Heavy metal adsorption not only depends on rapid cooling slag(RCS) characteristics but also on the nature of the metals involved and on their competitive behavior for RCS adsorption sites. The goal of this study was to investigate the competitive absorption characteristics of Cu, Cd and Zn in single- and multi-metal forms by RCS.
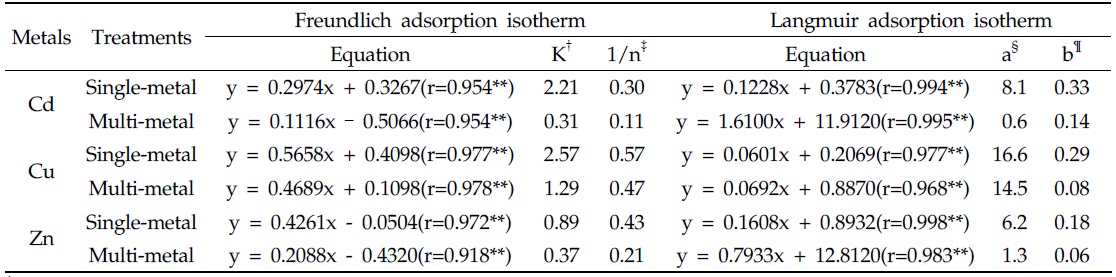
Both single- and multi-metal adsorption experiments were conducted to determine the adsorption characteristics of RCS for the heavy metals. Adsorption behaviors of the heavy metals by RCS were evaluated using both the Freundlich and Langmuir adsorption isotherm equations. The maximum adsorption capacities of metals by RCS were in the order of Cu(16.6 mg/g) > Cd(8.1 mg/g) > Zn(6.2 mg/g) in the single-metal adsorption isotherm and Cu(14.5 mg/g) >> Zn(1.3 mg/g) > Cd(0.6 mg/g) in the multi-metal adsorption isotherm. Based on data obtained from Freundlich and Langmuir adsorption models and three-dimensional simulation, multi-metal adsorption behaviors differed from single- metal adsorption due to competition. Cadmium and Zn were easily exchanged and substituted by Cu during multi-metal adsorption.
Results from adsorption experiments indicate that competitive adsorption among metals increases the mobility of these metals.
최근 급격한 산업화 및 도시화로 인하여 중금속 폐수에 의한 수질 및 토양 오염은 선진국과 개발도상국에서 가장 중요한 환경 문제 중 하나로 대두되기 시작하였다(Shi
중금속 폐수처리를 위한 다양한 방법이 개발되었으나 일반적으로 물리 · 화학적 처리 방법이 가장 많이 이용되고 있다. 물리적인 방법에는 침전법 및 막분리법 등이 있고, 화학적인 방법에는 응집침전법 및 이온교환법 등이 있다. 이들 공법들은 처리효율이 낮고, 운영 및 관리에 많은 비용이 소요되며, 폐수처리시 발생되는 슬러지 때문에 수계 및 토양에 2차오염을 유발할 수 있기 때문에 이를 대체 할 수 있는 새로운 처리방법이 요구되고 있는 실정이다(Kim
이에 중금속 폐수 처리시 운전 및 유지관리비용이 적고, 중금속 폐수를 효율적으로 제거할 수 있는 흡착제에 대해 다양한 연구가 진행되고 있으며, 특히 키토산, Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), 슬래그 및 제올라이트 등 다양한 흡착제를 이용한 중금속 흡착에 관한 연구가 다양한 방면에서 시작되었다(Gupta
일반적으로 중금속 폐수는 단일 오염물질에 의한 오염보다는 2종 이상의 복합 오염물질로 오염되어 있으며, 복합중금속 용액에서의 각 중금속의 흡착은 흡착제의 흡착점을 두고 경쟁하기 때문에 단일 용액에서 각 중금속의 흡착 특성 결과만으로 복합용액에서의 흡착특성을 예측하는데 한계가 있다. 특히, 중금속 간의 흡착 경쟁을 체계적으로 이해하기 위해서는 중금속간의 경쟁흡착 연구가 필요할 것으로 판단된다.
