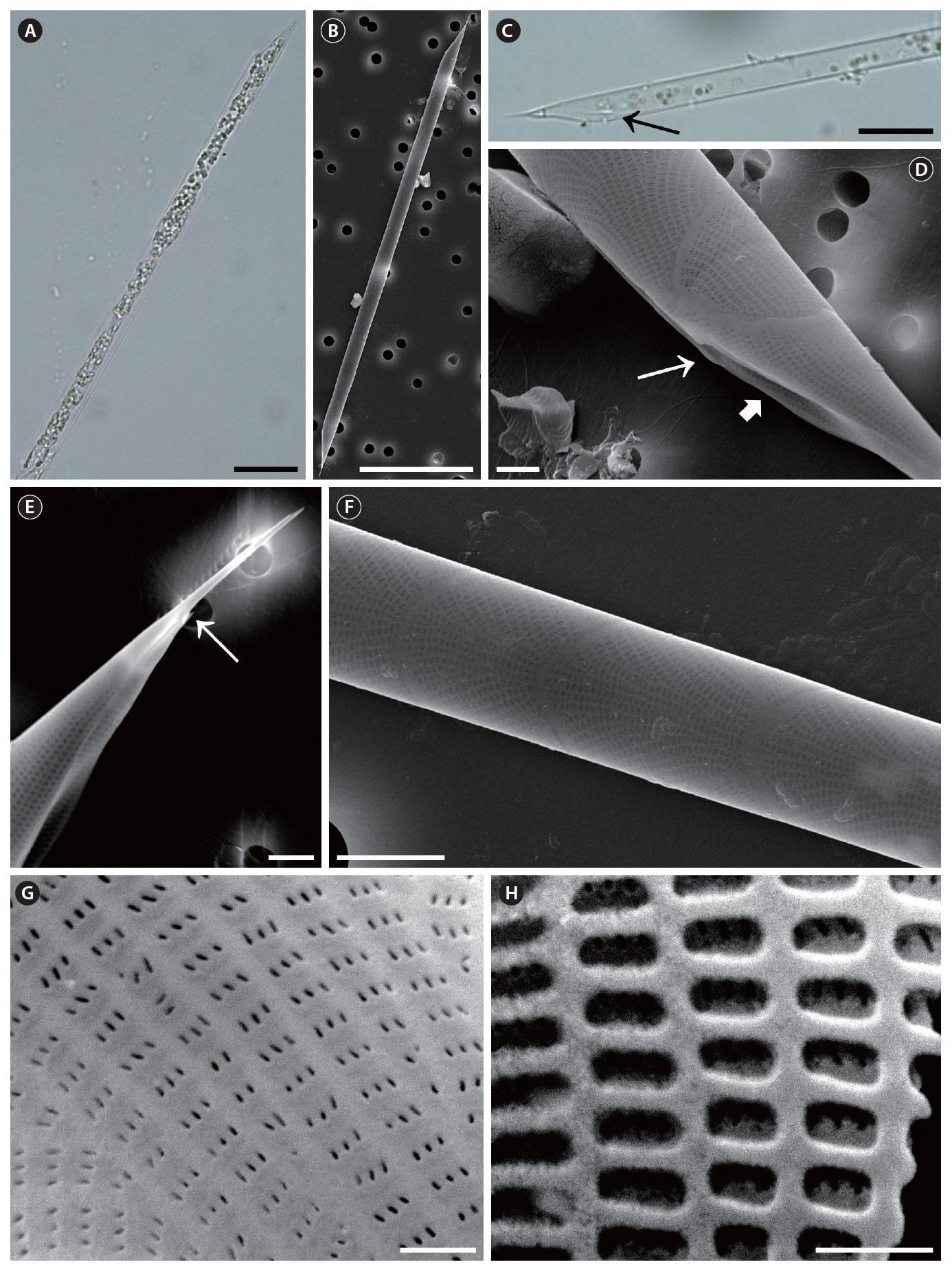
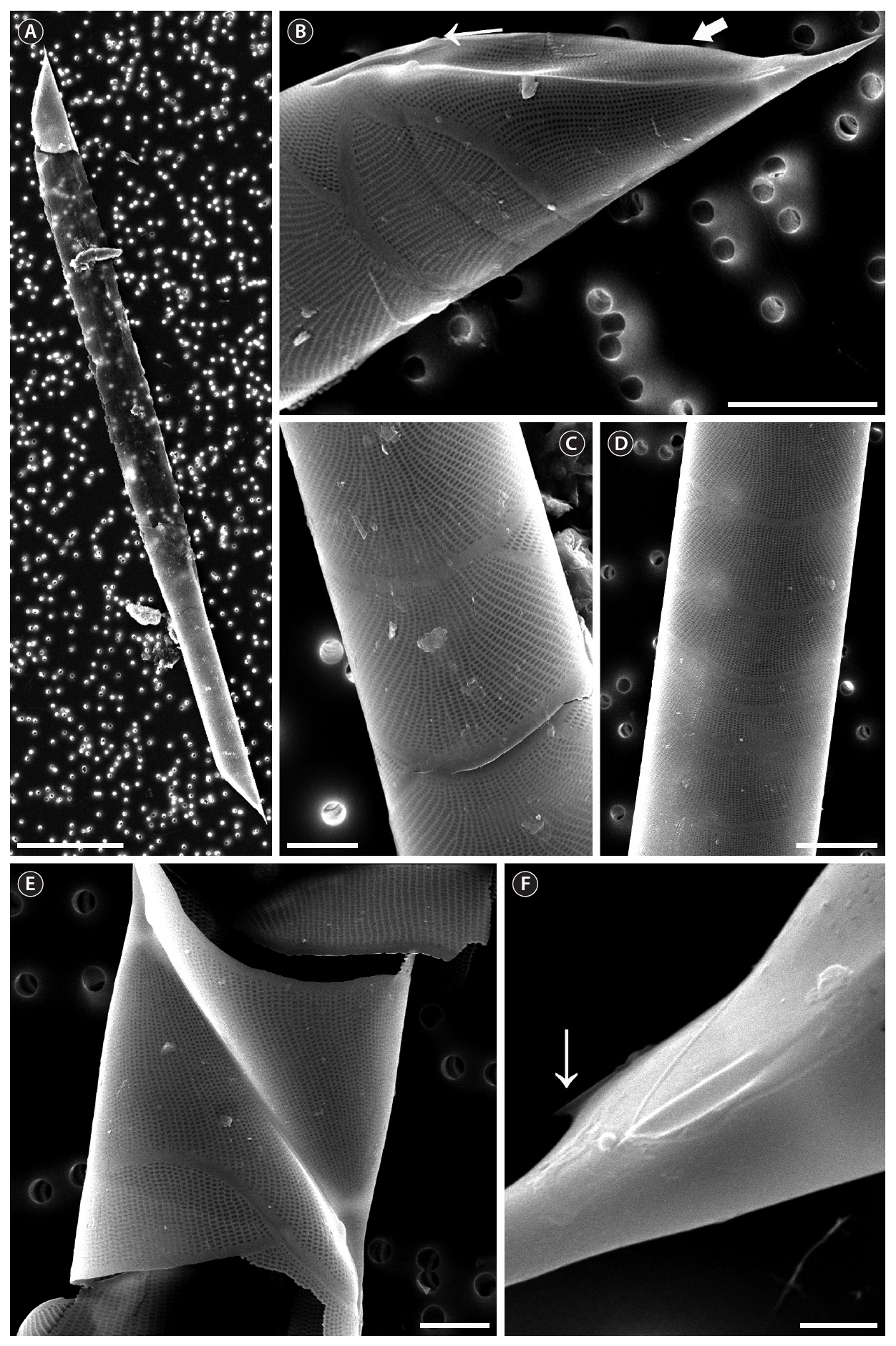
Rhizosolenia fallax Sundstrom, 1986 (
Sundstrom 1986, p. 89, Fig. 38 & 227-233; Hasle and Syvertsen 1996, p. 156, Pl. 29.
The cells are solitary, short chains forming, long and narrow cylindrical, bilaterally symmetrical, circular to slightly elliptical in cross-section. Specimens found in Korean coastal waters are 2.2-13.9 ㎛ in diameter and 70.0-248.5 ㎛ long. The valve is conoidal to sub-conoidal,bilaterally symmetrical, with the ventral part being much longer than the dorsal part. The contiguous area is large and limited by a well-developed, marginal ridge part, with noticeable claspers. The external process is displaced toward the apex of the apical valve, 3.3-9.1 ㎛ long, wide at the base, becoming tapering and tubular toward the distal part. Otaria are small and extend along the wide, basal part of the process, with the outer margin forming a finely pointed tip. The valve areolae are rounded rectangles, 21-22 in 10 ㎛, appearing in striae that converge at the apex. The segment horizontal and perpendicular axes are 2.2-13.9 ㎛ and 6.0-14.5 ㎛, respectively. The segments comprise a valvocopula, contiguous with most of the valve margin, and two lateral columns of squamiform to trapezoidal segments with hyaline edges. First segment close to the valvocopula gives the impression of an adjacent valve process at one side. The areolae of segments are rectangular, 20-42 in 10 ㎛. Striation in the girdle segments arranged in two patterns; straight in the central region and curved in the marginal region. A middle row of slit pores (usually 3 pores), with their long axes usually parallel to the areolae, perforate the velum structure of the valve and segments.
