어떤 물질에 대한 독성을 평가하기 위해서는 그 물질이 일으킬 수 있는 급성 또는 만성적인 유해 작용과 이들 유해 작용 각각의 용량-반응관계를 확인해야 하는데 이러한 정보를 얻는데 가장 중요한 것이 바로 동물을 이용한 시험성적이다. 즉, 독성실험은 의약품 등의 시험물질 안전성 평가를 하기 위하여 중요한 기초자료이며, 필수적이라 할수 있다1).
독성연구의 주요목적은 신약의 안전성을 평가하여 임상적 용약의 안전을 확보하기 위해 시행하는 것으로, 독성실험은 크게 급성 독성실험(단회 투여 독성시험), 아급성 독성실험(;4주 반복투여 독성시험), 그리고 만성독성실험(;3개월 이상 반복투여 독성시험)으로 구분한다2).
이 중 4주 반복 독성실험은 아급성 독성실험에 해당되며, mouse와 rat와 같은 설치류와 개, 원숭이 등의 비설치류에 대한 독성실험 결과를 전임상 실험에서 요구하고 있다3). 4주 반복 독성실험의 의의는 시료의 독성에 대한 반응의 심각성 검토와 만성독성실험을 위한 적정 용량의 설정에 있다.
봉약침요법이란 살아 있는 꿀벌(Apis melifera)의 독낭에 들어있는 독을 인위적으로 추출·정제하여 질병과 유관한 부위 및 경혈에 주입함으로써 자침의 효과와 벌의 독이 지니고 있는 생화학적인 약리작용을 질병의 치료에 이용하는 신침요법을 말한다4).
벌의 독은 진통, 소염,5-6)항암7) 효과 등이 있어 퇴행성 관절염8-10)이나 류마티스 관절염11-12), 추간판 탈출증13-15), 편타 손상 등16-17)에 유효한 것으로 알려져 있다. 하지만 시술후에 나타나는 알레르기 반응과 벌의 독에 과민한 체질에서 발생하는 전신 알레르기 반응(;anaphylactic shock)등의 문제로 인해 대중화에 어려움을 겪고 있다.
이러한 문제점을 해결하기 위하여 개발된 것이 Sweet Bee Venom(특허 제 10-0744755, 이하 Sweet BV)이다18). Sweet BV는 건조 봉독에서 약 40-50%를 차지하는 분자량 2840의 melittin을 주성분으로19) 하며, gel filtration이라는단백질 분리기법을 이용하여 얻을 수 있다18). 이미 melittin은 소염, 진통, 항암 효과 등이 있음이 많은 연구보고20-21)를 통하여 알려져 있으며, 김 등22)이 “Sweet BV의 rat에 대한 단회 근육시술 독성시험”을 보고한 연속 연구의 일환으로 저자는 식품의약품 안전청의 독성시험기준3)에 근거하여 비설치류인 비글견을 대상으로 Sweet BV의 4주 반복 독성을 평가하여 유의한 결과를 얻었기에 보고하는 바이다.
시험물질을 전자저울 (;LA230S, CP323S, Sartorius, Germany)로 측량하여 조제병에 넣고, 부형제(;Normal Saline)를 일부 넣어 vortex mixer로 용해시키고, 실험에 필요한 농도로 만들어 사용하였다. Sweet BV는 시술 당일에 조제하여 사용하였다.
2.1) 실험동물 및 사육 환경
실험에 사용된 동물은 5∼6개월령의 Beagle 견(;Beijing Marshall Biotechonology, China)으로 암·수 각각 8마리씩 입수하여 사용하였다. 입수 시 수컷의 체중은 5.83∼7.27 ㎏이었고, 암컷은 5.45∼7.44 ㎏이었다. 입수 후 14일간의 검역·순화 기간 중 매일 1회씩 일반증상을 관찰하였고, 주 1회 체중을 측정하였으며 검역기간 종료 후에도 건강상태를 확인하였다. 실험실의 온도는 19.8∼23.2°C, 습도는 37.0∼69.8%를 유지하였고, 실험동물용 개 사료(;Agribrands Purina, Korea23)을 준수하여 비임상시험 인증기관인 (주)바이오톡스텍에서 시행하였다.
실험 개시 시 수컷의 체중은 6.54∼8.10 ㎏이었고, 암컷은 5.51∼8.14 ㎏이었다.
2.2) 군의 분리
군 분리는 검역·순화 기간 종료 후 체중을 기초로 하여 암·수 각각 대조군 2마리, Sweet BV 시술군(저, 중, 고용량군) 2마리씩 분리하였다.(Table 1.)
2.3) 1회 시술 용량의 설정 및 시술
Sweet BV의 임상적용 예정용량인 약 0.1∼0.4 ㎎/1회 (성인 60 kg 기준시 최대 0.007 ㎎/㎏)인 것을 참조하여 임상적용 예정용량의 약 80배인 0.56 ㎎/㎏을 고용량으로 설정하고, 0.14 및 0.28 ㎎/㎏을 저용량 및 중간 용량으로 설정하였다. 대조군에는 시험물질 시술군과 동일한액량의 부형제(;normal saline)를 시술하였다. 먼저 모든실험군의 좌측 대퇴부에 4주간 매일 1회씩 시술하였다.
3.1) 일반증상 관찰
관찰 기간 중 1일 1회 이상 음식물의 섭취나 호흡 등 Beagle 견의 일반적인 상태와 운동성, 불안 증상이나 수면 등 자율신경계의 이상 유무, 그리고 배설물 등의 변화를 관찰하였다. 그리고 1일 2회 사망동물의 유무를 확인하였으며, 최종 시술 후 14일까지 관찰하였다.
3.2) 체중측정 및 사료섭취량
체중은 시술당일 (시술 전), 시술 후 주 1회 측정하였으며, 상대 장기중량을 측정하기 위해 부검 시에는 절식체중을 측정하였다. 사료섭취량은 측정일의 전날에 공급한 사료(마리당 250g)와 동일한 시간대에 잔량을 측정하여 섭취량을 산출하였다.
3.3) 뇨 검사
시술 전 및 시술 4주에 자연배뇨방법으로 약 3 ㎖의 신선 뇨(배설 후 약 3시간 이내의 소변)를 채취하여 색상, 뇨비중, pH, protein 함량, glucose, 케톤체 그리고 bilirubin 등을 소변 화학 분석기(;MIDITRON Junior Ⅱ, Roche, Germany)를 사용하여 검사하였다.
3.4) 혈액학적 검사(CBC)
모든 동물에 대하여 시술 전 및 시술 4주 후 약 16시간 절식시킨 후 요측피정맥으로부터 약 3 ㎖의 혈액을 채취한 후 EDTA가 함유된 CBC bottle에 보관한 후 혈구분석기(;ADVIA 120, SIMENS, Germany)로 RBC, HGB, hematocrit, RBC indices(;MCV, MCH, MCHC), WBC, platelet count, 그리고 reticulocytes 등을 분석하였고, 혈액과 3.2 % sodium citrate을 9 : 1의 비율로 섞어 3,000 rpm으로 10분간 원심 분리하여 혈장을 분리한 후, 응고시간 분석기(ACL 7,000, Instrumentation Laboratory, USA)를 이용하여 prothrombin time, activated partial thromboplastin time 등을 관찰하였다.
3.5) 혈액생화학적 검사(;Biochemistry)
혈액학적 검사와 동일한 시간에 약 3 ㎖의 혈액을 채취한 후 3,000 rpm으로 10분간 원심 분리하여 혈장을 분리하였다. 분리한 혈장은 혈액생화학분석기(7080, HITACHI, Japan) 및 전기영동 분석기(Epalyzer2, HELENA, Japan)를 이용하여 AST, ALT, ALP, creatinine, total bilirubin, total protein, albumin, globulin, A/G ratio, total cholesterol, glucose, triglycerides, phosphorus, 그리고 calcium 등을 분석하였다.
3.6) 부검
관찰기간 종료 후, 모든 개체는 마취 하(;Lot No.: HAQ 8AV, thiopental sodium, 중외제약)에 방혈하여 안락사시킨 후 체표 및 전신의 조직에 대하여 상세한 육안 검사를 시행하였다.
3.7) 장기 중량 측정
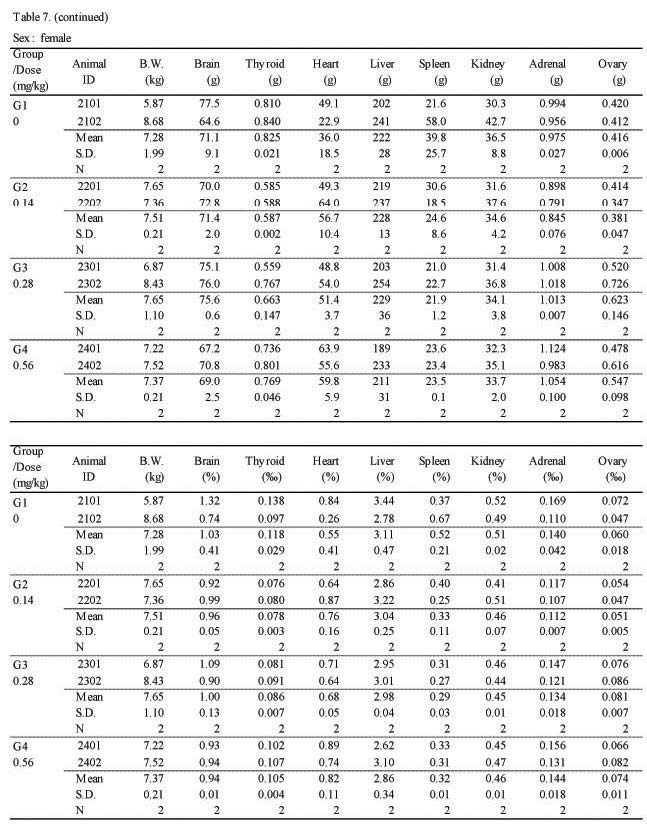
부검 시 개체별로 뇌, 심장, 간, 비장, 신장, 갑상선, 부신, 난소 그리고 고환 등의 장기들을 적출하여 습중량을 측정하였고, 체중에 대한 상대 장기중량을 산출하였다. 좌우가 있는 장기들은 합하여 무게를 측정하였다.
3.8) 조직병리학적 검사
부검 시 개체별로 실시한 대조군 및 실험군의 모든 동물에 대하여 뇌, 뇌하수체, 갑상선 및 부갑상선, 흉선, 폐 및 기관지, 심장, 간 및 담낭, 비장, 신장, 부신, 악하선(;mandibular gland), 하악림프절(;mandibular lymph node), 위, 공장(;jejunum), 결장(;colon), 맹장, 고환, 부고환(;epididymis), 전립선, 자궁, 대퇴골, 췌장, 난소, 방광, 안구및 시신경, 척수 및 투여 부위 등의 조직을 적출하여 10% 중성완충 포르말린용액 (;neutral buffered formalin)에 고정하였다.
고정한 조직은 삭정, 탈수 및 파라핀 포매 등의 일반적인 조직처리과정을 거쳐 조직절편을 제작하여 박절한 후, Hematoxylin & Eosin (;E) 염색을 실시하였다. 골조직의 탈회는 Calci-Clear-RapidTM액(;National diagnostics, USA)으로 실시하였다.
3.9) 통계처리
각각의 실험군의 개체가 2마리이므로 체중, 사료섭취량, 뇨검사, 혈액학적 검사, 혈액생화학적 검사 등에 대한 통계처리는 시행하지 않았고, 평균 및 표준편차를 구한 후 변화의 경향성을 파악하였다.
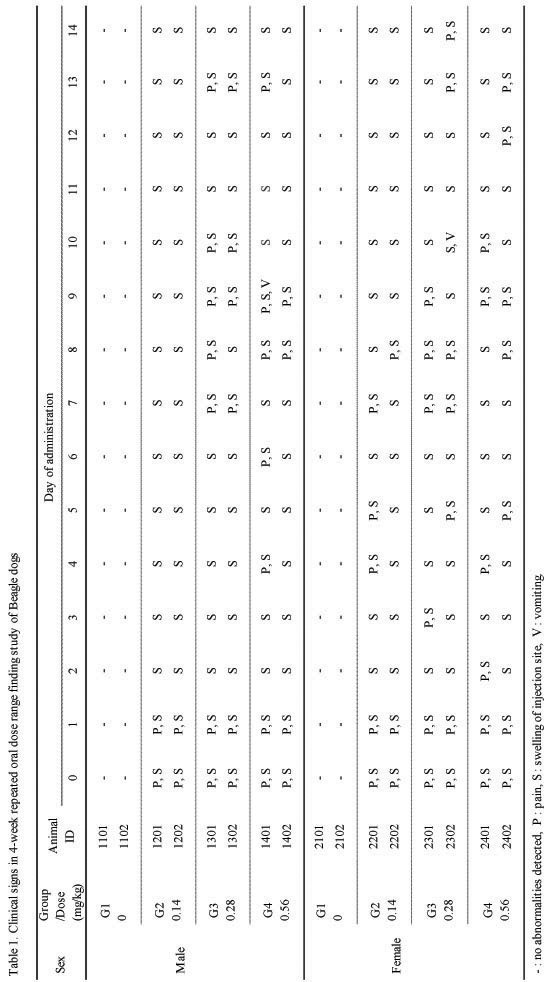
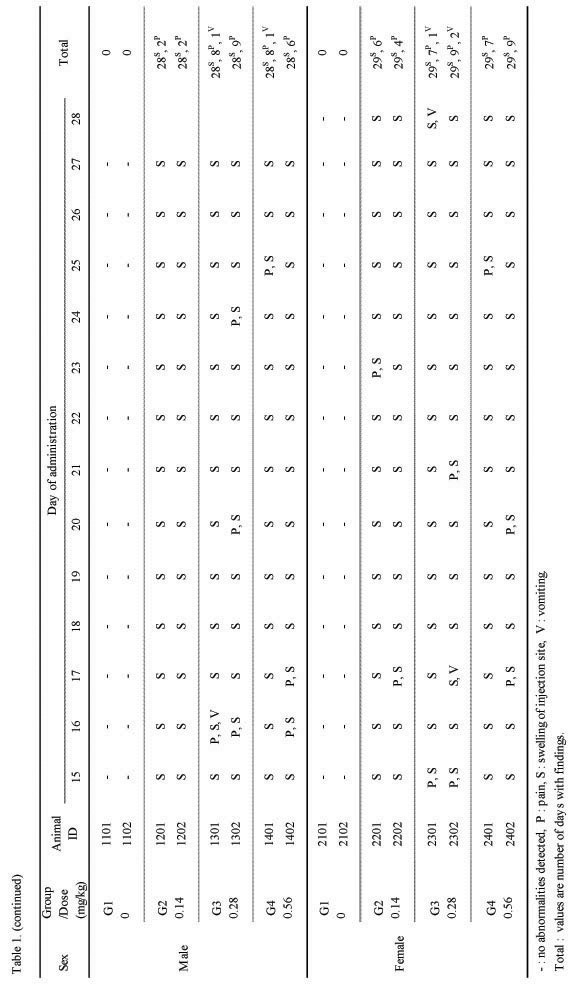
실험기간 동안, Beagle의 암·수 모두에서 사망 개체는 관찰되지 않았다. 일반증상의 관찰에서 용량에 상관없이 모든 실험군에서 Sweet BV 시술 후 약 10초간 지속되는 통증 반응이 관찰되었다. 이러한 반응은 첫 시술과 두 번째 시술에서 비교적 심하게 나타났고, 그 이후부터는 점차 감소하였으며, 점차 산발적으로 관찰되었다.