본 실험에 사용된 제강급랭슬래그는 최근 철강회사에서 새롭게 도입한 BSSF(Baosteel Slag Short Flow)설비로 기존의 제강슬래그를 배제 · 냉각해 재처리하는 프로세스와는 달리 고온의 용융 슬래그를 기계적으로 냉각 ·분쇄 ·고형화 처리하고, 발생되는 철분은 별도로 회수해 재사용하며, 분리 처리된 슬래그는 별도로 재활용할 수 있도록 구성되어 있다.
하지만 현재까지 제강급랭슬래그의 재활용방안에 대한 연구는 미비한 실정으로 다양한 용도 모색으로 슬래그의 우수한 고유 특성을 발견하고 이를 부가가치가 높은 물질로 전환시키는 새로운 기술 개발이 필요하다.
이에 본 연구는 제강급랭슬래그의 중금속 폐수 처리에 대한 적용가능성을 평가하기 위한 선행연구로서 제강급랭슬래그의 단일 및 복합중금속 용액에 대한 경쟁 흡착특성을 조사하였다.
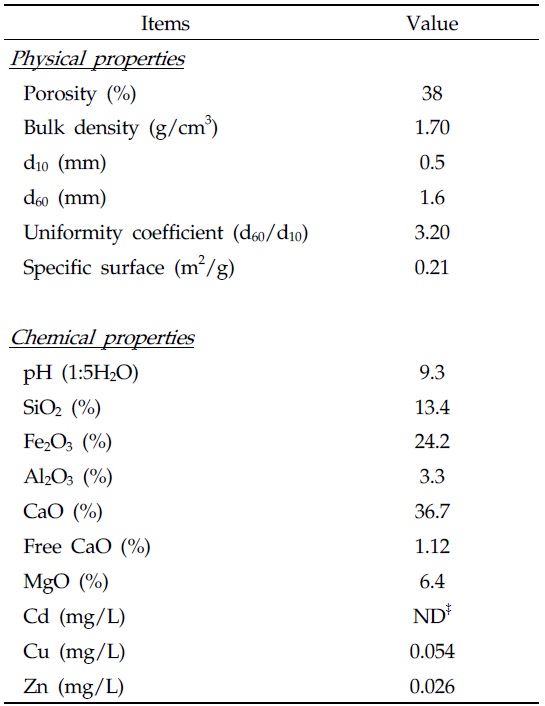
본 실험에 사용된 제강급랭슬래그는 BSSF설비에서 발생되는 제강급랭슬래그를 국내 철강회사인 P사로부터 수거하였다. 수거한 제강급랭슬래그는 균등계수(여재를 입경 순으로 나열하였을 때 작은 입경으로부터 중량 60%되는 입경과 10% 되는 입경과의 비; d60/d10)가 3.20이었다. 제강급랭슬래그의 화학적인 특성은 Table 1에서 보는 것과 같다. Seo 등(2006)의 연구결과에 따르면 일반적인 제강슬래그의 경우 높은 유리칼슘 함량으로 인하여 여과제로 적용시 수중 pH가 증가하게 되고, 이로 인하여 수중 미생물의 생육저하를 야기시켜 인을 제외한 오염물질의 처리효율을 저하시킨다고 보고한 바 있다. 하지만 본 실험에서 사용된 제강급랭슬래그의 경우는 기존의 제강슬래그에 비해 유리칼슘의 함량이 낮고, 표면적 및 공극률이 높아 수질 여과제로 충분히 활용 가능할 것으로 판단된다.
[Table 1.] Physicochemical characteristics of rapid cooling slag used in the study
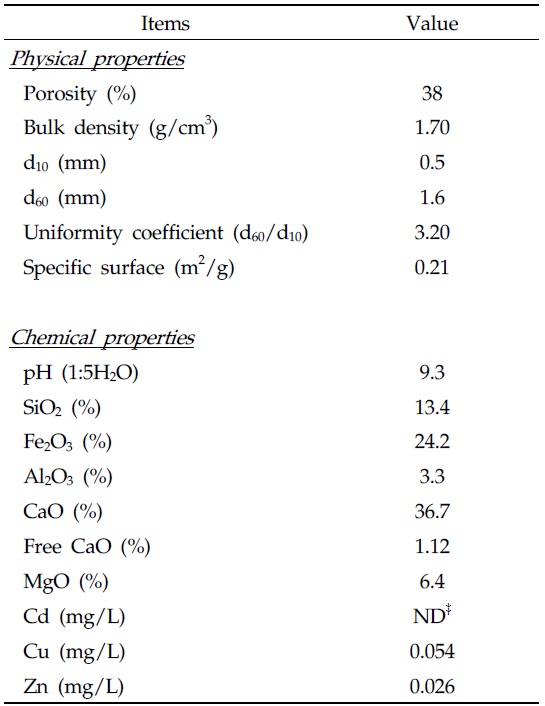
Physicochemical characteristics of rapid cooling slag used in the study
제강급랭슬래그의 단일 및 복합중금속에 대한 경쟁흡착특성 조사에 사용한 중금속은 Cu, Cd 및 Zn으로 총 3종이며, 중금속 시약은 Cu(NO3)2 · 2.5H2O, Cd(NO3)2 · 4H2O 및 Zn(NO3)2 · 6H2O(GR grade, Fisher Scientific, USA)를 사용하였다. 실험에 사용된 중금속용액의 농도를 Cu, Cd 및 Zn이 단일로 존재하는 단일용액(Single-metal)과 이들 중금속을 혼합한 복합용액(Multi-metal)으로 구분하였다.