Distribution. According to Sundstrom (1986), the distribution of
Remarks. Hasle (1975) newly recorded
>
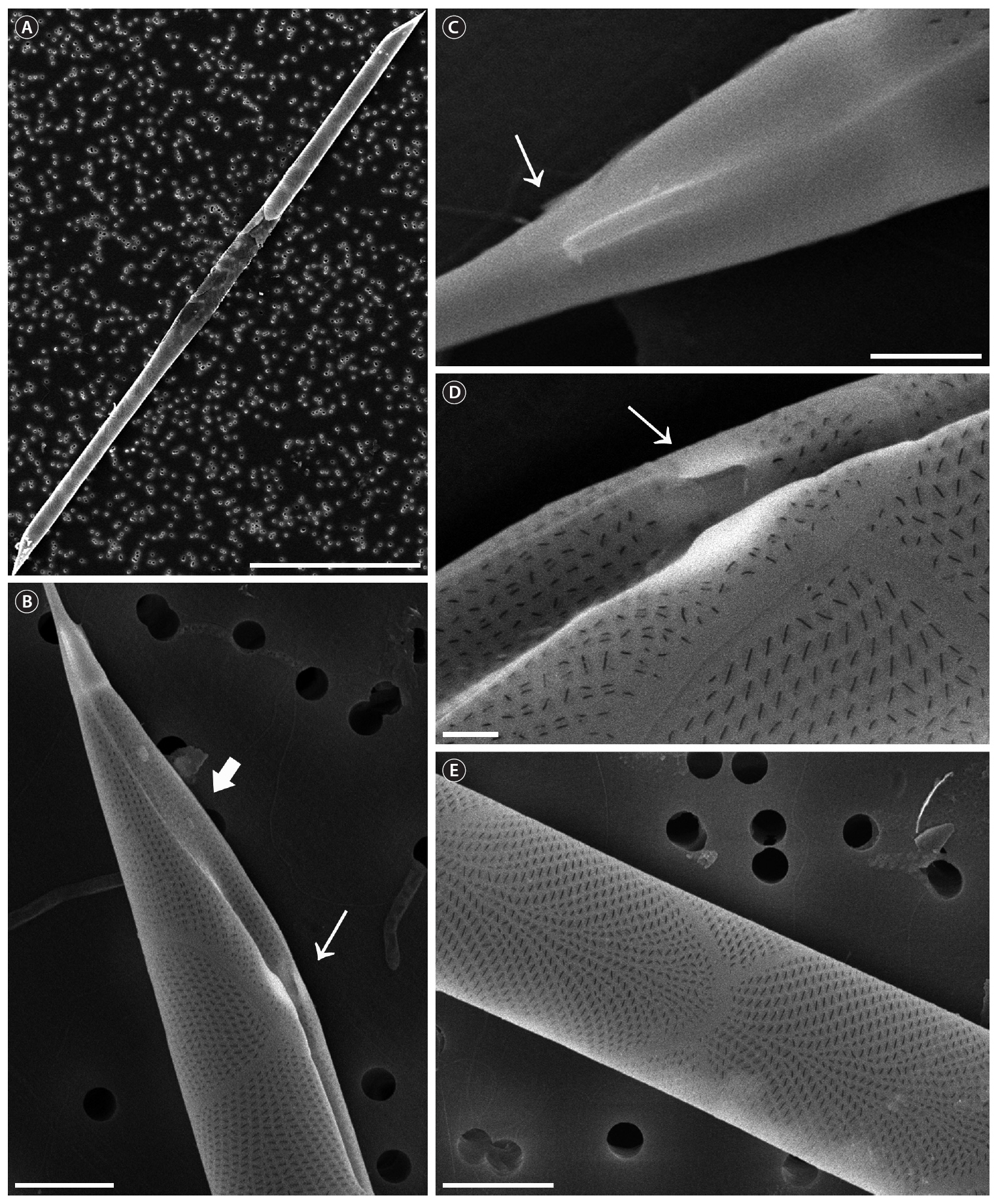
Rhizosolenia imbricata Brightwell, 1858 (
Brightwell 1858, p. 94, Pl. 5, Fig. 6; Van Heurck 1880-1881, Pl. 79, Fig. 5 & 6; Peragallo 1892, p. 113, Pl. 18, Fig. 2 & 3; Schroder 1906, Fig. 8; Hustedt 1930, p. 580, Fig. 331; Hendey 1964, p. 149, Pl. 3, Fig. 1 as
Synonyms.