또한 모든 실험군에서 시술 부위에 종창이 발생하였는데, 경미하지만 용량 의존적인 경향을 나타내었고, 24시간 경과 후에는 많이 호전되는 순환적 양상을 나타내었다. 그 외, 일부 개체에서 우발적인 구토 증상이 2회 관찰되었다(Table 1.). 기타 음식물의 섭취나 대·소변, 수면 등에서는 정상군이나 대조군에 비하여 특이한 변화를 나타내지 않았고, 사망한 개체도 관찰되지 않았다.
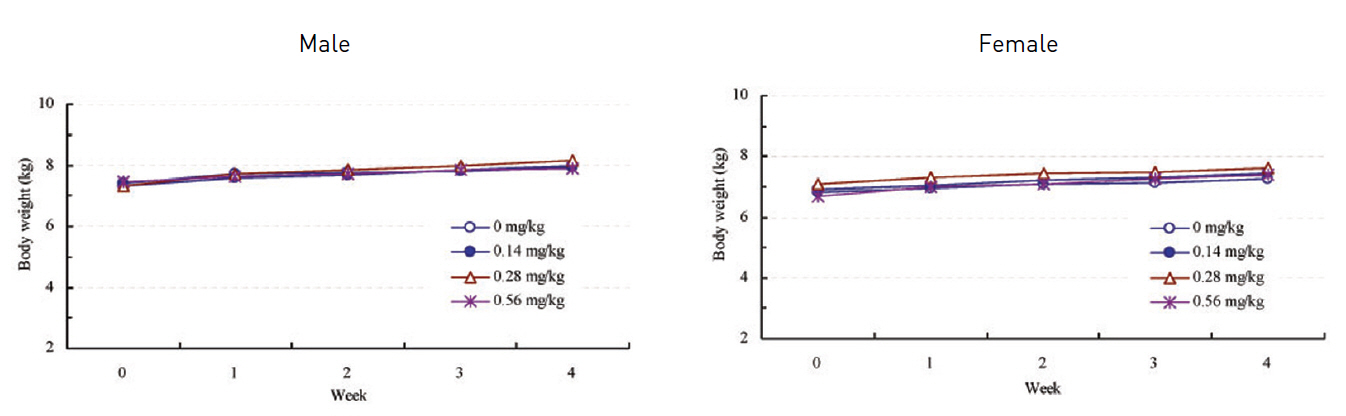
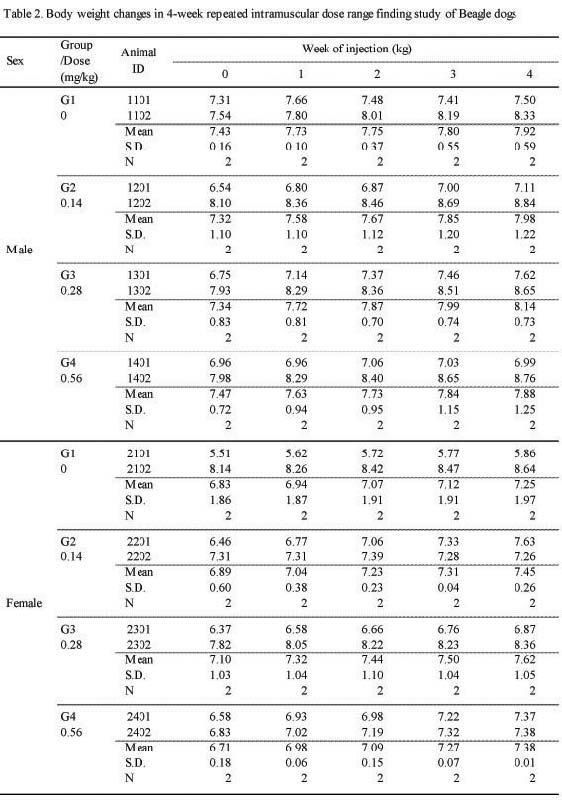
관찰기간 동안 실험군에서 암·수 모두 대조군과의 유의한 차이는 관찰되지 않았다(;Fig. 1, Table 2.).
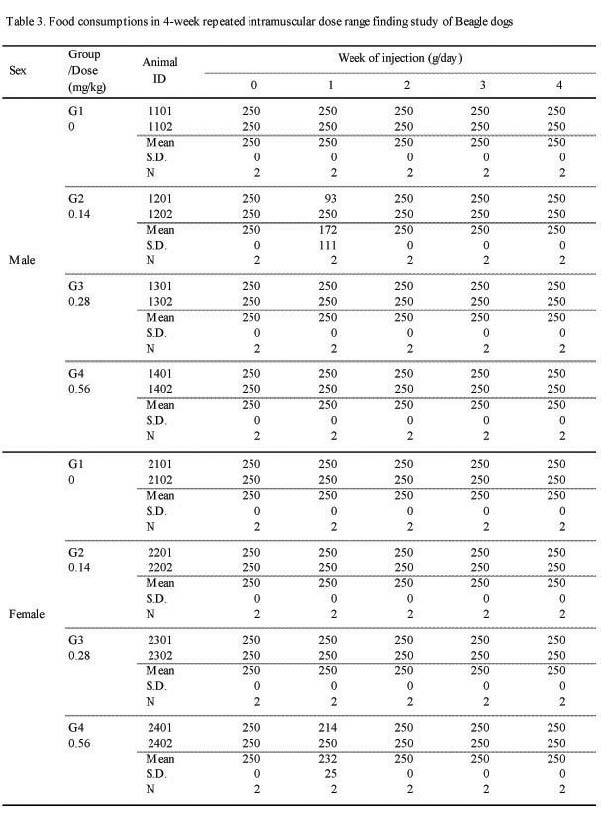
관찰기간 동안 실험군 모두 대조군과의 유의한 차이는관찰되지 않았다(Table 3.).
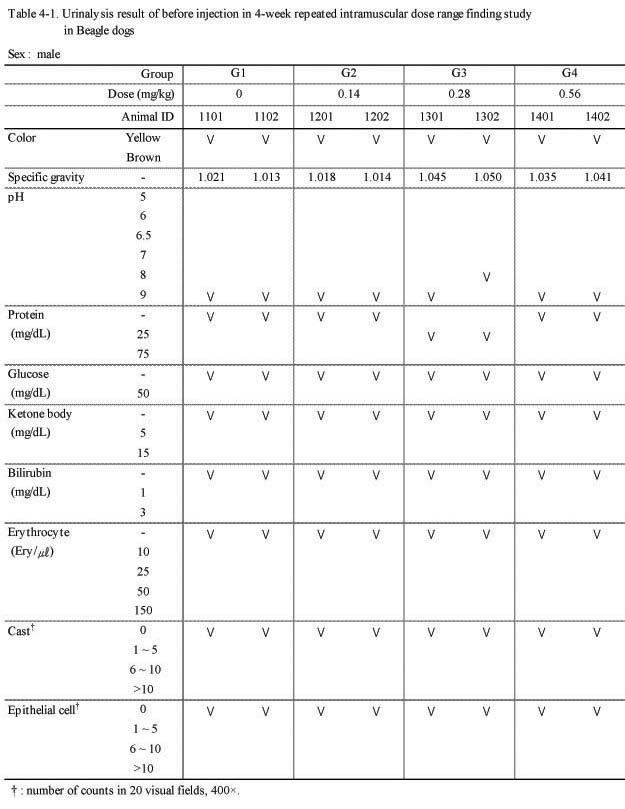
뇨 검사에서 실험군 모두 대조군과의 특이한 이상 변화는 관찰되지 않았다(Table 4-1., 4-2.).
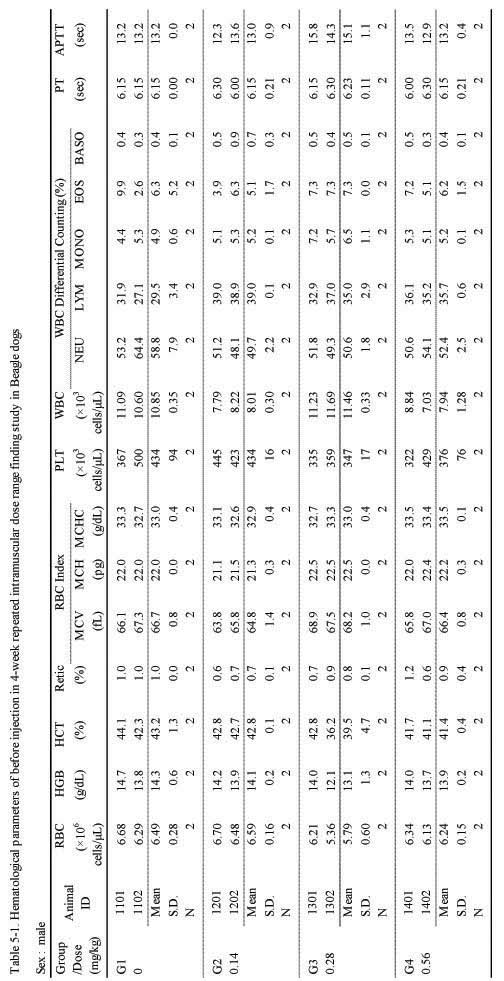
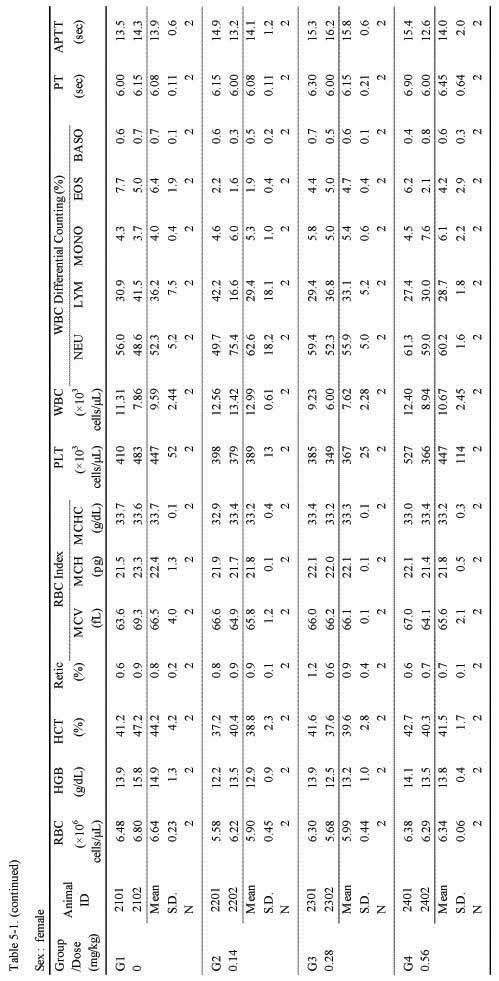
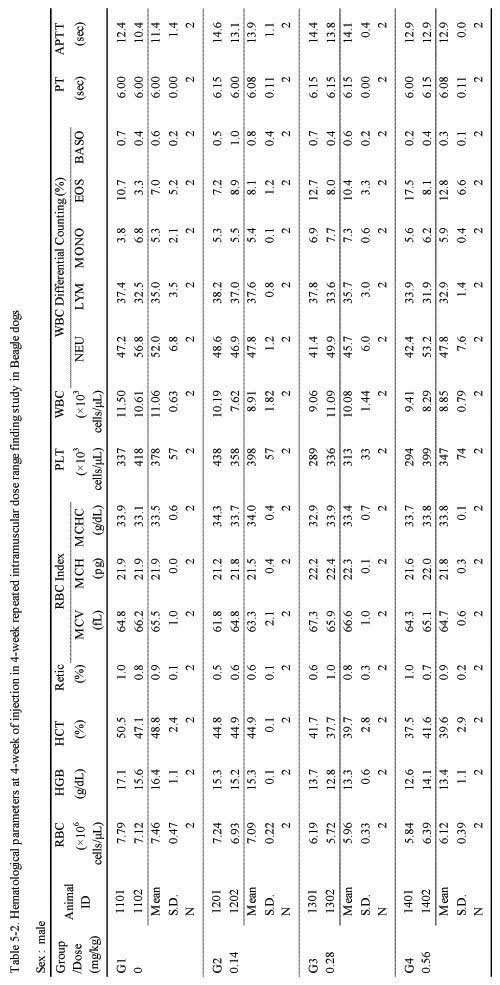
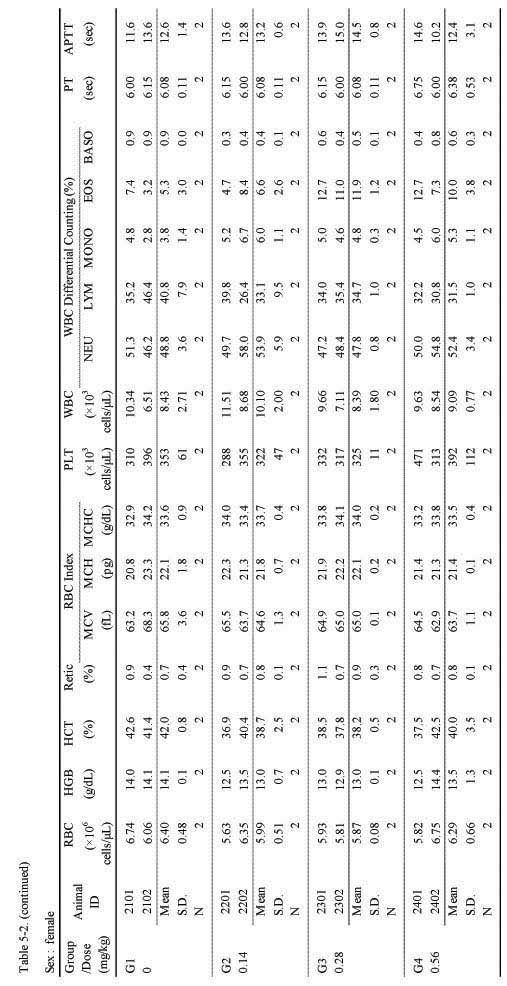
혈액학적 검사에서는 실험군 모두 대조군에 비하여 Sweet BV 시술로 추정할만한 이상 변화는 관찰되지 않았다(;Table 5-1, 5-2.).