>
실험방법 및 분석방법 단일 및 복합 중금속 용액에 대한 제강급랭슬래그의 경쟁 흡착특성
제강급랭슬래그의 단일 및 복합중금속 대한 경쟁흡착특성 조사는 제강급랭슬래그를 1.0 g씩 삼각플라스크에 주입하고 단일 및 복합 중금속용액을 2.5, 5, 10, 20, 40, 80, 160 및 320 mg/L되게 제조하였다.
제강급랭슬래그가 충진된 삼각플라스크에 단일 및 복합중금속 용액을 각각 50 mL되게 주입하여 밀봉한 후 삼각플라스크를 shacking incubator(KASI KSI-200L, Korea)에서 175 rpm으로 24시간 20℃ 조건하에 항온시켜 침전시킨 후 Whatman GF/C filter로서 필터한 후 Standard Method에 의해 Inductively coupled plasma–optical emission spectroscopy(ICP–OES, Perkin Elmer Optima 4300 DV, USA)를 이용하여 Cu, Cd 및 Zn의 농도를 측정하였다.
제강급랭슬래그의 단위 g당 흡착된 Cu, Cd 및 Zn의 양과 평형상태에서 용액 중 남아있는 Cu, Cd 및 Zn의 농도를 구하여 이를 Freundlich 및 Langmuir 등온흡착식에 적용하였다. Fruendlich 등온흡착식의 일반식은 다음(Eq. 1)과 같다(Bohn, 1979; Seo
제강급랭슬래그의 단일 및 복합중금속에 대한 경쟁흡착특성 조사를 위한 Langmuir 등온흡착식의 일반식은 다음 (2) 식과 같다(Seo
이상의 Langmuir 및 Freundlich의 직선식의 결과를 이용하여 제강급랭슬래그의 단일 및 복합중금속에 대한 최대흡착능을 조사하고, 본 실험에 적용된 두 흡착식과 실제 흡착량을 비교하여 제강급랭슬래그의 중금속 흡착능 예측을 위한 최적흡착식을 선정하였으며, 또한 각 조건에서의 흡착량 결과를 이용하여 3D simulation기법으로 흡착패턴을 조사하였다.