The cells are solitary, short chain forming, long cylindrical,bilaterally symmetrical, circular to slightly elliptical in cross-section. Specimens found in Korean coastal waters are 7.3-60.0 ㎛ in diameter, 246.7-400.0 ㎛ long. The valve is obliquely conoidal, with the ventral part being much longer than the dorsal part. The contiguous area is broad, variable in shape, and it is limited by well-developed marginal ridges with noticeable claspers. The external process is narrow and distally tube-shaped, displaced toward the apical valve’s dorsal apex, 6.7-13.3 ㎛ long. Otaria are comparatively small and extend along the swollen basal part of the process, with the outer margin forming a fine point at the tip. The valve areolae are rounded rectangles arranged in striae, which converge
format the apex. The segment horizontal and perpendicular axes are 7.3-60.0 ㎛ and 10.0-18.2 ㎛, respectively. First segment close to the valvocopula bears the impression of the adjacent valve process toward one side. The segments’areolae are rectangular, 21-26 in 10 ㎛. Striation in the girdle segments curves toward the central region. A middle row of slit pores (usually 1 pore), with their long axes usually parallel to the areolae, perforate the velum structure of the valve and segments.
Distribution.
Remarks. Within its section,
>
Rhizosolenia sp. 1 (
Sundstrom 1986, p. 89, Fig. 38 & 227-233; Hasle and Syvertsen 1996, p. 156, Pl. 29.
The cells are solitary, short chain forming, long and narrow cylindrical, bilaterally symmetrical, circular to slightly elliptical in cross-section. Specimens are 15.5-35.3 ㎛ in diameter and 176.5-394.4 ㎛ long. The valve is conoidal to sub-conoidal, bilaterally symmetrical, with the ventral part being much longer than the dorsal part. contiguous area is broad, limited by a well-developed, marginal ridge part, with noticeable claspers. The external process is displaced toward the apical valve’s apex, 9.3-10.3 ㎛ long, and wide at the base, with a tapering tube shape toward the distal part. Otaria are small, extended along the wide basal part of the process, with the outer margin forming a fine point at the tip. The valve areolae are rounded rectangles, 21 in 10 ㎛, arranged in striae converging at the apex. The segment horizontal and perpendicular axes are 15.5-35.3 ㎛ and 11.7-12.8 ㎛, respectively. The segments comprise a valvocopula, contiguous with most of the valve margin, and squamiform to trapezoidal segments with hyaline edges, in two lateral columns. First segment close to the valvocopula shows the impression of the adjacent valve process toward one side. The areolae of segments are rectangular, 30-34 in 10 ㎛. Striation in the girdle segment arranged in two patterns: straight in the central region and curved in the marginal region. The velum structure of valve and segments are perforated by a middle row of slit pores (usually 3 pores) with long axes usually parallel to the areolae.
Distribution. In September 2008, we newly observed
Remarks.
>
Rhizosolenia sp. 2 (
Brightwell 1858, p. 94, Pl. 5, Fig. 6; Van Heurck 1880-1881, Pl. 79, Fig. 5 & 6; Peragallo 1892, p. 113, Pl. 18, Fig. 2 & 3; Schroder 1906, Fig. 8; Hustedt 1930, p. 580, Fig. 331; Hendey 1964, p. 149, Pl. 3, Fig. 1 as
The cells are solitary, short chain forming, long cylindrical,bilaterally symmetrical, circular to slightly elliptical in cross-section. Specimens are 7.6-20.8 ㎛ in diameter,426.7-437.0 ㎛ long. The valve is obliquely conoidal, with the ventral part much longer than the dorsal part. The broad contiguous area is limited by well-developed marginal ridges, with noticeable claspers. The external process is narrow, distally tubular, displaced toward the dorsal apex of the apical valve, 9.4-17.5 ㎛ long. Otaria are comparatively small, extending along the swollen basal part of the process, with the outer margin form-
ing a fine point at the tip. The valve areolae are rounded rectangles, arranged in striae converging at the apex. The segment horizontal and perpendicular axes are 7.6-20.8 ㎛ and 12.0-15.8 ㎛, respectively. First segment close to the valvocopula shows the impression of the adjacent valve process toward one side. The areolae of segments are rectangular, 26-35 in 10 ㎛. Striation in the girdle segments curves toward the central region. The velum structure of valve and segments are perforated by a middle row of slit pores (usually 1 pore) with the long axes commonly parallel to the areolae.
Distribution. In September 2008, we newly observed
Remarks.
In the present study, we recorded 5 species (including 2 unidentified species) belonging to the genus
According to Brunel (1962),
Sundstrom (1986) hesitated to consider
We provide here a key to the representatives of the genus