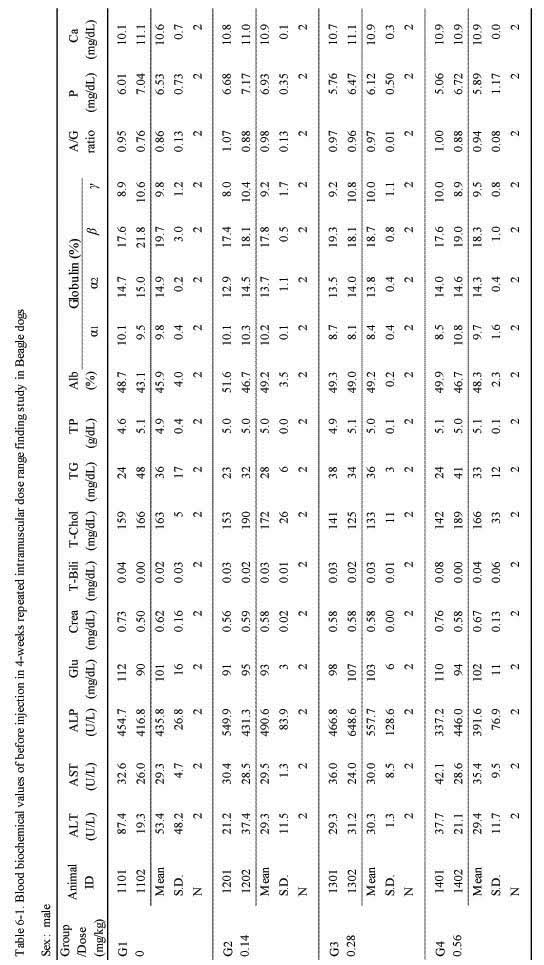
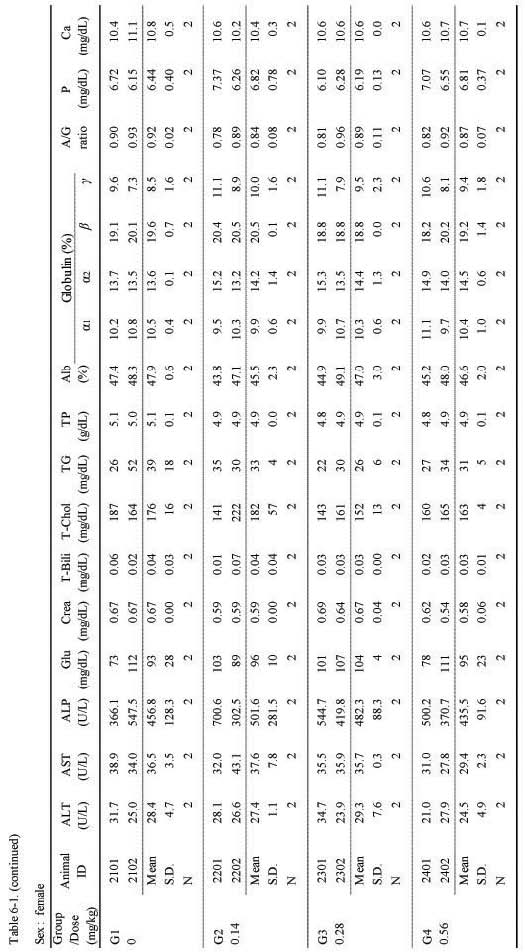
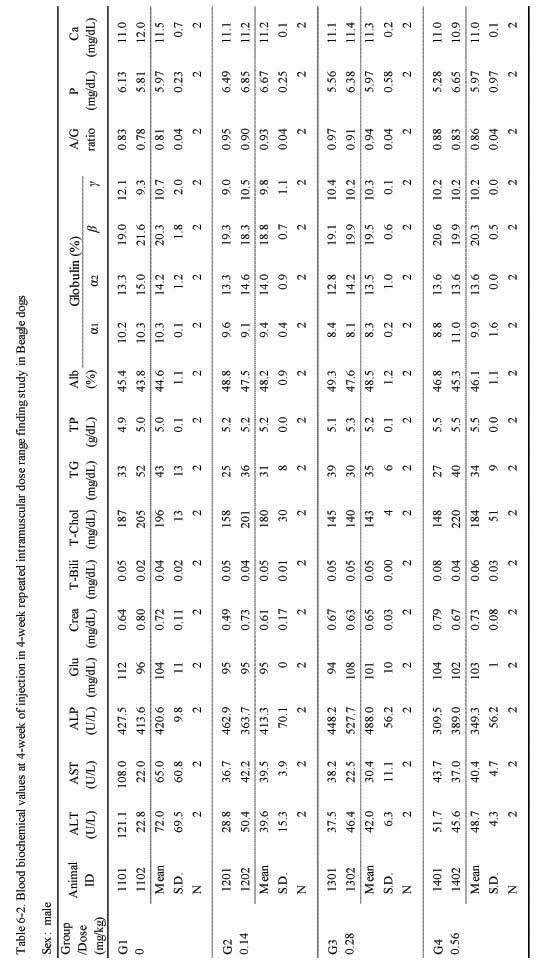
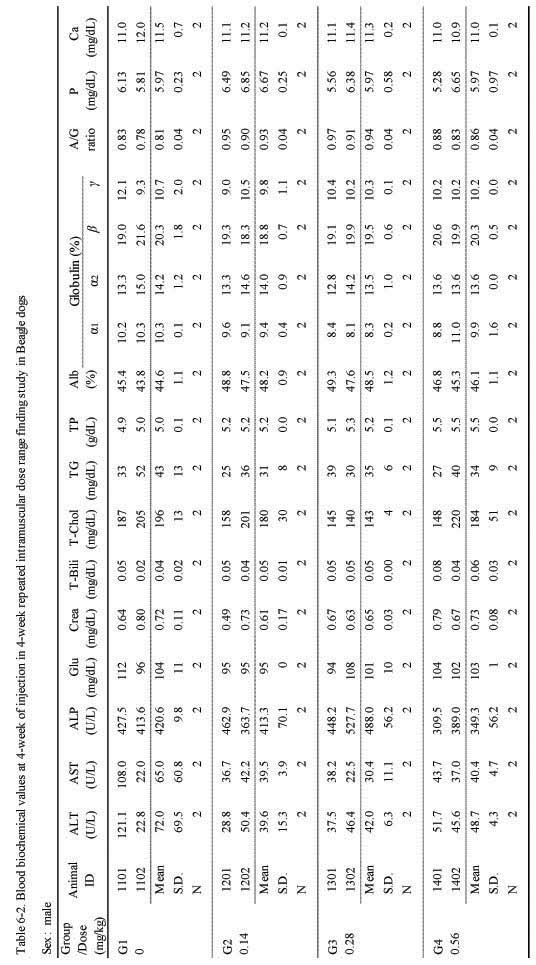
혈액생화학적 검사에서는 실험군 모두 대조군에 비하여 Sweet BV 시술로 추정할만한 이상 변화는 관찰되지 않았다(;Table 6-1., 6-2.).
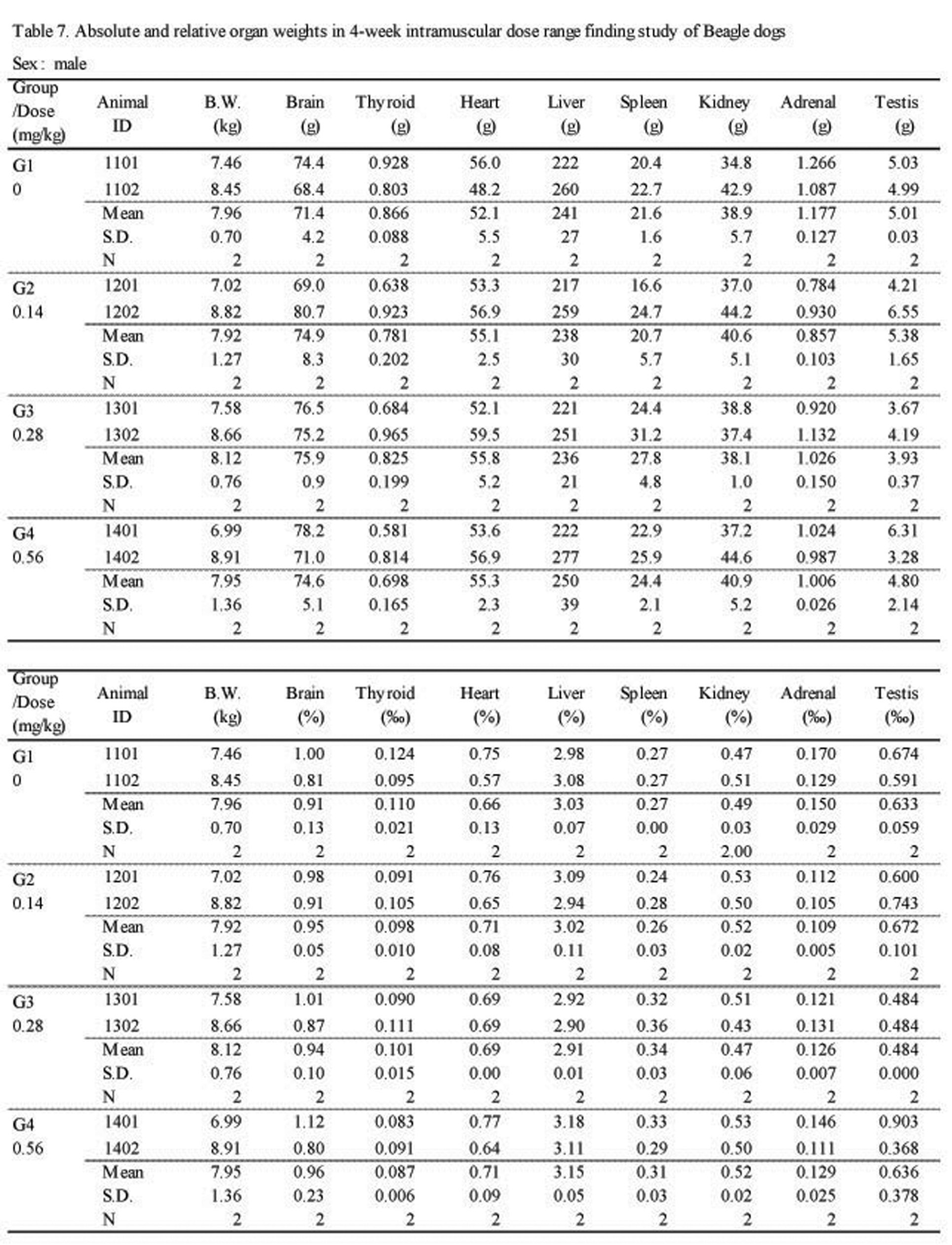
절대 및 상대 장기 중량 검사에서 실험군 모두 대조군에 비하여 Sweet BV 시술로 인한 이상변화는 관찰되지 않았다(Table 7.).
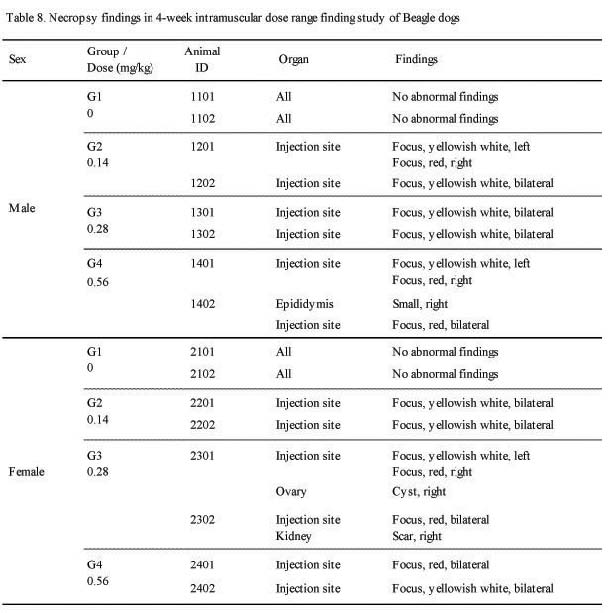
부검에서 암·수 모든 실험군에서 Sweet BV 시술 부위인 대퇴 근육에 국소성 황백색(;yellowish white), 또는 적색의 병소(;focus, red or pink)가 관찰되었고, 용량의존적인 경향을 나타내었다. 그 외 수컷 0.56 ㎎/㎏ 1례(;1402)에서 우측 부고환의 소형화가 발견되었고, 암컷 0.28 ㎎/㎏ 1례(;2301)에서 우측 난소의 낭포(;cyst) 및 우측 신장의 반흔(;scar) 조직이 관찰되었으나 이것이 Sweet BV 시술로 인한 것으로는 추정되지 않았다(Table 8.).