>
제강급랭슬래그의 단일 및 복합중금속에 대한 경쟁흡착특성
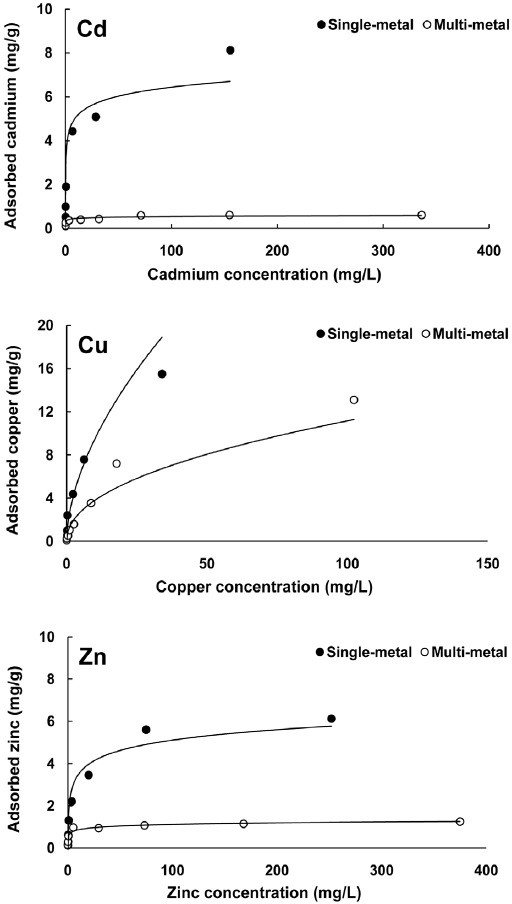
제강급랭슬래그(흡착제)의 단위 g당 흡착된 Cd, Cu 및 Zn의 흡착량과 평형상태에서 용액 중 남아있는 Cd, Cu 및 Zn의 농도를 측정한 결과는 Fig. 1과 같다. 제강급랭슬래그의 단일 용액일 때의 흡착량이 복합 용액일 때의 흡착량에 비해 높았다. 특히 Cu의 경우 복합용액일 때가 단일용액에 비해 흡착능의 감소폭이 비교적 낮았으나, Cd와 Zn의 경우는 복합용액일 때가 단일용액에 비해 흡착능이 현저하게 떨어졌다.
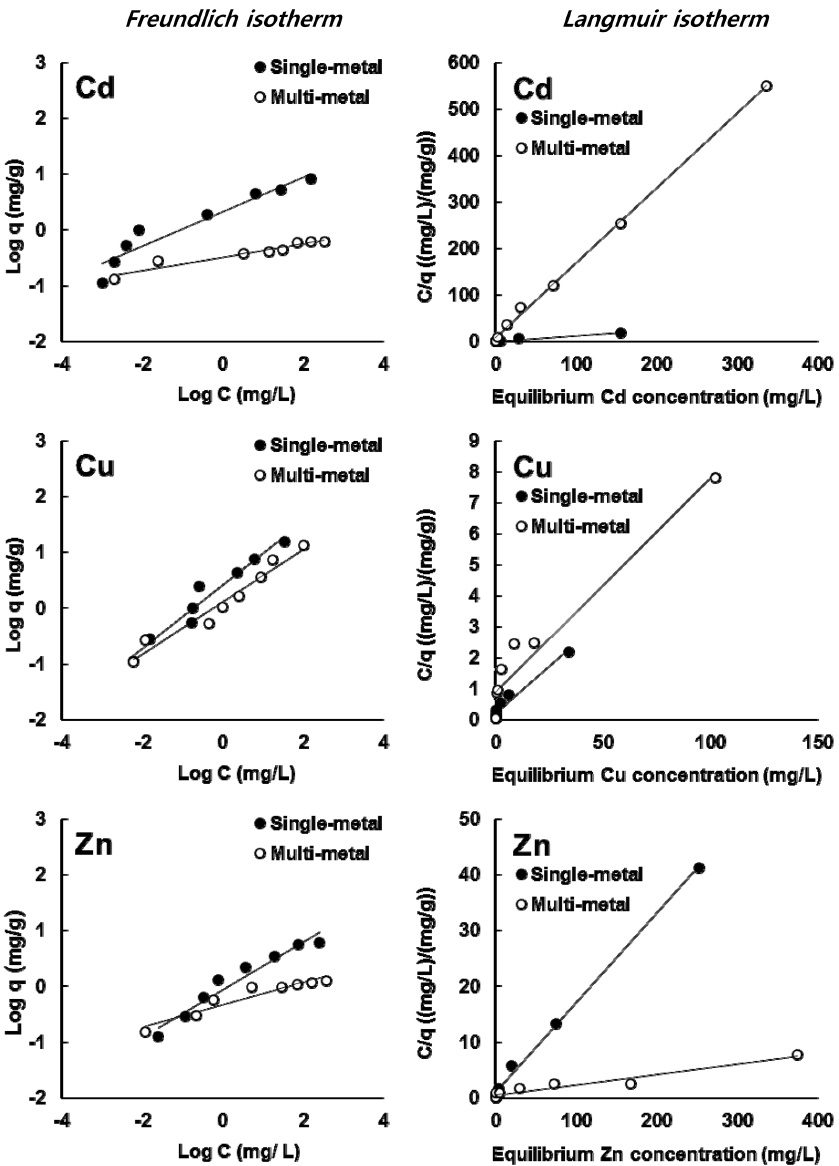
Freundlich 및 Langmuir 등온흡착식에 적용하여 Freundlich 등온흡착식으로부터 흡착능(
Freundlich 등온흡착식을 이용한 Cd, Cu 및 Zn의 흡착능(
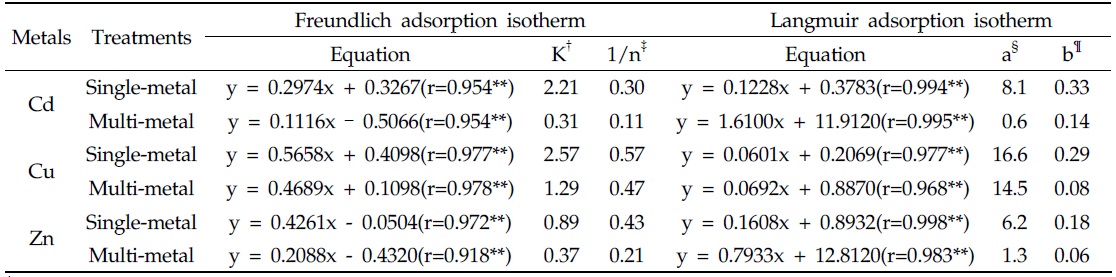
Determination of the parameters for the Freundlich and Langmuir adsorption isotherm by test fit approach in batch experiment of single- and mulit-metal adsorption to rapid cooling slag
제강급랭슬래그의 단일 및 복합중금속 용액에 대한 흡착강도(
Langmuir 등온흡착식을 이용한 제강급랭슬래그의 단일 및 복합 중금속 용액에서 최대흡착능(a)은 단일 용액일 때 Cu(16.6 mg/g) > Cd(8.1 mg/g) > Zn(6.2 mg/g)순이었으며, 복합 용액일 때 Cu(14.5 mg/g) >> Zn(1.3 mg/g) > Cd(0.6 mg/g)순으로 복합 용액일 때 최대흡착능은 단일 용액에 비해 모든 금속이 감소하는 경향이었다(Fig. 2 및 Table 2). 