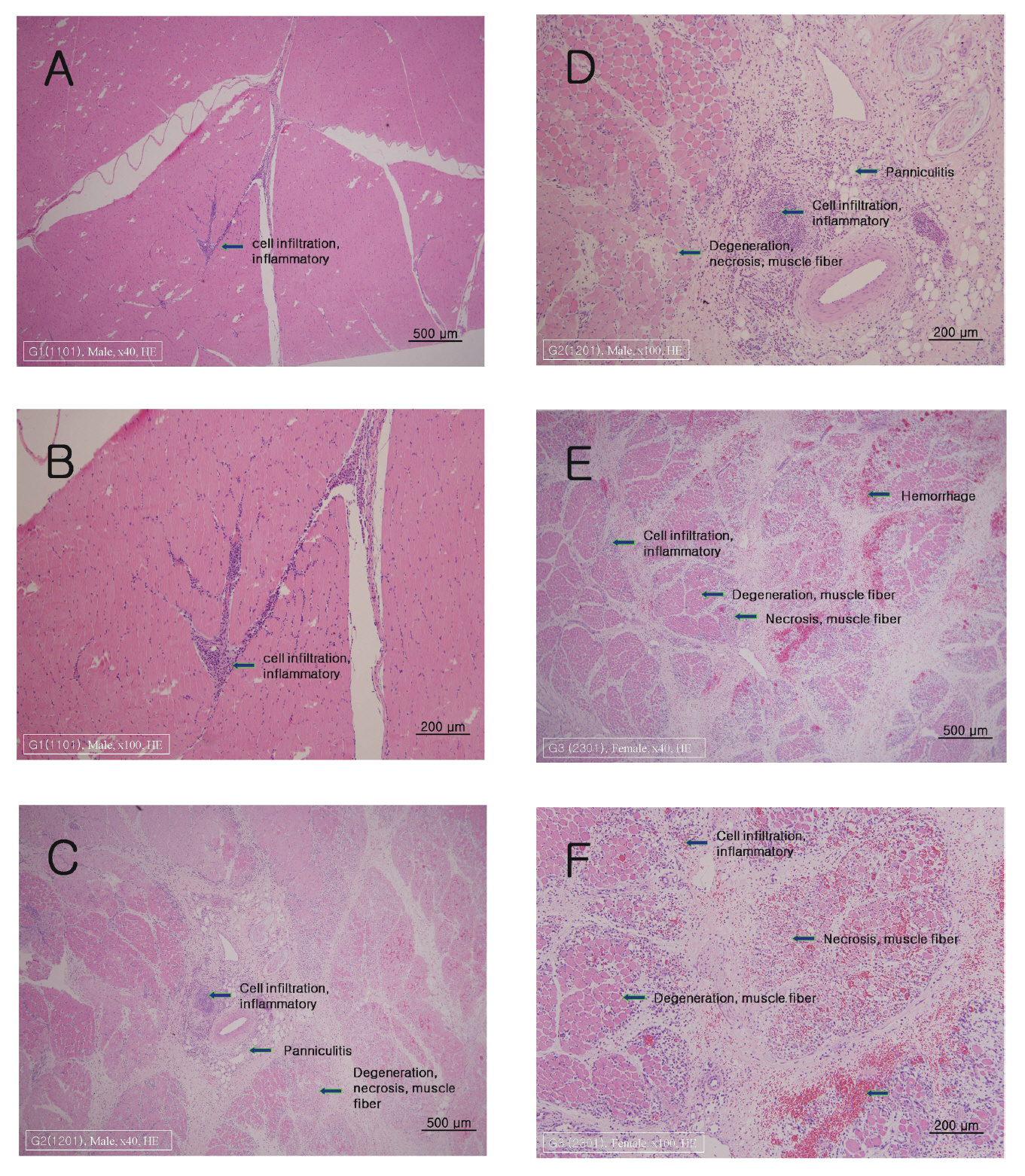
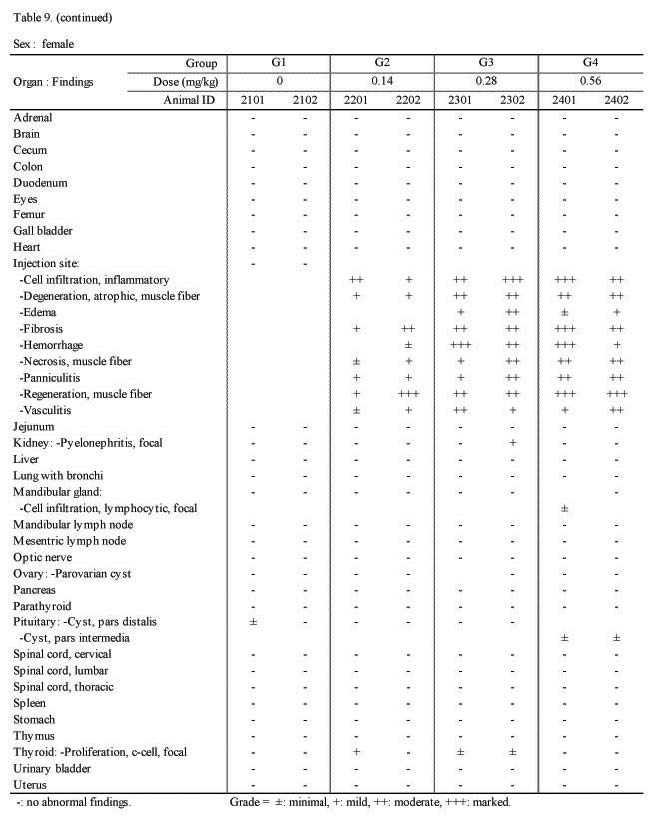
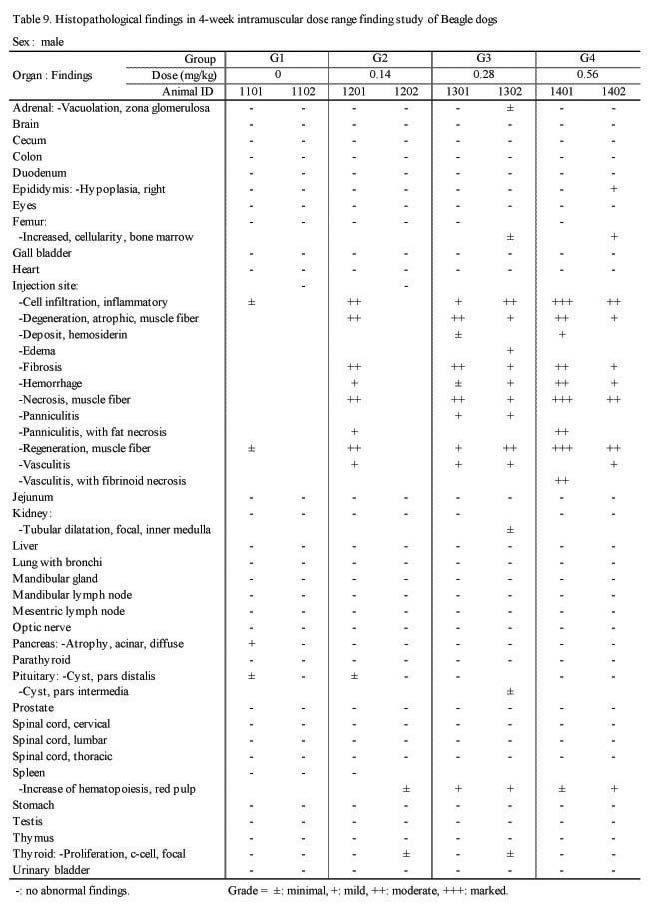
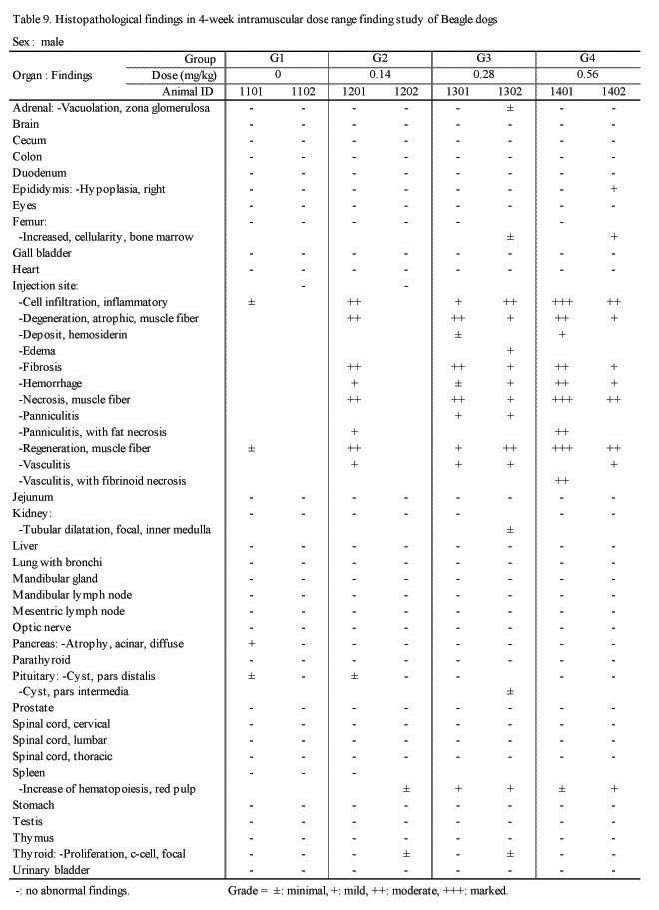
H&E 염색을 실시하여 조직 병리학적 검사를 시행한 결과 실험군의 암·수 모두 대조군과 비교하여 Sweet BV 시술 부위인 대퇴부의 근육에 근섬유의 괴사(;necrosis), 위축성 병변(;degenerative, atrophic change) 및 재생(;regeneration), 염증성 세포 침윤(;cell infiltration, inflammatory response), 혈관염(;vasculitis), 출혈(;hemorrhage), 혈철소 침착(;deposit, hemosiderin), 섬유화(;fibrosis), 부종(;edema) 및 지방층염(;panniculitis)등이 관찰되었다(Fig. 2, Table 9.).
또한 대조군에서도 주사침의 삽입에 의한 경미한 염증성 세포침윤 또는 근섬유의 재생소견이 관찰되었으며, 수컷의 대퇴골수에서 경미한 세포 충실도의 증가(;increased cellularity) 및 비장의 조혈반응(;increased of hematopoiesis)이 관찰되었다.
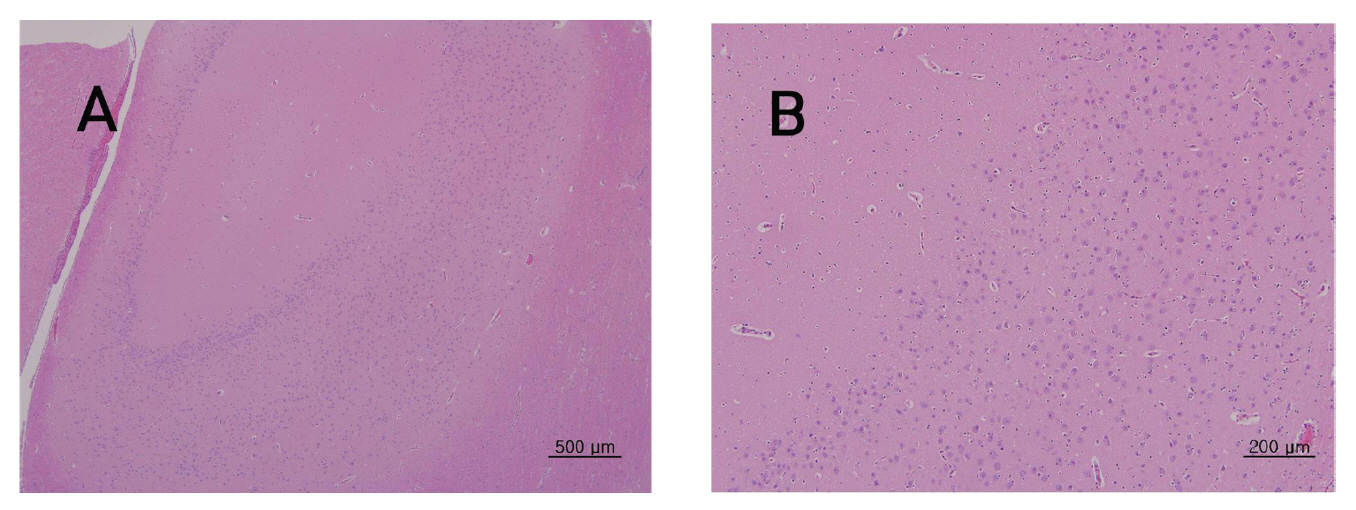
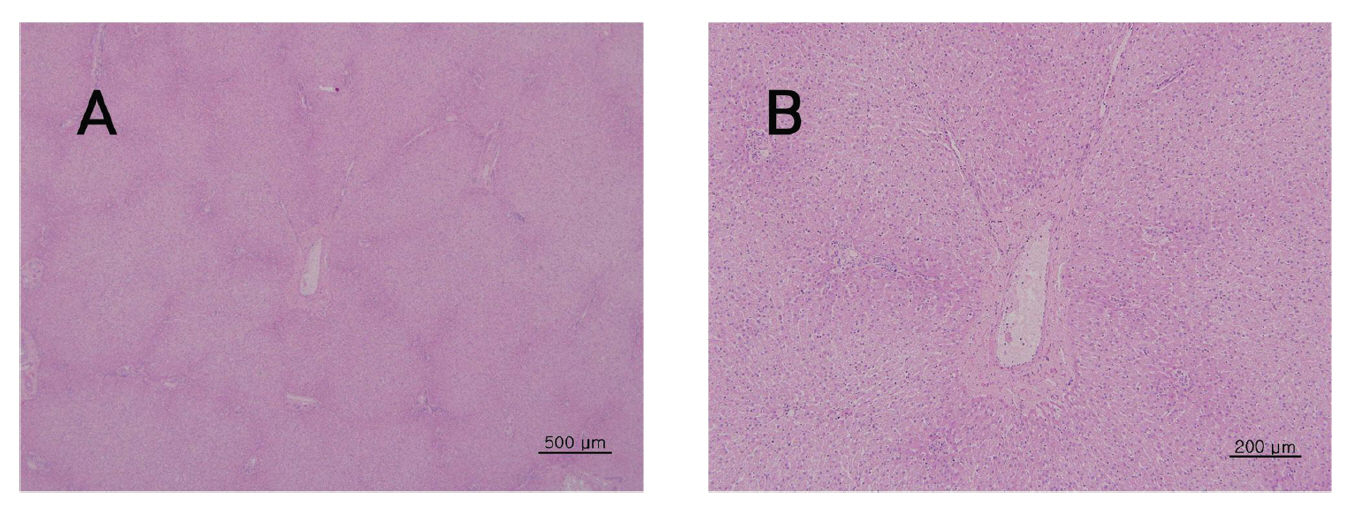
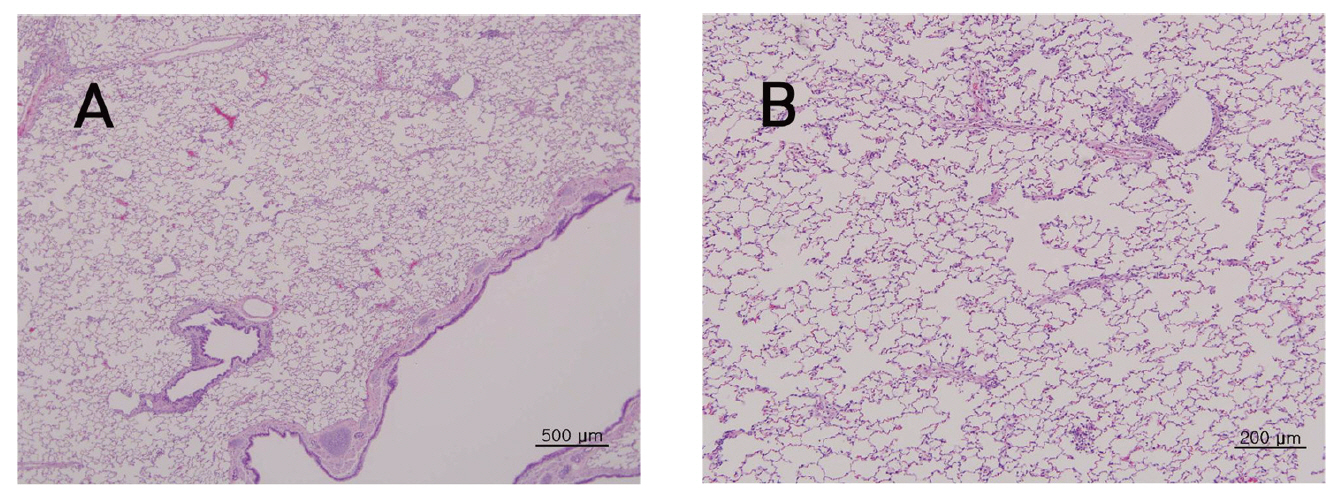
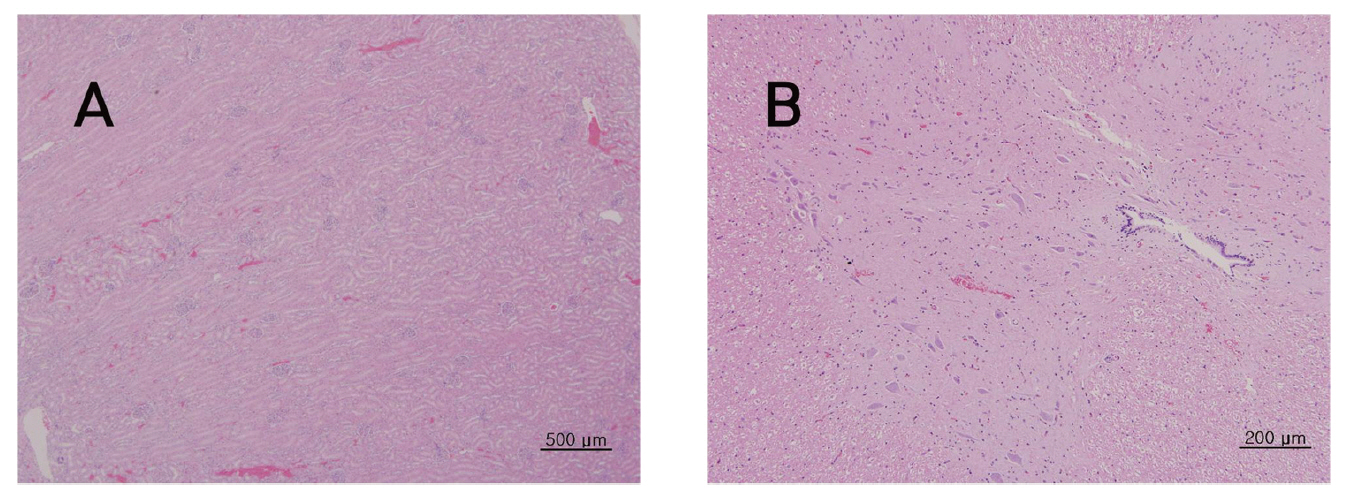
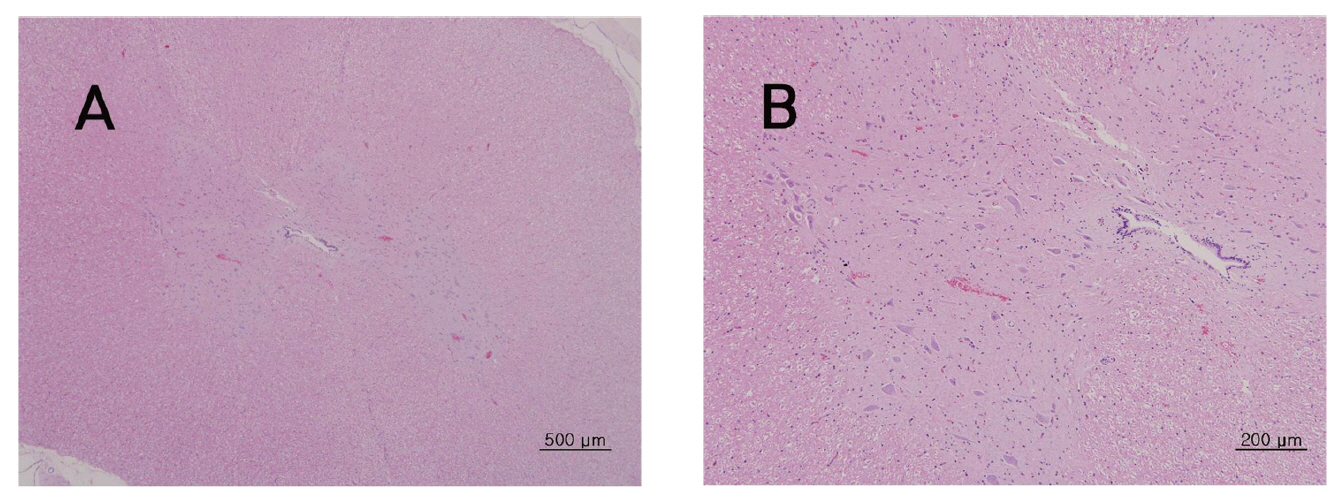
뇌, 간, 폐, 신장, 척수 등의 조직학적 관찰에서 대조군에 비하여 실험군에서 Sweet BV 시술로 인한 어떠한 이상소견도 관찰되지 않았다.(Fig 3-7)
그 외 육안소견에서 관찰된 우측 부고환의 소형화는 저형성(;hypoplasia), 우측 난소의 낭포(;cyst), 우측 신장의 국소성 신우신염(;pyelonephritis) 등은 개체의 우발적인 변화로 확인되었다.
기타 대조군 및 실험군에서 부신 사구체의 공포화(;vacuolation, zona glomerulosa), 신장의 바깥 수질에 국소성의 세뇨관 확장(;tubular dilatation, focal, inner medula), 췌장 선방세포의 미만성 위축(;atrophy, acina,diffuse), 뇌하수체의 원위부와 중간부에 낭(;cyst), 악하선에 국소성의 림프구성 침윤(;cell infiltration, lymphocytic, focal), 갑상선에 국소성의 c 세포증식(;proliferation,c-cell) 등의 소견이 확인되었으며, 이러한 변화는 자연발생적이거나 개체의 우발적인 이상조직으로 확인되었다(Fig. 3-7).
약침요법은 침구요법과 약물요법을 결합한 新鍼療法의 일종이다. 침구요법은 經絡論을, 약침요법은 氣味論을 바탕으로 하므로 약침요법은 經絡論과 氣味論을 근간으로 한다. 시술과정에서 주사기를 사용하나 치료 약물의 선정은 氣味論, 치료 부위의 선정은 經絡論을 위주로 하므로 약침요법은 과학기술 및 의료기기의 발달로 탄생한 한국 한의학의 독특한 치료기술이라고 할 수 있다4).
약침요법의 하나인 봉약침요법은 살아 있는 꿀벌(;Apis melifera)의 독낭에 들어있는 독을 인위적으로 추출·정제하여 질병과 유관한 부위 및 경혈에 주입함으로써 자침의 효과와 벌의 독이 지니고 있는 생화학적인 약리작용을 질병의 치료에 이용하는 新鍼療法으로, 자연계에 존재하는 동물성 독을 치료에 이용하는 “以毒治病”의 침구치료를 구현한 새로운 치료기술이다. 毒(;;poison, toxin, toxicant)이란 “여러 가지 경로를 통해서 소량이 체내로 들어오면, 생체조직에 기능적 혹은 형태적으로 장애를 주거나 혹은 치사작용을 일으키는 물질2)” 로 정의하고 있는 것처럼 봉약침도 벌의 독을 치료에 이용하므로 소량의 사용으로도 환자에게 심각한 부작용을 야기할 수 있다4).
한의학에서도 약재에 대하여 有毒, 無毒 등의 표현으로 독성을 분류하여 임상에 사용하고 있고, 본초학의 고서인 神農本草經에서도 독성의 强弱에 따라 上藥, 中藥,下藥의 세 가지로 나누어 上藥은 거의 無毒하면서 장기간 복용하여 輕身益氣, 不老延年 등의 효능이 있는 약으로,中藥은 약간의 독성을 지니면서 질병의 예방과 치료에 사용되는 약으로, 그리고 下藥은 독성이 강하여 장기간의 복용이 곤란하면서 질병을 치료하는 효과가 강한 약으로구분하고 있다24).
어떤 물질에 대한 독성을 평가하기 위해서는 그 물질이 일으킬 수 있는 급성 또는 만성적인 유해 작용과 이들 유해 작용 각각의 용량-반응관계를 확인해야 하는데 이러한 정보를 얻는데 가장 중요한 것이 바로 동물을 이용한 시험성적이다. 즉, 독성실험은 의약품 등의 시험물질 안전성 평가를 하기 위하여 중요한 기초자료이며, 필수적이라 할 수 있다3).
독성연구의 주요목적은 신약의 안정성을 평가하여 임상적 용약의 안전을 확보하기 위해 시행하는 것으로, 독성실험은 크게 급성 독성실험(단회 투여 독성시험), 아급성 독성실험(;4주 반복투여 독성시험), 그리고 만성독성실험(;3개월 이상 반복투여 독성시험)으로 나눈다2).
일반적으로 화학적 물질의 독성 반응은 물질의 물리-화학적 특성이나 노출경로, 생체 또는 사람의 감수성(;susceptibility)에 따라 다양한 결과를 나타낼 수 있으므로 독성의 측정은 다방면에서 실시되어야 한다. 특이적 화학물질의 노출 상태에 따라 독성에 영향을 미치는 주요인자는 투여경로, 시간, 빈도 등이 있다. 노출 경로는 독성 발현에 큰 변화를 나타내는데 생체 내에 노출되는 경로에 따라 정맥 내 > 흡입 > 복강 주사(;i.p) > 피하주사(;s.c) > 근육주사(;i.m) > 내피(경피) > 경구 > 국소(;topical)의 순으로 빠르고 강하게 나타나는 경향이 있다.
노출 기간과 빈도도 독성에 영향을 미치는 중요한 인자이고, 동물학자들은 동물의 노출을 급성, 아급성, 아만성, 만성의 4가지 범주로 나눈다. 급성은 24시간 내의 노출을, 아급성은 1개월 또는 1개월 이내의 노출을, 아만성은 1-3개월 간, 만성 노출은 3개월 이상을 말한다. 노출의 방법도 독의 작용에 차이를 가져올 수 있는데, 이에 따라 4주 반복 투여, 혹은 3개월 반복 투여 등으로 나누어 평가한다3).
화학물질의 원치 않는 독성효과에 대한 기준을 마련하기 위하여 우리나라에서도 이미 오랜 기간 독성의 성적수집을 촉진시키는 일련의 시험계획지침서(;testing protocol guideline)와 급·만성 도는 특수 독성 시험에 관한 지침이 공포되어 적용되고 있다.
식품의약품 안전청에서도 독성시험기준2)을 엄격하게제안하고 있고, 이러한 시험은 모두 GLP 규정에 의해 평가되어야 인정을 받을 수 있다23). 또한 의약품의 품목 허가 신고·심사 규정2)에서도 의약품의 안전성·유효성 심사를 위하여 제출해야 하는 자료로 첫째, 기원 및 발견의경위(배합목적 및 용도에 관한 자료 포함), 둘째, 물리화학적 성질, 규격에 관한 자료, 셋째, 안정성에 관한 자료,넷째, 독성에 관한 자료(보존제 및 타르색소의 경우에는 신약의 첨부자료에 준하며 그 외에는 4주 반복 투여독성, 반복투여독성, 기타 필요한 독성시험자료)를 제출해야 한다고 규정하고 있다. 이 중 4주 반복 투여 독성실험은 아급성 독성실험에 해당되며, 시료의 독성에 대한 반응의 심각성 검토와 만성독성실험을 위한 적정 용량의 설정을 위해 시행된다.
봉약침의 원료인 봉독은 크게 효소, 펩티드, 저분자 유기물질로 구성되어 있고 현재까지 약 40여개의 물질이 보고되고 있다19).
그동안의 연구 보고에 의하면 봉약침은 진통 소염효과5-6)가 있고, 면역계에 작용하며11-12, 20-21) 이미 많은 임상 보고를 통하여 퇴행성 슬관절염8-9)이나 고관절염10), 류마티스 관절염11-12), 요추간판 탈출증13-15), 중풍 후유증16-17)등의 질환이나 다발성 경화증25), 근위축성 측삭경화증26), 그리고 근이영양증27)과 같은 난치성 질환에도 유의한 치료효과가 있음이 보고되고 있다.
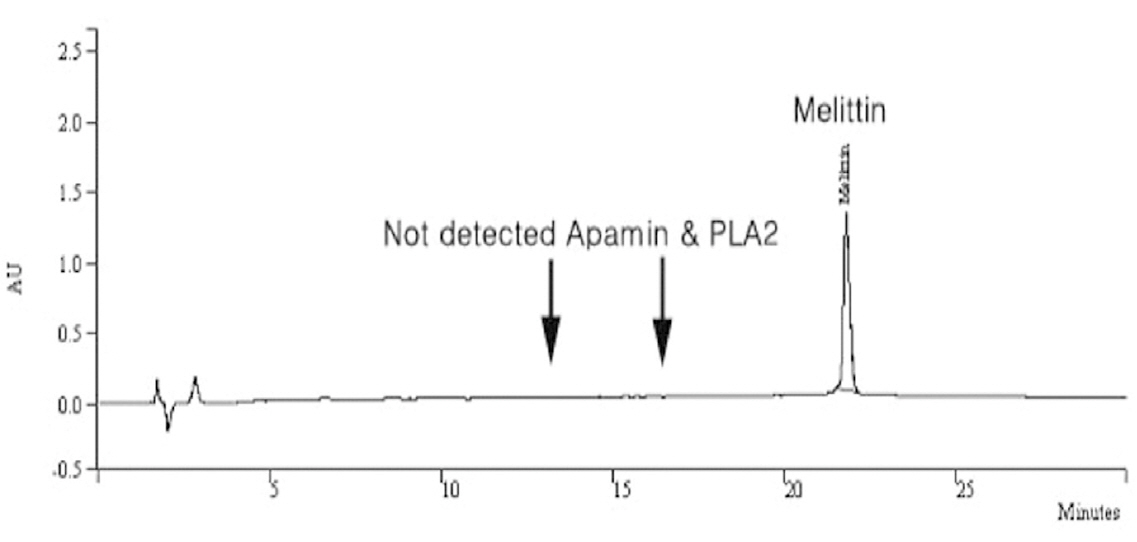
그러나 대부분의 독과 같이 벌의 독에 노출되었을 때도 과민한 면역반응이 나타날 수 있고, 특히 치명적인 아낙필락시 반응은 봉약침의 임상 사용에 중요한 걸림돌이되고 있어28-30) 이러한 문제를 개선하고자 봉약침의 항원역할을 하는 효소인 phospholipase A2(이하 PLA2)나hyaluronidase 등의 고분자 물질과 histamine 등의 저분자 물질을 함께 제거하고, 벌의 독에서 가장 주된 성분인 melittin을 주성분으로 분리 정제한 Sweet BV가 개발되었고18, 31)(;Fig. 8), 선행 연구를 통하여 봉약침에 의한 아나필락시 반응의 위험과 국소 알레르기 반응을 낮출 수 있음이 보고32-33)된 바 있다.
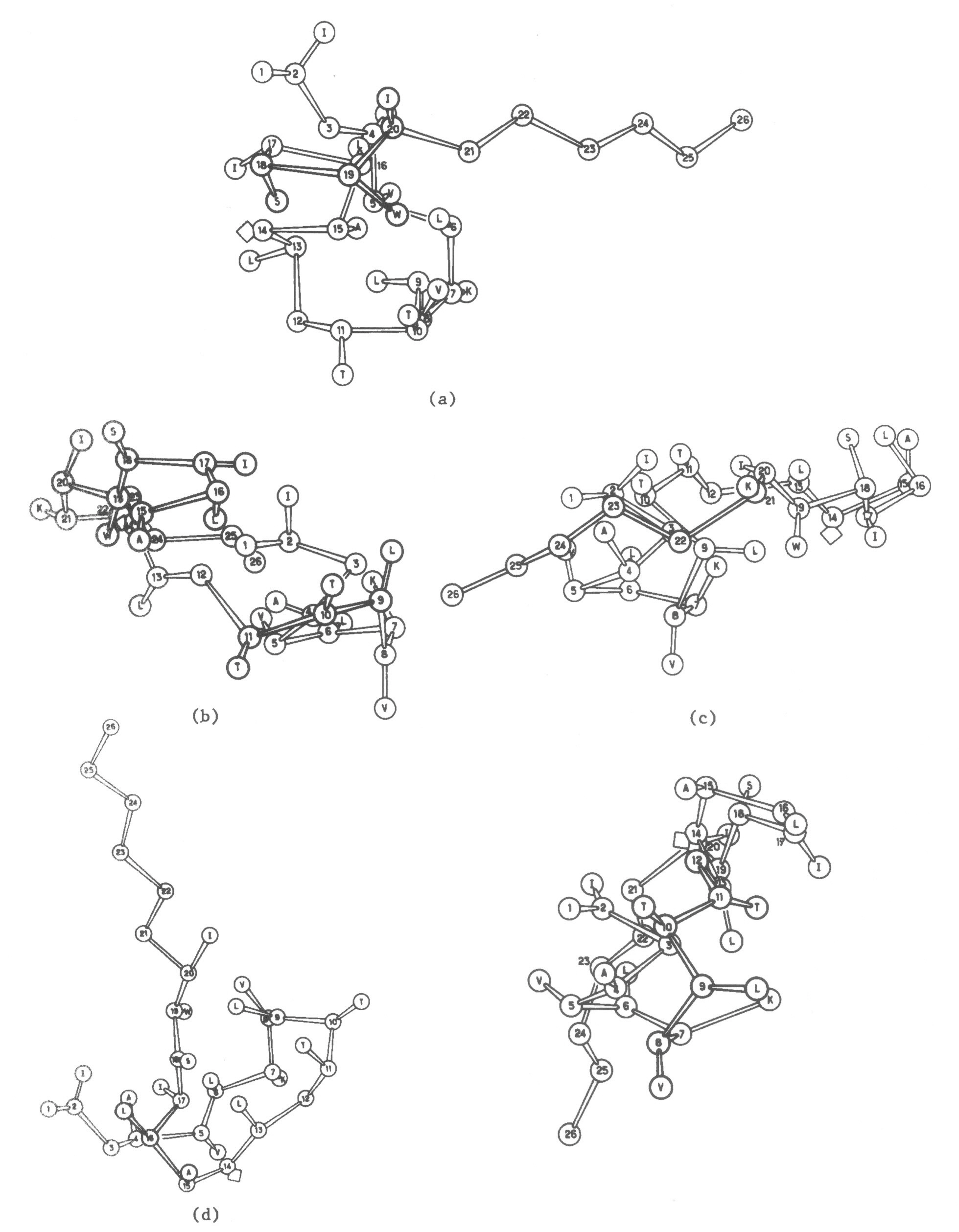
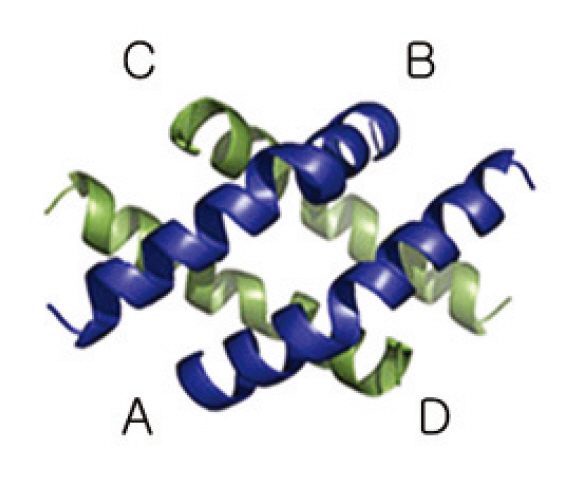
Melittin은 26개의 아미노산으로 구성된 peptide로 벌의 독에서 건조 중량 40-50%를 차지하는 분자량 2840의 수용성 물질이다34)(;Fig. 9-10). Melittin은 벌의 독에서 가장 중요한 allergen인 PLA2를 활성화시키고 세포막에 구멍을 뚫어 파괴시키는 작용이 있는 것으로 알려져 있는데 이러한 작용은 melittin의 구조(;Fig. 8, 9)와 관련이 있는 것으로 알려져 있다35). 각각의 사슬은 두 개의 나선구조로 되어 있고, 모두 휘어진 막대기 모양을 하고 있다. 이러한 구조는 세포의 용해 작용이 용이하고, 따라서 melittin이 암세포의 사멸이나 소염효과를 나타내는 것과 밀접한 관련이 있는 것으로 추정된다.