특히 Cu의 최대흡착능은 다른 금속에 비해 단일용액에 비해 복합용액에서 감소폭이 작으나 Cd 및 Zn의 최대흡착능은 큰 폭으로 감소하였다. 또한 Cd의 최대흡착능은 단일 용액에서는 Zn에 비해 높은 반면, 복합 용액에서는 Zn에 비해 낮은 최대흡착능을 보였다.
제강급랭슬래그의 단일 및 복합중금속 용액에서 최대흡착능 결과를 이용하여 복합용액에서의 Cd, Cu 및 Zn의 저감효율을 비교한 결과 Cu는 12.6% 감소하였고, Cd는 92.6% 감소하였며, Zn은 79.0% 감소하였다.
이상의 결과를 미루어 볼 때, Cd는 경쟁 이온이 없는 단일 용액에서는 흡착제에 대해 높은 흡착능을 보였으나, 복합용액에서는 경쟁관계인 Cu에 의해 상대적으로 흡착능이 감소한 것으로 판단된다.
Mohapatra와 Anand(2010) 및 McBride 등(2000)은 흡착제의 중금속에 대한 선택성은 몇 가지 요소에 의해 결정된다고 보고하였다. 흡착물질로의 흡착에 있어 중금속 성분의 상대적인 선택성은 이온반경, 원자량, 전기음성도, 가수분해상수, softness 등의 중금속 특성과 흡착물질의 물리 · 화학적 특성에 영향을 받는 것으로 보고하였다.
중금속 흡착실험에서 Cu에 대한 흡착의 선택성은 Cd, Ni 및 Zn에 비해 뚜렷하게 높은 것으로 보고하였으며(Covelo
Saha 등(2002) 연구결과에 따르면, 복합 중금속 용액에서 각 중금속의 농도가 낮을 때에는 흡착제에 대해 복합용액내의 중금속 모두가 흡착능이 높으나, 각 중금속의 농도가 높을 때에는 흡착제에 대한 각 중금속의 흡착능은 경쟁관계에 의해 중금속의 흡착능이 떨어진다고 보고하였다. Fontes와 Comes(2003)의 연구결과에 따르면 중금속 복합 용액내에 Cu와 Cd가 공존할 경우 Cd의 흡착능은 단일 용액에서의 흡착능에 비해 떨어진다고 보고하였는데, 본 연구결과와 동일한 경향이었다.