이미 이전의 보고21, 35)에서 melittin은 nuclear factor-κB(이하 NF-κB)의 활성을 조절하여 lipopolysaccharide(;LPS), tumor necrosis factor-α(;TNF-α), 그리고 sodium nitroprusside(;SNP)의 활성을 저해하여 염증의활성을 억제하는 것으로 알려져 있다.
NF-κB는 면역과 염증에 관여하는 많은 유전자들을 조절하는 인자이며 세포자멸사를 억제하는 것으로 알려져있다34). NF-κB군에는 NF-κB1(;p50), NF-κB2(;p52), Rel 단백인 RelA(p65), RelB, c-Rel 등이 있는데 NF-κB p50은 암세포의 발현에서 가장 빈번하게 발현되는 단백으로 특히 대장, 직장암의 발생과정에서 증가하는 것으로 알려져 있으며35) 암의 진행에 중요하게 작용하는 단백질이다. Melittin은 NF-κB p50의 활성을 저해하고 이를 통해 류마티스 관절염과 같은 염증성 질환을 억제하는 것으로 보고되고 있다36).
이에 저자는 이전의 결과22)를 바탕으로 Sweet BV의 4주 반복 독성을 알아보기 위해 Sweet BV의 임상적용 예정용량인 약 0.1∼0.4 ㎎/human/회 (성인 60 kg 기준시 최대 0.007 ㎎/㎏)을 참조하여 임상적용 예정용량의 약 80배인 0.56 ㎎/㎏을 고용량으로 설정하고, 0.14및 0.28 ㎎/㎏을 저용량 및 중간 용량으로 설정한 후 비설치류인 비글견 암·수 각각 4마리를 대조군과 실험군으로 나누어 4주간 반복적으로 대퇴부의 근육부위에 매일 1회씩 시술하여 나타나는 독성반응을 관찰하고자 하였다.
그 결과 일반증상 관찰에서 실험기간 동안 모든 실험군에서 사망 개체는 관찰되지 않았다. 그리고 용량에 상관없이 모든 실험군에서 Sweet BV 시술 후 약 10초간 지속되는 순간적인 통증 반응을 나타내었다. 이러한 반응은 첫 시술과 두 번째 시술에서 비교적 심하게 나타났고, 그 이후부터는 점차 감소하였으며, 점차 산발적으로 관찰되었다. 이러한 양상은 Sweet BV의 항원성에 대한 안정화 과정으로 시술 초기에는 알레르기 반응이 심하게 나타나지만 항원에 노출될수록 생체의 면역계가 점차 안정화되어 반응이 약화되는 봉약침과 동일한 경향을 나타내고있음을 알 수 있었다4).
또한 모든 실험군에서 시술 부위에 종창이 발생하였는데, 경미하지만 용량 의존적인 경향을 나타내었고, 24시간 경과 후에는 많이 호전되는 순환적 양상을 나타내었으며 통증에 대한 반응과 유사하게 점차 약해지는 경향을나타내었다. 그 외, 일부 개체에서 우발적인 구토 증상이 관찰되었는데, 이는 Sweet BV의 항원성에 대한 알레르기 반응에 의한 개체의 특이성으로 추정되었다.
체중의 변화는 관찰기간 동안 실험군에서 암·수 모두 대조군과의 유의한 차이는 관찰되지 않았다. 또한 사료섭취량에서도 실험군 모두 대조군과의 유의한 차이는 관찰되지 않았다.
뇨 검사 및 혈액학적 변화, 혈액 생화학 검사 등에서 실험군 모두 대조군과의 특이한 이상 변화는 관찰되지 않았다. 절대 및 상대 장기 중량 검사에서도 실험군 모두 대조군에 비하여 Sweet BV 시술로 인한 이상변화는 관찰되지 않았다.
부검에서는 암·수 모든 실험군에서 Sweet BV 시술부위인 대퇴 근육에 국소성 황백색(;yellowish white), 또는 적색의 병소(;focus, red or pink)가 관찰되었고, 용량의존적인 경향을 나타내었고 기타 부분적인 개체의 우측 부고환의 소형화, 우측 난소의 낭포 및 우측 신장의 반흔 조직 등이 관찰되었으나 이것이 Sweet BV 시술로 인한 것으로는 추정되지 않았다.
조직병리학적 검사에서는 실험군의 암·수 모두 대조군과 비교하여 Sweet BV 시술 부위인 대퇴부의 근육에 근섬유의 괴사(;necrosis), 위축성 병변(;degenerative, atrophic change) 및 재생(;regeneration), 염증성 세포침윤(;cell infiltration, inflammatory response), 혈관염(;vasculitis), 출혈(;hemorrhage), 혈철소 침착(;deposit, hemosiderin), 섬유화(;fibrosis), 부종(;edema) 및 지방층염(;panniculitis) 등이 관찰되었다(Fig. 2).