>
제강급랭슬래그의 단일 및 복합중금속에 대한 최적흡착식 선정
제강급랭슬래그의 Cd, Cu 및 Zn에 대한 흡착능력을 예측하기에 적합한 최적 등온흡착식을 선정하기 위해 Table 2로부터 도출한 Freundlich와 Langmuir 등온흡착 일반식을 실제 흡착결과에 적용하였다. 제강급랭슬래그의 실제 흡착량과 Freundlich와 Langmuir 등온흡착 일반식을 Fig. 3에 나타내었다. 제강급랭슬래그의 단일 및 복합중금속 용액에서 Cd, Cu 및 Zn의 흡착량은 전반적으로 Langmuir 등온흡착식이 Freundlich 등온흡착식에 비해 잘 일치하였다. 일반적으로 두 등온흡착식을 비교하면 Langmuir 등온흡착식의 경우는 표면전하의 영향을 고려하지 못할 뿐만 아니라 그 복잡성으로 인하여 Freundlich 등온흡착식에 비하여 선호성이 떨어진다. 하지만 Langmuir 등온식은 흡착제의 물리‧ 화학적특성, 흡착능 및 적용성 등의 인자를 포함하고 있다는 이론적인 측면에서는 Freundlich 등온흡착식 보다 더 선호된다고 보고하였다(Lee and Jang, 2004; Choi
>
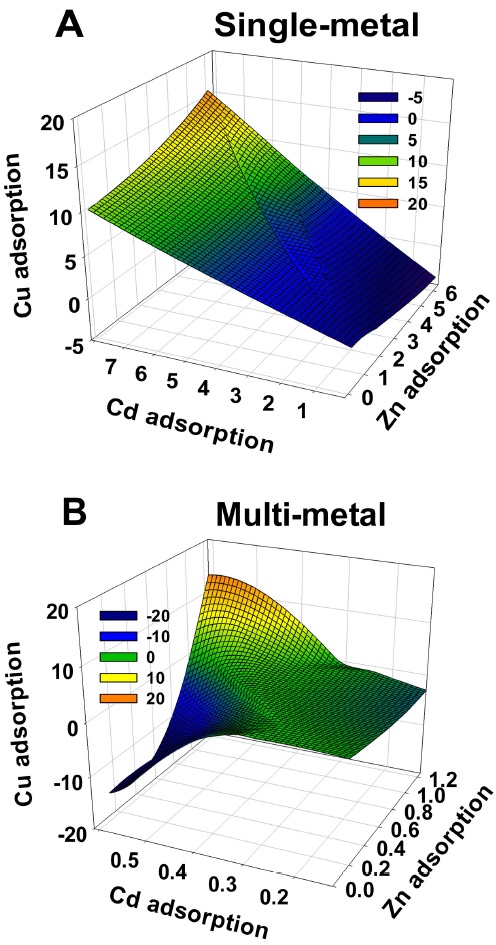
제강급랭슬래그의 단일 및 복합중금속에 대한 흡착패턴
제강급랭슬래그의 단일 및 복합중금속용액에 대한 흡착패턴 연구결과는 제강급랭슬래그의 단일 및 복합 중금속 표준용액에서 단위 g당 흡착량의 결과를 이용하여 3D simulation으로 조사되었으며, 그 결과는 Fig. 4에서 보는 것과 같다. 단일 용액에서 Cu 및 Cd는 Zn에 비해 상대적으로 흡착능이 증가하는 패턴을 보였으나 복합 용액에서는 Cd은 Cu와의 경쟁으로 인하여 흡착능이 현저하게 감소하는 패턴을 확인할 수 있었다. 이와 같이 단일 및 복합 중금속 용액에서 각각의 금속은 서로 다른 패턴을 보이는 것을 알 수가 있었고, 각 금속간의 경쟁관계는 흡착패턴에 지배적인 영향을 주는 것으로 판단된다.


![Experimental and calculated values from the Freundlich and Langmuir adsorption isotherms for the single- and multi-metal conditions. ●: Experimental data; ━: Freundlich equation [equation (2)]; ---:Langmuir equation [equation (3)].](http://oak.go.kr/repository/journal/21018/HGNHB8_2016_v35n1_24_f003.jpg)