또한 대조군에서도 주사침의 삽입에 의한 경미한 염증성 세포침윤 또는 근섬유의 재생소견이 관찰되었으며, 수컷의 대퇴골수에서 경미한 세포 충실도의 증가(;increased cellularity) 및 비장의 조혈반응(;increased of hematopoiesis)이 관찰되었다.
그 외 육안소견에서 관찰된 우측 부고환의 소형화는 저형성(;hypoplasia), 우측 난소의 낭포(;cyst), 우측 신장의 국소성 신우신염(;pyelonephritis) 등은 개체의 우발적인 변화로 확인되었다.
기타 부신 사구체의 공포화(;vacuolation, zona glomerulosa), 신장의 바깥 수질에 국소성의 세뇨관 확장(;tubular dilatation, focal, inner medula), 췌장 선방세포의 미만성 위축(;atrophy, acina, diffuse), 뇌하수체의 원위부와 중간부에 낭(;cyst) 등의 소견이 확인되었으나 이러한 변화는 자연발생적이거나 개체의 우발적인 이상조직으로 확인되었다.
그 외에 뇌와 간, 폐, 신장, 척수 등의 장기조직에서도 Sweet BV의 시술에 의한 장기나 조직의 이상 유무는 관찰되지 않았다.
이상의 연구 결과 Sweet BV는 과량 주입할 때에 시술 부위를 중심으로 심한 통증과 국소적인 근육 조직의염증과 파괴, 그리고 이로 인한 섬유화를 발생시킬 수 있으며 장기나 조직에는 특별한 이상을 유발하지 않는 것으로 판단되었다. 또한 13주 반복 근육시술 독성실험에서는 장기간의 시술을 감안하여 본 실험에서의 1/2 용량인 0.07 및 0.14 ㎎/㎏을 저용량 및 중간 용량으로 설정하고 0.28 ㎎/㎏을 고용량으로 설정하는 것이 바람직할 것으로 판단되었다.
본 연구는 벌의 독에서 추출한 Sweet BV(;melittin)의 비설치류(비글견)에 대한 4주 반복 독성을 평가하고자 식품의약품안전청고시의 Good Laboratory Practice (;G LP) 규정을 준수하여 시도하였다. 그 결과 다음과 같은 결론을 얻었다.
1. 모든 실험군에서 사망한 계체가 관찰되지 않았다.
2. 시술 후 일반증상의 관찰에서 시술량에 상관없이 모든 실험군은 대조군에 비하여 시술 시에 심한 통증을 호소하였고 그 반응은 약 10초간 지속되었다. 통증은 시술이 반복될수록 점차 감소하거나 용량의존적으로 변하였다. 또한 시술 부위를 중심으로 충혈, 부종 등이 관찰되었고, 부종은 약 24시간 지속되었다. 전신 증상은 일부 개체에서 우발적인 구토가 간혹 관찰되었다.
3. 체중의 변화와 사료의 섭취량을 측정한 결과 암·수모두에서 대조군과 유의한 차이를 나타내지 않았다.
4. 뇨 검사, 혈액학적 검사, 혈액 생화학적 검사 등을 시행한 결과 실험군 모두에서 대조군과 유의한 차이를 나타내지 않았다.
5. 장기의 중량 측정에서도 실험군 모두 대조군과 유의한 차이를 나타내지 않았다.
6. 장기와 조직의 이상 유무를 확인하기 위하여 조직학적 관찰을 시도한 결과 시술 부위의 대퇴부의 근육에서는 근섬유의 괴사, 위축성 병변 및 재생, 염증성 세포 침윤, 혈관염, 출혈 등이 관찰되었다. 기타 장기와 조직에는 이상 소견이 관찰되지 않았고 개체의 특이성이나 우발적인 병소 소견이 간헐적으로 관찰되었으며 Sweet BV의 시술로 추정될만한 변화는 없었다.
7. 13주 반복 근육시술 독성실험에서는 장기간의 시술을 감안하여 본 실험에서의 1/2 용량인 0.07 및 0.14 ㎎/㎏을 저용량 및 중간 용량으로 설정하고 0.28 ㎎/㎏을 고용량으로 설정하는 것이 바람직할 것으로 판단되었다.
이상의 연구 결과를 바탕으로 Sweet BV는 약침으로 임상에 사용하기에 안전한 치료제임을 알 수 있었다. 향후 이에 대한 보다 다양한 연구가 진행되어야 할 것으로 사려된다.
[Table 1-1] Clinical signs in 4-week repeated oral dose range finding study of Beagle dogs
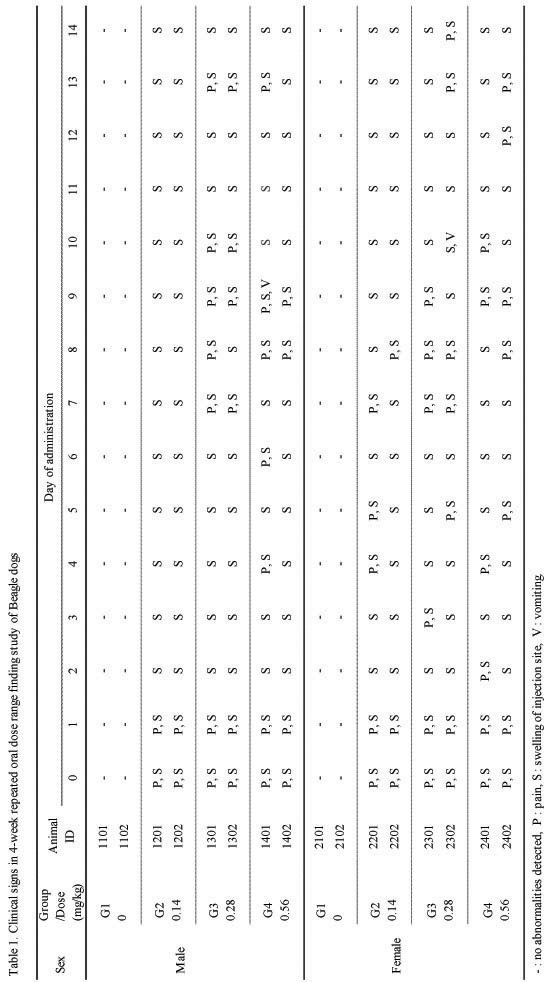
Clinical signs in 4-week repeated oral dose range finding study of Beagle dogs
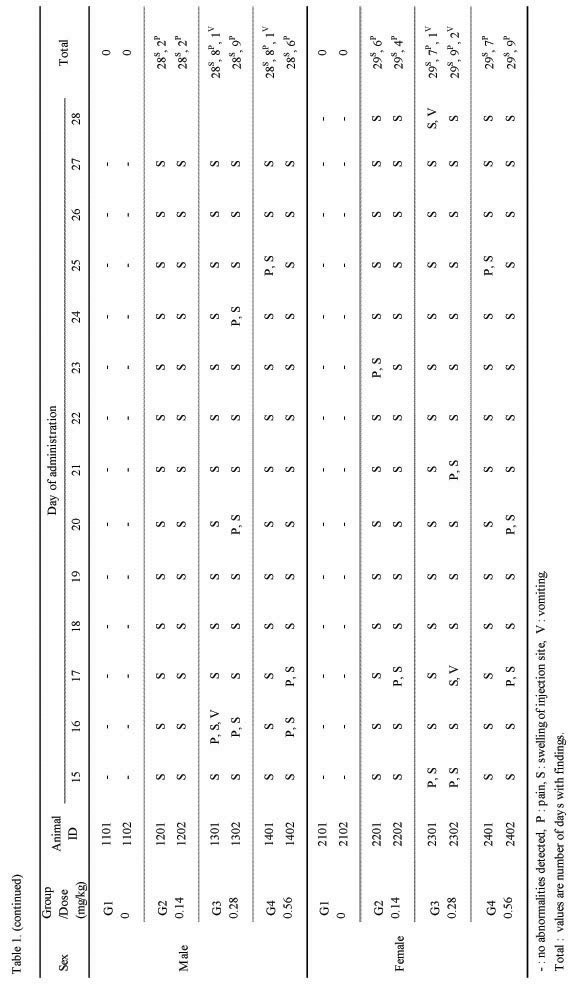
(continued)
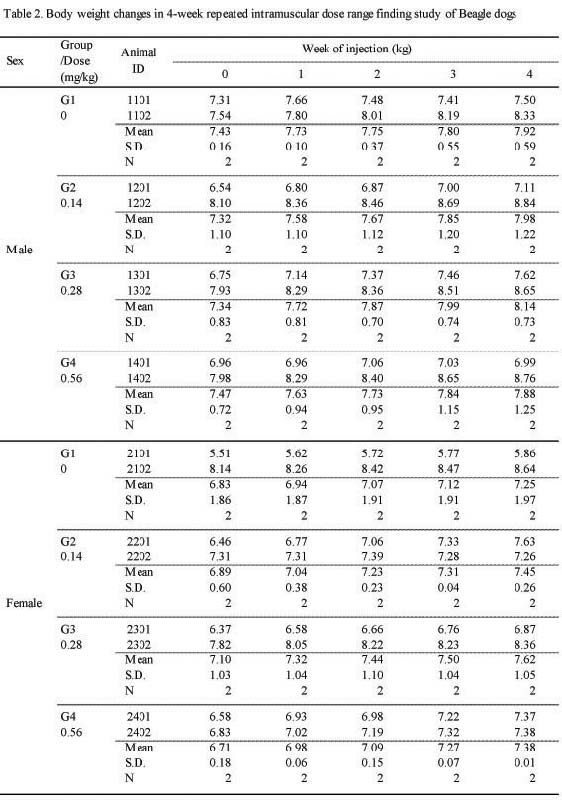
Body weight changes in 4-week repeated intramuscular dose range finding study of Beagle dogs
[Table 3] Food consumptions in 4-week repeated intramuscular dose range finding study of Beagle dogs
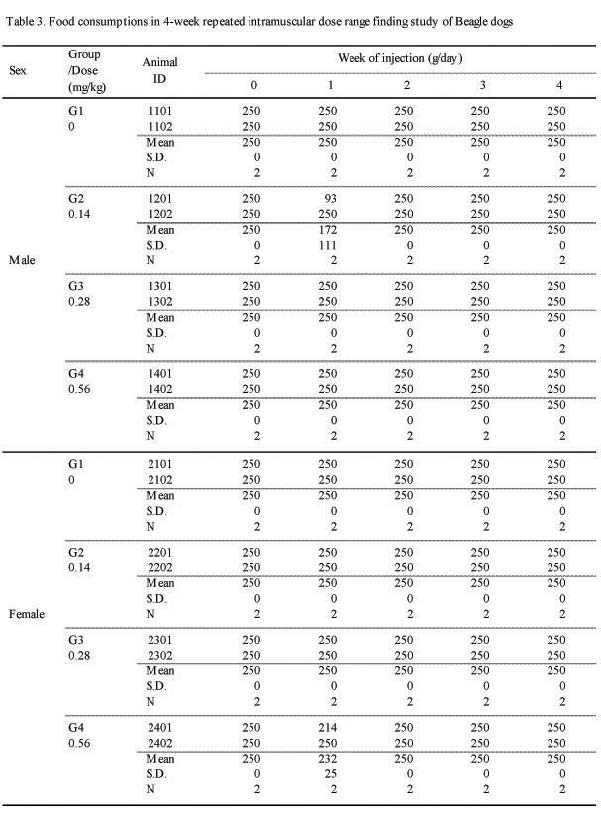
Food consumptions in 4-week repeated intramuscular dose range finding study of Beagle dogs
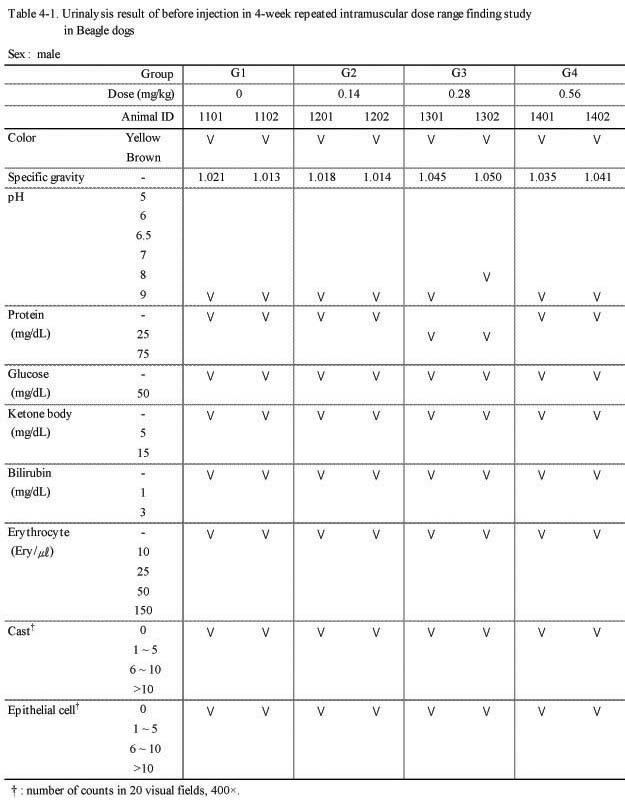
Urinalysis result of before injection in 4-week repeated intramuscular dose range finding study in Beagle dogs
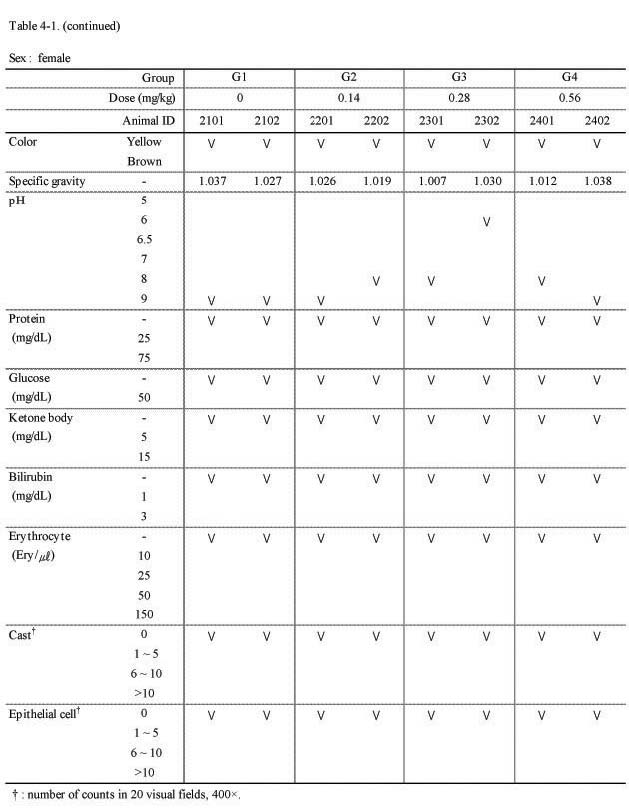
(continued)
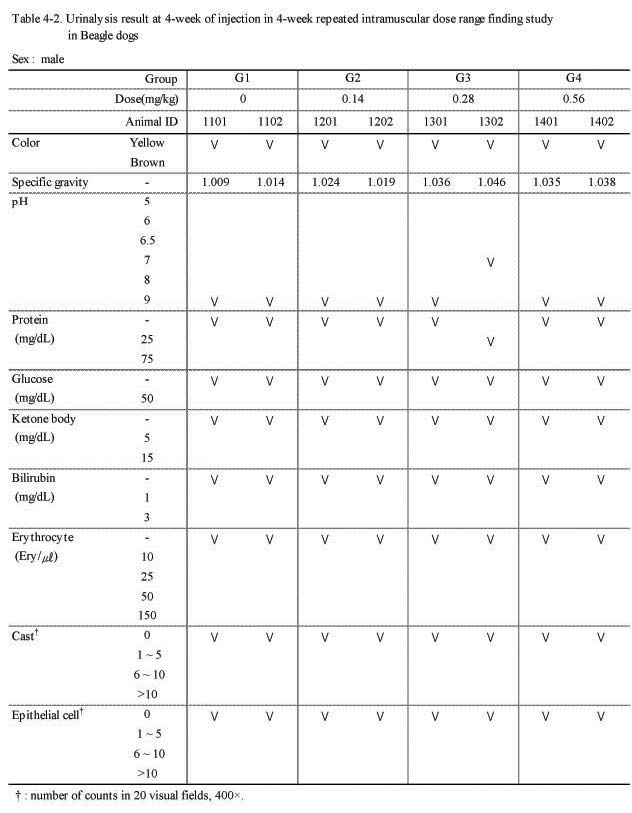
Urinalysis result at 4-week of injection in 4-week repeated intramuscular dose range finding study in Beagle dogs
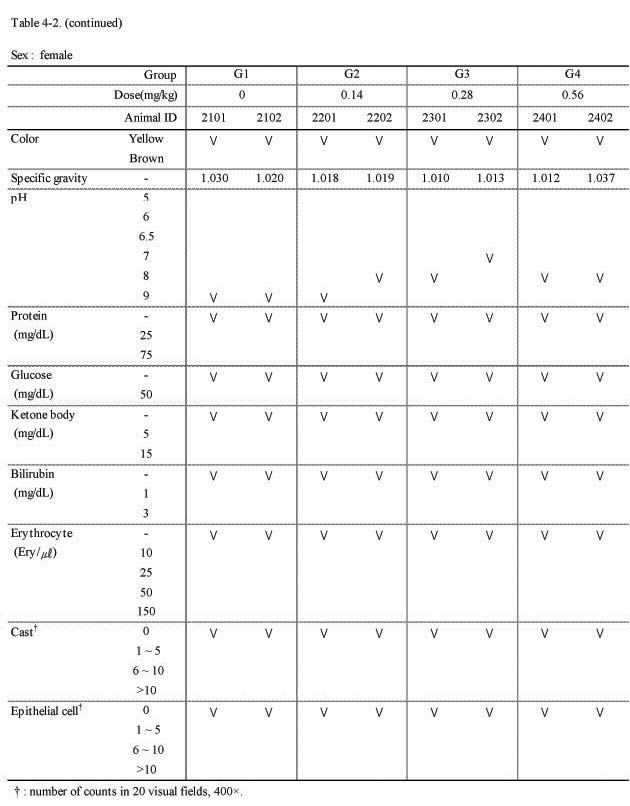
(continued)
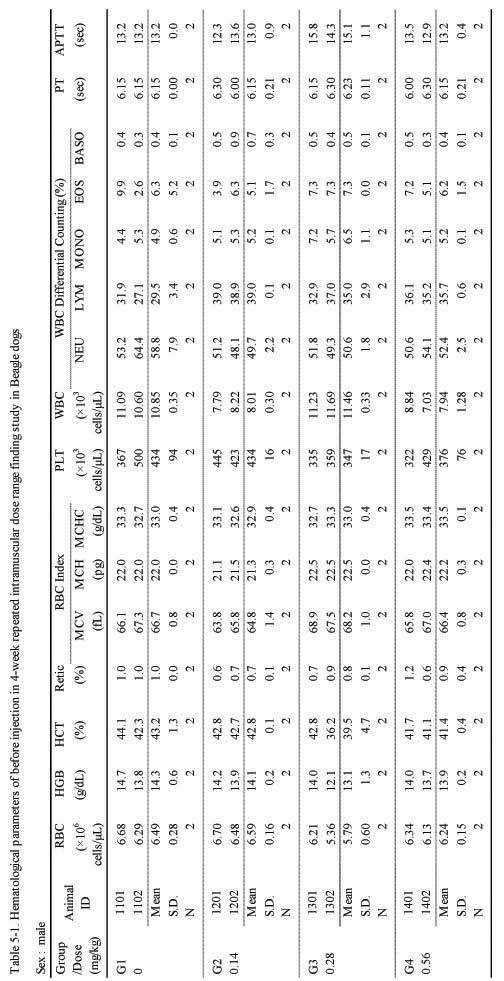
Hematological parameters of before injection in 4-week repeated intramuscular dose range finding study in Beagle dogs
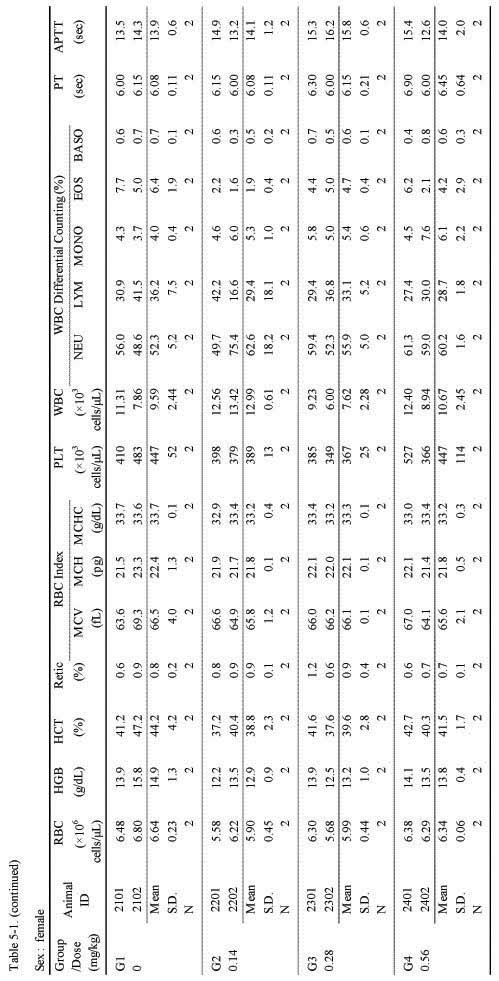
(continued)
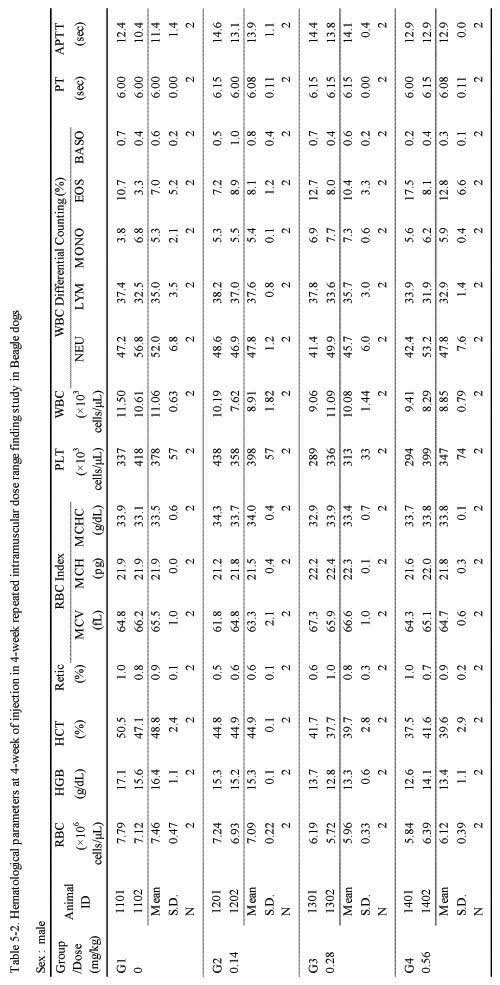
Hematological parameters at 4-week of injection in 4-week repeated intramuscular dose range finding study in Beagle dogs
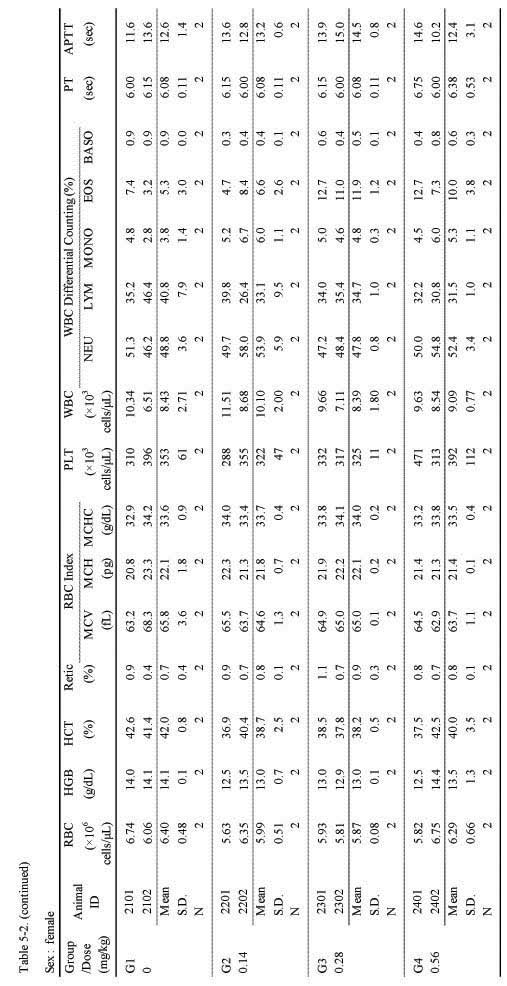
(continued)
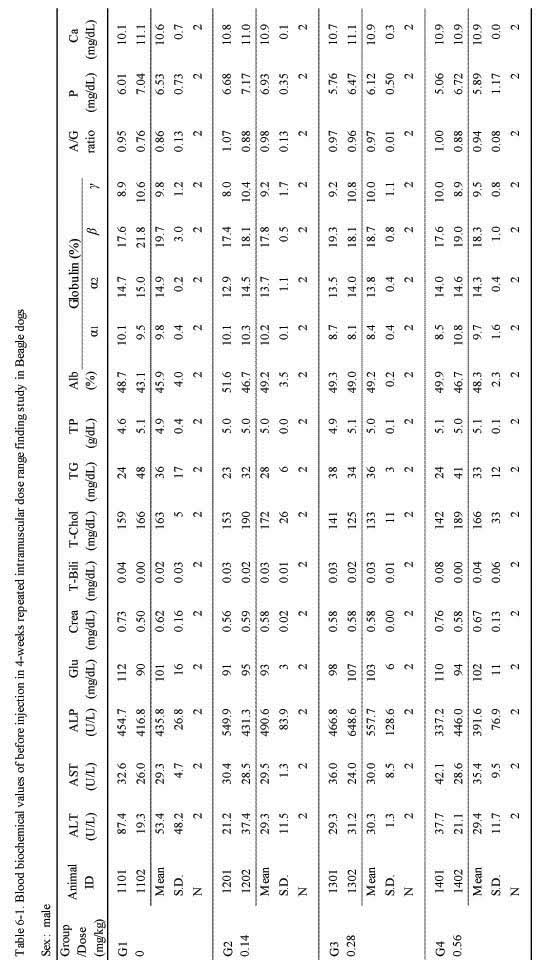
Blood biochemical values of before injection in 4-week repeated intramuscular dose range finding study in Beagle dogs
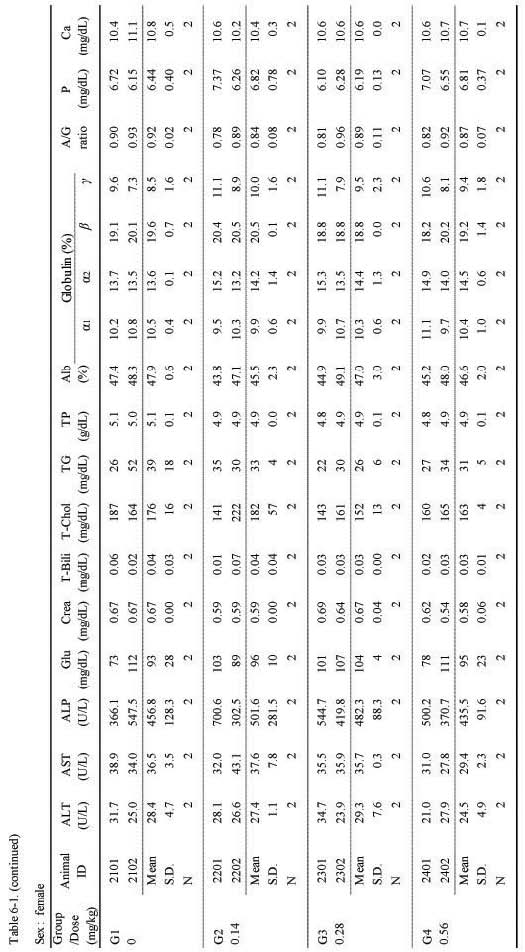
(continued)
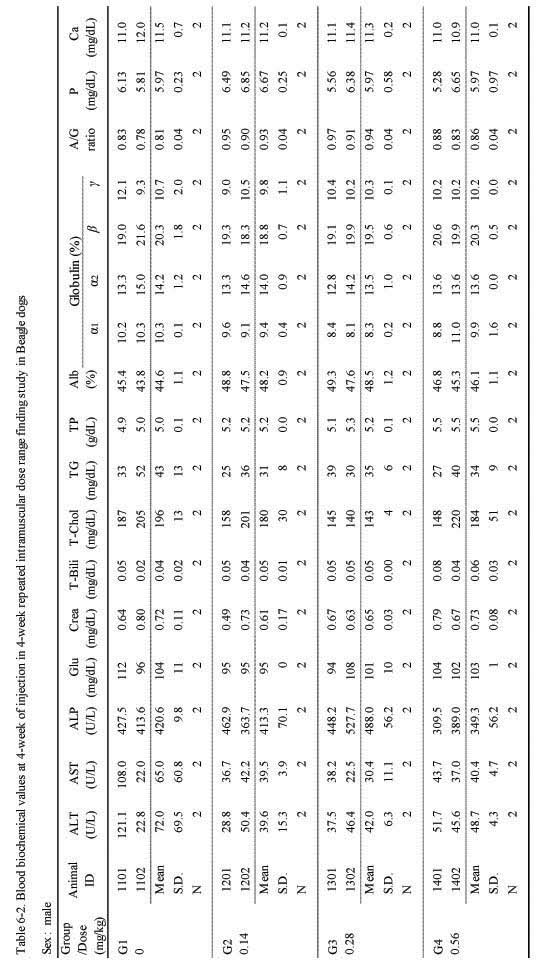
Blook biochemical values at 4-week of injection in 4-week repeated intramuscular dose range finding study in Beagle dogs
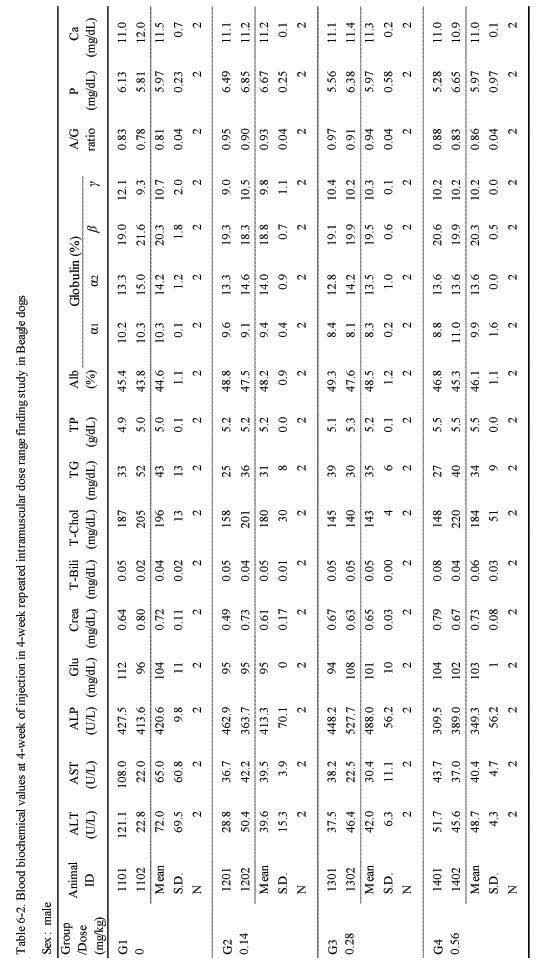
(continued)
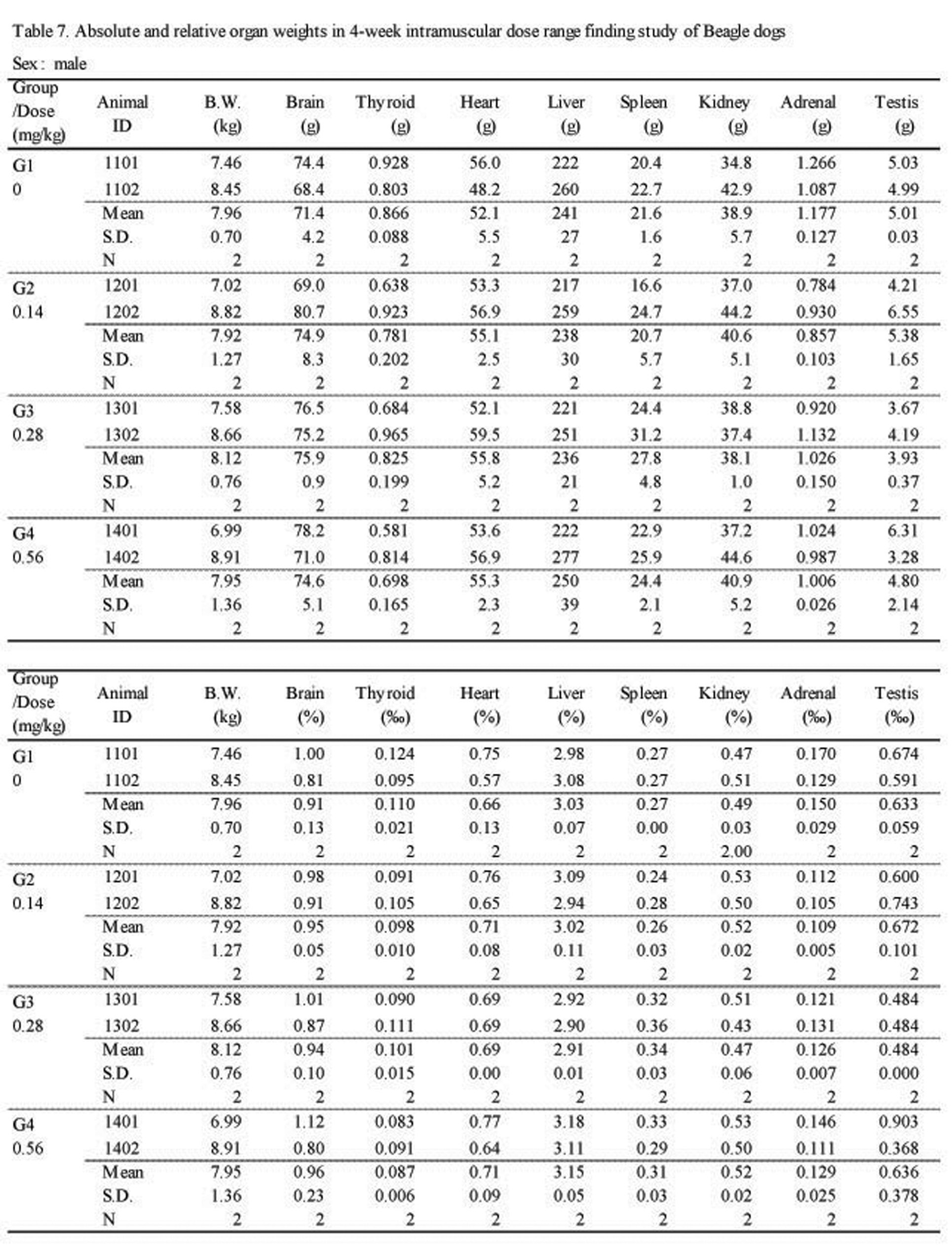
Absolute and relative organ weights in 4-week intramuscular dose range finding study in Beagle dogs
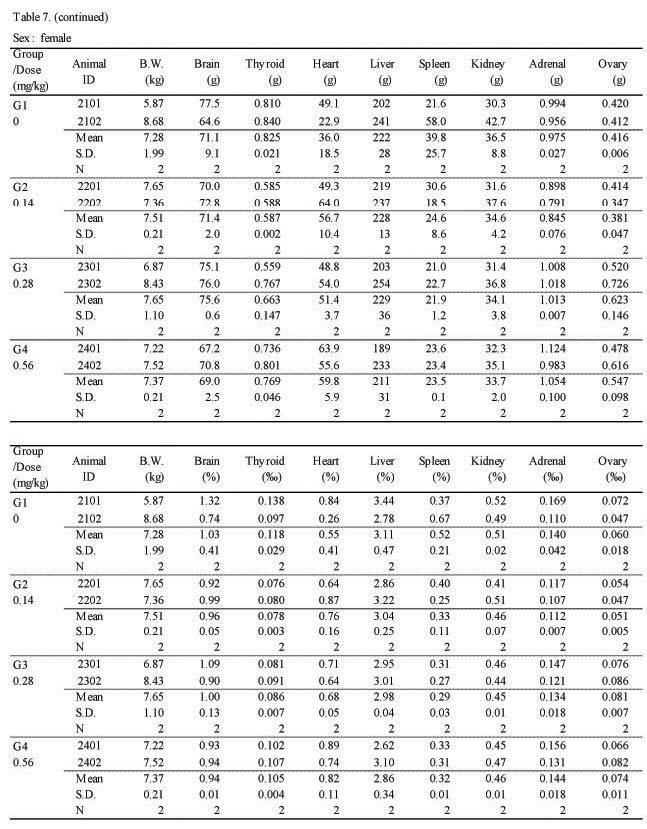
(continued)
[Table 8] Necropsy finding in 4-week intramuscular dose range finding study in Beagle dogs
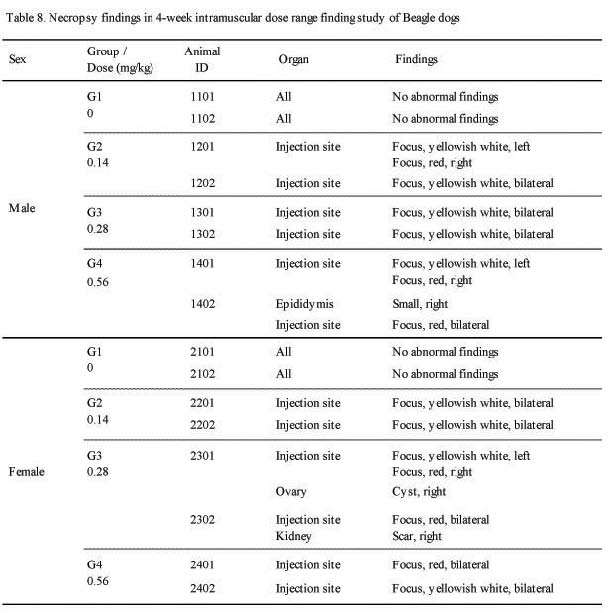
Necropsy finding in 4-week intramuscular dose range finding study in Beagle dogs
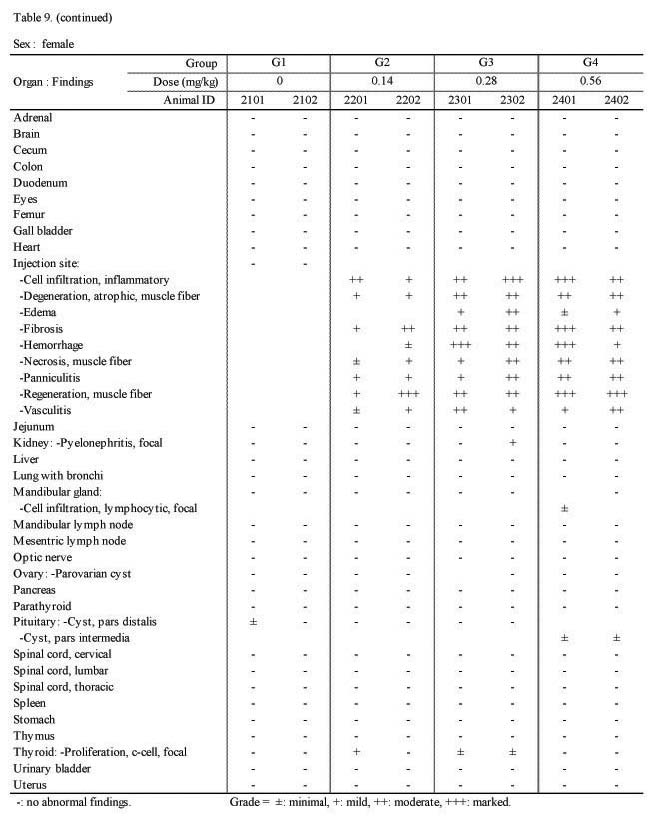
Histopathological findings in 4-week intramuscular dose range finding study in Beagle dogs
(continued)